+
+
+
+
+
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/CODE_OF_CONDUCT.md b/CODE_OF_CONDUCT.md
deleted file mode 100644
index dad69f52..00000000
--- a/CODE_OF_CONDUCT.md
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,128 +0,0 @@
-# Contributor Covenant Code of Conduct
-
-## Our Pledge
-
-We as members, contributors, and leaders pledge to make participation in our
-community a harassment-free experience for everyone, regardless of age, body
-size, visible or invisible disability, ethnicity, sex characteristics, gender
-identity and expression, level of experience, education, socio-economic status,
-nationality, personal appearance, race, religion, or sexual identity
-and orientation.
-
-We pledge to act and interact in ways that contribute to an open, welcoming,
-diverse, inclusive, and healthy community.
-
-## Our Standards
-
-Examples of behavior that contributes to a positive environment for our
-community include:
-
-- Demonstrating empathy and kindness toward other people
-- Being respectful of differing opinions, viewpoints, and experiences
-- Giving and gracefully accepting constructive feedback
-- Accepting responsibility and apologizing to those affected by our mistakes,
- and learning from the experience
-- Focusing on what is best not just for us as individuals, but for the
- overall community
-
-Examples of unacceptable behavior include:
-
-- The use of sexualized language or imagery, and sexual attention or
- advances of any kind
-- Trolling, insulting or derogatory comments, and personal or political attacks
-- Public or private harassment
-- Publishing others' private information, such as a physical or email
- address, without their explicit permission
-- Other conduct which could reasonably be considered inappropriate in a
- professional setting
-
-## Enforcement Responsibilities
-
-Community leaders are responsible for clarifying and enforcing our standards of
-acceptable behavior and will take appropriate and fair corrective action in
-response to any behavior that they deem inappropriate, threatening, offensive,
-or harmful.
-
-Community leaders have the right and responsibility to remove, edit, or reject
-comments, commits, code, wiki edits, issues, and other contributions that are
-not aligned to this Code of Conduct, and will communicate reasons for moderation
-decisions when appropriate.
-
-## Scope
-
-This Code of Conduct applies within all community spaces, and also applies when
-an individual is officially representing the community in public spaces.
-Examples of representing our community include using an official e-mail address,
-posting via an official social media account, or acting as an appointed
-representative at an online or offline event.
-
-## Enforcement
-
-Instances of abusive, harassing, or otherwise unacceptable behavior may be
-reported to the community leaders responsible for enforcement at
-hemant.rajput_cs20@gla.ac.in.
-All complaints will be reviewed and investigated promptly and fairly.
-
-All community leaders are obligated to respect the privacy and security of the
-reporter of any incident.
-
-## Enforcement Guidelines
-
-Community leaders will follow these Community Impact Guidelines in determining
-the consequences for any action they deem in violation of this Code of Conduct:
-
-### 1. Correction
-
-**Community Impact**: Use of inappropriate language or other behavior deemed
-unprofessional or unwelcome in the community.
-
-**Consequence**: A private, written warning from community leaders, providing
-clarity around the nature of the violation and an explanation of why the
-behavior was inappropriate. A public apology may be requested.
-
-### 2. Warning
-
-**Community Impact**: A violation through a single incident or series
-of actions.
-
-**Consequence**: A warning with consequences for continued behavior. No
-interaction with the people involved, including unsolicited interaction with
-those enforcing the Code of Conduct, for a specified period of time. This
-includes avoiding interactions in community spaces as well as external channels
-like social media. Violating these terms may lead to a temporary or
-permanent ban.
-
-### 3. Temporary Ban
-
-**Community Impact**: A serious violation of community standards, including
-sustained inappropriate behavior.
-
-**Consequence**: A temporary ban from any sort of interaction or public
-communication with the community for a specified period of time. No public or
-private interaction with the people involved, including unsolicited interaction
-with those enforcing the Code of Conduct, is allowed during this period.
-Violating these terms may lead to a permanent ban.
-
-### 4. Permanent Ban
-
-**Community Impact**: Demonstrating a pattern of violation of community
-standards, including sustained inappropriate behavior, harassment of an
-individual, or aggression toward or disparagement of classes of individuals.
-
-**Consequence**: A permanent ban from any sort of public interaction within
-the community.
-
-## Attribution
-
-This Code of Conduct is adapted from the [Contributor Covenant][homepage],
-version 2.0, available at
-https://www.contributor-covenant.org/version/2/0/code_of_conduct.html.
-
-Community Impact Guidelines were inspired by [Mozilla's code of conduct
-enforcement ladder](https://github.com/mozilla/diversity).
-
-[homepage]: https://www.contributor-covenant.org
-
-For answers to common questions about this code of conduct, see the FAQ at
-https://www.contributor-covenant.org/faq. Translations are available at
-https://www.contributor-covenant.org/translations.
diff --git a/CONTRIBUTING.md b/CONTRIBUTING.md
deleted file mode 100644
index 4df1d819..00000000
--- a/CONTRIBUTING.md
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,40 +0,0 @@
-# Contributing Guidelines
-
-Thank you for your interest in contributing to our project. Whether it's a bug report, new submission, correction, or additional
-documentation, we greatly value feedback and contributions from our community.
-
-Please read through this document before submitting any issues or pull requests to ensure we have all the necessary
-information to effectively respond to your bug report or contribution.
-
-## Reporting Bugs/Feature Requests
-
-We welcome you to use the GitHub issue tracker to report bugs or suggest features.
-
-When filing an issue, please check existing open, or recently closed, issues to make sure somebody else hasn't already
-reported the issue. Please try to include as much information as you can. Details like these are incredibly useful:
-
-- A test case or series of steps to reproduce
-- Any modifications you've made relevant to the bug
-- Anything unusual about your environment or deployment
-
-## Contributing via Pull Requests
-
-Contributions via pull requests are much appreciated. Before sending us a pull request, please ensure that:
-
-1. You are working against the latest source on the _master_ branch.
-2. You check existing open, and recently merged, pull requests to make sure someone else hasn't addressed the problem already.
-
-To send us a pull request, please:
-
-1. Fork the repository.
-2. Modify the source or Add your solution.
-3. Ensure all testcases passes.
-4. Commit to your fork with relevant commit messages.
-5. Send us a pull request.
-
-GitHub provides additional document on [forking a repository](https://help.github.com/articles/fork-a-repo/) and
-[creating a pull request](https://help.github.com/articles/creating-a-pull-request/).
-
-## Licensing
-
-See the [LICENSE](./LICENSE) file for our project's licensing.
diff --git a/LICENSE b/LICENSE
deleted file mode 100644
index 690e06d3..00000000
--- a/LICENSE
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,21 +0,0 @@
-MIT License
-
-Copyright (c) 2022 Hemant Rajput
-
-Permission is hereby granted, free of charge, to any person obtaining a copy
-of this software and associated documentation files (the "Software"), to deal
-in the Software without restriction, including without limitation the rights
-to use, copy, modify, merge, publish, distribute, sublicense, and/or sell
-copies of the Software, and to permit persons to whom the Software is
-furnished to do so, subject to the following conditions:
-
-The above copyright notice and this permission notice shall be included in all
-copies or substantial portions of the Software.
-
-THE SOFTWARE IS PROVIDED "AS IS", WITHOUT WARRANTY OF ANY KIND, EXPRESS OR
-IMPLIED, INCLUDING BUT NOT LIMITED TO THE WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY,
-FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE AND NONINFRINGEMENT. IN NO EVENT SHALL THE
-AUTHORS OR COPYRIGHT HOLDERS BE LIABLE FOR ANY CLAIM, DAMAGES OR OTHER
-LIABILITY, WHETHER IN AN ACTION OF CONTRACT, TORT OR OTHERWISE, ARISING FROM,
-OUT OF OR IN CONNECTION WITH THE SOFTWARE OR THE USE OR OTHER DEALINGS IN THE
-SOFTWARE.
diff --git a/README.md b/README.md
deleted file mode 100644
index 28ba6833..00000000
--- a/README.md
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,237 +0,0 @@
-
-
-- Fork [this repository][leetcode] to your own GitHub account and then clone it to your local machine.
-- Checkout a new branch.
-- Make some changes to your leetcode repository, then push the changes to your remote GitHub repository.
-- Create a pull request with your changes!
-- See [CONTRIBUTING](./CONTRIBUTING.md) or [GitHub Help](https://help.github.com/en) for more details.
-
-```mermaid
- graph TD;
- A[rajput-hemant/leetcode] --1--> B[create a fork your-username/leetcode];
- B --2--> C[clone your fork to your local machine];
- C --3--> D[checkout new branch, update or add your solution in relevant folder];
- D --4--> E[commit & push changes];
- E --5--> B;
- B --6--> F[create a pull request];
- F --7--> A;
-```
-
-
-
-## Contributors
-
-[![][contributors]][contributors-graph]
-
-### Show Some ❤️ by giving ⭐ to the Repository
-
-
',1),o=[g];function c(y,h,x,m,u,b){return n(),i("div",null,o)}const T=r(l,[["render",c]]);export{f as __pageData,T as default};
diff --git a/assets/SERIALWISE.md.cba008fe.lean.js b/assets/SERIALWISE.md.cba008fe.lean.js
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..0a185e09
--- /dev/null
+++ b/assets/SERIALWISE.md.cba008fe.lean.js
@@ -0,0 +1 @@
+import{_ as t,a as e}from"./chunks/dark.0b1a1d54.js";import{_ as r,o as n,c as i,a as s}from"./app.e4604e86.js";const f=JSON.parse('{"title":"","description":"","frontmatter":{},"headers":[{"level":2,"title":"🏆 Curated solutions to Leetcode problems in multiple languages to ace the Coding Interviews.","slug":"🏆-curated-solutions-to-leetcode-problems-in-multiple-languages-to-ace-the-coding-interviews","link":"#🏆-curated-solutions-to-leetcode-problems-in-multiple-languages-to-ace-the-coding-interviews","children":[{"level":3,"title":"🔍 Press Ctrl+F or ⌘+F to search for a specific problem","slug":"🔍-press-ctrl-f-or-⌘-f-to-search-for-a-specific-problem","link":"#🔍-press-ctrl-f-or-⌘-f-to-search-for-a-specific-problem","children":[]}]}],"relativePath":"SERIALWISE.md","lastUpdated":1689264763000}'),l={name:"SERIALWISE.md"},a=t,d=e,g=s("",1),o=[g];function c(y,h,x,m,u,b){return n(),i("div",null,o)}const T=r(l,[["render",c]]);export{f as __pageData,T as default};
diff --git a/assets/TOPICWISE.md.cd380769.js b/assets/TOPICWISE.md.cd380769.js
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..ad79a5f8
--- /dev/null
+++ b/assets/TOPICWISE.md.cd380769.js
@@ -0,0 +1 @@
+import{_ as t,a as e}from"./chunks/dark.0b1a1d54.js";import{_ as r,o as n,c as i,a}from"./app.e4604e86.js";const p=JSON.parse('{"title":"","description":"","frontmatter":{},"headers":[{"level":2,"title":"🏆 Curated solutions to Leetcode problems in multiple languages to ace the Coding Interviews.","slug":"🏆-curated-solutions-to-leetcode-problems-in-multiple-languages-to-ace-the-coding-interviews","link":"#🏆-curated-solutions-to-leetcode-problems-in-multiple-languages-to-ace-the-coding-interviews","children":[{"level":3,"title":"🔍 Press Ctrl+F or ⌘+F to search for a specific problem","slug":"🔍-press-ctrl-f-or-⌘-f-to-search-for-a-specific-problem","link":"#🔍-press-ctrl-f-or-⌘-f-to-search-for-a-specific-problem","children":[]}]},{"level":2,"title":"Array","slug":"array","link":"#array","children":[]},{"level":2,"title":"String","slug":"string","link":"#string","children":[]},{"level":2,"title":"Hash Table","slug":"hash-table","link":"#hash-table","children":[]},{"level":2,"title":"Dynamic Programming","slug":"dynamic-programming","link":"#dynamic-programming","children":[]},{"level":2,"title":"Math","slug":"math","link":"#math","children":[]},{"level":2,"title":"Sorting","slug":"sorting","link":"#sorting","children":[]},{"level":2,"title":"Depth First Search","slug":"depth-first-search","link":"#depth-first-search","children":[]},{"level":2,"title":"Greedy","slug":"greedy","link":"#greedy","children":[]},{"level":2,"title":"Database","slug":"database","link":"#database","children":[]},{"level":2,"title":"Breadth First Search","slug":"breadth-first-search","link":"#breadth-first-search","children":[]},{"level":2,"title":"Tree","slug":"tree","link":"#tree","children":[]},{"level":2,"title":"Binary Search","slug":"binary-search","link":"#binary-search","children":[]},{"level":2,"title":"Matrix","slug":"matrix","link":"#matrix","children":[]},{"level":2,"title":"Binary Tree","slug":"binary-tree","link":"#binary-tree","children":[]},{"level":2,"title":"Two Pointers","slug":"two-pointers","link":"#two-pointers","children":[]},{"level":2,"title":"Bit Manipulation","slug":"bit-manipulation","link":"#bit-manipulation","children":[]},{"level":2,"title":"Stack","slug":"stack","link":"#stack","children":[]},{"level":2,"title":"Design","slug":"design","link":"#design","children":[]},{"level":2,"title":"Heap (Priority Queue)","slug":"heap-priority-queue","link":"#heap-priority-queue","children":[]},{"level":2,"title":"Graph","slug":"graph","link":"#graph","children":[]},{"level":2,"title":"Simulation","slug":"simulation","link":"#simulation","children":[]},{"level":2,"title":"Backtracking","slug":"backtracking","link":"#backtracking","children":[]},{"level":2,"title":"Prefix Sum","slug":"prefix-sum","link":"#prefix-sum","children":[]},{"level":2,"title":"Counting","slug":"counting","link":"#counting","children":[]},{"level":2,"title":"Sliding Window","slug":"sliding-window","link":"#sliding-window","children":[]},{"level":2,"title":"Linked List","slug":"linked-list","link":"#linked-list","children":[]},{"level":2,"title":"Union Find","slug":"union-find","link":"#union-find","children":[]},{"level":2,"title":"Ordered Set","slug":"ordered-set","link":"#ordered-set","children":[]},{"level":2,"title":"Monotonic Stack","slug":"monotonic-stack","link":"#monotonic-stack","children":[]},{"level":2,"title":"Recursion","slug":"recursion","link":"#recursion","children":[]},{"level":2,"title":"Trie","slug":"trie","link":"#trie","children":[]},{"level":2,"title":"Binary Search Tree","slug":"binary-search-tree","link":"#binary-search-tree","children":[]},{"level":2,"title":"Divide and Conquer","slug":"divide-and-conquer","link":"#divide-and-conquer","children":[]},{"level":2,"title":"Enumeration","slug":"enumeration","link":"#enumeration","children":[]},{"level":2,"title":"Bitmask","slug":"bitmask","link":"#bitmask","children":[]},{"level":2,"title":"Queue","slug":"queue","link":"#queue","children":[]},{"level":2,"title":"Memoization","slug":"memoization","link":"#memoization","children":[]},{"level":2,"title":"Geometry","slug":"geometry","link":"#geometry","children":[]},{"level":2,"title":"Topological Sort","slug":"topological-sort","link":"#topological-sort","children":[]},{"level":2,"title":"Segment Tree","slug":"segment-tree","link":"#segment-tree","children":[]},{"level":2,"title":"Game Theory","slug":"game-theory","link":"#game-theory","children":[]},{"level":2,"title":"Hash Function","slug":"hash-function","link":"#hash-function","children":[]},{"level":2,"title":"Binary Indexed Tree","slug":"binary-indexed-tree","link":"#binary-indexed-tree","children":[]},{"level":2,"title":"Interactive","slug":"interactive","link":"#interactive","children":[]},{"level":2,"title":"String Matching","slug":"string-matching","link":"#string-matching","children":[]},{"level":2,"title":"Rolling Hash","slug":"rolling-hash","link":"#rolling-hash","children":[]},{"level":2,"title":"Shortest Path","slug":"shortest-path","link":"#shortest-path","children":[]},{"level":2,"title":"Number Theory","slug":"number-theory","link":"#number-theory","children":[]},{"level":2,"title":"Data Stream","slug":"data-stream","link":"#data-stream","children":[]},{"level":2,"title":"Combinatorics","slug":"combinatorics","link":"#combinatorics","children":[]},{"level":2,"title":"Randomized","slug":"randomized","link":"#randomized","children":[]},{"level":2,"title":"Monotonic Queue","slug":"monotonic-queue","link":"#monotonic-queue","children":[]},{"level":2,"title":"Iterator","slug":"iterator","link":"#iterator","children":[]},{"level":2,"title":"Merge Sort","slug":"merge-sort","link":"#merge-sort","children":[]},{"level":2,"title":"Concurrency","slug":"concurrency","link":"#concurrency","children":[]},{"level":2,"title":"Doubly Linked List","slug":"doubly-linked-list","link":"#doubly-linked-list","children":[]},{"level":2,"title":"Brainteaser","slug":"brainteaser","link":"#brainteaser","children":[]},{"level":2,"title":"Probability and Statistics","slug":"probability-and-statistics","link":"#probability-and-statistics","children":[]},{"level":2,"title":"Quickselect","slug":"quickselect","link":"#quickselect","children":[]},{"level":2,"title":"Bucket Sort","slug":"bucket-sort","link":"#bucket-sort","children":[]},{"level":2,"title":"Suffix Array","slug":"suffix-array","link":"#suffix-array","children":[]},{"level":2,"title":"Minimum Spanning Tree","slug":"minimum-spanning-tree","link":"#minimum-spanning-tree","children":[]},{"level":2,"title":"Counting Sort","slug":"counting-sort","link":"#counting-sort","children":[]},{"level":2,"title":"Shell","slug":"shell","link":"#shell","children":[]},{"level":2,"title":"Line Sweep","slug":"line-sweep","link":"#line-sweep","children":[]},{"level":2,"title":"Reservoir Sampling","slug":"reservoir-sampling","link":"#reservoir-sampling","children":[]},{"level":2,"title":"Eulerian Circuit","slug":"eulerian-circuit","link":"#eulerian-circuit","children":[]},{"level":2,"title":"Radix Sort","slug":"radix-sort","link":"#radix-sort","children":[]},{"level":2,"title":"Strongly Connected Component","slug":"strongly-connected-component","link":"#strongly-connected-component","children":[]},{"level":2,"title":"Rejection Sampling","slug":"rejection-sampling","link":"#rejection-sampling","children":[]},{"level":2,"title":"Biconnected Component","slug":"biconnected-component","link":"#biconnected-component","children":[]}],"relativePath":"TOPICWISE.md","lastUpdated":1689264763000}'),l={name:"TOPICWISE.md"},s=t,d=e,g=a('
🏆 Curated solutions to Leetcode problems in multiple languages to ace the Coding Interviews. #
🔍 Press Ctrl+F or ⌘+F to search for a specific problem #
',4),N=JSON.parse('{"title":"rajput-hemant","titleTemplate":"Leetcode","description":"","frontmatter":{"title":"rajput-hemant","titleTemplate":"Leetcode","sidebar":false,"aside":false,"editLink":false,"next":"Go To First Problem"},"headers":[{"level":3,"title":"🏆 Curated solutions to Leetcode problems in multiple languages to ace the Coding Interviews.","slug":"🏆-curated-solutions-to-leetcode-problems-in-multiple-languages-to-ace-the-coding-interviews","link":"#🏆-curated-solutions-to-leetcode-problems-in-multiple-languages-to-ace-the-coding-interviews","children":[]},{"level":2,"title":"Solutions","slug":"solutions","link":"#solutions","children":[{"level":3,"title":"Total Problems Solved: 193","slug":"total-problems-solved-193","link":"#total-problems-solved-193","children":[]}]},{"level":2,"title":"Contributors","slug":"contributors","link":"#contributors","children":[]}],"relativePath":"index.md","lastUpdated":1689264752000}'),x={name:"index.md"},R=Object.assign(x,{setup(w){const{isDark:i}=l();return(B,D)=>{const n=h("Badge");return r(),o("div",null,[d,u,e("div",S,[c(i)?(r(),o("img",f)):(r(),o("img",T)),C,P,e("p",null,[e("a",p,[a(n,{type:"warning"},{default:s(()=>[t(" "),E,t(),W,t(),O,t(" ")]),_:1})]),t(" "),e("a",_,[a(n,{type:"warning"},{default:s(()=>[t(" "),b,t(),y,t(),k,t(" ")]),_:1})])]),v])])}}});export{N as __pageData,R as default};
diff --git a/assets/index.md.7b37d749.lean.js b/assets/index.md.7b37d749.lean.js
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..8b87e7af
--- /dev/null
+++ b/assets/index.md.7b37d749.lean.js
@@ -0,0 +1 @@
+import{a as m,_ as g}from"./chunks/dark.0b1a1d54.js";import{u as l,r as h,o as r,c as o,b as e,d as c,e as a,w as s,f as t,a as I}from"./app.e4604e86.js";const d=e("div",{class:"warning custom-block"},[e("p",{class:"custom-block-title"},"💡 Note"),e("p",null,"It might take some time to reflect changes from the repository.")],-1),u=e("br",null,null,-1),S={align:"center"},f={key:0,src:m},T={key:1,src:g},C=e("h3",{id:"🏆-curated-solutions-to-leetcode-problems-in-multiple-languages-to-ace-the-coding-interviews",tabindex:"-1"},[t("🏆 Curated solutions to Leetcode problems in multiple languages to ace the Coding Interviews. "),e("a",{class:"header-anchor",href:"#🏆-curated-solutions-to-leetcode-problems-in-multiple-languages-to-ace-the-coding-interviews","aria-hidden":"true"},"#")],-1),P=e("h2",{id:"solutions",tabindex:"-1"},[t("Solutions "),e("a",{class:"header-anchor",href:"#solutions","aria-hidden":"true"},"#")],-1),p={href:"./TOPICWISE"},E=e("br",null,null,-1),W=e("strong",null,[e("em",null,"Topic Wise")],-1),O=e("br",null,null,-1),_={href:"./SERIALWISE"},b=e("br",null,null,-1),y=e("strong",null,[e("em",null,"Serial Wise")],-1),k=e("br",null,null,-1),v=I("",4),N=JSON.parse('{"title":"rajput-hemant","titleTemplate":"Leetcode","description":"","frontmatter":{"title":"rajput-hemant","titleTemplate":"Leetcode","sidebar":false,"aside":false,"editLink":false,"next":"Go To First Problem"},"headers":[{"level":3,"title":"🏆 Curated solutions to Leetcode problems in multiple languages to ace the Coding Interviews.","slug":"🏆-curated-solutions-to-leetcode-problems-in-multiple-languages-to-ace-the-coding-interviews","link":"#🏆-curated-solutions-to-leetcode-problems-in-multiple-languages-to-ace-the-coding-interviews","children":[]},{"level":2,"title":"Solutions","slug":"solutions","link":"#solutions","children":[{"level":3,"title":"Total Problems Solved: 193","slug":"total-problems-solved-193","link":"#total-problems-solved-193","children":[]}]},{"level":2,"title":"Contributors","slug":"contributors","link":"#contributors","children":[]}],"relativePath":"index.md","lastUpdated":1689264752000}'),x={name:"index.md"},R=Object.assign(x,{setup(w){const{isDark:i}=l();return(B,D)=>{const n=h("Badge");return r(),o("div",null,[d,u,e("div",S,[c(i)?(r(),o("img",f)):(r(),o("img",T)),C,P,e("p",null,[e("a",p,[a(n,{type:"warning"},{default:s(()=>[t(" "),E,t(),W,t(),O,t(" ")]),_:1})]),t(" "),e("a",_,[a(n,{type:"warning"},{default:s(()=>[t(" "),b,t(),y,t(),k,t(" ")]),_:1})])]),v])])}}});export{N as __pageData,R as default};
diff --git a/assets/inter-cyrillic-ext.0877b0d9.woff2 b/assets/inter-cyrillic-ext.0877b0d9.woff2
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..f2728758
Binary files /dev/null and b/assets/inter-cyrillic-ext.0877b0d9.woff2 differ
diff --git a/assets/inter-cyrillic.f8750142.woff2 b/assets/inter-cyrillic.f8750142.woff2
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..de6a128b
Binary files /dev/null and b/assets/inter-cyrillic.f8750142.woff2 differ
diff --git a/assets/inter-greek-ext.3e6f6728.woff2 b/assets/inter-greek-ext.3e6f6728.woff2
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..701afd3c
Binary files /dev/null and b/assets/inter-greek-ext.3e6f6728.woff2 differ
diff --git a/assets/inter-greek.117e1956.woff2 b/assets/inter-greek.117e1956.woff2
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..74125bbc
Binary files /dev/null and b/assets/inter-greek.117e1956.woff2 differ
diff --git a/assets/inter-italic-cyrillic-ext.33bd5a8e.woff2 b/assets/inter-italic-cyrillic-ext.33bd5a8e.woff2
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..2a687296
Binary files /dev/null and b/assets/inter-italic-cyrillic-ext.33bd5a8e.woff2 differ
diff --git a/assets/inter-italic-cyrillic.ea42a392.woff2 b/assets/inter-italic-cyrillic.ea42a392.woff2
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..f6403515
Binary files /dev/null and b/assets/inter-italic-cyrillic.ea42a392.woff2 differ
diff --git a/assets/inter-italic-greek-ext.4fbe9427.woff2 b/assets/inter-italic-greek-ext.4fbe9427.woff2
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..00218960
Binary files /dev/null and b/assets/inter-italic-greek-ext.4fbe9427.woff2 differ
diff --git a/assets/inter-italic-greek.8f4463c4.woff2 b/assets/inter-italic-greek.8f4463c4.woff2
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..71c265f8
Binary files /dev/null and b/assets/inter-italic-greek.8f4463c4.woff2 differ
diff --git a/assets/inter-italic-latin-ext.bd8920cc.woff2 b/assets/inter-italic-latin-ext.bd8920cc.woff2
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..9c1b9440
Binary files /dev/null and b/assets/inter-italic-latin-ext.bd8920cc.woff2 differ
diff --git a/assets/inter-italic-latin.bd3b6f56.woff2 b/assets/inter-italic-latin.bd3b6f56.woff2
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..01fcf207
Binary files /dev/null and b/assets/inter-italic-latin.bd3b6f56.woff2 differ
diff --git a/assets/inter-italic-vietnamese.6ce511fb.woff2 b/assets/inter-italic-vietnamese.6ce511fb.woff2
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..e4f788ee
Binary files /dev/null and b/assets/inter-italic-vietnamese.6ce511fb.woff2 differ
diff --git a/assets/inter-latin-ext.7cc429bc.woff2 b/assets/inter-latin-ext.7cc429bc.woff2
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..2fa148c3
Binary files /dev/null and b/assets/inter-latin-ext.7cc429bc.woff2 differ
diff --git a/assets/inter-latin.4fe6132f.woff2 b/assets/inter-latin.4fe6132f.woff2
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..1a4cd429
Binary files /dev/null and b/assets/inter-latin.4fe6132f.woff2 differ
diff --git a/assets/inter-roman-cyrillic-ext.e75737ce.woff2 b/assets/inter-roman-cyrillic-ext.e75737ce.woff2
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..28593ccb
Binary files /dev/null and b/assets/inter-roman-cyrillic-ext.e75737ce.woff2 differ
diff --git a/assets/inter-roman-cyrillic.5f2c6c8c.woff2 b/assets/inter-roman-cyrillic.5f2c6c8c.woff2
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..a20adc16
Binary files /dev/null and b/assets/inter-roman-cyrillic.5f2c6c8c.woff2 differ
diff --git a/assets/inter-roman-greek-ext.ab0619bc.woff2 b/assets/inter-roman-greek-ext.ab0619bc.woff2
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..e3b0be76
Binary files /dev/null and b/assets/inter-roman-greek-ext.ab0619bc.woff2 differ
diff --git a/assets/inter-roman-greek.d5a6d92a.woff2 b/assets/inter-roman-greek.d5a6d92a.woff2
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..f790e047
Binary files /dev/null and b/assets/inter-roman-greek.d5a6d92a.woff2 differ
diff --git a/assets/inter-roman-latin-ext.0030eebd.woff2 b/assets/inter-roman-latin-ext.0030eebd.woff2
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..715bd903
Binary files /dev/null and b/assets/inter-roman-latin-ext.0030eebd.woff2 differ
diff --git a/assets/inter-roman-latin.2ed14f66.woff2 b/assets/inter-roman-latin.2ed14f66.woff2
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..a540b7af
Binary files /dev/null and b/assets/inter-roman-latin.2ed14f66.woff2 differ
diff --git a/assets/inter-roman-vietnamese.14ce25a6.woff2 b/assets/inter-roman-vietnamese.14ce25a6.woff2
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..5a9f9cb9
Binary files /dev/null and b/assets/inter-roman-vietnamese.14ce25a6.woff2 differ
diff --git a/assets/inter-vietnamese.2c644a25.woff2 b/assets/inter-vietnamese.2c644a25.woff2
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..c2ffbb09
Binary files /dev/null and b/assets/inter-vietnamese.2c644a25.woff2 differ
diff --git a/assets/solution_0001-0100_001 - Two Sum.md.9e2ed953.js b/assets/solution_0001-0100_001 - Two Sum.md.9e2ed953.js
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..6db49d77
--- /dev/null
+++ b/assets/solution_0001-0100_001 - Two Sum.md.9e2ed953.js
@@ -0,0 +1,35 @@
+import{_ as s,o as a,c as n,a as l}from"./app.e4604e86.js";const i=JSON.parse('{"title":"1. Two Sum","description":"","frontmatter":{},"headers":[{"level":2,"title":"Problem Statement:","slug":"problem-statement","link":"#problem-statement","children":[{"level":3,"title":"Example 1:","slug":"example-1","link":"#example-1","children":[]},{"level":3,"title":"Example 2:","slug":"example-2","link":"#example-2","children":[]},{"level":3,"title":"Example 3:","slug":"example-3","link":"#example-3","children":[]},{"level":3,"title":"Constraints:","slug":"constraints","link":"#constraints","children":[]}]},{"level":2,"title":"Solution:","slug":"solution","link":"#solution","children":[{"level":3,"title":"...","slug":"","link":"#","children":[]}]}],"relativePath":"solution/0001-0100/001 - Two Sum.md","lastUpdated":1671291107000}'),p={name:"solution/0001-0100/001 - Two Sum.md"},o=l(`
`,19),e=[o];function t(c,r,D,y,C,A){return a(),n("div",null,e)}const u=s(p,[["render",t]]);export{i as __pageData,u as default};
diff --git a/assets/solution_0001-0100_001 - Two Sum.md.9e2ed953.lean.js b/assets/solution_0001-0100_001 - Two Sum.md.9e2ed953.lean.js
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..2a19b257
--- /dev/null
+++ b/assets/solution_0001-0100_001 - Two Sum.md.9e2ed953.lean.js
@@ -0,0 +1 @@
+import{_ as s,o as a,c as n,a as l}from"./app.e4604e86.js";const i=JSON.parse('{"title":"1. Two Sum","description":"","frontmatter":{},"headers":[{"level":2,"title":"Problem Statement:","slug":"problem-statement","link":"#problem-statement","children":[{"level":3,"title":"Example 1:","slug":"example-1","link":"#example-1","children":[]},{"level":3,"title":"Example 2:","slug":"example-2","link":"#example-2","children":[]},{"level":3,"title":"Example 3:","slug":"example-3","link":"#example-3","children":[]},{"level":3,"title":"Constraints:","slug":"constraints","link":"#constraints","children":[]}]},{"level":2,"title":"Solution:","slug":"solution","link":"#solution","children":[{"level":3,"title":"...","slug":"","link":"#","children":[]}]}],"relativePath":"solution/0001-0100/001 - Two Sum.md","lastUpdated":1671291107000}'),p={name:"solution/0001-0100/001 - Two Sum.md"},o=l("",19),e=[o];function t(c,r,D,y,C,A){return a(),n("div",null,e)}const u=s(p,[["render",t]]);export{i as __pageData,u as default};
diff --git a/assets/solution_0001-0100_002 - Add Two Numbers.md.bf9d46ea.js b/assets/solution_0001-0100_002 - Add Two Numbers.md.bf9d46ea.js
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..df506bdc
--- /dev/null
+++ b/assets/solution_0001-0100_002 - Add Two Numbers.md.bf9d46ea.js
@@ -0,0 +1,29 @@
+import{_ as s,o as a,c as n,a as l}from"./app.e4604e86.js";const F=JSON.parse('{"title":"2. Add Two Numbers","description":"","frontmatter":{},"headers":[{"level":2,"title":"Problem Statement:","slug":"problem-statement","link":"#problem-statement","children":[{"level":3,"title":"Example 1:","slug":"example-1","link":"#example-1","children":[]},{"level":3,"title":"Example 2:","slug":"example-2","link":"#example-2","children":[]},{"level":3,"title":"Example 3:","slug":"example-3","link":"#example-3","children":[]},{"level":3,"title":"Constraints:","slug":"constraints","link":"#constraints","children":[]}]},{"level":2,"title":"Solution:","slug":"solution","link":"#solution","children":[{"level":3,"title":"...","slug":"","link":"#","children":[]}]}],"relativePath":"solution/0001-0100/002 - Add Two Numbers.md","lastUpdated":1671291107000}'),p={name:"solution/0001-0100/002 - Add Two Numbers.md"},e=l(`
You are given two non-empty linked lists representing two non-negative integers. The digits are stored in reverse order, and each of their nodes contains a single digit. Add the two numbers and return the sum as a linked list.
You may assume the two numbers do not contain any leading zero, except the number 0 itself.
`,18),o=[e];function t(r,c,D,C,y,A){return a(),n("div",null,o)}const d=s(p,[["render",t]]);export{F as __pageData,d as default};
diff --git a/assets/solution_0001-0100_002 - Add Two Numbers.md.bf9d46ea.lean.js b/assets/solution_0001-0100_002 - Add Two Numbers.md.bf9d46ea.lean.js
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..79d3edc4
--- /dev/null
+++ b/assets/solution_0001-0100_002 - Add Two Numbers.md.bf9d46ea.lean.js
@@ -0,0 +1 @@
+import{_ as s,o as a,c as n,a as l}from"./app.e4604e86.js";const F=JSON.parse('{"title":"2. Add Two Numbers","description":"","frontmatter":{},"headers":[{"level":2,"title":"Problem Statement:","slug":"problem-statement","link":"#problem-statement","children":[{"level":3,"title":"Example 1:","slug":"example-1","link":"#example-1","children":[]},{"level":3,"title":"Example 2:","slug":"example-2","link":"#example-2","children":[]},{"level":3,"title":"Example 3:","slug":"example-3","link":"#example-3","children":[]},{"level":3,"title":"Constraints:","slug":"constraints","link":"#constraints","children":[]}]},{"level":2,"title":"Solution:","slug":"solution","link":"#solution","children":[{"level":3,"title":"...","slug":"","link":"#","children":[]}]}],"relativePath":"solution/0001-0100/002 - Add Two Numbers.md","lastUpdated":1671291107000}'),p={name:"solution/0001-0100/002 - Add Two Numbers.md"},e=l("",18),o=[e];function t(r,c,D,C,y,A){return a(),n("div",null,o)}const d=s(p,[["render",t]]);export{F as __pageData,d as default};
diff --git a/assets/solution_0001-0100_004 - Median of Two Sorted Arrays.md.2001f2e0.js b/assets/solution_0001-0100_004 - Median of Two Sorted Arrays.md.2001f2e0.js
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..b4ca2424
--- /dev/null
+++ b/assets/solution_0001-0100_004 - Median of Two Sorted Arrays.md.2001f2e0.js
@@ -0,0 +1,31 @@
+import{_ as s,o as a,c as n,a as l}from"./app.e4604e86.js";const i=JSON.parse('{"title":"4. Median of Two Sorted Arrays","description":"","frontmatter":{},"headers":[{"level":2,"title":"Problem Statement:","slug":"problem-statement","link":"#problem-statement","children":[{"level":3,"title":"Example 1:","slug":"example-1","link":"#example-1","children":[]},{"level":3,"title":"Example 2:","slug":"example-2","link":"#example-2","children":[]},{"level":3,"title":"Constraints:","slug":"constraints","link":"#constraints","children":[]}]},{"level":2,"title":"Solution:","slug":"solution","link":"#solution","children":[{"level":3,"title":"...","slug":"","link":"#","children":[]}]}],"relativePath":"solution/0001-0100/004 - Median of Two Sorted Arrays.md","lastUpdated":1671697454000}'),p={name:"solution/0001-0100/004 - Median of Two Sorted Arrays.md"},o=l(`
`,15),e=[o];function t(r,c,D,C,y,A){return a(),n("div",null,e)}const d=s(p,[["render",t]]);export{i as __pageData,d as default};
diff --git a/assets/solution_0001-0100_004 - Median of Two Sorted Arrays.md.2001f2e0.lean.js b/assets/solution_0001-0100_004 - Median of Two Sorted Arrays.md.2001f2e0.lean.js
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..1b2dcffa
--- /dev/null
+++ b/assets/solution_0001-0100_004 - Median of Two Sorted Arrays.md.2001f2e0.lean.js
@@ -0,0 +1 @@
+import{_ as s,o as a,c as n,a as l}from"./app.e4604e86.js";const i=JSON.parse('{"title":"4. Median of Two Sorted Arrays","description":"","frontmatter":{},"headers":[{"level":2,"title":"Problem Statement:","slug":"problem-statement","link":"#problem-statement","children":[{"level":3,"title":"Example 1:","slug":"example-1","link":"#example-1","children":[]},{"level":3,"title":"Example 2:","slug":"example-2","link":"#example-2","children":[]},{"level":3,"title":"Constraints:","slug":"constraints","link":"#constraints","children":[]}]},{"level":2,"title":"Solution:","slug":"solution","link":"#solution","children":[{"level":3,"title":"...","slug":"","link":"#","children":[]}]}],"relativePath":"solution/0001-0100/004 - Median of Two Sorted Arrays.md","lastUpdated":1671697454000}'),p={name:"solution/0001-0100/004 - Median of Two Sorted Arrays.md"},o=l("",15),e=[o];function t(r,c,D,C,y,A){return a(),n("div",null,e)}const d=s(p,[["render",t]]);export{i as __pageData,d as default};
diff --git a/assets/solution_0001-0100_007 - Reverse Integer.md.c5e5d46f.js b/assets/solution_0001-0100_007 - Reverse Integer.md.c5e5d46f.js
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..d05976d1
--- /dev/null
+++ b/assets/solution_0001-0100_007 - Reverse Integer.md.c5e5d46f.js
@@ -0,0 +1,16 @@
+import{_ as s,o as a,c as e,a as n}from"./app.e4604e86.js";const y=JSON.parse('{"title":"7. Reverse Integer","description":"","frontmatter":{},"headers":[{"level":2,"title":"Problem Statement:","slug":"problem-statement","link":"#problem-statement","children":[{"level":3,"title":"Example 1:","slug":"example-1","link":"#example-1","children":[]},{"level":3,"title":"Example 2:","slug":"example-2","link":"#example-2","children":[]},{"level":3,"title":"Example 3:","slug":"example-3","link":"#example-3","children":[]},{"level":3,"title":"Constraints:","slug":"constraints","link":"#constraints","children":[]}]},{"level":2,"title":"Solution:","slug":"solution","link":"#solution","children":[{"level":3,"title":"...","slug":"","link":"#","children":[]}]}],"relativePath":"solution/0001-0100/007 - Reverse Integer.md","lastUpdated":1671291107000}'),l={name:"solution/0001-0100/007 - Reverse Integer.md"},p=n(`
Given a signed 32-bit integer x, return x with its digits reversed. If reversing x causes the value to go outside the signed 32-bit integer range [-231, 231 - 1], then return 0.
Assume the environment does not allow you to store 64-bit integers (signed or unsigned).
Input: x = -121
+Output: false
+Explanation: From left to right, it reads -121. From right to left, it becomes 121-. Therefore it is not a palindrome.
+
`,19),p=[o];function t(r,c,i,C,d,D){return a(),n("div",null,p)}const h=s(e,[["render",t]]);export{y as __pageData,h as default};
diff --git a/assets/solution_0001-0100_009 - Palindrome Number.md.93ab32fc.lean.js b/assets/solution_0001-0100_009 - Palindrome Number.md.93ab32fc.lean.js
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..3cefd2b8
--- /dev/null
+++ b/assets/solution_0001-0100_009 - Palindrome Number.md.93ab32fc.lean.js
@@ -0,0 +1 @@
+import{_ as s,o as a,c as n,a as l}from"./app.e4604e86.js";const y=JSON.parse('{"title":"9. Palindrome Number","description":"","frontmatter":{},"headers":[{"level":2,"title":"Problem Statement:","slug":"problem-statement","link":"#problem-statement","children":[{"level":3,"title":"Example 1:","slug":"example-1","link":"#example-1","children":[]},{"level":3,"title":"Example 2:","slug":"example-2","link":"#example-2","children":[]},{"level":3,"title":"Example 3:","slug":"example-3","link":"#example-3","children":[]},{"level":3,"title":"Constraints:","slug":"constraints","link":"#constraints","children":[]}]},{"level":2,"title":"Solution:","slug":"solution","link":"#solution","children":[{"level":3,"title":"...","slug":"","link":"#","children":[]}]}],"relativePath":"solution/0001-0100/009 - Palindrome Number.md","lastUpdated":1671291107000}'),e={name:"solution/0001-0100/009 - Palindrome Number.md"},o=l("",19),p=[o];function t(r,c,i,C,d,D){return a(),n("div",null,p)}const h=s(e,[["render",t]]);export{y as __pageData,h as default};
diff --git a/assets/solution_0001-0100_013 - Roman to Integer.md.1346a5a7.js b/assets/solution_0001-0100_013 - Roman to Integer.md.1346a5a7.js
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..d9575898
--- /dev/null
+++ b/assets/solution_0001-0100_013 - Roman to Integer.md.1346a5a7.js
@@ -0,0 +1,40 @@
+import{_ as s,o as a,c as n,a as l}from"./app.e4604e86.js";const F=JSON.parse('{"title":"13. Roman to Integer","description":"","frontmatter":{},"headers":[{"level":2,"title":"Problem Statement:","slug":"problem-statement","link":"#problem-statement","children":[{"level":3,"title":"Example 1:","slug":"example-1","link":"#example-1","children":[]},{"level":3,"title":"Example 2:","slug":"example-2","link":"#example-2","children":[]},{"level":3,"title":"Example 3:","slug":"example-3","link":"#example-3","children":[]},{"level":3,"title":"Constraints:","slug":"constraints","link":"#constraints","children":[]}]},{"level":2,"title":"Solution:","slug":"solution","link":"#solution","children":[{"level":3,"title":"...","slug":"","link":"#","children":[]}]}],"relativePath":"solution/0001-0100/013 - Roman to Integer.md","lastUpdated":1671697454000}'),e={name:"solution/0001-0100/013 - Roman to Integer.md"},o=l(`
Roman numerals are represented by seven different symbols: I, V, X, L, C, D and M.
Symbol Value
+I 1
+V 5
+X 10
+L 50
+C 100
+D 500
+M 1000
+
For example, 2 is written as II in Roman numeral, just two ones added together. 12 is written as XII, which is simply X + II. The number 27 is written as XXVII, which is XX + V + II.
Roman numerals are usually written largest to smallest from left to right. However, the numeral for four is not IIII. Instead, the number four is written as IV. Because the one is before the five we subtract it making four. The same principle applies to the number nine, which is written as IX. There are six instances where subtraction is used:
I can be placed before V (5) and X (10) to make 4 and 9.
X can be placed before L (50) and C (100) to make 40 and 90.
C can be placed before D (500) and M (1000) to make 400 and 900. Given a roman numeral, convert it to an integer.
- 1 <= s.length <= 15
+- s contains only the characters \`('I', 'V', 'X', 'L', 'C', 'D', 'M')\`.
+- It is guaranteed that s is a valid roman numeral in the range [\`1, 3999]\`.
+
`,20),p=[o];function t(c,r,D,i,C,y){return a(),n("div",null,p)}const d=s(e,[["render",t]]);export{F as __pageData,d as default};
diff --git a/assets/solution_0001-0100_013 - Roman to Integer.md.1346a5a7.lean.js b/assets/solution_0001-0100_013 - Roman to Integer.md.1346a5a7.lean.js
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..58fbac30
--- /dev/null
+++ b/assets/solution_0001-0100_013 - Roman to Integer.md.1346a5a7.lean.js
@@ -0,0 +1 @@
+import{_ as s,o as a,c as n,a as l}from"./app.e4604e86.js";const F=JSON.parse('{"title":"13. Roman to Integer","description":"","frontmatter":{},"headers":[{"level":2,"title":"Problem Statement:","slug":"problem-statement","link":"#problem-statement","children":[{"level":3,"title":"Example 1:","slug":"example-1","link":"#example-1","children":[]},{"level":3,"title":"Example 2:","slug":"example-2","link":"#example-2","children":[]},{"level":3,"title":"Example 3:","slug":"example-3","link":"#example-3","children":[]},{"level":3,"title":"Constraints:","slug":"constraints","link":"#constraints","children":[]}]},{"level":2,"title":"Solution:","slug":"solution","link":"#solution","children":[{"level":3,"title":"...","slug":"","link":"#","children":[]}]}],"relativePath":"solution/0001-0100/013 - Roman to Integer.md","lastUpdated":1671697454000}'),e={name:"solution/0001-0100/013 - Roman to Integer.md"},o=l("",20),p=[o];function t(c,r,D,i,C,y){return a(),n("div",null,p)}const d=s(e,[["render",t]]);export{F as __pageData,d as default};
diff --git a/assets/solution_0001-0100_014 - Longest Common Prefix.md.7401d23f.js b/assets/solution_0001-0100_014 - Longest Common Prefix.md.7401d23f.js
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..4ad4f1d3
--- /dev/null
+++ b/assets/solution_0001-0100_014 - Longest Common Prefix.md.7401d23f.js
@@ -0,0 +1,19 @@
+import{_ as s,o as n,c as a,a as o}from"./app.e4604e86.js";const F=JSON.parse('{"title":"14. Longest Common Prefix","description":"","frontmatter":{},"headers":[{"level":2,"title":"Problem Statement","slug":"problem-statement","link":"#problem-statement","children":[]},{"level":2,"title":"Solution:","slug":"solution","link":"#solution","children":[{"level":3,"title":"...","slug":"","link":"#","children":[]}]}],"relativePath":"solution/0001-0100/014 - Longest Common Prefix.md","lastUpdated":1671952530000}'),l={name:"solution/0001-0100/014 - Longest Common Prefix.md"},e=o(`
Given a linked list, swap every two adjacent nodes and return its head. You must solve the problem without modifying the values in the list's nodes (i.e., only nodes themselves may be changed.)
Given an integer array nums sorted in non-decreasing order, remove the duplicates in-place such that each unique element appears only once. The relative order of the elements should be kept the same.
Since it is impossible to change the length of the array in some languages, you must instead have the result be placed in the first part of the array nums. More formally, if there are k elements after removing the duplicates, then the first k elements of nums should hold the final result. It does not matter what you leave beyond the first k elements.
Return k after placing the final result in the first k slots of nums.
Do not allocate extra space for another array. You must do this by modifying the input array in-place with O(1) extra memory.
The judge will test your solution with the following code:
+
+int[] nums = [...]; // Input array
+int[] expectedNums = [...]; // The expected answer with correct length
+
+int k = removeDuplicates(nums); // Calls your implementation
+
+assert k == expectedNums.length;
+for (int i = 0; i < k; i++) {
+ assert nums[i] == expectedNums[i];
+}
+
If all assertions pass, then your solution will be accepted.
Input: nums = [1,1,2]
+Output: 2, nums = [1,2,_]
+Explanation: Your function should return k = 2, with the first two elements of nums being 1 and 2 respectively.
+It does not matter what you leave beyond the returned k (hence they are underscores).
+
Input: nums = [0,0,1,1,1,2,2,3,3,4]
+Output: 5, nums = [0,1,2,3,4,_,_,_,_,_]
+Explanation: Your function should return k = 5, with the first five elements of nums being 0, 1, 2, 3, and 4 respectively.
+It does not matter what you leave beyond the returned k (hence they are underscores).
+
Given an integer array nums and an integer val, remove all occurrences of val in nums in-place. The relative order of the elements may be changed.
Since it is impossible to change the length of the array in some languages, you must instead have the result be placed in the first part of the array nums. More formally, if there are k elements after removing the duplicates, then the first k elements of nums should hold the final result. It does not matter what you leave beyond the first k elements.
Return k after placing the final result in the first k slots of nums.
Do not allocate extra space for another array. You must do this by modifying the input array in-place with O(1) extra memory.
The judge will test your solution with the following code:
+
+int[] nums = [...]; // Input array
+int val = ...; // Value to remove
+int[] expectedNums = [...]; // The expected answer with correct length.
+// It is sorted with no values equaling val.
+
+int k = removeElement(nums, val); // Calls your implementation
+
+assert k == expectedNums.length;
+sort(nums, 0, k); // Sort the first k elements of nums
+for (int i = 0; i < actualLength; i++) {
+assert nums[i] == expectedNums[i];
+}
+
If all assertions pass, then your solution will be accepted.
Input: nums = [3,2,2,3], val = 3
+Output: 2, nums = [2,2,_,_]
+Explanation: Your function should return k = 2, with the first two elements of nums being 2.
+It does not matter what you leave beyond the returned k (hence they are underscores).
+
Input: nums = [0,1,2,2,3,0,4,2], val = 2
+Output: 5, nums = [0,1,4,0,3,_,_,_]
+Explanation: Your function should return k = 5, with the first five elements of nums containing 0, 0, 1, 3, and 4.
+Note that the five elements can be returned in any order.
+It does not matter what you leave beyond the returned k (hence they are underscores).
+
`,20),o=[t];function p(r,c,i,d,C,u){return n(),a("div",null,o)}const A=s(l,[["render",p]]);export{h as __pageData,A as default};
diff --git a/assets/solution_0001-0100_027 - Remove Element.md.9692244b.lean.js b/assets/solution_0001-0100_027 - Remove Element.md.9692244b.lean.js
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..718c71ad
--- /dev/null
+++ b/assets/solution_0001-0100_027 - Remove Element.md.9692244b.lean.js
@@ -0,0 +1 @@
+import{_ as s,o as n,c as a,a as e}from"./app.e4604e86.js";const h=JSON.parse('{"title":"27. Remove Element","description":"","frontmatter":{},"headers":[{"level":2,"title":"Problem Statement:","slug":"problem-statement","link":"#problem-statement","children":[{"level":3,"title":"Custom Judge:","slug":"custom-judge","link":"#custom-judge","children":[]},{"level":3,"title":"Example 1:","slug":"example-1","link":"#example-1","children":[]},{"level":3,"title":"Example 2:","slug":"example-2","link":"#example-2","children":[]},{"level":3,"title":"Constraints:","slug":"constraints","link":"#constraints","children":[]}]},{"level":2,"title":"Solution:","slug":"solution","link":"#solution","children":[{"level":3,"title":"...","slug":"","link":"#","children":[]}]}],"relativePath":"solution/0001-0100/027 - Remove Element.md","lastUpdated":1671291107000}'),l={name:"solution/0001-0100/027 - Remove Element.md"},t=e("",20),o=[t];function p(r,c,i,d,C,u){return n(),a("div",null,o)}const A=s(l,[["render",p]]);export{h as __pageData,A as default};
diff --git a/assets/solution_0001-0100_028 - Find the Index of the First Occurrence in a String.md.94646e7c.js b/assets/solution_0001-0100_028 - Find the Index of the First Occurrence in a String.md.94646e7c.js
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..5c016b59
--- /dev/null
+++ b/assets/solution_0001-0100_028 - Find the Index of the First Occurrence in a String.md.94646e7c.js
@@ -0,0 +1,29 @@
+import{_ as s,o as n,c as a,a as e}from"./app.e4604e86.js";const A=JSON.parse('{"title":"28. Find the Index of the First Occurrence in a String","description":"","frontmatter":{},"headers":[{"level":2,"title":"Problem Statement","slug":"problem-statement","link":"#problem-statement","children":[]},{"level":2,"title":"Solution:","slug":"solution","link":"#solution","children":[{"level":3,"title":"...","slug":"","link":"#","children":[]}]}],"relativePath":"solution/0001-0100/028 - Find the Index of the First Occurrence in a String.md","lastUpdated":1677958804000}'),l={name:"solution/0001-0100/028 - Find the Index of the First Occurrence in a String.md"},o=e(`
28. Find the Index of the First Occurrence in a String #
Given two strings needle and haystack, return the index of the first occurrence of needle in haystack, or -1 if needle is not part of haystack.
Example 1:
Input: haystack = "sadbutsad", needle = "sad"
+Output: 0
+Explanation: "sad" occurs at index 0 and 6.
+The first occurrence is at index 0, so we return 0.
+
Example 2:
Input: haystack = "leetcode", needle = "leeto"
+Output: -1
+Explanation: "leeto" did not occur in "leetcode", so we return -1.
+
Constraints:
1 <= haystack.length, needle.length <= 104
haystack and needle consist of only lowercase English characters.
implSolution{
+pubfnstr_str(haystack:String, needle:String)->i32{
+let(m, n)=(haystack.len(), needle.len());
+
+if m < n {
+return-1;
+}
+
+ // iterate over the haystack from 0 to m - n
+ // because the needle can't be longer than the haystack
+for i in0..=m - n {
+if haystack[i..i + n]== needle {
+return i asi32;
+}
+}
+
+-1
+}
+}
+
+
`,16),p=[o];function t(c,r,i,C,D,y){return n(),a("div",null,p)}const F=s(l,[["render",t]]);export{A as __pageData,F as default};
diff --git a/assets/solution_0001-0100_028 - Find the Index of the First Occurrence in a String.md.94646e7c.lean.js b/assets/solution_0001-0100_028 - Find the Index of the First Occurrence in a String.md.94646e7c.lean.js
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..5681e4f1
--- /dev/null
+++ b/assets/solution_0001-0100_028 - Find the Index of the First Occurrence in a String.md.94646e7c.lean.js
@@ -0,0 +1 @@
+import{_ as s,o as n,c as a,a as e}from"./app.e4604e86.js";const A=JSON.parse('{"title":"28. Find the Index of the First Occurrence in a String","description":"","frontmatter":{},"headers":[{"level":2,"title":"Problem Statement","slug":"problem-statement","link":"#problem-statement","children":[]},{"level":2,"title":"Solution:","slug":"solution","link":"#solution","children":[{"level":3,"title":"...","slug":"","link":"#","children":[]}]}],"relativePath":"solution/0001-0100/028 - Find the Index of the First Occurrence in a String.md","lastUpdated":1677958804000}'),l={name:"solution/0001-0100/028 - Find the Index of the First Occurrence in a String.md"},o=e("",16),p=[o];function t(c,r,i,C,D,y){return n(),a("div",null,p)}const F=s(l,[["render",t]]);export{A as __pageData,F as default};
diff --git a/assets/solution_0001-0100_035 - Search Insert Position.md.a30de18c.js b/assets/solution_0001-0100_035 - Search Insert Position.md.a30de18c.js
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..166dcbd9
--- /dev/null
+++ b/assets/solution_0001-0100_035 - Search Insert Position.md.a30de18c.js
@@ -0,0 +1,42 @@
+import{_ as s,o as n,c as a,a as l}from"./app.e4604e86.js";const F=JSON.parse('{"title":"35. Search Insert Position","description":"","frontmatter":{},"headers":[{"level":2,"title":"Problem Statement","slug":"problem-statement","link":"#problem-statement","children":[]},{"level":2,"title":"Solution:","slug":"solution","link":"#solution","children":[{"level":3,"title":"...","slug":"","link":"#","children":[]}]}],"relativePath":"solution/0001-0100/035 - Search Insert Position.md","lastUpdated":1677114573000}'),p={name:"solution/0001-0100/035 - Search Insert Position.md"},o=l(`
Given a sorted array of distinct integers and a target value, return the index if the target is found. If not, return the index where it would be if it were inserted in order.
You must write an algorithm with O(log n) runtime complexity.
Example 1:
Input: nums = [1,3,5,6], target = 5
+Output: 2
+
Example 2:
Input: nums = [1,3,5,6], target = 2
+Output: 1
+
Example 3:
Input: nums = [1,3,5,6], target = 7
+Output: 4
+
Constraints:
1 <= nums.length <= 104
-104 <= nums[i] <= 104
nums contains distinct values sorted in ascending order.
/*
+A sudoku solution must satisfy all of the following rules:
+-> Each of the digits 1-9 must occur exactly once in each row.
+-> Each of the digits 1-9 must occur exactly once in each column.
+-> Each of the digits 1-9 must occur exactly once in each of the 9 3x3 sub-boxes of the grid.
+The "." character indicates empty cells.
+*/
+
+publicclassSudokuSolver2{
+publicvoidsolveSudoku(char[][]board){
+helper(board,0,0);
+}
+
+// a utility function to solve the board
+booleanhelper(char[][]board,introw,intcol){
+// base case -> recursion stops at the 10th row
+if(row == board.length)
+returntrue;
+int newRow =0, newCol =0;
+// when its the last col of the board, goto next row & first col
+if(col == board.length -1){
+ newRow = row +1;
+ newCol =0;
+}
+// else, keep increasing the col by one & the row remains the same
+else{
+ newRow = row;
+ newCol = col +1;
+}
+// if the cell isn't empty, i.e. there is a number present in that cell
+if(board[row][col]!='.'){
+// do a recursive call, if the fn returns true, i.e. the board is solved,
+// we'll also return true
+if(helper(board, newRow, newCol))
+returntrue;
+}
+// if cell is empty
+else{
+for(int i =1; i <=9; i++){
+// if it's safe to place 'i' at that cell
+if(isValidPlacement(board, row, col, i)){
+ board[row][col]=(char)(i +'0');
+// after placing the number, do a recursive call,
+// if the fn returns true, we'll also return true
+if(helper(board, newRow, newCol))
+returntrue;
+// if the recursive call returns false, i.e. it wasn't safe to place 'i',
+// we'll empty the cell & and will try for the next value of 'i' (backtracking)
+else
+ board[row][col]='.';
+}
+}
+}
+// return false if it isn't posssible to place a number in the cell
+returnfalse;
+}
+
+// a utility fn to check for valid placement of a number in cell of Sudoku Board
+booleanisValidPlacement(char[][]board,introw,intcol,intnumber){
+// to check if 'number' is present in the row or the col
+for(int i =0; i < board.length; i++){
+// return false if 'number' is present in the col
+if(board[i][col]==(char)(number +'0'))
+returnfalse;
+// return false if 'number' is present in the row
+if(board[row][i]==(char)(number +'0'))
+returnfalse;
+}
+// to check if the 'number' is present in the 3X3 grid
+// There are two ways to get the initial row and column of 3X3 grid
+// 1
+int startingRow =(row /3)*3;
+int startingCol =(col /3)*3;
+// 2
+// int startingRow = (row % 3) - row;
+// int startingCol = (col % 3) - col;
+for(int i = startingRow; i < startingRow +3; i++)
+for(int j = startingCol; j < startingCol +3; j++)
+// return false if 'number' is present in the 3X3 grid or matrix
+if(board[i][j]==(char)(number +'0'))
+returnfalse;
+// return true if 'number' isn't present in row, col & grid
+returntrue;
+}
+}
+
packagemain
+
+funcfirstMissingPositive(nums []int)int{
+ i :=0
+
+for i <len(nums){
+if nums[i]>0&& nums[i]<=len(nums)&& nums[nums[i]-1]!= nums[i]{
+ nums[nums[i]-1], nums[i]= nums[i], nums[nums[i]-1]
+}else{
+ i++
+}
+}
+
+for i, num :=range nums {
+if num != i+1{
+return i +1
+}
+}
+
+returnlen(nums)+1
+}
+
+
rs
implSolution{
+pubfnfirst_missing_positive(nums:Vec<i32>)->i32{
+let(mut nums,mut i)=(nums,0);
+
+while i < nums.len(){
+let num = nums[i];
+
+ // if the number is in the range [1, nums.len()] and not in the right position
+ // swap it with the number at the right position
+if num >0&& num <= nums.len()asi32&& num != nums[num asusize-1]{
+ nums.swap(i, num asusize-1);
+}else{
+ i +=1;
+}
+}
+
+ // find the first missing positive number
+for(i, num)in nums.iter().enumerate(){
+if num !=&(i asi32+1){
+return i asi32+1;
+}
+}
+
+ nums.len()asi32+1
+}
+}
+
+
Given n non-negative integers representing an elevation map where the width of each bar is 1, compute how much water it can trap after raining.
Example 1:
Input: height = [0,1,0,2,1,0,1,3,2,1,2,1]
+Output: 6
+Explanation: The above elevation map (black section) is represented by array [0,1,0,2,1,0,1,3,2,1,2,1]. In this case, 6 units of rain water (blue section) are being trapped.
+
implSolution{
+pubfntrap(height:Vec<i32>)->i32{
+let(mut left,mut right)=(0, height.len()-1);
+let(mut left_max,mut right_max)=(0,0);
+letmut ans =0;
+
+ // iterate from both sides to the middle
+while left < right {
+ // if left is lower than right, then the water level depends on left
+ // else the water level depends on right
+if height[left]< height[right]{
+ // if left height is higher than left_max, then update left_max
+ // else add the difference between left_max and left height to ans
+if height[left]>= left_max {
+ left_max = height[left];
+}else{
+ ans += left_max - height[left];
+}
+ left +=1;
+}else{
+ // if right height is higher than right_max, then update right_max
+ // else add the difference between right_max and right height to ans
+if height[right]>= right_max {
+ right_max = height[right];
+}else{
+ ans += right_max - height[right];
+}
+ right -=1;
+}
+}
+
+ ans
+}
+}
+
+
You are given an n x n 2D matrix representing an image, rotate the image by 90 degrees (clockwise).
You have to rotate the image in-place, which means you have to modify the input 2D matrix directly. DO NOT allocate another 2D matrix and do the rotation.
The n-queens puzzle is the problem of placing n queens on an n x n chessboard such that no two queens attack each other.
Given an integer n, return all distinct solutions to the n-queens puzzle. You may return the answer in any order.
Each solution contains a distinct board configuration of the n-queens' placement, where 'Q' and '.' both indicate a queen and an empty space, respectively.
publicclassNQueens2{
+
+publicstaticList<List<String>>nQueens(intn){
+// List of Lists of boards
+List<List<String>> allBoards =newArrayList<>();
+char[][] board =newchar[n][n];
+helper(board, allBoards,0);
+return allBoards;
+}
+
+staticvoidhelper(char[][]board,List<List<String>>allBoards,intcol){
+// save board to allBoards after placing Queens on all possible cols
+if(col == board.length){
+saveBoard(board, allBoards);
+return;
+}
+for(int row =0; row < board.length; row++){
+// if it's safe, place queen at row
+if(isSafe(row, col, board)){
+ board[row][col]='Q';
+helper(board, allBoards, col +1);
+// backtracking
+ board[row][col]='.';
+}
+}
+}
+
+// Fn to check if it's safe to place Queen
+staticbooleanisSafe(introw,intcol,char[][]board){
+int len = board.length;
+// traverse in all cols to check if a queen is already present or not
+for(int i =0; i < len; i++){
+if(board[row][i]=='Q')
+returnfalse;
+}
+// traverse in all rows to check if a queen is already present or not
+for(int i =0; i < len; i++){
+if(board[i][col]=='Q')
+returnfalse;
+}
+// traverse through upper left diagonal to check if queen is present
+int r = row;
+for(int c = col; c >=0&& r >=0; r--, c--){
+if(board[r][c]=='Q')
+returnfalse;
+}
+// traverse through upper right diagonal to check if queen is present
+ r = row;
+for(int c = col; c < len && r >=0; r--, c++){
+if(board[r][c]=='Q')
+returnfalse;
+}
+// traverse through lower left diagonal to check if queen is present
+ r = row;
+for(int c = col; c >=0&& r < len; r++, c--){
+if(board[r][c]=='Q')
+returnfalse;
+}
+// traverse through lower right diagonal to check if queen is present
+ r = row;
+for(int c = col; c < len && r < len; r++, c++){
+if(board[r][c]=='Q')
+returnfalse;
+}
+returntrue;
+}
+
+// Fn to save a board to List of Boards
+staticvoidsaveBoard(char[][]board,List<List<String>>allBoards){
+int len = board.length;
+String row ="";
+List<String> newBoard =newArrayList<>();
+for(int i =0; i < len; i++){
+ row ="";
+for(int j =0; j < len; j++){
+if(board[i][j]=='Q')
+ row +='Q';
+else
+ row +='.';
+}
+// this adds the row to the newBoards -> "Q..." or "..Q."
+ newBoard.add(row);
+}
+// this add the board to the list of boards -> [[..Q., Q..., ...Q, .Q..],...]
+ allBoards.add(newBoard);
+}
+}
+
`,18),e=[o];function t(r,c,D,y,C,A){return n(),a("div",null,e)}const d=s(p,[["render",t]]);export{i as __pageData,d as default};
diff --git a/assets/solution_0001-0100_051 - N-Queens.md.36f60070.lean.js b/assets/solution_0001-0100_051 - N-Queens.md.36f60070.lean.js
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..e6a54920
--- /dev/null
+++ b/assets/solution_0001-0100_051 - N-Queens.md.36f60070.lean.js
@@ -0,0 +1 @@
+import{_ as s,o as n,c as a,a as l}from"./app.e4604e86.js";const i=JSON.parse('{"title":"51. N-Queens","description":"","frontmatter":{},"headers":[{"level":2,"title":"Problem Statement:","slug":"problem-statement","link":"#problem-statement","children":[{"level":3,"title":"Example 1:","slug":"example-1","link":"#example-1","children":[]},{"level":3,"title":"Example 2:","slug":"example-2","link":"#example-2","children":[]},{"level":3,"title":"Constraints:","slug":"constraints","link":"#constraints","children":[]}]},{"level":2,"title":"Solution:","slug":"solution","link":"#solution","children":[{"level":3,"title":"...","slug":"","link":"#","children":[]}]}],"relativePath":"solution/0001-0100/051 - N-Queens.md","lastUpdated":1671697454000}'),p={name:"solution/0001-0100/051 - N-Queens.md"},o=l("",18),e=[o];function t(r,c,D,y,C,A){return n(),a("div",null,e)}const d=s(p,[["render",t]]);export{i as __pageData,d as default};
diff --git a/assets/solution_0001-0100_053 - Maximum Subarray.md.edde9bbd.js b/assets/solution_0001-0100_053 - Maximum Subarray.md.edde9bbd.js
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..625d6125
--- /dev/null
+++ b/assets/solution_0001-0100_053 - Maximum Subarray.md.edde9bbd.js
@@ -0,0 +1,29 @@
+import{_ as s,o as a,c as n,a as l}from"./app.e4604e86.js";const A=JSON.parse('{"title":"53. Maximum Subarray","description":"","frontmatter":{},"headers":[{"level":2,"title":"Problem Statement","slug":"problem-statement","link":"#problem-statement","children":[]},{"level":2,"title":"Solution:","slug":"solution","link":"#solution","children":[{"level":3,"title":"...","slug":"","link":"#","children":[]}]}],"relativePath":"solution/0001-0100/053 - Maximum Subarray.md","lastUpdated":1676656807000}'),p={name:"solution/0001-0100/053 - Maximum Subarray.md"},o=l(`
`,20),e=[o];function t(r,c,i,y,D,u){return a(),n("div",null,e)}const d=s(p,[["render",t]]);export{A as __pageData,d as default};
diff --git a/assets/solution_0001-0100_053 - Maximum Subarray.md.edde9bbd.lean.js b/assets/solution_0001-0100_053 - Maximum Subarray.md.edde9bbd.lean.js
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..9625e61f
--- /dev/null
+++ b/assets/solution_0001-0100_053 - Maximum Subarray.md.edde9bbd.lean.js
@@ -0,0 +1 @@
+import{_ as s,o as a,c as n,a as l}from"./app.e4604e86.js";const A=JSON.parse('{"title":"53. Maximum Subarray","description":"","frontmatter":{},"headers":[{"level":2,"title":"Problem Statement","slug":"problem-statement","link":"#problem-statement","children":[]},{"level":2,"title":"Solution:","slug":"solution","link":"#solution","children":[{"level":3,"title":"...","slug":"","link":"#","children":[]}]}],"relativePath":"solution/0001-0100/053 - Maximum Subarray.md","lastUpdated":1676656807000}'),p={name:"solution/0001-0100/053 - Maximum Subarray.md"},o=l("",20),e=[o];function t(r,c,i,y,D,u){return a(),n("div",null,e)}const d=s(p,[["render",t]]);export{A as __pageData,d as default};
diff --git a/assets/solution_0001-0100_055 - Jump Game.md.dc2f1b6e.js b/assets/solution_0001-0100_055 - Jump Game.md.dc2f1b6e.js
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..87654e36
--- /dev/null
+++ b/assets/solution_0001-0100_055 - Jump Game.md.dc2f1b6e.js
@@ -0,0 +1,21 @@
+import{_ as s,o as a,c as n,a as l}from"./app.e4604e86.js";const d=JSON.parse('{"title":"55. Jump Game","description":"","frontmatter":{},"headers":[{"level":2,"title":"Problem Statement:","slug":"problem-statement","link":"#problem-statement","children":[{"level":3,"title":"Example 1:","slug":"example-1","link":"#example-1","children":[]},{"level":3,"title":"Example 2:","slug":"example-2","link":"#example-2","children":[]},{"level":3,"title":"Constraints:","slug":"constraints","link":"#constraints","children":[]}]},{"level":2,"title":"Solution:","slug":"solution","link":"#solution","children":[{"level":3,"title":"...","slug":"","link":"#","children":[]}]}],"relativePath":"solution/0001-0100/055 - Jump Game.md","lastUpdated":1671291107000}'),e={name:"solution/0001-0100/055 - Jump Game.md"},p=l(`
You are given an integer array nums. You are initially positioned at the array's first index, and each element in the array represents your maximum jump length at that position.
Return true if you can reach the last index, or false otherwise.
Input: nums = [3,2,1,0,4]
+Output: false
+Explanation: You will always arrive at index 3 no matter what. Its maximum jump length is 0, which makes it impossible to reach the last index.
+
publicbooleancanJump(int[] nums){
+int n = nums.length,
+ max =0;
+if(n ==1)
+returntrue;
+for(int i =0; i < n -1&& max >= i; i++){
+if(max < i + nums[i])
+ max = i + nums[i];
+if(max >= n -1)
+returntrue;
+}
+returnfalse;
+}
+
`,15),o=[p];function t(r,c,i,D,C,y){return a(),n("div",null,o)}const F=s(e,[["render",t]]);export{d as __pageData,F as default};
diff --git a/assets/solution_0001-0100_055 - Jump Game.md.dc2f1b6e.lean.js b/assets/solution_0001-0100_055 - Jump Game.md.dc2f1b6e.lean.js
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..f909fc8e
--- /dev/null
+++ b/assets/solution_0001-0100_055 - Jump Game.md.dc2f1b6e.lean.js
@@ -0,0 +1 @@
+import{_ as s,o as a,c as n,a as l}from"./app.e4604e86.js";const d=JSON.parse('{"title":"55. Jump Game","description":"","frontmatter":{},"headers":[{"level":2,"title":"Problem Statement:","slug":"problem-statement","link":"#problem-statement","children":[{"level":3,"title":"Example 1:","slug":"example-1","link":"#example-1","children":[]},{"level":3,"title":"Example 2:","slug":"example-2","link":"#example-2","children":[]},{"level":3,"title":"Constraints:","slug":"constraints","link":"#constraints","children":[]}]},{"level":2,"title":"Solution:","slug":"solution","link":"#solution","children":[{"level":3,"title":"...","slug":"","link":"#","children":[]}]}],"relativePath":"solution/0001-0100/055 - Jump Game.md","lastUpdated":1671291107000}'),e={name:"solution/0001-0100/055 - Jump Game.md"},p=l("",15),o=[p];function t(r,c,i,D,C,y){return a(),n("div",null,o)}const F=s(e,[["render",t]]);export{d as __pageData,F as default};
diff --git a/assets/solution_0001-0100_058 - Length of Last Word.md.af3582e3.js b/assets/solution_0001-0100_058 - Length of Last Word.md.af3582e3.js
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..09fefe6c
--- /dev/null
+++ b/assets/solution_0001-0100_058 - Length of Last Word.md.af3582e3.js
@@ -0,0 +1,21 @@
+import{_ as s,o as a,c as n,a as l}from"./app.e4604e86.js";const A=JSON.parse('{"title":"58. Length of Last Word","description":"","frontmatter":{},"headers":[{"level":2,"title":"Problem Statement:","slug":"problem-statement","link":"#problem-statement","children":[{"level":3,"title":"Example 1:","slug":"example-1","link":"#example-1","children":[]},{"level":3,"title":"Example 2:","slug":"example-2","link":"#example-2","children":[]},{"level":3,"title":"Example 3:","slug":"example-3","link":"#example-3","children":[]},{"level":3,"title":"Constraints:","slug":"constraints","link":"#constraints","children":[]}]},{"level":2,"title":"Solution:","slug":"solution","link":"#solution","children":[{"level":3,"title":"...","slug":"","link":"#","children":[]}]}],"relativePath":"solution/0001-0100/058 - Length of Last Word.md","lastUpdated":1671291107000}'),e={name:"solution/0001-0100/058 - Length of Last Word.md"},o=l(`
`,17),t=[o];function p(r,c,i,C,D,d){return a(),n("div",null,t)}const h=s(e,[["render",p]]);export{A as __pageData,h as default};
diff --git a/assets/solution_0001-0100_058 - Length of Last Word.md.af3582e3.lean.js b/assets/solution_0001-0100_058 - Length of Last Word.md.af3582e3.lean.js
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..786df1f5
--- /dev/null
+++ b/assets/solution_0001-0100_058 - Length of Last Word.md.af3582e3.lean.js
@@ -0,0 +1 @@
+import{_ as s,o as a,c as n,a as l}from"./app.e4604e86.js";const A=JSON.parse('{"title":"58. Length of Last Word","description":"","frontmatter":{},"headers":[{"level":2,"title":"Problem Statement:","slug":"problem-statement","link":"#problem-statement","children":[{"level":3,"title":"Example 1:","slug":"example-1","link":"#example-1","children":[]},{"level":3,"title":"Example 2:","slug":"example-2","link":"#example-2","children":[]},{"level":3,"title":"Example 3:","slug":"example-3","link":"#example-3","children":[]},{"level":3,"title":"Constraints:","slug":"constraints","link":"#constraints","children":[]}]},{"level":2,"title":"Solution:","slug":"solution","link":"#solution","children":[{"level":3,"title":"...","slug":"","link":"#","children":[]}]}],"relativePath":"solution/0001-0100/058 - Length of Last Word.md","lastUpdated":1671291107000}'),e={name:"solution/0001-0100/058 - Length of Last Word.md"},o=l("",17),t=[o];function p(r,c,i,C,D,d){return a(),n("div",null,t)}const h=s(e,[["render",p]]);export{A as __pageData,h as default};
diff --git a/assets/solution_0001-0100_061 - Rotate List .md.27b79047.js b/assets/solution_0001-0100_061 - Rotate List .md.27b79047.js
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..7b58ed0c
--- /dev/null
+++ b/assets/solution_0001-0100_061 - Rotate List .md.27b79047.js
@@ -0,0 +1,30 @@
+import{_ as s,o as a,c as n,a as l}from"./app.e4604e86.js";const F=JSON.parse('{"title":"61. Rotate List","description":"","frontmatter":{},"headers":[{"level":2,"title":"Problem Statement:","slug":"problem-statement","link":"#problem-statement","children":[{"level":3,"title":"Example 1:","slug":"example-1","link":"#example-1","children":[]},{"level":3,"title":"Example 2:","slug":"example-2","link":"#example-2","children":[]},{"level":3,"title":"Constraints:","slug":"constraints","link":"#constraints","children":[]}]},{"level":2,"title":"Solution:","slug":"solution","link":"#solution","children":[{"level":3,"title":"...","slug":"","link":"#","children":[]}]}],"relativePath":"solution/0001-0100/061 - Rotate List .md","lastUpdated":1671697454000}'),p={name:"solution/0001-0100/061 - Rotate List .md"},e=l(`
`,16),o=[e];function t(c,r,D,i,C,A){return a(),n("div",null,o)}const d=s(p,[["render",t]]);export{F as __pageData,d as default};
diff --git a/assets/solution_0001-0100_061 - Rotate List .md.27b79047.lean.js b/assets/solution_0001-0100_061 - Rotate List .md.27b79047.lean.js
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..ad28676e
--- /dev/null
+++ b/assets/solution_0001-0100_061 - Rotate List .md.27b79047.lean.js
@@ -0,0 +1 @@
+import{_ as s,o as a,c as n,a as l}from"./app.e4604e86.js";const F=JSON.parse('{"title":"61. Rotate List","description":"","frontmatter":{},"headers":[{"level":2,"title":"Problem Statement:","slug":"problem-statement","link":"#problem-statement","children":[{"level":3,"title":"Example 1:","slug":"example-1","link":"#example-1","children":[]},{"level":3,"title":"Example 2:","slug":"example-2","link":"#example-2","children":[]},{"level":3,"title":"Constraints:","slug":"constraints","link":"#constraints","children":[]}]},{"level":2,"title":"Solution:","slug":"solution","link":"#solution","children":[{"level":3,"title":"...","slug":"","link":"#","children":[]}]}],"relativePath":"solution/0001-0100/061 - Rotate List .md","lastUpdated":1671697454000}'),p={name:"solution/0001-0100/061 - Rotate List .md"},e=l("",16),o=[e];function t(c,r,D,i,C,A){return a(),n("div",null,o)}const d=s(p,[["render",t]]);export{F as __pageData,d as default};
diff --git a/assets/solution_0001-0100_066 - Plus One.md.4a367264.js b/assets/solution_0001-0100_066 - Plus One.md.4a367264.js
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..f64705fc
--- /dev/null
+++ b/assets/solution_0001-0100_066 - Plus One.md.4a367264.js
@@ -0,0 +1,32 @@
+import{_ as s,o as n,c as a,a as l}from"./app.e4604e86.js";const F=JSON.parse('{"title":"66. Plus One","description":"","frontmatter":{},"headers":[{"level":2,"title":"Problem Statement","slug":"problem-statement","link":"#problem-statement","children":[]},{"level":2,"title":"Solution:","slug":"solution","link":"#solution","children":[{"level":3,"title":"...","slug":"","link":"#","children":[]}]}],"relativePath":"solution/0001-0100/066 - Plus One.md","lastUpdated":1674542557000}'),e={name:"solution/0001-0100/066 - Plus One.md"},p=l(`
You are given a large integer represented as an integer array digits, where each digits[i] is the ith digit of the integer. The digits are ordered from most significant to least significant in left-to-right order. The large integer does not contain any leading 0's.
Increment the large integer by one and return the resulting array of digits.
Example 1:
Input: digits = [1,2,3]
+Output: [1,2,4]
+Explanation: The array represents the integer 123.
+Incrementing by one gives 123 + 1 = 124.
+Thus, the result should be [1,2,4].
+
Example 2:
Input: digits = [4,3,2,1]
+Output: [4,3,2,2]
+Explanation: The array represents the integer 4321.
+Incrementing by one gives 4321 + 1 = 4322.
+Thus, the result should be [4,3,2,2].
+
Example 3:
Input: digits = [9]
+Output: [1,0]
+Explanation: The array represents the integer 9.
+Incrementing by one gives 9 + 1 = 10.
+Thus, the result should be [1,0].
+
`,19),o=[p];function t(c,r,i,y,D,C){return n(),a("div",null,o)}const d=s(e,[["render",t]]);export{F as __pageData,d as default};
diff --git a/assets/solution_0001-0100_066 - Plus One.md.4a367264.lean.js b/assets/solution_0001-0100_066 - Plus One.md.4a367264.lean.js
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..b3345161
--- /dev/null
+++ b/assets/solution_0001-0100_066 - Plus One.md.4a367264.lean.js
@@ -0,0 +1 @@
+import{_ as s,o as n,c as a,a as l}from"./app.e4604e86.js";const F=JSON.parse('{"title":"66. Plus One","description":"","frontmatter":{},"headers":[{"level":2,"title":"Problem Statement","slug":"problem-statement","link":"#problem-statement","children":[]},{"level":2,"title":"Solution:","slug":"solution","link":"#solution","children":[{"level":3,"title":"...","slug":"","link":"#","children":[]}]}],"relativePath":"solution/0001-0100/066 - Plus One.md","lastUpdated":1674542557000}'),e={name:"solution/0001-0100/066 - Plus One.md"},p=l("",19),o=[p];function t(c,r,i,y,D,C){return n(),a("div",null,o)}const d=s(e,[["render",t]]);export{F as __pageData,d as default};
diff --git a/assets/solution_0001-0100_067 - Add Binary.md.19cdcaa1.js b/assets/solution_0001-0100_067 - Add Binary.md.19cdcaa1.js
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..80bb582d
--- /dev/null
+++ b/assets/solution_0001-0100_067 - Add Binary.md.19cdcaa1.js
@@ -0,0 +1,11 @@
+import{_ as s,o as a,c as n,a as l}from"./app.e4604e86.js";const C=JSON.parse('{"title":"67. Add Binary","description":"","frontmatter":{},"headers":[{"level":2,"title":"Problem Statement","slug":"problem-statement","link":"#problem-statement","children":[]},{"level":2,"title":"Solution:","slug":"solution","link":"#solution","children":[{"level":3,"title":"...","slug":"","link":"#","children":[]}]}],"relativePath":"solution/0001-0100/067 - Add Binary.md","lastUpdated":1674542557000}'),o={name:"solution/0001-0100/067 - Add Binary.md"},e=l(`
packagemain
+
+funcmySqrt(x int)int{
+ start :=0
+ end := x
+
+for start < end {
+// this is to floor the mid value
+// mid of 8 will be 4 , (8+1)/2 = 4.5
+// mid of 9 will be 5 , (9+1)/2 = 5
+ mid := start +(end-start+1)/2
+if mid*mid > x {
+ end = mid -1
+}else{
+ start = mid
+}
+}
+
+return end
+}
+
+
Given an array nums with n objects colored red, white, or blue, sort them in-place so that objects of the same color are adjacent, with the colors in the order red, white, and blue.
We will use the integers 0, 1, and 2 to represent the color red, white, and blue, respectively.
You must solve this problem without using the library's sort function.
packagemain
+
+funcsubsets(nums []int)[][]int{
+ res :=make([][]int,0)
+ curr_subset :=make([]int,0)
+
+var backtrack func(i int)
+
+ backtrack =func(i int){
+println(i)
+if i >=len(nums){
+ curr_dup :=make([]int,len(curr_subset))
+copy(curr_dup, curr_subset)
+ res =append(res, curr_dup)
+return
+}
+
+// include the current element
+ curr_subset =append(curr_subset, nums[i])
+backtrack(i +1)
+
+// exclude the current element
+ curr_subset = curr_subset[:len(curr_subset)-1]// pop the last element
+backtrack(i +1)
+}
+
+backtrack(0)
+
+return res
+}
+
+
py
classSolution:
+defsubsets(self,nums: list[int])-> list[list[int]]:
+ res, curr =[],[]
+
+defbacktrack(i:int)->None:
+if i >=len(nums):
+print(curr.copy())
+ res.append(curr.copy())
+return
+
+# include the current element
+ curr.append(nums[i])
+backtrack(i +1)
+
+# exclude the current element
+ curr.pop()
+backtrack(i +1)
+
+backtrack(0)
+
+return res
+
+
You are given two integer arrays nums1 and nums2, sorted in non-decreasing order, and two integers m and n, representing the number of elements in nums1 and nums2 respectively.
Mergenums1 and nums2 into a single array sorted in non-decreasing order.
The final sorted array should not be returned by the function, but instead be stored inside the array nums1. To accommodate this, nums1 has a length of m + n, where the first m elements denote the elements that should be merged, and the last n elements are set to 0 and should be ignored. nums2 has a length of n.
Example 1:
Input: nums1 = [1,2,3,0,0,0], m = 3, nums2 = [2,5,6], n = 3
+Output: [1,2,2,3,5,6]
+Explanation: The arrays we are merging are [1,2,3] and [2,5,6].
+The result of the merge is [1,2,2,3,5,6] with the underlined elements coming from nums1.
+
Example 2:
Input: nums1 = [1], m = 1, nums2 = [], n = 0
+Output: [1]
+Explanation: The arrays we are merging are [1] and [].
+The result of the merge is [1].
+
Example 3:
Input: nums1 = [0], m = 0, nums2 = [1], n = 1
+Output: [1]
+Explanation: The arrays we are merging are [] and [1].
+The result of the merge is [1].
+Note that because m = 0, there are no elements in nums1. The 0 is only there to ensure the merge result can fit in nums1.
+
Constraints:
nums1.length == m + n
nums2.length == n
0 <= m, n <= 200
1 <= m + n <= 200
-109 <= nums1[i], nums2[j] <= 109
Follow up: Can you come up with an algorithm that runs in O(m + n) time?
Click to open Hints
You can easily solve this problem if you simply think about two elements at a time rather than two arrays. We know that each of the individual arrays is sorted. What we don't know is how they will intertwine. Can we take a local decision and arrive at an optimal solution?
If you simply consider one element each at a time from the two arrays and make a decision and proceed accordingly, you will arrive at the optimal solution.
`,20),o=[p];function t(r,c,i,D,C,A){return a(),e("div",null,o)}const F=s(l,[["render",t]]);export{d as __pageData,F as default};
diff --git a/assets/solution_0001-0100_100 - Same Tree.md.38f2f9a7.lean.js b/assets/solution_0001-0100_100 - Same Tree.md.38f2f9a7.lean.js
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..de7e4f1f
--- /dev/null
+++ b/assets/solution_0001-0100_100 - Same Tree.md.38f2f9a7.lean.js
@@ -0,0 +1 @@
+import{_ as s,o as a,c as e,a as n}from"./app.e4604e86.js";const d=JSON.parse('{"title":"100. Same Tree","description":"","frontmatter":{},"headers":[{"level":2,"title":"Problem Statement:","slug":"problem-statement","link":"#problem-statement","children":[{"level":3,"title":"Example 1:","slug":"example-1","link":"#example-1","children":[]},{"level":3,"title":"Example 2:","slug":"example-2","link":"#example-2","children":[]},{"level":3,"title":"Example 3:","slug":"example-3","link":"#example-3","children":[]},{"level":3,"title":"Constraints:","slug":"constraints","link":"#constraints","children":[]}]},{"level":2,"title":"Solution:","slug":"solution","link":"#solution","children":[{"level":3,"title":"...","slug":"","link":"#","children":[]}]}],"relativePath":"solution/0001-0100/100 - Same Tree.md","lastUpdated":1671291107000}'),l={name:"solution/0001-0100/100 - Same Tree.md"},p=n("",20),o=[p];function t(r,c,i,D,C,A){return a(),e("div",null,o)}const F=s(l,[["render",t]]);export{d as __pageData,F as default};
diff --git a/assets/solution_0101-0200_101 - Symmetric Tree.md.c2f61c5c.js b/assets/solution_0101-0200_101 - Symmetric Tree.md.c2f61c5c.js
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..947eeaa6
--- /dev/null
+++ b/assets/solution_0101-0200_101 - Symmetric Tree.md.c2f61c5c.js
@@ -0,0 +1,49 @@
+import{_ as n,o as a,c as l,f as p,a as s}from"./app.e4604e86.js";const d=JSON.parse('{"title":"101. Symmetric Tree","description":"","frontmatter":{},"headers":[{"level":2,"title":"Problem Statement","slug":"problem-statement","link":"#problem-statement","children":[]},{"level":2,"title":"Solution:","slug":"solution","link":"#solution","children":[{"level":3,"title":"...","slug":"","link":"#","children":[]}]}],"relativePath":"solution/0101-0200/101 - Symmetric Tree.md","lastUpdated":1678822270000}'),o={name:"solution/0101-0200/101 - Symmetric Tree.md"},e=s(`
`,4);function r(c,D,y,F,A,C){return a(),l("div",null,[e,p(" Could you solve it both recursively and iteratively? "),t])}const m=n(o,[["render",r]]);export{d as __pageData,m as default};
diff --git a/assets/solution_0101-0200_101 - Symmetric Tree.md.c2f61c5c.lean.js b/assets/solution_0101-0200_101 - Symmetric Tree.md.c2f61c5c.lean.js
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..5aa3d8dc
--- /dev/null
+++ b/assets/solution_0101-0200_101 - Symmetric Tree.md.c2f61c5c.lean.js
@@ -0,0 +1 @@
+import{_ as n,o as a,c as l,f as p,a as s}from"./app.e4604e86.js";const d=JSON.parse('{"title":"101. Symmetric Tree","description":"","frontmatter":{},"headers":[{"level":2,"title":"Problem Statement","slug":"problem-statement","link":"#problem-statement","children":[]},{"level":2,"title":"Solution:","slug":"solution","link":"#solution","children":[{"level":3,"title":"...","slug":"","link":"#","children":[]}]}],"relativePath":"solution/0101-0200/101 - Symmetric Tree.md","lastUpdated":1678822270000}'),o={name:"solution/0101-0200/101 - Symmetric Tree.md"},e=s("",16),t=s("",4);function r(c,D,y,F,A,C){return a(),l("div",null,[e,p(" Could you solve it both recursively and iteratively? "),t])}const m=n(o,[["render",r]]);export{d as __pageData,m as default};
diff --git a/assets/solution_0101-0200_103 - Binary Tree Zigzag Level Order Traversal.md.919e5381.js b/assets/solution_0101-0200_103 - Binary Tree Zigzag Level Order Traversal.md.919e5381.js
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..0740f726
--- /dev/null
+++ b/assets/solution_0101-0200_103 - Binary Tree Zigzag Level Order Traversal.md.919e5381.js
@@ -0,0 +1,111 @@
+import{_ as s,o as n,c as a,a as l}from"./app.e4604e86.js";const i=JSON.parse('{"title":"103. Binary Tree Zigzag Level Order Traversal","description":"","frontmatter":{},"headers":[{"level":2,"title":"Problem Statement:","slug":"problem-statement","link":"#problem-statement","children":[{"level":3,"title":"Example 1:","slug":"example-1","link":"#example-1","children":[]},{"level":3,"title":"Example 2:","slug":"example-2","link":"#example-2","children":[]},{"level":3,"title":"Example 3:","slug":"example-3","link":"#example-3","children":[]},{"level":3,"title":"Constraints:","slug":"constraints","link":"#constraints","children":[]}]},{"level":2,"title":"Solution:","slug":"solution","link":"#solution","children":[{"level":3,"title":"...","slug":"","link":"#","children":[]}]}],"relativePath":"solution/0101-0200/103 - Binary Tree Zigzag Level Order Traversal.md","lastUpdated":1676855631000}'),p={name:"solution/0101-0200/103 - Binary Tree Zigzag Level Order Traversal.md"},o=l(`
Given the root of a binary tree, return the zigzag level order traversal of its nodes' values. (i.e., from left to right, then right to left for the next level and alternate between).
`,17),e=[o];function t(r,c,D,y,A,F){return n(),a("div",null,e)}const d=s(p,[["render",t]]);export{i as __pageData,d as default};
diff --git a/assets/solution_0101-0200_103 - Binary Tree Zigzag Level Order Traversal.md.919e5381.lean.js b/assets/solution_0101-0200_103 - Binary Tree Zigzag Level Order Traversal.md.919e5381.lean.js
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..4494eb2b
--- /dev/null
+++ b/assets/solution_0101-0200_103 - Binary Tree Zigzag Level Order Traversal.md.919e5381.lean.js
@@ -0,0 +1 @@
+import{_ as s,o as n,c as a,a as l}from"./app.e4604e86.js";const i=JSON.parse('{"title":"103. Binary Tree Zigzag Level Order Traversal","description":"","frontmatter":{},"headers":[{"level":2,"title":"Problem Statement:","slug":"problem-statement","link":"#problem-statement","children":[{"level":3,"title":"Example 1:","slug":"example-1","link":"#example-1","children":[]},{"level":3,"title":"Example 2:","slug":"example-2","link":"#example-2","children":[]},{"level":3,"title":"Example 3:","slug":"example-3","link":"#example-3","children":[]},{"level":3,"title":"Constraints:","slug":"constraints","link":"#constraints","children":[]}]},{"level":2,"title":"Solution:","slug":"solution","link":"#solution","children":[{"level":3,"title":"...","slug":"","link":"#","children":[]}]}],"relativePath":"solution/0101-0200/103 - Binary Tree Zigzag Level Order Traversal.md","lastUpdated":1676855631000}'),p={name:"solution/0101-0200/103 - Binary Tree Zigzag Level Order Traversal.md"},o=l("",17),e=[o];function t(r,c,D,y,A,F){return n(),a("div",null,e)}const d=s(p,[["render",t]]);export{i as __pageData,d as default};
diff --git a/assets/solution_0101-0200_104 - Maximum Depth of Binary Tree.md.3f09bfed.js b/assets/solution_0101-0200_104 - Maximum Depth of Binary Tree.md.3f09bfed.js
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..25521f8b
--- /dev/null
+++ b/assets/solution_0101-0200_104 - Maximum Depth of Binary Tree.md.3f09bfed.js
@@ -0,0 +1,15 @@
+import{_ as s,o as a,c as n,a as e}from"./app.e4604e86.js";const h=JSON.parse('{"title":"104. Maximum Depth of Binary Tree","description":"","frontmatter":{},"headers":[{"level":2,"title":"Problem Statement:","slug":"problem-statement","link":"#problem-statement","children":[{"level":3,"title":"Example 1:","slug":"example-1","link":"#example-1","children":[]},{"level":3,"title":"Example 2:","slug":"example-2","link":"#example-2","children":[]},{"level":3,"title":"Constraints:","slug":"constraints","link":"#constraints","children":[]}]},{"level":2,"title":"Solution:","slug":"solution","link":"#solution","children":[{"level":3,"title":"...","slug":"","link":"#","children":[]}]}],"relativePath":"solution/0101-0200/104 - Maximum Depth of Binary Tree.md","lastUpdated":1671291107000}'),l={name:"solution/0101-0200/104 - Maximum Depth of Binary Tree.md"},o=e(`
`,16),p=[o];function t(r,c,i,d,y,D){return a(),n("div",null,p)}const A=s(l,[["render",t]]);export{h as __pageData,A as default};
diff --git a/assets/solution_0101-0200_104 - Maximum Depth of Binary Tree.md.3f09bfed.lean.js b/assets/solution_0101-0200_104 - Maximum Depth of Binary Tree.md.3f09bfed.lean.js
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..c2735000
--- /dev/null
+++ b/assets/solution_0101-0200_104 - Maximum Depth of Binary Tree.md.3f09bfed.lean.js
@@ -0,0 +1 @@
+import{_ as s,o as a,c as n,a as e}from"./app.e4604e86.js";const h=JSON.parse('{"title":"104. Maximum Depth of Binary Tree","description":"","frontmatter":{},"headers":[{"level":2,"title":"Problem Statement:","slug":"problem-statement","link":"#problem-statement","children":[{"level":3,"title":"Example 1:","slug":"example-1","link":"#example-1","children":[]},{"level":3,"title":"Example 2:","slug":"example-2","link":"#example-2","children":[]},{"level":3,"title":"Constraints:","slug":"constraints","link":"#constraints","children":[]}]},{"level":2,"title":"Solution:","slug":"solution","link":"#solution","children":[{"level":3,"title":"...","slug":"","link":"#","children":[]}]}],"relativePath":"solution/0101-0200/104 - Maximum Depth of Binary Tree.md","lastUpdated":1671291107000}'),l={name:"solution/0101-0200/104 - Maximum Depth of Binary Tree.md"},o=e("",16),p=[o];function t(r,c,i,d,y,D){return a(),n("div",null,p)}const A=s(l,[["render",t]]);export{h as __pageData,A as default};
diff --git a/assets/solution_0101-0200_106 - Construct Binary Tree from Inorder and Postorder Traversal.md.106c3d58.js b/assets/solution_0101-0200_106 - Construct Binary Tree from Inorder and Postorder Traversal.md.106c3d58.js
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..bbeb4213
--- /dev/null
+++ b/assets/solution_0101-0200_106 - Construct Binary Tree from Inorder and Postorder Traversal.md.106c3d58.js
@@ -0,0 +1,42 @@
+import{_ as s,o as n,c as a,a as o}from"./app.e4604e86.js";const A=JSON.parse('{"title":"106. Construct Binary Tree from Inorder and Postorder Traversal","description":"","frontmatter":{},"headers":[{"level":2,"title":"Problem Statement","slug":"problem-statement","link":"#problem-statement","children":[]},{"level":2,"title":"Solution:","slug":"solution","link":"#solution","children":[{"level":3,"title":"...","slug":"","link":"#","children":[]}]}],"relativePath":"solution/0101-0200/106 - Construct Binary Tree from Inorder and Postorder Traversal.md","lastUpdated":1680513503000}'),l={name:"solution/0101-0200/106 - Construct Binary Tree from Inorder and Postorder Traversal.md"},e=o(`
106. Construct Binary Tree from Inorder and Postorder Traversal #
Given two integer arrays inorder and postorder where inorder is the inorder traversal of a binary tree and postorder is the postorder traversal of the same tree, construct and return the binary tree.
`,17),p=[e];function r(t,c,D,y,i,C){return n(),a("div",null,p)}const d=s(l,[["render",r]]);export{A as __pageData,d as default};
diff --git a/assets/solution_0101-0200_106 - Construct Binary Tree from Inorder and Postorder Traversal.md.106c3d58.lean.js b/assets/solution_0101-0200_106 - Construct Binary Tree from Inorder and Postorder Traversal.md.106c3d58.lean.js
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..e751f9f6
--- /dev/null
+++ b/assets/solution_0101-0200_106 - Construct Binary Tree from Inorder and Postorder Traversal.md.106c3d58.lean.js
@@ -0,0 +1 @@
+import{_ as s,o as n,c as a,a as o}from"./app.e4604e86.js";const A=JSON.parse('{"title":"106. Construct Binary Tree from Inorder and Postorder Traversal","description":"","frontmatter":{},"headers":[{"level":2,"title":"Problem Statement","slug":"problem-statement","link":"#problem-statement","children":[]},{"level":2,"title":"Solution:","slug":"solution","link":"#solution","children":[{"level":3,"title":"...","slug":"","link":"#","children":[]}]}],"relativePath":"solution/0101-0200/106 - Construct Binary Tree from Inorder and Postorder Traversal.md","lastUpdated":1680513503000}'),l={name:"solution/0101-0200/106 - Construct Binary Tree from Inorder and Postorder Traversal.md"},e=o("",17),p=[e];function r(t,c,D,y,i,C){return n(),a("div",null,p)}const d=s(l,[["render",r]]);export{A as __pageData,d as default};
diff --git a/assets/solution_0101-0200_108 - Convert Sorted Array to Binary Search Tree.md.da20b39a.js b/assets/solution_0101-0200_108 - Convert Sorted Array to Binary Search Tree.md.da20b39a.js
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..fb2a0275
--- /dev/null
+++ b/assets/solution_0101-0200_108 - Convert Sorted Array to Binary Search Tree.md.da20b39a.js
@@ -0,0 +1,38 @@
+import{_ as s,o as n,c as a,a as l}from"./app.e4604e86.js";const F=JSON.parse('{"title":"108. Convert Sorted Array to Binary Search Tree","description":"","frontmatter":{},"headers":[{"level":2,"title":"Problem Statement","slug":"problem-statement","link":"#problem-statement","children":[]},{"level":2,"title":"Solution:","slug":"solution","link":"#solution","children":[{"level":3,"title":"...","slug":"","link":"#","children":[]}]}],"relativePath":"solution/0101-0200/108 - Convert Sorted Array to Binary Search Tree.md","lastUpdated":1676656807000}'),p={name:"solution/0101-0200/108 - Convert Sorted Array to Binary Search Tree.md"},o=l(`
`,18),e=[o];function t(r,c,D,y,C,i){return n(),a("div",null,e)}const d=s(p,[["render",t]]);export{F as __pageData,d as default};
diff --git a/assets/solution_0101-0200_108 - Convert Sorted Array to Binary Search Tree.md.da20b39a.lean.js b/assets/solution_0101-0200_108 - Convert Sorted Array to Binary Search Tree.md.da20b39a.lean.js
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..53049f2b
--- /dev/null
+++ b/assets/solution_0101-0200_108 - Convert Sorted Array to Binary Search Tree.md.da20b39a.lean.js
@@ -0,0 +1 @@
+import{_ as s,o as n,c as a,a as l}from"./app.e4604e86.js";const F=JSON.parse('{"title":"108. Convert Sorted Array to Binary Search Tree","description":"","frontmatter":{},"headers":[{"level":2,"title":"Problem Statement","slug":"problem-statement","link":"#problem-statement","children":[]},{"level":2,"title":"Solution:","slug":"solution","link":"#solution","children":[{"level":3,"title":"...","slug":"","link":"#","children":[]}]}],"relativePath":"solution/0101-0200/108 - Convert Sorted Array to Binary Search Tree.md","lastUpdated":1676656807000}'),p={name:"solution/0101-0200/108 - Convert Sorted Array to Binary Search Tree.md"},o=l("",18),e=[o];function t(r,c,D,y,C,i){return n(),a("div",null,e)}const d=s(p,[["render",t]]);export{F as __pageData,d as default};
diff --git a/assets/solution_0101-0200_109 - Convert Sorted List to Binary Search Tree.md.c39d8c6b.js b/assets/solution_0101-0200_109 - Convert Sorted List to Binary Search Tree.md.c39d8c6b.js
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..3c910487
--- /dev/null
+++ b/assets/solution_0101-0200_109 - Convert Sorted List to Binary Search Tree.md.c39d8c6b.js
@@ -0,0 +1,52 @@
+import{_ as s,o as n,c as a,a as l}from"./app.e4604e86.js";const F=JSON.parse('{"title":"109. Convert Sorted List to Binary Search Tree","description":"","frontmatter":{},"headers":[{"level":2,"title":"Problem Statement","slug":"problem-statement","link":"#problem-statement","children":[]},{"level":2,"title":"Solution:","slug":"solution","link":"#solution","children":[{"level":3,"title":"...","slug":"","link":"#","children":[]}]}],"relativePath":"solution/0101-0200/109 - Convert Sorted List to Binary Search Tree.md","lastUpdated":1678822270000}'),p={name:"solution/0101-0200/109 - Convert Sorted List to Binary Search Tree.md"},e=l(`
Given the head of a singly linked list where elements are sorted in ascending order, convert it to a height-balancedbinary search tree.
Example 1:
Input: head = [-10,-3,0,5,9]
+Output: [0,-3,9,-10,null,5]
+Explanation: One possible answer is [0,-3,9,-10,null,5], which represents the shown height balanced BST.
+
Example 2:
Input: head = []
+Output: []
+
Constraints:
The number of nodes in head is in the range [0, 2 * 104].
packagemain
+
+// Definition for singly-linked list.
+typeListNodestruct{
+ Val int
+ Next *ListNode
+}
+
+// Definition for a binary tree node.
+typeTreeNodestruct{
+ Val int
+ Left *TreeNode
+ Right *TreeNode
+}
+
+funcsortedListToBST(head *ListNode)*TreeNode {
+if head ==nil{
+returnnil
+}
+
+if head.Next ==nil{
+return&TreeNode{Val: head.Val}
+}
+
+ slow, fast := head, head
+ prev := slow
+
+for fast !=nil&& fast.Next !=nil{
+ prev = slow
+ slow = slow.Next
+ fast = fast.Next.Next
+}
+
+// slow points to the root of the current subtree
+
+// break the link between the left subtree and the root
+ prev.Next =nil
+
+ root :=&TreeNode{Val: slow.Val}
+ root.Left =sortedListToBST(head)
+ root.Right =sortedListToBST(slow.Next)
+
+return root
+}
+
+
Given the root of a binary tree and an integer targetSum, return true if the tree has a root-to-leaf path such that adding up all the values along the path equals targetSum.
A leaf is a node with no children.
Example 1:
Input: root = [5,4,8,11,null,13,4,7,2,null,null,null,1], targetSum = 22
+Output: true
+Explanation: The root-to-leaf path with the target sum is shown.
+
Example 2:
Input: root = [1,2,3], targetSum = 5
+Output: false
+Explanation: There two root-to-leaf paths in the tree:
+(1 --> 2): The sum is 3.
+(1 --> 3): The sum is 4.
+There is no root-to-leaf path with sum = 5.
+
Example 3:
Input: root = [], targetSum = 0
+Output: false
+Explanation: Since the tree is empty, there are no root-to-leaf paths.
+
Constraints:
The number of nodes in the tree is in the range [0, 5000].
implSolution{
+pubfnget_row(row_index:i32)->Vec<i32>{
+ // create a vector of 1s with length row_index + 1
+letmut row =vec![1;(row_index +1)asusize];
+
+ // loop through the vector, starting at 1
+for i in1..row_index {
+ // loop through the vector, starting at i + 1 and going backwards
+for j in(1..=i).rev(){
+ // add the value at the current index to the value at the previous index
+ row[j asusize]+= row[(j -1)asusize];
+}
+}
+
+ row
+}
+}
+
+
`,22),e=[p];function t(r,c,i,C,y,D){return a(),n("div",null,e)}const F=s(o,[["render",t]]);export{d as __pageData,F as default};
diff --git a/assets/solution_0101-0200_119 - Pascals Triangle II.md.c0152e68.lean.js b/assets/solution_0101-0200_119 - Pascals Triangle II.md.c0152e68.lean.js
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..2868c250
--- /dev/null
+++ b/assets/solution_0101-0200_119 - Pascals Triangle II.md.c0152e68.lean.js
@@ -0,0 +1 @@
+import{_ as s,o as a,c as n,a as l}from"./app.e4604e86.js";const d=JSON.parse('{"title":"119. Pascals Triangle II","description":"","frontmatter":{},"headers":[{"level":2,"title":"Problem Statement","slug":"problem-statement","link":"#problem-statement","children":[]},{"level":2,"title":"Solution:","slug":"solution","link":"#solution","children":[{"level":3,"title":"...","slug":"","link":"#","children":[]}]}],"relativePath":"solution/0101-0200/119 - Pascals Triangle II.md","lastUpdated":1677645016000}'),o={name:"solution/0101-0200/119 - Pascals Triangle II.md"},p=l("",22),e=[p];function t(r,c,i,C,y,D){return a(),n("div",null,e)}const F=s(o,[["render",t]]);export{d as __pageData,F as default};
diff --git a/assets/solution_0101-0200_121 - Best Time to Buy and Sell Stock.md.0356a772.js b/assets/solution_0101-0200_121 - Best Time to Buy and Sell Stock.md.0356a772.js
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..398c7460
--- /dev/null
+++ b/assets/solution_0101-0200_121 - Best Time to Buy and Sell Stock.md.0356a772.js
@@ -0,0 +1,47 @@
+import{_ as s,o as n,c as a,a as l}from"./app.e4604e86.js";const F=JSON.parse('{"title":"121. Best Time to Buy and Sell Stock","description":"","frontmatter":{},"headers":[{"level":2,"title":"Problem Statement","slug":"problem-statement","link":"#problem-statement","children":[]},{"level":2,"title":"Solution:","slug":"solution","link":"#solution","children":[{"level":3,"title":"...","slug":"","link":"#","children":[]}]}],"relativePath":"solution/0101-0200/121 - Best Time to Buy and Sell Stock.md","lastUpdated":1677374362000}'),p={name:"solution/0101-0200/121 - Best Time to Buy and Sell Stock.md"},o=l(`
You are given an array prices where prices[i] is the price of a given stock on the ith day.
You want to maximize your profit by choosing a single day to buy one stock and choosing a different day in the future to sell that stock.
Return the maximum profit you can achieve from this transaction. If you cannot achieve any profit, return 0.
Example 1:
Input: prices = [7,1,5,3,6,4]
+Output: 5
+Explanation: Buy on day 2 (price = 1) and sell on day 5 (price = 6), profit = 6-1 = 5.
+Note that buying on day 2 and selling on day 1 is not allowed because you must buy before you sell.
+
Example 2:
Input: prices = [7,6,4,3,1]
+Output: 0
+Explanation: In this case, no transactions are done and the max profit = 0.
+
implSolution{
+pubfnmax_profit(prices:Vec<i32>)->i32{
+let(mut profit,mut min)=(0, prices[0]);
+
+ // loop through the vector, starting at 1
+for i in1..prices.len(){
+ // if the current value is less than the minimum value, set the minimum value to the current value
+if prices[i]< min {
+ min = prices[i];
+}
+ // else if the current value minus the minimum value is greater than the current profit, set the profit to the current value minus the minimum value
+elseif prices[i]- min > profit {
+ profit = prices[i]- min;
+}
+}
+
+ profit
+}
+}
+
+
go
packagemain
+
+funcmaxProfit(prices []int)int{
+ profit, min :=0, prices[0]
+
+for _, price :=range prices {
+// if the current price is lower than the min price, update the min price to the current price
+// else if the current price minus the min price is greater than the profit, update the profit to the current price minus the min price
+if price < min {
+ min = price
+}elseif price-min > profit {
+ profit = price - min
+}
+}
+
+return profit
+}
+
+
`,18),e=[o];function t(c,r,i,D,y,C){return n(),a("div",null,e)}const u=s(p,[["render",t]]);export{F as __pageData,u as default};
diff --git a/assets/solution_0101-0200_121 - Best Time to Buy and Sell Stock.md.0356a772.lean.js b/assets/solution_0101-0200_121 - Best Time to Buy and Sell Stock.md.0356a772.lean.js
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..11bbab14
--- /dev/null
+++ b/assets/solution_0101-0200_121 - Best Time to Buy and Sell Stock.md.0356a772.lean.js
@@ -0,0 +1 @@
+import{_ as s,o as n,c as a,a as l}from"./app.e4604e86.js";const F=JSON.parse('{"title":"121. Best Time to Buy and Sell Stock","description":"","frontmatter":{},"headers":[{"level":2,"title":"Problem Statement","slug":"problem-statement","link":"#problem-statement","children":[]},{"level":2,"title":"Solution:","slug":"solution","link":"#solution","children":[{"level":3,"title":"...","slug":"","link":"#","children":[]}]}],"relativePath":"solution/0101-0200/121 - Best Time to Buy and Sell Stock.md","lastUpdated":1677374362000}'),p={name:"solution/0101-0200/121 - Best Time to Buy and Sell Stock.md"},o=l("",18),e=[o];function t(c,r,i,D,y,C){return n(),a("div",null,e)}const u=s(p,[["render",t]]);export{F as __pageData,u as default};
diff --git a/assets/solution_0101-0200_122 - Best Time to Buy and Sell Stock II.md.4ca5a16f.js b/assets/solution_0101-0200_122 - Best Time to Buy and Sell Stock II.md.4ca5a16f.js
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..3f5ab282
--- /dev/null
+++ b/assets/solution_0101-0200_122 - Best Time to Buy and Sell Stock II.md.4ca5a16f.js
@@ -0,0 +1,22 @@
+import{_ as s,o as a,c as n,a as e}from"./app.e4604e86.js";const A=JSON.parse('{"title":"122. Best Time to Buy and Sell Stock II","description":"","frontmatter":{},"headers":[{"level":2,"title":"Problem Statement:","slug":"problem-statement","link":"#problem-statement","children":[{"level":3,"title":"Example 1:","slug":"example-1","link":"#example-1","children":[]},{"level":3,"title":"Example 2:","slug":"example-2","link":"#example-2","children":[]},{"level":3,"title":"Example 3:","slug":"example-3","link":"#example-3","children":[]},{"level":3,"title":"Constraints:","slug":"constraints","link":"#constraints","children":[]}]},{"level":2,"title":"Solution:","slug":"solution","link":"#solution","children":[{"level":3,"title":"...","slug":"","link":"#","children":[]}]}],"relativePath":"solution/0101-0200/122 - Best Time to Buy and Sell Stock II.md","lastUpdated":1671291107000}'),l={name:"solution/0101-0200/122 - Best Time to Buy and Sell Stock II.md"},o=e(`
You are given an integer array prices where prices[i] is the price of a given stock on the ith day.
On each day, you may decide to buy and/or sell the stock. You can only hold at most one share of the stock at any time. However, you can buy it then immediately sell it on the same day.
Find and return the maximum profit you can achieve.
Input: prices = [7,6,4,3,1]
+Output: 0
+Explanation: There is no way to make a positive profit, so we never buy the stock to achieve the maximum profit of 0.
+
`,18),p=[o];function t(c,r,i,y,d,C){return a(),n("div",null,p)}const h=s(l,[["render",t]]);export{A as __pageData,h as default};
diff --git a/assets/solution_0101-0200_122 - Best Time to Buy and Sell Stock II.md.4ca5a16f.lean.js b/assets/solution_0101-0200_122 - Best Time to Buy and Sell Stock II.md.4ca5a16f.lean.js
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..018dd2ff
--- /dev/null
+++ b/assets/solution_0101-0200_122 - Best Time to Buy and Sell Stock II.md.4ca5a16f.lean.js
@@ -0,0 +1 @@
+import{_ as s,o as a,c as n,a as e}from"./app.e4604e86.js";const A=JSON.parse('{"title":"122. Best Time to Buy and Sell Stock II","description":"","frontmatter":{},"headers":[{"level":2,"title":"Problem Statement:","slug":"problem-statement","link":"#problem-statement","children":[{"level":3,"title":"Example 1:","slug":"example-1","link":"#example-1","children":[]},{"level":3,"title":"Example 2:","slug":"example-2","link":"#example-2","children":[]},{"level":3,"title":"Example 3:","slug":"example-3","link":"#example-3","children":[]},{"level":3,"title":"Constraints:","slug":"constraints","link":"#constraints","children":[]}]},{"level":2,"title":"Solution:","slug":"solution","link":"#solution","children":[{"level":3,"title":"...","slug":"","link":"#","children":[]}]}],"relativePath":"solution/0101-0200/122 - Best Time to Buy and Sell Stock II.md","lastUpdated":1671291107000}'),l={name:"solution/0101-0200/122 - Best Time to Buy and Sell Stock II.md"},o=e("",18),p=[o];function t(c,r,i,y,d,C){return a(),n("div",null,p)}const h=s(l,[["render",t]]);export{A as __pageData,h as default};
diff --git a/assets/solution_0101-0200_125 - Valid Palindrome.md.e80bb385.js b/assets/solution_0101-0200_125 - Valid Palindrome.md.e80bb385.js
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..2ff2cf41
--- /dev/null
+++ b/assets/solution_0101-0200_125 - Valid Palindrome.md.e80bb385.js
@@ -0,0 +1,42 @@
+import{_ as s,o as a,c as n,a as l}from"./app.e4604e86.js";const F=JSON.parse('{"title":"125. Valid Palindrome","description":"","frontmatter":{},"headers":[{"level":2,"title":"Problem Statement","slug":"problem-statement","link":"#problem-statement","children":[]},{"level":2,"title":"Solution:","slug":"solution","link":"#solution","children":[{"level":3,"title":"...","slug":"","link":"#","children":[]}]}],"relativePath":"solution/0101-0200/125 - Valid Palindrome.md","lastUpdated":1676656807000}'),p={name:"solution/0101-0200/125 - Valid Palindrome.md"},o=l(`
A phrase is a palindrome if, after converting all uppercase letters into lowercase letters and removing all non-alphanumeric characters, it reads the same forward and backward. Alphanumeric characters include letters and numbers.
Given a string s, return true if it is a palindrome, or false otherwise.
Example 1:
Input: s = "A man, a plan, a canal: Panama"
+Output: true
+Explanation: "amanaplanacanalpanama" is a palindrome.
+
Example 2:
Input: s = "race a car"
+Output: false
+Explanation: "raceacar" is not a palindrome.
+
Example 3:
Input: s = " "
+Output: true
+Explanation: s is an empty string "" after removing non-alphanumeric characters.
+Since an empty string reads the same forward and backward, it is a palindrome.
+
`,19),e=[o];function t(c,r,D,C,i,y){return a(),n("div",null,e)}const d=s(p,[["render",t]]);export{F as __pageData,d as default};
diff --git a/assets/solution_0101-0200_125 - Valid Palindrome.md.e80bb385.lean.js b/assets/solution_0101-0200_125 - Valid Palindrome.md.e80bb385.lean.js
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..ab6ede52
--- /dev/null
+++ b/assets/solution_0101-0200_125 - Valid Palindrome.md.e80bb385.lean.js
@@ -0,0 +1 @@
+import{_ as s,o as a,c as n,a as l}from"./app.e4604e86.js";const F=JSON.parse('{"title":"125. Valid Palindrome","description":"","frontmatter":{},"headers":[{"level":2,"title":"Problem Statement","slug":"problem-statement","link":"#problem-statement","children":[]},{"level":2,"title":"Solution:","slug":"solution","link":"#solution","children":[{"level":3,"title":"...","slug":"","link":"#","children":[]}]}],"relativePath":"solution/0101-0200/125 - Valid Palindrome.md","lastUpdated":1676656807000}'),p={name:"solution/0101-0200/125 - Valid Palindrome.md"},o=l("",19),e=[o];function t(c,r,D,C,i,y){return a(),n("div",null,e)}const d=s(p,[["render",t]]);export{F as __pageData,d as default};
diff --git a/assets/solution_0101-0200_129 - Sum Root to Leaf Numbers.md.d631d681.js b/assets/solution_0101-0200_129 - Sum Root to Leaf Numbers.md.d631d681.js
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..dbff627f
--- /dev/null
+++ b/assets/solution_0101-0200_129 - Sum Root to Leaf Numbers.md.d631d681.js
@@ -0,0 +1,41 @@
+import{_ as s,o as n,c as a,a as l}from"./app.e4604e86.js";const F=JSON.parse('{"title":"129. Sum Root to Leaf Numbers","description":"","frontmatter":{},"headers":[{"level":2,"title":"Problem Statement","slug":"problem-statement","link":"#problem-statement","children":[]},{"level":2,"title":"Solution:","slug":"solution","link":"#solution","children":[{"level":3,"title":"...","slug":"","link":"#","children":[]}]}],"relativePath":"solution/0101-0200/129 - Sum Root to Leaf Numbers.md","lastUpdated":1678822270000}'),o={name:"solution/0101-0200/129 - Sum Root to Leaf Numbers.md"},e=l(`
`,22),p=[e];function t(r,c,D,i,C,A){return n(),a("div",null,p)}const d=s(o,[["render",t]]);export{F as __pageData,d as default};
diff --git a/assets/solution_0101-0200_129 - Sum Root to Leaf Numbers.md.d631d681.lean.js b/assets/solution_0101-0200_129 - Sum Root to Leaf Numbers.md.d631d681.lean.js
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..4a7006fa
--- /dev/null
+++ b/assets/solution_0101-0200_129 - Sum Root to Leaf Numbers.md.d631d681.lean.js
@@ -0,0 +1 @@
+import{_ as s,o as n,c as a,a as l}from"./app.e4604e86.js";const F=JSON.parse('{"title":"129. Sum Root to Leaf Numbers","description":"","frontmatter":{},"headers":[{"level":2,"title":"Problem Statement","slug":"problem-statement","link":"#problem-statement","children":[]},{"level":2,"title":"Solution:","slug":"solution","link":"#solution","children":[{"level":3,"title":"...","slug":"","link":"#","children":[]}]}],"relativePath":"solution/0101-0200/129 - Sum Root to Leaf Numbers.md","lastUpdated":1678822270000}'),o={name:"solution/0101-0200/129 - Sum Root to Leaf Numbers.md"},e=l("",22),p=[e];function t(r,c,D,i,C,A){return n(),a("div",null,p)}const d=s(o,[["render",t]]);export{F as __pageData,d as default};
diff --git a/assets/solution_0101-0200_136 - Single Number.md.3349dbec.js b/assets/solution_0101-0200_136 - Single Number.md.3349dbec.js
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..17bb8ca7
--- /dev/null
+++ b/assets/solution_0101-0200_136 - Single Number.md.3349dbec.js
@@ -0,0 +1,23 @@
+import{_ as s,o as a,c as n,a as l}from"./app.e4604e86.js";const A=JSON.parse('{"title":"136. Single Number","description":"","frontmatter":{},"headers":[{"level":2,"title":"Problem Statement","slug":"problem-statement","link":"#problem-statement","children":[]},{"level":2,"title":"Solution:","slug":"solution","link":"#solution","children":[{"level":3,"title":"...","slug":"","link":"#","children":[]}]}],"relativePath":"solution/0101-0200/136 - Single Number.md","lastUpdated":1676656807000}'),e={name:"solution/0101-0200/136 - Single Number.md"},p=l(`
implSolution{
+pubfnsingle_number(nums:Vec<i32>)->i32{
+letmut res =0;
+for num in nums {
+ // a ^ a = 0
+ // a ^ a ^ a = a
+ // a ^ a ^ b = b
+ // also position of a and b doesn't matter
+ res ^= num;
+}
+
+ res
+}
+}
+
+
`,19),o=[p];function t(c,r,i,C,d,y){return a(),n("div",null,o)}const D=s(e,[["render",t]]);export{A as __pageData,D as default};
diff --git a/assets/solution_0101-0200_136 - Single Number.md.3349dbec.lean.js b/assets/solution_0101-0200_136 - Single Number.md.3349dbec.lean.js
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..e104a235
--- /dev/null
+++ b/assets/solution_0101-0200_136 - Single Number.md.3349dbec.lean.js
@@ -0,0 +1 @@
+import{_ as s,o as a,c as n,a as l}from"./app.e4604e86.js";const A=JSON.parse('{"title":"136. Single Number","description":"","frontmatter":{},"headers":[{"level":2,"title":"Problem Statement","slug":"problem-statement","link":"#problem-statement","children":[]},{"level":2,"title":"Solution:","slug":"solution","link":"#solution","children":[{"level":3,"title":"...","slug":"","link":"#","children":[]}]}],"relativePath":"solution/0101-0200/136 - Single Number.md","lastUpdated":1676656807000}'),e={name:"solution/0101-0200/136 - Single Number.md"},p=l("",19),o=[p];function t(c,r,i,C,d,y){return a(),n("div",null,o)}const D=s(e,[["render",t]]);export{A as __pageData,D as default};
diff --git a/assets/solution_0101-0200_141 - Linked List Cycle.md.1872d26d.js b/assets/solution_0101-0200_141 - Linked List Cycle.md.1872d26d.js
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..43f5a3d8
--- /dev/null
+++ b/assets/solution_0101-0200_141 - Linked List Cycle.md.1872d26d.js
@@ -0,0 +1,37 @@
+import{_ as s,o as n,c as a,a as l}from"./app.e4604e86.js";const A=JSON.parse('{"title":"141. Linked List Cycle","description":"","frontmatter":{},"headers":[{"level":2,"title":"Problem Statement","slug":"problem-statement","link":"#problem-statement","children":[]},{"level":2,"title":"Solution:","slug":"solution","link":"#solution","children":[{"level":3,"title":"...","slug":"","link":"#","children":[]}]}],"relativePath":"solution/0101-0200/141 - Linked List Cycle.md","lastUpdated":1676656807000}'),e={name:"solution/0101-0200/141 - Linked List Cycle.md"},p=l(`
Given head, the head of a linked list, determine if the linked list has a cycle in it.
There is a cycle in a linked list if there is some node in the list that can be reached again by continuously following the next pointer. Internally, pos is used to denote the index of the node that tail's next pointer is connected to. Note that pos is not passed as a parameter.
Return true if there is a cycle in the linked list. Otherwise, return false.
Example 1:
Input: head = [3,2,0,-4], pos = 1
+Output: true
+Explanation: There is a cycle in the linked list, where the tail connects to the 1st node (0-indexed).
+
Example 2:
Input: head = [1,2], pos = 0
+Output: true
+Explanation: There is a cycle in the linked list, where the tail connects to the 0th node.
+
Example 3:
Input: head = [1], pos = -1
+Output: false
+Explanation: There is no cycle in the linked list.
+
Constraints:
The number of the nodes in the list is in the range [0, 104].
-105 <= Node.val <= 105
pos is -1 or a valid index in the linked-list.
Follow up: Can you solve it using O(1) (i.e. constant) memory?
`,25),o=[p];function t(c,i,r,d,D,y){return n(),a("div",null,o)}const h=s(e,[["render",t]]);export{A as __pageData,h as default};
diff --git a/assets/solution_0101-0200_141 - Linked List Cycle.md.1872d26d.lean.js b/assets/solution_0101-0200_141 - Linked List Cycle.md.1872d26d.lean.js
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..95fe17a6
--- /dev/null
+++ b/assets/solution_0101-0200_141 - Linked List Cycle.md.1872d26d.lean.js
@@ -0,0 +1 @@
+import{_ as s,o as n,c as a,a as l}from"./app.e4604e86.js";const A=JSON.parse('{"title":"141. Linked List Cycle","description":"","frontmatter":{},"headers":[{"level":2,"title":"Problem Statement","slug":"problem-statement","link":"#problem-statement","children":[]},{"level":2,"title":"Solution:","slug":"solution","link":"#solution","children":[{"level":3,"title":"...","slug":"","link":"#","children":[]}]}],"relativePath":"solution/0101-0200/141 - Linked List Cycle.md","lastUpdated":1676656807000}'),e={name:"solution/0101-0200/141 - Linked List Cycle.md"},p=l("",25),o=[p];function t(c,i,r,d,D,y){return n(),a("div",null,o)}const h=s(e,[["render",t]]);export{A as __pageData,h as default};
diff --git a/assets/solution_0101-0200_142 - Linked List Cycle II.md.8c585262.js b/assets/solution_0101-0200_142 - Linked List Cycle II.md.8c585262.js
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..be68e995
--- /dev/null
+++ b/assets/solution_0101-0200_142 - Linked List Cycle II.md.8c585262.js
@@ -0,0 +1,40 @@
+import{_ as s,o as n,c as a,a as l}from"./app.e4604e86.js";const A=JSON.parse('{"title":"142. Linked List Cycle II","description":"","frontmatter":{},"headers":[{"level":2,"title":"Problem Statement","slug":"problem-statement","link":"#problem-statement","children":[]},{"level":2,"title":"Solution:","slug":"solution","link":"#solution","children":[{"level":3,"title":"...","slug":"","link":"#","children":[]}]}],"relativePath":"solution/0101-0200/142 - Linked List Cycle II.md","lastUpdated":1678822270000}'),e={name:"solution/0101-0200/142 - Linked List Cycle II.md"},o=l(`
Given the head of a linked list, return the node where the cycle begins. If there is no cycle, return null.
There is a cycle in a linked list if there is some node in the list that can be reached again by continuously following the next pointer. Internally, pos is used to denote the index of the node that tail's next pointer is connected to (0-indexed). It is -1 if there is no cycle. Note thatposis not passed as a parameter.
Do not modify the linked list.
Example 1:
Input: head = [3,2,0,-4], pos = 1
+Output: tail connects to node index 1
+Explanation: There is a cycle in the linked list, where tail connects to the second node.
+
Example 2:
Input: head = [1,2], pos = 0
+Output: tail connects to node index 0
+Explanation: There is a cycle in the linked list, where tail connects to the first node.
+
Example 3:
Input: head = [1], pos = -1
+Output: no cycle
+Explanation: There is no cycle in the linked list.
+
Constraints:
The number of the nodes in the list is in the range [0, 104].
-105 <= Node.val <= 105
pos is -1 or a valid index in the linked-list.
Follow up: Can you solve it using O(1) (i.e. constant) memory?
`,25),p=[o];function t(c,i,r,d,D,y){return n(),a("div",null,p)}const F=s(e,[["render",t]]);export{A as __pageData,F as default};
diff --git a/assets/solution_0101-0200_142 - Linked List Cycle II.md.8c585262.lean.js b/assets/solution_0101-0200_142 - Linked List Cycle II.md.8c585262.lean.js
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..b03d7fd6
--- /dev/null
+++ b/assets/solution_0101-0200_142 - Linked List Cycle II.md.8c585262.lean.js
@@ -0,0 +1 @@
+import{_ as s,o as n,c as a,a as l}from"./app.e4604e86.js";const A=JSON.parse('{"title":"142. Linked List Cycle II","description":"","frontmatter":{},"headers":[{"level":2,"title":"Problem Statement","slug":"problem-statement","link":"#problem-statement","children":[]},{"level":2,"title":"Solution:","slug":"solution","link":"#solution","children":[{"level":3,"title":"...","slug":"","link":"#","children":[]}]}],"relativePath":"solution/0101-0200/142 - Linked List Cycle II.md","lastUpdated":1678822270000}'),e={name:"solution/0101-0200/142 - Linked List Cycle II.md"},o=l("",25),p=[o];function t(c,i,r,d,D,y){return n(),a("div",null,p)}const F=s(e,[["render",t]]);export{A as __pageData,F as default};
diff --git a/assets/solution_0101-0200_144 - Binary Tree Preorder Traversal.md.a71cb20b.js b/assets/solution_0101-0200_144 - Binary Tree Preorder Traversal.md.a71cb20b.js
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..def49d09
--- /dev/null
+++ b/assets/solution_0101-0200_144 - Binary Tree Preorder Traversal.md.a71cb20b.js
@@ -0,0 +1,36 @@
+import{_ as s,o as a,c as n,a as l}from"./app.e4604e86.js";const F=JSON.parse('{"title":"144. Binary Tree Preorder Traversal","description":"","frontmatter":{},"headers":[{"level":2,"title":"Problem Statement:","slug":"problem-statement","link":"#problem-statement","children":[{"level":3,"title":"Example 1:","slug":"example-1","link":"#example-1","children":[]},{"level":3,"title":"Example 2:","slug":"example-2","link":"#example-2","children":[]},{"level":3,"title":"Example 3:","slug":"example-3","link":"#example-3","children":[]},{"level":3,"title":"Constraints:","slug":"constraints","link":"#constraints","children":[]}]},{"level":2,"title":"Solution:","slug":"solution","link":"#solution","children":[{"level":3,"title":"...","slug":"","link":"#","children":[]}]}],"relativePath":"solution/0101-0200/144 - Binary Tree Preorder Traversal.md","lastUpdated":1671291107000}'),e={name:"solution/0101-0200/144 - Binary Tree Preorder Traversal.md"},p=l(`
`,18),o=[p];function r(t,c,D,i,y,A){return a(),n("div",null,o)}const d=s(e,[["render",r]]);export{F as __pageData,d as default};
diff --git a/assets/solution_0101-0200_144 - Binary Tree Preorder Traversal.md.a71cb20b.lean.js b/assets/solution_0101-0200_144 - Binary Tree Preorder Traversal.md.a71cb20b.lean.js
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..af756ff9
--- /dev/null
+++ b/assets/solution_0101-0200_144 - Binary Tree Preorder Traversal.md.a71cb20b.lean.js
@@ -0,0 +1 @@
+import{_ as s,o as a,c as n,a as l}from"./app.e4604e86.js";const F=JSON.parse('{"title":"144. Binary Tree Preorder Traversal","description":"","frontmatter":{},"headers":[{"level":2,"title":"Problem Statement:","slug":"problem-statement","link":"#problem-statement","children":[{"level":3,"title":"Example 1:","slug":"example-1","link":"#example-1","children":[]},{"level":3,"title":"Example 2:","slug":"example-2","link":"#example-2","children":[]},{"level":3,"title":"Example 3:","slug":"example-3","link":"#example-3","children":[]},{"level":3,"title":"Constraints:","slug":"constraints","link":"#constraints","children":[]}]},{"level":2,"title":"Solution:","slug":"solution","link":"#solution","children":[{"level":3,"title":"...","slug":"","link":"#","children":[]}]}],"relativePath":"solution/0101-0200/144 - Binary Tree Preorder Traversal.md","lastUpdated":1671291107000}'),e={name:"solution/0101-0200/144 - Binary Tree Preorder Traversal.md"},p=l("",18),o=[p];function r(t,c,D,i,y,A){return a(),n("div",null,o)}const d=s(e,[["render",r]]);export{F as __pageData,d as default};
diff --git a/assets/solution_0101-0200_145 - Binary Tree Postorder Traversal.md.291be10d.js b/assets/solution_0101-0200_145 - Binary Tree Postorder Traversal.md.291be10d.js
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..48a5fd09
--- /dev/null
+++ b/assets/solution_0101-0200_145 - Binary Tree Postorder Traversal.md.291be10d.js
@@ -0,0 +1,32 @@
+import{_ as s,o as a,c as n,a as l}from"./app.e4604e86.js";const F=JSON.parse('{"title":"145. Binary Tree Postorder Traversal","description":"","frontmatter":{},"headers":[{"level":2,"title":"Problem Statement:","slug":"problem-statement","link":"#problem-statement","children":[{"level":3,"title":"Example 1:","slug":"example-1","link":"#example-1","children":[]},{"level":3,"title":"Example 2:","slug":"example-2","link":"#example-2","children":[]},{"level":3,"title":"Example 3:","slug":"example-3","link":"#example-3","children":[]},{"level":3,"title":"Constraints:","slug":"constraints","link":"#constraints","children":[]}]},{"level":2,"title":"Solution:","slug":"solution","link":"#solution","children":[{"level":3,"title":"...","slug":"","link":"#","children":[]}]}],"relativePath":"solution/0101-0200/145 - Binary Tree Postorder Traversal.md","lastUpdated":1671291107000}'),e={name:"solution/0101-0200/145 - Binary Tree Postorder Traversal.md"},p=l(`
`,18),o=[p];function t(r,c,D,i,y,A){return a(),n("div",null,o)}const d=s(e,[["render",t]]);export{F as __pageData,d as default};
diff --git a/assets/solution_0101-0200_145 - Binary Tree Postorder Traversal.md.291be10d.lean.js b/assets/solution_0101-0200_145 - Binary Tree Postorder Traversal.md.291be10d.lean.js
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..1366ee61
--- /dev/null
+++ b/assets/solution_0101-0200_145 - Binary Tree Postorder Traversal.md.291be10d.lean.js
@@ -0,0 +1 @@
+import{_ as s,o as a,c as n,a as l}from"./app.e4604e86.js";const F=JSON.parse('{"title":"145. Binary Tree Postorder Traversal","description":"","frontmatter":{},"headers":[{"level":2,"title":"Problem Statement:","slug":"problem-statement","link":"#problem-statement","children":[{"level":3,"title":"Example 1:","slug":"example-1","link":"#example-1","children":[]},{"level":3,"title":"Example 2:","slug":"example-2","link":"#example-2","children":[]},{"level":3,"title":"Example 3:","slug":"example-3","link":"#example-3","children":[]},{"level":3,"title":"Constraints:","slug":"constraints","link":"#constraints","children":[]}]},{"level":2,"title":"Solution:","slug":"solution","link":"#solution","children":[{"level":3,"title":"...","slug":"","link":"#","children":[]}]}],"relativePath":"solution/0101-0200/145 - Binary Tree Postorder Traversal.md","lastUpdated":1671291107000}'),e={name:"solution/0101-0200/145 - Binary Tree Postorder Traversal.md"},p=l("",18),o=[p];function t(r,c,D,i,y,A){return a(),n("div",null,o)}const d=s(e,[["render",t]]);export{F as __pageData,d as default};
diff --git a/assets/solution_0101-0200_160 - Intersection of Two Linked Lists.md.a8640b62.js b/assets/solution_0101-0200_160 - Intersection of Two Linked Lists.md.a8640b62.js
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..f42d5d7d
--- /dev/null
+++ b/assets/solution_0101-0200_160 - Intersection of Two Linked Lists.md.a8640b62.js
@@ -0,0 +1,48 @@
+import{_ as a,o as t,c as o,f as s,a as n,b as e}from"./app.e4604e86.js";const g=JSON.parse('{"title":"160. Intersection of Two Linked Lists","description":"","frontmatter":{},"headers":[{"level":2,"title":"Problem Statement","slug":"problem-statement","link":"#problem-statement","children":[]},{"level":2,"title":"Solution:","slug":"solution","link":"#solution","children":[{"level":3,"title":"...","slug":"","link":"#","children":[]}]}],"relativePath":"solution/0101-0200/160 - Intersection of Two Linked Lists.md","lastUpdated":1676656807000}'),l={name:"solution/0101-0200/160 - Intersection of Two Linked Lists.md"},p=n(`
Given the heads of two singly linked-lists headA and headB, return the node at which the two lists intersect. If the two linked lists have no intersection at all, return null.
For example, the following two linked lists begin to intersect at node c1:
The test cases are generated such that there are no cycles anywhere in the entire linked structure.
Note that the linked lists must retain their original structure after the function returns.
Custom Judge:
The inputs to the judge are given as follows (your program is not given these inputs):
intersectVal - The value of the node where the intersection occurs. This is 0 if there is no intersected node.
listA - The first linked list.
listB - The second linked list.
skipA - The number of nodes to skip ahead in listA (starting from the head) to get to the intersected node.
skipB - The number of nodes to skip ahead in listB (starting from the head) to get to the intersected node.
The judge will then create the linked structure based on these inputs and pass the two heads, headA and headB to your program. If you correctly return the intersected node, then your solution will be accepted.
Example 1:
Input: intersectVal = 8, listA = [4,1,8,4,5], listB = [5,6,1,8,4,5], skipA = 2, skipB = 3
+Output: Intersected at '8'
+Explanation: The intersected node's value is 8 (note that this must not be 0 if the two lists intersect).
+From the head of A, it reads as [4,1,8,4,5]. From the head of B, it reads as [5,6,1,8,4,5]. There are 2 nodes before the intersected node in A; There are 3 nodes before the intersected node in B.
+- Note that the intersected node's value is not 1 because the nodes with value 1 in A and B (2nd node in A and 3rd node in B) are different node references. In other words, they point to two different locations in memory, while the nodes with value 8 in A and B (3rd node in A and 4th node in B) point to the same location in memory.
+
Example 2:
Input: intersectVal = 2, listA = [1,9,1,2,4], listB = [3,2,4], skipA = 3, skipB = 1
+Output: Intersected at '2'
+Explanation: The intersected node's value is 2 (note that this must not be 0 if the two lists intersect).
+From the head of A, it reads as [1,9,1,2,4]. From the head of B, it reads as [3,2,4]. There are 3 nodes before the intersected node in A; There are 1 node before the intersected node in B.
+
Example 3:
Input: intersectVal = 0, listA = [2,6,4], listB = [1,5], skipA = 3, skipB = 2
+Output: No intersection
+Explanation: From the head of A, it reads as [2,6,4]. From the head of B, it reads as [1,5]. Since the two lists do not intersect, intersectVal must be 0, while skipA and skipB can be arbitrary values.
+Explanation: The two lists do not intersect, so return null.
+
Constraints:
The number of nodes of listA is in the m.
The number of nodes of listB is in the n.
1 <= m, n <= 3 * 104
1 <= Node.val <= 105
0 <= skipA < m
0 <= skipB < n
intersectVal is 0 if listA and listB do not intersect.
intersectVal == listA[skipA] == listB[skipB] if listA and listB intersect.
`,4);function d(A,D,h,C,y,F){return t(),o("div",null,[p,s(" Could you write a solution that runs in "),c,s(" time and use only "),i,s(" memory? "),r])}const m=a(l,[["render",d]]);export{g as __pageData,m as default};
diff --git a/assets/solution_0101-0200_160 - Intersection of Two Linked Lists.md.a8640b62.lean.js b/assets/solution_0101-0200_160 - Intersection of Two Linked Lists.md.a8640b62.lean.js
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..b0c84e4a
--- /dev/null
+++ b/assets/solution_0101-0200_160 - Intersection of Two Linked Lists.md.a8640b62.lean.js
@@ -0,0 +1 @@
+import{_ as a,o as t,c as o,f as s,a as n,b as e}from"./app.e4604e86.js";const g=JSON.parse('{"title":"160. Intersection of Two Linked Lists","description":"","frontmatter":{},"headers":[{"level":2,"title":"Problem Statement","slug":"problem-statement","link":"#problem-statement","children":[]},{"level":2,"title":"Solution:","slug":"solution","link":"#solution","children":[{"level":3,"title":"...","slug":"","link":"#","children":[]}]}],"relativePath":"solution/0101-0200/160 - Intersection of Two Linked Lists.md","lastUpdated":1676656807000}'),l={name:"solution/0101-0200/160 - Intersection of Two Linked Lists.md"},p=n("",27),c=e("code",null,"O(m + n)",-1),i=e("code",null,"O(1)",-1),r=n("",4);function d(A,D,h,C,y,F){return t(),o("div",null,[p,s(" Could you write a solution that runs in "),c,s(" time and use only "),i,s(" memory? "),r])}const m=a(l,[["render",d]]);export{g as __pageData,m as default};
diff --git a/assets/solution_0101-0200_169 - Majority Element.md.015189a4.js b/assets/solution_0101-0200_169 - Majority Element.md.015189a4.js
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..8434f2e0
--- /dev/null
+++ b/assets/solution_0101-0200_169 - Majority Element.md.015189a4.js
@@ -0,0 +1,26 @@
+import{_ as a,o as l,c as e,f as s,a as n,b as p}from"./app.e4604e86.js";const u=JSON.parse('{"title":"169. Majority Element","description":"","frontmatter":{},"headers":[{"level":2,"title":"Problem Statement","slug":"problem-statement","link":"#problem-statement","children":[]},{"level":2,"title":"Solution:","slug":"solution","link":"#solution","children":[{"level":3,"title":"...","slug":"","link":"#","children":[]}]}],"relativePath":"solution/0101-0200/169 - Majority Element.md","lastUpdated":1676656807000}'),o={name:"solution/0101-0200/169 - Majority Element.md"},t=n(`
`,4);function i(C,y,D,A,F,d){return l(),e("div",null,[t,s(" Could you solve the problem in linear time and in "),c,s(" space? "),r])}const h=a(o,[["render",i]]);export{u as __pageData,h as default};
diff --git a/assets/solution_0101-0200_169 - Majority Element.md.015189a4.lean.js b/assets/solution_0101-0200_169 - Majority Element.md.015189a4.lean.js
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..3fc39172
--- /dev/null
+++ b/assets/solution_0101-0200_169 - Majority Element.md.015189a4.lean.js
@@ -0,0 +1 @@
+import{_ as a,o as l,c as e,f as s,a as n,b as p}from"./app.e4604e86.js";const u=JSON.parse('{"title":"169. Majority Element","description":"","frontmatter":{},"headers":[{"level":2,"title":"Problem Statement","slug":"problem-statement","link":"#problem-statement","children":[]},{"level":2,"title":"Solution:","slug":"solution","link":"#solution","children":[{"level":3,"title":"...","slug":"","link":"#","children":[]}]}],"relativePath":"solution/0101-0200/169 - Majority Element.md","lastUpdated":1676656807000}'),o={name:"solution/0101-0200/169 - Majority Element.md"},t=n("",15),c=p("code",null,"O(1)",-1),r=n("",4);function i(C,y,D,A,F,d){return l(),e("div",null,[t,s(" Could you solve the problem in linear time and in "),c,s(" space? "),r])}const h=a(o,[["render",i]]);export{u as __pageData,h as default};
diff --git a/assets/solution_0101-0200_172 - Factorial Trailing Zeroes.md.1462e553.js b/assets/solution_0101-0200_172 - Factorial Trailing Zeroes.md.1462e553.js
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..68d4ceab
--- /dev/null
+++ b/assets/solution_0101-0200_172 - Factorial Trailing Zeroes.md.1462e553.js
@@ -0,0 +1,18 @@
+import{_ as a,o as s,c as n,a as e}from"./app.e4604e86.js";const y=JSON.parse('{"title":"172. Factorial Trailing Zeroes","description":"","frontmatter":{},"headers":[{"level":2,"title":"Problem Statement:","slug":"problem-statement","link":"#problem-statement","children":[{"level":3,"title":"Example 1:","slug":"example-1","link":"#example-1","children":[]},{"level":3,"title":"Example 2:","slug":"example-2","link":"#example-2","children":[]},{"level":3,"title":"Example 3:","slug":"example-3","link":"#example-3","children":[]},{"level":3,"title":"Constraints:","slug":"constraints","link":"#constraints","children":[]}]},{"level":2,"title":"Solution:","slug":"solution","link":"#solution","children":[{"level":3,"title":"...","slug":"","link":"#","children":[]}]}],"relativePath":"solution/0101-0200/172 - Factorial Trailing Zeroes.md","lastUpdated":1671291107000}'),l={name:"solution/0101-0200/172 - Factorial Trailing Zeroes.md"},o=e(`
Note that in some languages, such as Java, there is no unsigned integer type. In this case, both input and output will be given as a signed integer type. They should not affect your implementation, as the integer's internal binary representation is the same, whether it is signed or unsigned.
In Java, the compiler represents the signed integers using 2's complement notation. Therefore, in Example 2 above, the input represents the signed integer -3 and the output represents the signed integer -1073741825.
Example 1:
Input: n = 00000010100101000001111010011100
+Output: 964176192 (00111001011110000010100101000000)
+Explanation: The input binary string 00000010100101000001111010011100 represents the unsigned integer 43261596, so return 964176192 which its binary representation is 00111001011110000010100101000000.
+
Example 2:
Input: n = 11111111111111111111111111111101
+Output: 3221225471 (10111111111111111111111111111111)
+Explanation: The input binary string 11111111111111111111111111111101 represents the unsigned integer 4294967293, so return 3221225471 which its binary representation is 10111111111111111111111111111111.
+
Constraints:
The input must be a binary string of length 32
Follow up: If this function is called many times, how would you optimize it?
implSolution{
+pubfnreverse_bits(x:u32)->u32{
+let(mut x,mut res)=(x,0);
+
+ // iterate 32 times, once for each bit
+for _ in0..32{
+ // left-shift res by 1 bit to make room for the next bit
+ res <<=1;
+ // adding the least significant bit of x to the result
+ // using bitwise AND with 1
+ res += x &1;
+ // right-shift x by 1 bit, discarding the least significant bit
+ // that was just added to the result
+ x >>=1;
+}
+
+ res
+}
+}
+
+
`,20),p=[t];function o(r,i,c,C,y,d){return n(),a("div",null,p)}const h=s(l,[["render",o]]);export{A as __pageData,h as default};
diff --git a/assets/solution_0101-0200_190 - Reverse Bits.md.8531cca3.lean.js b/assets/solution_0101-0200_190 - Reverse Bits.md.8531cca3.lean.js
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..db6e8373
--- /dev/null
+++ b/assets/solution_0101-0200_190 - Reverse Bits.md.8531cca3.lean.js
@@ -0,0 +1 @@
+import{_ as s,o as n,c as a,a as e}from"./app.e4604e86.js";const A=JSON.parse('{"title":"190. Reverse Bits","description":"","frontmatter":{},"headers":[{"level":2,"title":"Problem Statement","slug":"problem-statement","link":"#problem-statement","children":[]},{"level":2,"title":"Solution:","slug":"solution","link":"#solution","children":[{"level":3,"title":"...","slug":"","link":"#","children":[]}]}],"relativePath":"solution/0101-0200/190 - Reverse Bits.md","lastUpdated":1677374362000}'),l={name:"solution/0101-0200/190 - Reverse Bits.md"},t=e("",20),p=[t];function o(r,i,c,C,y,d){return n(),a("div",null,p)}const h=s(l,[["render",o]]);export{A as __pageData,h as default};
diff --git a/assets/solution_0101-0200_191 - Number of 1 Bits.md.b5946bbe.js b/assets/solution_0101-0200_191 - Number of 1 Bits.md.b5946bbe.js
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..1c57f305
--- /dev/null
+++ b/assets/solution_0101-0200_191 - Number of 1 Bits.md.b5946bbe.js
@@ -0,0 +1,21 @@
+import{_ as s,o as a,c as n,a as e}from"./app.e4604e86.js";const D=JSON.parse('{"title":"191. Number of 1 Bits","description":"","frontmatter":{},"headers":[{"level":2,"title":"Problem Statement:","slug":"problem-statement","link":"#problem-statement","children":[{"level":3,"title":"Example 1:","slug":"example-1","link":"#example-1","children":[]},{"level":3,"title":"Example 2:","slug":"example-2","link":"#example-2","children":[]},{"level":3,"title":"Example 3:","slug":"example-3","link":"#example-3","children":[]},{"level":3,"title":"Constraints:","slug":"constraints","link":"#constraints","children":[]}]},{"level":2,"title":"Solution:","slug":"solution","link":"#solution","children":[{"level":3,"title":"...","slug":"","link":"#","children":[]}]}],"relativePath":"solution/0101-0200/191 - Number of 1 Bits.md","lastUpdated":1671291107000}'),l={name:"solution/0101-0200/191 - Number of 1 Bits.md"},t=e(`
Write a function that takes an unsigned integer and returns the number of '1' bits it has (also known as the Hamming weight).
Note:
Note that in some languages, such as Java, there is no unsigned integer type. In this case, the input will be given as a signed integer type. It should not affect your implementation, as the integer's internal binary representation is the same, whether it is signed or unsigned.
In Java, the compiler represents the signed integers using 2's complement notation. Therefore, in Example 3, the input represents the signed integer. -3.
Input: n = 00000000000000000000000000001011
+Output: 3
+Explanation: The input binary string 00000000000000000000000000001011 has a total of three '1' bits.
+
Input: n = 00000000000000000000000010000000
+Output: 1
+Explanation: The input binary string 00000000000000000000000010000000 has a total of one '1' bit.
+
Input: n = 11111111111111111111111111111101
+Output: 31
+Explanation: The input binary string 11111111111111111111111111111101 has a total of thirty one '1' bits.
+
`,19),o=[t];function p(r,i,c,d,C,h){return a(),n("div",null,o)}const u=s(l,[["render",p]]);export{D as __pageData,u as default};
diff --git a/assets/solution_0101-0200_191 - Number of 1 Bits.md.b5946bbe.lean.js b/assets/solution_0101-0200_191 - Number of 1 Bits.md.b5946bbe.lean.js
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..786763bf
--- /dev/null
+++ b/assets/solution_0101-0200_191 - Number of 1 Bits.md.b5946bbe.lean.js
@@ -0,0 +1 @@
+import{_ as s,o as a,c as n,a as e}from"./app.e4604e86.js";const D=JSON.parse('{"title":"191. Number of 1 Bits","description":"","frontmatter":{},"headers":[{"level":2,"title":"Problem Statement:","slug":"problem-statement","link":"#problem-statement","children":[{"level":3,"title":"Example 1:","slug":"example-1","link":"#example-1","children":[]},{"level":3,"title":"Example 2:","slug":"example-2","link":"#example-2","children":[]},{"level":3,"title":"Example 3:","slug":"example-3","link":"#example-3","children":[]},{"level":3,"title":"Constraints:","slug":"constraints","link":"#constraints","children":[]}]},{"level":2,"title":"Solution:","slug":"solution","link":"#solution","children":[{"level":3,"title":"...","slug":"","link":"#","children":[]}]}],"relativePath":"solution/0101-0200/191 - Number of 1 Bits.md","lastUpdated":1671291107000}'),l={name:"solution/0101-0200/191 - Number of 1 Bits.md"},t=e("",19),o=[t];function p(r,i,c,d,C,h){return a(),n("div",null,o)}const u=s(l,[["render",p]]);export{D as __pageData,u as default};
diff --git a/assets/solution_0101-0200_193 - Valid Phone Numbers.md.c98e421d.js b/assets/solution_0101-0200_193 - Valid Phone Numbers.md.c98e421d.js
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..41e35039
--- /dev/null
+++ b/assets/solution_0101-0200_193 - Valid Phone Numbers.md.c98e421d.js
@@ -0,0 +1,10 @@
+import{_ as e,o as a,c as s,a as n}from"./app.e4604e86.js";const b=JSON.parse('{"title":"193. Valid Phone Numbers","description":"","frontmatter":{},"headers":[{"level":2,"title":"Problem Statement","slug":"problem-statement","link":"#problem-statement","children":[]},{"level":2,"title":"Solution:","slug":"solution","link":"#solution","children":[{"level":3,"title":"...","slug":"","link":"#","children":[]}]}],"relativePath":"solution/0101-0200/193 - Valid Phone Numbers.md","lastUpdated":1671952530000}'),t={name:"solution/0101-0200/193 - Valid Phone Numbers.md"},l=n(`
Your script should output the tenth line, which is:
Line 10
+
Note: 1. If the file contains less than 10 lines, what should you output? 2. There's at least three different solutions. Try to explore all possibilities.
`,14),l=[i];function o(r,p,c,h,d,u){return t(),n("div",null,l)}const m=e(a,[["render",o]]);export{b as __pageData,m as default};
diff --git a/assets/solution_0101-0200_195 - Tenth Line.md.e150afd0.lean.js b/assets/solution_0101-0200_195 - Tenth Line.md.e150afd0.lean.js
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..5c07bd77
--- /dev/null
+++ b/assets/solution_0101-0200_195 - Tenth Line.md.e150afd0.lean.js
@@ -0,0 +1 @@
+import{_ as e,o as t,c as n,a as s}from"./app.e4604e86.js";const b=JSON.parse('{"title":"195. Tenth Line","description":"","frontmatter":{},"headers":[{"level":2,"title":"Problem Statement","slug":"problem-statement","link":"#problem-statement","children":[]},{"level":2,"title":"Solution:","slug":"solution","link":"#solution","children":[{"level":3,"title":"...","slug":"","link":"#","children":[]}]}],"relativePath":"solution/0101-0200/195 - Tenth Line.md","lastUpdated":1671952530000}'),a={name:"solution/0101-0200/195 - Tenth Line.md"},i=s("",14),l=[i];function o(r,p,c,h,d,u){return t(),n("div",null,l)}const m=e(a,[["render",o]]);export{b as __pageData,m as default};
diff --git a/assets/solution_0101-0200_199 - Binary Tree Right Side View.md.82de7b92.js b/assets/solution_0101-0200_199 - Binary Tree Right Side View.md.82de7b92.js
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..fe418bbd
--- /dev/null
+++ b/assets/solution_0101-0200_199 - Binary Tree Right Side View.md.82de7b92.js
@@ -0,0 +1,28 @@
+import{_ as s,o as a,c as n,a as l}from"./app.e4604e86.js";const d=JSON.parse('{"title":"199. Binary Tree Right Side View","description":"","frontmatter":{},"headers":[{"level":2,"title":"Problem Statement:","slug":"problem-statement","link":"#problem-statement","children":[{"level":3,"title":"Example 1:","slug":"example-1","link":"#example-1","children":[]},{"level":3,"title":"Example 2:","slug":"example-2","link":"#example-2","children":[]},{"level":3,"title":"Example 3:","slug":"example-3","link":"#example-3","children":[]},{"level":3,"title":"Constraints:","slug":"constraints","link":"#constraints","children":[]}]},{"level":2,"title":"Solution:","slug":"solution","link":"#solution","children":[{"level":3,"title":"...","slug":"","link":"#","children":[]}]}],"relativePath":"solution/0101-0200/199 - Binary Tree Right Side View.md","lastUpdated":1671291107000}'),e={name:"solution/0101-0200/199 - Binary Tree Right Side View.md"},p=l(`
Given the root of a binary tree, imagine yourself standing on the right side of it, return the values of the nodes you can see ordered from top to bottom.
`,17),o=[p];function t(r,c,i,D,C,y){return a(),n("div",null,o)}const F=s(e,[["render",t]]);export{d as __pageData,F as default};
diff --git a/assets/solution_0101-0200_199 - Binary Tree Right Side View.md.82de7b92.lean.js b/assets/solution_0101-0200_199 - Binary Tree Right Side View.md.82de7b92.lean.js
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..091ca222
--- /dev/null
+++ b/assets/solution_0101-0200_199 - Binary Tree Right Side View.md.82de7b92.lean.js
@@ -0,0 +1 @@
+import{_ as s,o as a,c as n,a as l}from"./app.e4604e86.js";const d=JSON.parse('{"title":"199. Binary Tree Right Side View","description":"","frontmatter":{},"headers":[{"level":2,"title":"Problem Statement:","slug":"problem-statement","link":"#problem-statement","children":[{"level":3,"title":"Example 1:","slug":"example-1","link":"#example-1","children":[]},{"level":3,"title":"Example 2:","slug":"example-2","link":"#example-2","children":[]},{"level":3,"title":"Example 3:","slug":"example-3","link":"#example-3","children":[]},{"level":3,"title":"Constraints:","slug":"constraints","link":"#constraints","children":[]}]},{"level":2,"title":"Solution:","slug":"solution","link":"#solution","children":[{"level":3,"title":"...","slug":"","link":"#","children":[]}]}],"relativePath":"solution/0101-0200/199 - Binary Tree Right Side View.md","lastUpdated":1671291107000}'),e={name:"solution/0101-0200/199 - Binary Tree Right Side View.md"},p=l("",17),o=[p];function t(r,c,i,D,C,y){return a(),n("div",null,o)}const F=s(e,[["render",t]]);export{d as __pageData,F as default};
diff --git a/assets/solution_0101-0200_200 - Number of Islands.md.e951265d.js b/assets/solution_0101-0200_200 - Number of Islands.md.e951265d.js
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..75cbe17e
--- /dev/null
+++ b/assets/solution_0101-0200_200 - Number of Islands.md.e951265d.js
@@ -0,0 +1,59 @@
+import{_ as s,o as n,c as a,a as l}from"./app.e4604e86.js";const i=JSON.parse('{"title":"200. Number of Islands","description":"","frontmatter":{},"headers":[{"level":2,"title":"Problem Statement","slug":"problem-statement","link":"#problem-statement","children":[]},{"level":2,"title":"Solution:","slug":"solution","link":"#solution","children":[{"level":3,"title":"...","slug":"","link":"#","children":[]}]}],"relativePath":"solution/0101-0200/200 - Number of Islands.md","lastUpdated":1676656807000}'),o={name:"solution/0101-0200/200 - Number of Islands.md"},p=l(`
Given an m x n 2D binary grid grid which represents a map of '1's (land) and '0's (water), return the number of islands.
An island is surrounded by water and is formed by connecting adjacent lands horizontally or vertically. You may assume all four edges of the grid are all surrounded by water.
packagemain
+
+funcnumIslands(grid [][]byte)int{
+ result :=0
+
+for i :=0; i <len(grid); i++{
+for j :=0; j <len(grid[i]); j++{
+if grid[i][j]=='1'{
+dfs(grid, i, j)
+ result++
+}
+}
+}
+
+return result
+}
+
+funcdfs(grid [][]byte, row, col int){
+// return if it is out of bound horizontally
+if row <0|| row >=len(grid){
+return
+}
+
+// return if it is out of bound vertically
+if col <0|| col >=len(grid[row]){
+return
+}
+
+// return if it is not an island
+if grid[row][col]=='0'{
+return
+}
+
+// mark the current cell as visited
+ grid[row][col]='0'
+
+dfs(grid, row-1, col)
+dfs(grid, row+1, col)
+
+dfs(grid, row, col-1)
+dfs(grid, row, col+1)
+}
+
+
`,17),t=[p];function e(c,r,D,y,C,A){return n(),a("div",null,t)}const u=s(o,[["render",e]]);export{i as __pageData,u as default};
diff --git a/assets/solution_0101-0200_200 - Number of Islands.md.e951265d.lean.js b/assets/solution_0101-0200_200 - Number of Islands.md.e951265d.lean.js
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..17f6025b
--- /dev/null
+++ b/assets/solution_0101-0200_200 - Number of Islands.md.e951265d.lean.js
@@ -0,0 +1 @@
+import{_ as s,o as n,c as a,a as l}from"./app.e4604e86.js";const i=JSON.parse('{"title":"200. Number of Islands","description":"","frontmatter":{},"headers":[{"level":2,"title":"Problem Statement","slug":"problem-statement","link":"#problem-statement","children":[]},{"level":2,"title":"Solution:","slug":"solution","link":"#solution","children":[{"level":3,"title":"...","slug":"","link":"#","children":[]}]}],"relativePath":"solution/0101-0200/200 - Number of Islands.md","lastUpdated":1676656807000}'),o={name:"solution/0101-0200/200 - Number of Islands.md"},p=l("",17),t=[p];function e(c,r,D,y,C,A){return n(),a("div",null,t)}const u=s(o,[["render",e]]);export{i as __pageData,u as default};
diff --git a/assets/solution_0201-0300_202 - Happy Number.md.b9b908eb.js b/assets/solution_0201-0300_202 - Happy Number.md.b9b908eb.js
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..4f991603
--- /dev/null
+++ b/assets/solution_0201-0300_202 - Happy Number.md.b9b908eb.js
@@ -0,0 +1,43 @@
+import{_ as s,o as n,c as a,a as l}from"./app.e4604e86.js";const F=JSON.parse('{"title":"202. Happy Number","description":"","frontmatter":{},"headers":[{"level":2,"title":"Problem Statement","slug":"problem-statement","link":"#problem-statement","children":[]},{"level":2,"title":"Solution:","slug":"solution","link":"#solution","children":[{"level":3,"title":"...","slug":"","link":"#","children":[]}]}],"relativePath":"solution/0201-0300/202 - Happy Number.md","lastUpdated":1676656807000}'),p={name:"solution/0201-0300/202 - Happy Number.md"},o=l(`
Given two strings s and t, determine if they are isomorphic.
Two strings s and t are isomorphic if the characters in s can be replaced to get t.
All occurrences of a character must be replaced with another character while preserving the order of characters. No two characters may map to the same character, but a character may map to itself.
`,19),o=[p];function t(r,c,D,i,C,A){return a(),n("div",null,o)}const F=s(e,[["render",t]]);export{d as __pageData,F as default};
diff --git a/assets/solution_0201-0300_206 - Reverse Linked List.md.ab4ec40f.lean.js b/assets/solution_0201-0300_206 - Reverse Linked List.md.ab4ec40f.lean.js
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..23781da8
--- /dev/null
+++ b/assets/solution_0201-0300_206 - Reverse Linked List.md.ab4ec40f.lean.js
@@ -0,0 +1 @@
+import{_ as s,o as a,c as n,a as l}from"./app.e4604e86.js";const d=JSON.parse('{"title":"206. Reverse Linked List","description":"","frontmatter":{},"headers":[{"level":2,"title":"Problem Statement:","slug":"problem-statement","link":"#problem-statement","children":[{"level":3,"title":"Example 1:","slug":"example-1","link":"#example-1","children":[]},{"level":3,"title":"Example 2:","slug":"example-2","link":"#example-2","children":[]},{"level":3,"title":"Example 3:","slug":"example-3","link":"#example-3","children":[]},{"level":3,"title":"Constraints:","slug":"constraints","link":"#constraints","children":[]}]},{"level":2,"title":"Solution:","slug":"solution","link":"#solution","children":[{"level":3,"title":"...","slug":"","link":"#","children":[]}]}],"relativePath":"solution/0201-0300/206 - Reverse Linked List.md","lastUpdated":1671291107000}'),e={name:"solution/0201-0300/206 - Reverse Linked List.md"},p=l("",19),o=[p];function t(r,c,D,i,C,A){return a(),n("div",null,o)}const F=s(e,[["render",t]]);export{d as __pageData,F as default};
diff --git a/assets/solution_0201-0300_211 - Design Add and Search Words Data Structure.md.c4db6b8f.js b/assets/solution_0201-0300_211 - Design Add and Search Words Data Structure.md.c4db6b8f.js
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..a9fbc9cd
--- /dev/null
+++ b/assets/solution_0201-0300_211 - Design Add and Search Words Data Structure.md.c4db6b8f.js
@@ -0,0 +1,70 @@
+import{_ as s,o as a,c as n,a as o}from"./app.e4604e86.js";const d=JSON.parse('{"title":"211. Design Add and Search Words Data Structure","description":"","frontmatter":{},"headers":[{"level":2,"title":"Problem Statement","slug":"problem-statement","link":"#problem-statement","children":[]},{"level":2,"title":"Solution:","slug":"solution","link":"#solution","children":[{"level":3,"title":"...","slug":"","link":"#","children":[]}]}],"relativePath":"solution/0201-0300/211 - Design Add and Search Words Data Structure.md","lastUpdated":1680513503000}'),l={name:"solution/0201-0300/211 - Design Add and Search Words Data Structure.md"},p=o(`
Design a data structure that supports adding new words and finding if a string matches any previously added string.
Implement the WordDictionary class:
WordDictionary() Initializes the object.
void addWord(word) Adds word to the data structure, it can be matched later.
bool search(word) Returns true if there is any string in the data structure that matches word or false otherwise. word may contain dots '.' where dots can be matched with any letter.
`,17),e=[p];function t(r,c,D,i,y,C){return a(),n("div",null,e)}const F=s(l,[["render",t]]);export{d as __pageData,F as default};
diff --git a/assets/solution_0201-0300_211 - Design Add and Search Words Data Structure.md.c4db6b8f.lean.js b/assets/solution_0201-0300_211 - Design Add and Search Words Data Structure.md.c4db6b8f.lean.js
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..d708c6ca
--- /dev/null
+++ b/assets/solution_0201-0300_211 - Design Add and Search Words Data Structure.md.c4db6b8f.lean.js
@@ -0,0 +1 @@
+import{_ as s,o as a,c as n,a as o}from"./app.e4604e86.js";const d=JSON.parse('{"title":"211. Design Add and Search Words Data Structure","description":"","frontmatter":{},"headers":[{"level":2,"title":"Problem Statement","slug":"problem-statement","link":"#problem-statement","children":[]},{"level":2,"title":"Solution:","slug":"solution","link":"#solution","children":[{"level":3,"title":"...","slug":"","link":"#","children":[]}]}],"relativePath":"solution/0201-0300/211 - Design Add and Search Words Data Structure.md","lastUpdated":1680513503000}'),l={name:"solution/0201-0300/211 - Design Add and Search Words Data Structure.md"},p=o("",17),e=[p];function t(r,c,D,i,y,C){return a(),n("div",null,e)}const F=s(l,[["render",t]]);export{d as __pageData,F as default};
diff --git a/assets/solution_0201-0300_217 - Contains Duplicate.md.b212f1d3.js b/assets/solution_0201-0300_217 - Contains Duplicate.md.b212f1d3.js
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..4669b2db
--- /dev/null
+++ b/assets/solution_0201-0300_217 - Contains Duplicate.md.b212f1d3.js
@@ -0,0 +1,23 @@
+import{_ as s,o as a,c as n,a as l}from"./app.e4604e86.js";const d=JSON.parse('{"title":"217. Contains Duplicate","description":"","frontmatter":{},"headers":[{"level":2,"title":"Problem Statement","slug":"problem-statement","link":"#problem-statement","children":[]},{"level":2,"title":"Solution:","slug":"solution","link":"#solution","children":[{"level":3,"title":"...","slug":"","link":"#","children":[]}]}],"relativePath":"solution/0201-0300/217 - Contains Duplicate.md","lastUpdated":1676682664000}'),p={name:"solution/0201-0300/217 - Contains Duplicate.md"},e=l(`
Given an integer array nums and an integer k, return trueif there are two distinct indicesi and j in the array such that nums[i] == nums[j] and abs(i - j) <= k.
Example 1:
Input: nums = [1,2,3,1], k = 3
+Output: true
+
Example 2:
Input: nums = [1,0,1,1], k = 1
+Output: true
+
Example 3:
Input: nums = [1,2,3,1,2,3], k = 2
+Output: false
+
packagemain
+
+funccontainsNearbyDuplicate(nums []int, k int)bool{
+iflen(nums)<=1{
+returnfalse
+}
+
+ set :=make(map[int]int)
+
+// iterate over the array
+for i, v :=range nums {
+// check if the value is in the set
+if _, ok := set[v]; ok {
+// if the value is in the set,
+// check if the difference between the current index and the index of the value in the set
+// is less than or equal to k
+if i-set[v]<= k {
+returntrue
+}
+}
+// add the value to the set
+ set[v]= i
+}
+
+returnfalse
+}
+
+
Given the root of a complete binary tree, return the number of the nodes in the tree.
According to Wikipedia, every level, except possibly the last, is completely filled in a complete binary tree, and all nodes in the last level are as far left as possible. It can have between 1 and 2h nodes inclusive at the last level h.
Design an algorithm that runs in less than O(n) time complexity.
`,18),p=[o];function t(r,c,i,D,C,y){return a(),n("div",null,p)}const d=s(e,[["render",t]]);export{F as __pageData,d as default};
diff --git a/assets/solution_0201-0300_222 - Count Complete Tree Nodes.md.6017f601.lean.js b/assets/solution_0201-0300_222 - Count Complete Tree Nodes.md.6017f601.lean.js
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..b4fbb6d1
--- /dev/null
+++ b/assets/solution_0201-0300_222 - Count Complete Tree Nodes.md.6017f601.lean.js
@@ -0,0 +1 @@
+import{_ as s,o as a,c as n,a as l}from"./app.e4604e86.js";const F=JSON.parse('{"title":"222. Count Complete Tree Nodes","description":"","frontmatter":{},"headers":[{"level":2,"title":"Problem Statement:","slug":"problem-statement","link":"#problem-statement","children":[{"level":3,"title":"Example 1:","slug":"example-1","link":"#example-1","children":[]},{"level":3,"title":"Example 2:","slug":"example-2","link":"#example-2","children":[]},{"level":3,"title":"Example 3:","slug":"example-3","link":"#example-3","children":[]},{"level":3,"title":"Constraints:","slug":"constraints","link":"#constraints","children":[]}]},{"level":2,"title":"Solution:","slug":"solution","link":"#solution","children":[{"level":3,"title":"...","slug":"","link":"#","children":[]}]}],"relativePath":"solution/0201-0300/222 - Count Complete Tree Nodes.md","lastUpdated":1671291107000}'),e={name:"solution/0201-0300/222 - Count Complete Tree Nodes.md"},o=l("",18),p=[o];function t(r,c,i,D,C,y){return a(),n("div",null,p)}const d=s(e,[["render",t]]);export{F as __pageData,d as default};
diff --git a/assets/solution_0201-0300_225 - Implement Stack using Queues.md.02261001.js b/assets/solution_0201-0300_225 - Implement Stack using Queues.md.02261001.js
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..4bd420e3
--- /dev/null
+++ b/assets/solution_0201-0300_225 - Implement Stack using Queues.md.02261001.js
@@ -0,0 +1,53 @@
+import{_ as s,o as n,c as a,a as l}from"./app.e4604e86.js";const i=JSON.parse('{"title":"225. Implement Stack using Queues","description":"","frontmatter":{},"headers":[{"level":2,"title":"Problem Statement","slug":"problem-statement","link":"#problem-statement","children":[]},{"level":2,"title":"Solution:","slug":"solution","link":"#solution","children":[{"level":3,"title":"...","slug":"","link":"#","children":[]}]}],"relativePath":"solution/0201-0300/225 - Implement Stack using Queues.md","lastUpdated":1676769240000}'),p={name:"solution/0201-0300/225 - Implement Stack using Queues.md"},o=l(`
Implement a last-in-first-out (LIFO) stack using only two queues. The implemented stack should support all the functions of a normal stack (push, top, pop, and empty).
Implement the MyStack class:
void push(int x) Pushes element x to the top of the stack.
int pop() Removes the element on the top of the stack and returns it.
int top() Returns the element on the top of the stack.
boolean empty() Returns true if the stack is empty, false otherwise.
Notes:
You must use only standard operations of a queue, which means that only push to back, peek/pop from front, size and is empty operations are valid.
Depending on your language, the queue may not be supported natively. You may simulate a queue using a list or deque (double-ended queue) as long as you use only a queue's standard operations.
A range[a,b] is the set of all integers from a to b (inclusive).
Return the smallest sorted list of ranges that cover all the numbers in the array exactly. That is, each element of nums is covered by exactly one of the ranges, and there is no integer x such that x is in one of the ranges but not in nums.
`,20),e=[o];function t(c,r,D,y,C,F){return n(),a("div",null,e)}const u=s(p,[["render",t]]);export{i as __pageData,u as default};
diff --git a/assets/solution_0201-0300_228 - Summary Ranges.md.d08299a4.lean.js b/assets/solution_0201-0300_228 - Summary Ranges.md.d08299a4.lean.js
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..1cb2bc7f
--- /dev/null
+++ b/assets/solution_0201-0300_228 - Summary Ranges.md.d08299a4.lean.js
@@ -0,0 +1 @@
+import{_ as s,o as n,c as a,a as l}from"./app.e4604e86.js";const i=JSON.parse('{"title":"228. Summary Ranges","description":"","frontmatter":{},"headers":[{"level":2,"title":"Problem Statement","slug":"problem-statement","link":"#problem-statement","children":[]},{"level":2,"title":"Solution:","slug":"solution","link":"#solution","children":[{"level":3,"title":"...","slug":"","link":"#","children":[]}]}],"relativePath":"solution/0201-0300/228 - Summary Ranges.md","lastUpdated":1676855631000}'),p={name:"solution/0201-0300/228 - Summary Ranges.md"},o=l("",20),e=[o];function t(c,r,D,y,C,F){return n(),a("div",null,e)}const u=s(p,[["render",t]]);export{i as __pageData,u as default};
diff --git a/assets/solution_0201-0300_230 - Kth Smallest Element in a BST.md.e2a247db.js b/assets/solution_0201-0300_230 - Kth Smallest Element in a BST.md.e2a247db.js
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..22593426
--- /dev/null
+++ b/assets/solution_0201-0300_230 - Kth Smallest Element in a BST.md.e2a247db.js
@@ -0,0 +1,27 @@
+import{_ as s,o as a,c as n,a as l}from"./app.e4604e86.js";const F=JSON.parse('{"title":"230. Kth Smallest Element in a BST","description":"","frontmatter":{},"headers":[{"level":2,"title":"Problem Statement:","slug":"problem-statement","link":"#problem-statement","children":[{"level":3,"title":"Example 1:","slug":"example-1","link":"#example-1","children":[]},{"level":3,"title":"Example 2:","slug":"example-2","link":"#example-2","children":[]},{"level":3,"title":"Constraints:","slug":"constraints","link":"#constraints","children":[]}]},{"level":2,"title":"Solution:","slug":"solution","link":"#solution","children":[{"level":3,"title":"...","slug":"","link":"#","children":[]}]}],"relativePath":"solution/0201-0300/230 - Kth Smallest Element in a BST.md","lastUpdated":1671291107000}'),e={name:"solution/0201-0300/230 - Kth Smallest Element in a BST.md"},o=l(`
Follow up: If the BST is modified often (i.e., we can do insert and delete operations) and you need to find the kth smallest frequently, how would you optimize?
`,16),p=[o];function t(r,c,D,i,C,y){return a(),n("div",null,p)}const d=s(e,[["render",t]]);export{F as __pageData,d as default};
diff --git a/assets/solution_0201-0300_230 - Kth Smallest Element in a BST.md.e2a247db.lean.js b/assets/solution_0201-0300_230 - Kth Smallest Element in a BST.md.e2a247db.lean.js
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..74f61b11
--- /dev/null
+++ b/assets/solution_0201-0300_230 - Kth Smallest Element in a BST.md.e2a247db.lean.js
@@ -0,0 +1 @@
+import{_ as s,o as a,c as n,a as l}from"./app.e4604e86.js";const F=JSON.parse('{"title":"230. Kth Smallest Element in a BST","description":"","frontmatter":{},"headers":[{"level":2,"title":"Problem Statement:","slug":"problem-statement","link":"#problem-statement","children":[{"level":3,"title":"Example 1:","slug":"example-1","link":"#example-1","children":[]},{"level":3,"title":"Example 2:","slug":"example-2","link":"#example-2","children":[]},{"level":3,"title":"Constraints:","slug":"constraints","link":"#constraints","children":[]}]},{"level":2,"title":"Solution:","slug":"solution","link":"#solution","children":[{"level":3,"title":"...","slug":"","link":"#","children":[]}]}],"relativePath":"solution/0201-0300/230 - Kth Smallest Element in a BST.md","lastUpdated":1671291107000}'),e={name:"solution/0201-0300/230 - Kth Smallest Element in a BST.md"},o=l("",16),p=[o];function t(r,c,D,i,C,y){return a(),n("div",null,p)}const d=s(e,[["render",t]]);export{F as __pageData,d as default};
diff --git a/assets/solution_0201-0300_231 - Power of Two.md.30383506.js b/assets/solution_0201-0300_231 - Power of Two.md.30383506.js
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..3066ec8c
--- /dev/null
+++ b/assets/solution_0201-0300_231 - Power of Two.md.30383506.js
@@ -0,0 +1,16 @@
+import{_ as s,o as a,c as n,a as e}from"./app.e4604e86.js";const A=JSON.parse('{"title":"231. Power of Two","description":"","frontmatter":{},"headers":[{"level":2,"title":"Problem Statement:","slug":"problem-statement","link":"#problem-statement","children":[{"level":3,"title":"Example 1:","slug":"example-1","link":"#example-1","children":[]},{"level":3,"title":"Example 2:","slug":"example-2","link":"#example-2","children":[]},{"level":3,"title":"Example 3:","slug":"example-3","link":"#example-3","children":[]},{"level":3,"title":"Constraints:","slug":"constraints","link":"#constraints","children":[]}]},{"level":2,"title":"Solution:","slug":"solution","link":"#solution","children":[{"level":3,"title":"...","slug":"","link":"#","children":[]}]}],"relativePath":"solution/0201-0300/231 - Power of Two.md","lastUpdated":1671291107000}'),l={name:"solution/0201-0300/231 - Power of Two.md"},o=e(`
`,18),p=[o];function t(r,c,i,d,C,u){return a(),n("div",null,p)}const D=s(l,[["render",t]]);export{A as __pageData,D as default};
diff --git a/assets/solution_0201-0300_231 - Power of Two.md.30383506.lean.js b/assets/solution_0201-0300_231 - Power of Two.md.30383506.lean.js
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..70b24c99
--- /dev/null
+++ b/assets/solution_0201-0300_231 - Power of Two.md.30383506.lean.js
@@ -0,0 +1 @@
+import{_ as s,o as a,c as n,a as e}from"./app.e4604e86.js";const A=JSON.parse('{"title":"231. Power of Two","description":"","frontmatter":{},"headers":[{"level":2,"title":"Problem Statement:","slug":"problem-statement","link":"#problem-statement","children":[{"level":3,"title":"Example 1:","slug":"example-1","link":"#example-1","children":[]},{"level":3,"title":"Example 2:","slug":"example-2","link":"#example-2","children":[]},{"level":3,"title":"Example 3:","slug":"example-3","link":"#example-3","children":[]},{"level":3,"title":"Constraints:","slug":"constraints","link":"#constraints","children":[]}]},{"level":2,"title":"Solution:","slug":"solution","link":"#solution","children":[{"level":3,"title":"...","slug":"","link":"#","children":[]}]}],"relativePath":"solution/0201-0300/231 - Power of Two.md","lastUpdated":1671291107000}'),l={name:"solution/0201-0300/231 - Power of Two.md"},o=e("",18),p=[o];function t(r,c,i,d,C,u){return a(),n("div",null,p)}const D=s(l,[["render",t]]);export{A as __pageData,D as default};
diff --git a/assets/solution_0201-0300_232 - Implement Queue using Stacks.md.06884d6c.js b/assets/solution_0201-0300_232 - Implement Queue using Stacks.md.06884d6c.js
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..8e0f7e33
--- /dev/null
+++ b/assets/solution_0201-0300_232 - Implement Queue using Stacks.md.06884d6c.js
@@ -0,0 +1,53 @@
+import{_ as s,o as n,c as a,a as e}from"./app.e4604e86.js";const u=JSON.parse('{"title":"232. Implement Queue using Stacks","description":"","frontmatter":{},"headers":[{"level":2,"title":"Problem Statement","slug":"problem-statement","link":"#problem-statement","children":[]},{"level":2,"title":"Solution:","slug":"solution","link":"#solution","children":[{"level":3,"title":"...","slug":"","link":"#","children":[]}]}],"relativePath":"solution/0201-0300/232 - Implement Queue using Stacks.md","lastUpdated":1676769240000}'),l={name:"solution/0201-0300/232 - Implement Queue using Stacks.md"},p=e(`
Implement a first in first out (FIFO) queue using only two stacks. The implemented queue should support all the functions of a normal queue (push, peek, pop, and empty).
Implement the MyQueue class:
void push(int x) Pushes element x to the back of the queue.
int pop() Removes the element from the front of the queue and returns it.
int peek() Returns the element at the front of the queue.
boolean empty() Returns true if the queue is empty, false otherwise.
Notes:
You must use only standard operations of a stack, which means only push to top, peek/pop from top, size, and is empty operations are valid.
Depending on your language, the stack may not be supported natively. You may simulate a stack using a list or deque (double-ended queue) as long as you use only a stack's standard operations.
Example 1:
Input
+["MyQueue", "push", "push", "peek", "pop", "empty"]
+[[], [1], [2], [], [], []]
+Output
+[null, null, null, 1, 1, false]
+
+Explanation
+MyQueue myQueue = new MyQueue();
+myQueue.push(1); // queue is: [1]
+myQueue.push(2); // queue is: [1, 2] (leftmost is front of the queue)
+myQueue.peek(); // return 1
+myQueue.pop(); // return 1, queue is [2]
+myQueue.empty(); // return false
+
Constraints:
1 <= x <= 9
At most 100 calls will be made to push, pop, peek, and empty.
All the calls to pop and peek are valid.
Follow-up: Can you implement the queue such that each operation is amortizedO(1) time complexity? In other words, performing n operations will take overall O(n) time even if one of those operations may take longer.
packagemain
+
+typeMyQueuestruct{
+ stack []int
+}
+
+funcConstructor() MyQueue {
+return MyQueue{}
+}
+
+// Push element x to the back of queue.
+func(this *MyQueue)Push(x int){
+ this.stack =append(this.stack, x)
+}
+
+// Removes and returns the element at the front of queue.
+func(this *MyQueue)Pop()int{
+iflen(this.stack)==0{
+return0
+}
+ pop := this.stack[0]
+ this.stack = this.stack[1:]
+return pop
+}
+
+// Get the front element.
+func(this *MyQueue)Peek()int{
+iflen(this.stack)==0{
+return0
+}
+return this.stack[0]
+}
+
+// Return whether the queue is empty.
+func(this *MyQueue)Empty()bool{
+returnlen(this.stack)==0
+}
+
+
`,4);function i(C,A,y,F,d,h){return p(),e("div",null,[t,s(" Could you do it in "),c,s(" time and "),r,s(" space? "),D])}const _=l(o,[["render",i]]);export{m as __pageData,_ as default};
diff --git a/assets/solution_0201-0300_234 - Palindrome Linked List.md.cb51ca4c.lean.js b/assets/solution_0201-0300_234 - Palindrome Linked List.md.cb51ca4c.lean.js
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..1e93107c
--- /dev/null
+++ b/assets/solution_0201-0300_234 - Palindrome Linked List.md.cb51ca4c.lean.js
@@ -0,0 +1 @@
+import{_ as l,o as p,c as e,f as s,a,b as n}from"./app.e4604e86.js";const m=JSON.parse('{"title":"234. Palindrome Linked List","description":"","frontmatter":{},"headers":[{"level":2,"title":"Problem Statement","slug":"problem-statement","link":"#problem-statement","children":[]},{"level":2,"title":"Solution:","slug":"solution","link":"#solution","children":[{"level":3,"title":"...","slug":"","link":"#","children":[]}]}],"relativePath":"solution/0201-0300/234 - Palindrome Linked List.md","lastUpdated":1676855631000}'),o={name:"solution/0201-0300/234 - Palindrome Linked List.md"},t=a("",16),c=n("code",null,"O(n)",-1),r=n("code",null,"O(1)",-1),D=a("",4);function i(C,A,y,F,d,h){return p(),e("div",null,[t,s(" Could you do it in "),c,s(" time and "),r,s(" space? "),D])}const _=l(o,[["render",i]]);export{m as __pageData,_ as default};
diff --git a/assets/solution_0201-0300_236 - Lowest Common Ancestor of a Binary Tree.md.ba62af67.js b/assets/solution_0201-0300_236 - Lowest Common Ancestor of a Binary Tree.md.ba62af67.js
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..008997cb
--- /dev/null
+++ b/assets/solution_0201-0300_236 - Lowest Common Ancestor of a Binary Tree.md.ba62af67.js
@@ -0,0 +1,36 @@
+import{_ as s,o as n,c as a,a as o}from"./app.e4604e86.js";const d=JSON.parse('{"title":"236. Lowest Common Ancestor of a Binary Tree","description":"","frontmatter":{},"headers":[{"level":2,"title":"Problem Statement","slug":"problem-statement","link":"#problem-statement","children":[]},{"level":2,"title":"Solution:","slug":"solution","link":"#solution","children":[{"level":3,"title":"...","slug":"","link":"#","children":[]}]}],"relativePath":"solution/0201-0300/236 - Lowest Common Ancestor of a Binary Tree.md","lastUpdated":1676656807000}'),l={name:"solution/0201-0300/236 - Lowest Common Ancestor of a Binary Tree.md"},e=o(`
Given a binary tree, find the lowest common ancestor (LCA) of two given nodes in the tree.
According to the definition of LCA on Wikipedia: “The lowest common ancestor is defined between two nodes p and q as the lowest node in T that has both p and q as descendants (where we allow a node to be a descendant of itself).”
Example 1:
Input: root = [3,5,1,6,2,0,8,null,null,7,4], p = 5, q = 1
+Output: 3
+Explanation: The LCA of nodes 5 and 1 is 3.
+
Example 2:
Input: root = [3,5,1,6,2,0,8,null,null,7,4], p = 5, q = 4
+Output: 5
+Explanation: The LCA of nodes 5 and 4 is 5, since a node can be a descendant of itself according to the LCA definition.
+
Example 3:
Input: root = [1,2], p = 1, q = 2
+Output: 1
+
Constraints:
The number of nodes in the tree is in the range [2, 105].
packagemain
+
+// Definition for a binary tree node.
+typeTreeNodestruct{
+ Val int
+ Left *TreeNode
+ Right *TreeNode
+}
+
+funclowestCommonAncestor(root, p, q *TreeNode)*TreeNode {
+if root ==nil|| root == p || root == q {
+return root
+}
+
+ left :=lowestCommonAncestor(root.Left, p, q)
+ right :=lowestCommonAncestor(root.Right, p, q)
+
+if left ==nil{
+return right
+}elseif right ==nil{
+return left
+}else{
+return root
+}
+}
+
+
`,21),p=[e];function t(c,r,i,D,C,A){return n(),a("div",null,p)}const F=s(l,[["render",t]]);export{d as __pageData,F as default};
diff --git a/assets/solution_0201-0300_236 - Lowest Common Ancestor of a Binary Tree.md.ba62af67.lean.js b/assets/solution_0201-0300_236 - Lowest Common Ancestor of a Binary Tree.md.ba62af67.lean.js
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..bed8f839
--- /dev/null
+++ b/assets/solution_0201-0300_236 - Lowest Common Ancestor of a Binary Tree.md.ba62af67.lean.js
@@ -0,0 +1 @@
+import{_ as s,o as n,c as a,a as o}from"./app.e4604e86.js";const d=JSON.parse('{"title":"236. Lowest Common Ancestor of a Binary Tree","description":"","frontmatter":{},"headers":[{"level":2,"title":"Problem Statement","slug":"problem-statement","link":"#problem-statement","children":[]},{"level":2,"title":"Solution:","slug":"solution","link":"#solution","children":[{"level":3,"title":"...","slug":"","link":"#","children":[]}]}],"relativePath":"solution/0201-0300/236 - Lowest Common Ancestor of a Binary Tree.md","lastUpdated":1676656807000}'),l={name:"solution/0201-0300/236 - Lowest Common Ancestor of a Binary Tree.md"},e=o("",21),p=[e];function t(c,r,i,D,C,A){return n(),a("div",null,p)}const F=s(l,[["render",t]]);export{d as __pageData,F as default};
diff --git a/assets/solution_0201-0300_242 - Valid Anagram.md.1cd985ae.js b/assets/solution_0201-0300_242 - Valid Anagram.md.1cd985ae.js
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..a370acdc
--- /dev/null
+++ b/assets/solution_0201-0300_242 - Valid Anagram.md.1cd985ae.js
@@ -0,0 +1,111 @@
+import{_ as s,o as n,c as a,a as l}from"./app.e4604e86.js";const i=JSON.parse('{"title":"242. Valid Anagram","description":"","frontmatter":{},"headers":[{"level":2,"title":"Problem Statement","slug":"problem-statement","link":"#problem-statement","children":[]},{"level":2,"title":"Solution:","slug":"solution","link":"#solution","children":[{"level":3,"title":"...","slug":"","link":"#","children":[]}]}],"relativePath":"solution/0201-0300/242 - Valid Anagram.md","lastUpdated":1689264763000}'),p={name:"solution/0201-0300/242 - Valid Anagram.md"},o=l(`
implSolution{
+pubfnadd_digits(num:i32)->i32{
+letmut num = num;
+
+ // loop while the number is greater than 9
+while num >9{
+letmut sum =0;
+ // loop while the number is greater than 0,
+ // add the last digit to the sum,
+ // and divide the number by 10
+while num >0{
+ sum += num %10;
+ num /=10;
+}
+ // set the number to the sum
+ num = sum;
+}
+
+ num
+}
+}
+
+
implSolution{
+pubfnis_ugly(n:i32)->bool{
+if n <1{
+returnfalse;
+}
+
+let divisors =[2,3,5];
+letmut n = n;
+
+for divisor in divisors {
+ // Divide n by divisor as many times as possible
+while n % divisor ==0{
+ n /= divisor;
+}
+}
+
+ n ==1
+}
+}
+
+
Given an array nums containing n distinct numbers in the range [0, n], return the only number in the range that is missing from the array.
Example 1:
Input: nums = [3,0,1]
+Output: 2
+Explanation: n = 3 since there are 3 numbers, so all numbers are in the range [0,3]. 2 is the missing number in the range since it does not appear in nums.
+
Example 2:
Input: nums = [0,1]
+Output: 2
+Explanation: n = 2 since there are 2 numbers, so all numbers are in the range [0,2]. 2 is the missing number in the range since it does not appear in nums.
+
Example 3:
Input: nums = [9,6,4,2,3,5,7,0,1]
+Output: 8
+Explanation: n = 9 since there are 9 numbers, so all numbers are in the range [0,9]. 8 is the missing number in the range since it does not appear in nums.
+
Constraints:
n == nums.length
1 <= n <= 104
0 <= nums[i] <= n
All the numbers of nums are unique.
Follow up: Could you implement a solution using only O(1) extra space complexity and O(n) runtime complexity?
implSolution{
+pubfnmissing_number(nums:Vec<i32>)->i32{
+let len = nums.len();
+letmut sum = len *(len +1)/2;
+
+for num in nums {
+ sum -= num asusize;
+}
+
+ sum asi32
+}
+}
+
+
`,20),o=[p];function t(r,c,i,C,y,u){return n(),a("div",null,o)}const D=s(e,[["render",t]]);export{A as __pageData,D as default};
diff --git a/assets/solution_0201-0300_268 - Missing Number.md.bcd71582.lean.js b/assets/solution_0201-0300_268 - Missing Number.md.bcd71582.lean.js
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..586f1a63
--- /dev/null
+++ b/assets/solution_0201-0300_268 - Missing Number.md.bcd71582.lean.js
@@ -0,0 +1 @@
+import{_ as s,o as n,c as a,a as l}from"./app.e4604e86.js";const A=JSON.parse('{"title":"268. Missing Number","description":"","frontmatter":{},"headers":[{"level":2,"title":"Problem Statement","slug":"problem-statement","link":"#problem-statement","children":[]},{"level":2,"title":"Solution:","slug":"solution","link":"#solution","children":[{"level":3,"title":"...","slug":"","link":"#","children":[]}]}],"relativePath":"solution/0201-0300/268 - Missing Number.md","lastUpdated":1677028205000}'),e={name:"solution/0201-0300/268 - Missing Number.md"},p=l("",20),o=[p];function t(r,c,i,C,y,u){return n(),a("div",null,o)}const D=s(e,[["render",t]]);export{A as __pageData,D as default};
diff --git a/assets/solution_0201-0300_278 - First Bad Version.md.0ff223ca.js b/assets/solution_0201-0300_278 - First Bad Version.md.0ff223ca.js
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..60e5395a
--- /dev/null
+++ b/assets/solution_0201-0300_278 - First Bad Version.md.0ff223ca.js
@@ -0,0 +1,48 @@
+import{_ as s,o as a,c as n,a as l}from"./app.e4604e86.js";const F=JSON.parse('{"title":"278. First Bad Version","description":"","frontmatter":{},"headers":[{"level":2,"title":"Problem Statement:","slug":"problem-statement","link":"#problem-statement","children":[{"level":3,"title":"Example 1:","slug":"example-1","link":"#example-1","children":[]},{"level":3,"title":"Example 2:","slug":"example-2","link":"#example-2","children":[]},{"level":3,"title":"Constraints:","slug":"constraints","link":"#constraints","children":[]}]},{"level":2,"title":"Solution:","slug":"solution","link":"#solution","children":[{"level":3,"title":"...","slug":"","link":"#","children":[]}]}],"relativePath":"solution/0201-0300/278 - First Bad Version.md","lastUpdated":1689264763000}'),p={name:"solution/0201-0300/278 - First Bad Version.md"},o=l(`
You are a product manager and currently leading a team to develop a new product. Unfortunately, the latest version of your product fails the quality check. Since each version is developed based on the previous version, all the versions after a bad version are also bad.
Suppose you have n versions [1, 2, ..., n] and you want to find out the first bad one, which causes all the following ones to be bad.
You are given an API bool isBadVersion(version) which returns whether version is bad. Implement a function to find the first bad version. You should minimize the number of calls to the API.
`,16),e=[o];function t(r,c,D,C,i,A){return a(),n("div",null,e)}const d=s(p,[["render",t]]);export{F as __pageData,d as default};
diff --git a/assets/solution_0201-0300_278 - First Bad Version.md.0ff223ca.lean.js b/assets/solution_0201-0300_278 - First Bad Version.md.0ff223ca.lean.js
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..b05aff3c
--- /dev/null
+++ b/assets/solution_0201-0300_278 - First Bad Version.md.0ff223ca.lean.js
@@ -0,0 +1 @@
+import{_ as s,o as a,c as n,a as l}from"./app.e4604e86.js";const F=JSON.parse('{"title":"278. First Bad Version","description":"","frontmatter":{},"headers":[{"level":2,"title":"Problem Statement:","slug":"problem-statement","link":"#problem-statement","children":[{"level":3,"title":"Example 1:","slug":"example-1","link":"#example-1","children":[]},{"level":3,"title":"Example 2:","slug":"example-2","link":"#example-2","children":[]},{"level":3,"title":"Constraints:","slug":"constraints","link":"#constraints","children":[]}]},{"level":2,"title":"Solution:","slug":"solution","link":"#solution","children":[{"level":3,"title":"...","slug":"","link":"#","children":[]}]}],"relativePath":"solution/0201-0300/278 - First Bad Version.md","lastUpdated":1689264763000}'),p={name:"solution/0201-0300/278 - First Bad Version.md"},o=l("",16),e=[o];function t(r,c,D,C,i,A){return a(),n("div",null,e)}const d=s(p,[["render",t]]);export{F as __pageData,d as default};
diff --git a/assets/solution_0201-0300_279 - Perfect Squares.md.ca4aeddd.js b/assets/solution_0201-0300_279 - Perfect Squares.md.ca4aeddd.js
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..3be35b9a
--- /dev/null
+++ b/assets/solution_0201-0300_279 - Perfect Squares.md.ca4aeddd.js
@@ -0,0 +1,30 @@
+import{_ as s,o as a,c as n,a as l}from"./app.e4604e86.js";const F=JSON.parse('{"title":"279. Perfect Squares","description":"","frontmatter":{},"headers":[{"level":2,"title":"Problem Statement","slug":"problem-statement","link":"#problem-statement","children":[]},{"level":2,"title":"Solution:","slug":"solution","link":"#solution","children":[{"level":3,"title":"...","slug":"","link":"#","children":[]}]}],"relativePath":"solution/0201-0300/279 - Perfect Squares.md","lastUpdated":1688403179000}'),p={name:"solution/0201-0300/279 - Perfect Squares.md"},o=l(`
Given an integer n, return the least number of perfect square numbers that sum ton.
A perfect square is an integer that is the square of an integer; in other words, it is the product of some integer with itself. For example, 1, 4, 9, and 16 are perfect squares while 3 and 11 are not.
use std::cmp::min;
+
+implSolution{
+pubfnnum_squares(n:i32)->i32{
+ // make a dp array of size n + 1 and filled with 0
+letmut dp =vec![n; n asusize+1];
+
+ // set the first element to 0
+ dp[0]=0;
+
+ // iterate from 1 to n
+for i in1..=n asusize{
+ // iterate from 1 to sqrt(i)
+for j in1..=(i asf64).sqrt()asusize{
+ // set dp[i] to the minimum of dp[i] and dp[i - j * j] + 1
+ dp[i]=min(dp[i], dp[i - j * j]+1);
+}
+}
+
+ dp[n asusize]
+}
+}
+
`,16),e=[o];function t(c,r,D,C,y,A){return a(),n("div",null,e)}const d=s(p,[["render",t]]);export{F as __pageData,d as default};
diff --git a/assets/solution_0201-0300_283 - Move Zeroes.md.0f076f12.lean.js b/assets/solution_0201-0300_283 - Move Zeroes.md.0f076f12.lean.js
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..bba30b01
--- /dev/null
+++ b/assets/solution_0201-0300_283 - Move Zeroes.md.0f076f12.lean.js
@@ -0,0 +1 @@
+import{_ as s,o as a,c as n,a as l}from"./app.e4604e86.js";const F=JSON.parse('{"title":"283. Move Zeroes","description":"","frontmatter":{},"headers":[{"level":2,"title":"Problem Statement:","slug":"problem-statement","link":"#problem-statement","children":[{"level":3,"title":"Example 1:","slug":"example-1","link":"#example-1","children":[]},{"level":3,"title":"Example 2:","slug":"example-2","link":"#example-2","children":[]},{"level":3,"title":"Constraints:","slug":"constraints","link":"#constraints","children":[]}]},{"level":2,"title":"Solution:","slug":"solution","link":"#solution","children":[{"level":3,"title":"...","slug":"","link":"#","children":[]}]}],"relativePath":"solution/0201-0300/283 - Move Zeroes.md","lastUpdated":1689264763000}'),p={name:"solution/0201-0300/283 - Move Zeroes.md"},o=l("",16),e=[o];function t(c,r,D,C,y,A){return a(),n("div",null,e)}const d=s(p,[["render",t]]);export{F as __pageData,d as default};
diff --git a/assets/solution_0201-0300_290 - Word Pattern.md.be428cac.js b/assets/solution_0201-0300_290 - Word Pattern.md.be428cac.js
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..bea57f79
--- /dev/null
+++ b/assets/solution_0201-0300_290 - Word Pattern.md.be428cac.js
@@ -0,0 +1,45 @@
+import{_ as s,o as a,c as n,a as l}from"./app.e4604e86.js";const F=JSON.parse('{"title":"290. Word Pattern","description":"","frontmatter":{},"headers":[{"level":2,"title":"Problem Statement","slug":"problem-statement","link":"#problem-statement","children":[]},{"level":2,"title":"Solution:","slug":"solution","link":"#solution","children":[{"level":3,"title":"...","slug":"","link":"#","children":[]}]}],"relativePath":"solution/0201-0300/290 - Word Pattern.md","lastUpdated":1677028205000}'),p={name:"solution/0201-0300/290 - Word Pattern.md"},o=l(`
packagemain
+
+import"strings"
+
+funcwordPattern(pattern string, s string)bool{
+ words := strings.Split(s,"")
+
+iflen(pattern)!=len(words){
+returnfalse
+}
+
+ map_ :=make(map[byte]string)
+
+// loop through the pattern and process each character
+for i :=0; i <len(pattern); i++{
+// if the word is already in the map, check if it matches the pattern
+if val, ok := map_[pattern[i]]; ok {
+if val != words[i]{
+returnfalse
+}
+}else{
+// loop through the map to check if map contains the word
+for _, v :=range map_ {
+// if the word is in the map, return false
+if v == words[i]{
+returnfalse
+}
+}
+
+// if the word is not in the map, add it
+ map_[pattern[i]]= words[i]
+}
+}
+
+returntrue
+}
+
+
`,19),t=[o];function e(c,r,D,y,i,C){return a(),n("div",null,t)}const d=s(p,[["render",e]]);export{F as __pageData,d as default};
diff --git a/assets/solution_0201-0300_290 - Word Pattern.md.be428cac.lean.js b/assets/solution_0201-0300_290 - Word Pattern.md.be428cac.lean.js
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..a464f6ce
--- /dev/null
+++ b/assets/solution_0201-0300_290 - Word Pattern.md.be428cac.lean.js
@@ -0,0 +1 @@
+import{_ as s,o as a,c as n,a as l}from"./app.e4604e86.js";const F=JSON.parse('{"title":"290. Word Pattern","description":"","frontmatter":{},"headers":[{"level":2,"title":"Problem Statement","slug":"problem-statement","link":"#problem-statement","children":[]},{"level":2,"title":"Solution:","slug":"solution","link":"#solution","children":[{"level":3,"title":"...","slug":"","link":"#","children":[]}]}],"relativePath":"solution/0201-0300/290 - Word Pattern.md","lastUpdated":1677028205000}'),p={name:"solution/0201-0300/290 - Word Pattern.md"},o=l("",19),t=[o];function e(c,r,D,y,i,C){return a(),n("div",null,t)}const d=s(p,[["render",e]]);export{F as __pageData,d as default};
diff --git a/assets/solution_0201-0300_292 - Nim Game.md.006de971.js b/assets/solution_0201-0300_292 - Nim Game.md.006de971.js
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..54136959
--- /dev/null
+++ b/assets/solution_0201-0300_292 - Nim Game.md.006de971.js
@@ -0,0 +1,24 @@
+import{_ as s,o as n,c as a,a as e}from"./app.e4604e86.js";const h=JSON.parse('{"title":"292. Nim Game","description":"","frontmatter":{},"headers":[{"level":2,"title":"Problem Statement","slug":"problem-statement","link":"#problem-statement","children":[]},{"level":2,"title":"Solution:","slug":"solution","link":"#solution","children":[{"level":3,"title":"...","slug":"","link":"#","children":[]}]}],"relativePath":"solution/0201-0300/292 - Nim Game.md","lastUpdated":1677114573000}'),l={name:"solution/0201-0300/292 - Nim Game.md"},o=e(`
You are playing the following Nim Game with your friend:
Initially, there is a heap of stones on the table.
You and your friend will alternate taking turns, and you go first.
On each turn, the person whose turn it is will remove 1 to 3 stones from the heap.
The one who removes the last stone is the winner.
Given n, the number of stones in the heap, return true if you can win the game assuming both you and your friend play optimally, otherwise return false.
Example 1:
Input: n = 4
+Output: false
+Explanation: These are the possible outcomes:
+1. You remove 1 stone. Your friend removes 3 stones, including the last stone. Your friend wins.
+2. You remove 2 stones. Your friend removes 2 stones, including the last stone. Your friend wins.
+3. You remove 3 stones. Your friend removes the last stone. Your friend wins.
+In all outcomes, your friend wins.
+
Example 2:
Input: n = 1
+Output: true
+
Example 3:
Input: n = 2
+Output: true
+
Constraints:
1 <= n <= 231 - 1
Click to open Hints
If there are 5 stones in the heap, could you figure out a way to remove the stones such that you will always be the winner?
implSolution{
+pubfncan_win_nim(n:i32)->bool{
+ // if n is divisible by 4, then the first player will always lose
+if n %4==0{
+returnfalse;
+}
+
+true
+}
+}
+
+
You are given an integer array coins representing coins of different denominations and an integer amount representing a total amount of money.
Return the fewest number of coins that you need to make up that amount. If that amount of money cannot be made up by any combination of the coins, return -1.
You may assume that you have an infinite number of each kind of coin.
`,18),e=[p];function t(c,r,D,i,C,y){return a(),n("div",null,e)}const d=s(o,[["render",t]]);export{F as __pageData,d as default};
diff --git a/assets/solution_0301-0400_322 - Coin Change.md.6d01d772.lean.js b/assets/solution_0301-0400_322 - Coin Change.md.6d01d772.lean.js
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..10630b03
--- /dev/null
+++ b/assets/solution_0301-0400_322 - Coin Change.md.6d01d772.lean.js
@@ -0,0 +1 @@
+import{_ as s,o as a,c as n,a as l}from"./app.e4604e86.js";const F=JSON.parse('{"title":"322. Coin Change","description":"","frontmatter":{},"headers":[{"level":2,"title":"Problem Statement:","slug":"problem-statement","link":"#problem-statement","children":[{"level":3,"title":"Example 1:","slug":"example-1","link":"#example-1","children":[]},{"level":3,"title":"Example 2:","slug":"example-2","link":"#example-2","children":[]},{"level":3,"title":"Example 3:","slug":"example-3","link":"#example-3","children":[]},{"level":3,"title":"Constraints:","slug":"constraints","link":"#constraints","children":[]}]},{"level":2,"title":"Solution:","slug":"solution","link":"#solution","children":[{"level":3,"title":"...","slug":"","link":"#","children":[]}]}],"relativePath":"solution/0301-0400/322 - Coin Change.md","lastUpdated":1671291107000}'),o={name:"solution/0301-0400/322 - Coin Change.md"},p=l("",18),e=[p];function t(c,r,D,i,C,y){return a(),n("div",null,e)}const d=s(o,[["render",t]]);export{F as __pageData,d as default};
diff --git a/assets/solution_0301-0400_326 - Power Of Three.md.b7dde1c6.js b/assets/solution_0301-0400_326 - Power Of Three.md.b7dde1c6.js
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..e7e151bf
--- /dev/null
+++ b/assets/solution_0301-0400_326 - Power Of Three.md.b7dde1c6.js
@@ -0,0 +1,26 @@
+import{_ as a,o as n,c as l,f as e,a as s}from"./app.e4604e86.js";const u=JSON.parse('{"title":"326. Power Of Three","description":"","frontmatter":{},"headers":[{"level":2,"title":"Problem Statement","slug":"problem-statement","link":"#problem-statement","children":[]},{"level":2,"title":"Solution:","slug":"solution","link":"#solution","children":[{"level":3,"title":"...","slug":"","link":"#","children":[]}]}],"relativePath":"solution/0301-0400/326 - Power Of Three.md","lastUpdated":1677201121000}'),p={name:"solution/0301-0400/326 - Power Of Three.md"},o=s(`
`,4);function r(c,i,C,A,y,D){return n(),l("div",null,[o,e(" Could you solve it without loops/recursion? "),t])}const h=a(p,[["render",r]]);export{u as __pageData,h as default};
diff --git a/assets/solution_0301-0400_326 - Power Of Three.md.b7dde1c6.lean.js b/assets/solution_0301-0400_326 - Power Of Three.md.b7dde1c6.lean.js
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..eaf6a295
--- /dev/null
+++ b/assets/solution_0301-0400_326 - Power Of Three.md.b7dde1c6.lean.js
@@ -0,0 +1 @@
+import{_ as a,o as n,c as l,f as e,a as s}from"./app.e4604e86.js";const u=JSON.parse('{"title":"326. Power Of Three","description":"","frontmatter":{},"headers":[{"level":2,"title":"Problem Statement","slug":"problem-statement","link":"#problem-statement","children":[]},{"level":2,"title":"Solution:","slug":"solution","link":"#solution","children":[{"level":3,"title":"...","slug":"","link":"#","children":[]}]}],"relativePath":"solution/0301-0400/326 - Power Of Three.md","lastUpdated":1677201121000}'),p={name:"solution/0301-0400/326 - Power Of Three.md"},o=s("",17),t=s("",4);function r(c,i,C,A,y,D){return n(),l("div",null,[o,e(" Could you solve it without loops/recursion? "),t])}const h=a(p,[["render",r]]);export{u as __pageData,h as default};
diff --git a/assets/solution_0301-0400_337 - House Robber III.md.d865bde5.js b/assets/solution_0301-0400_337 - House Robber III.md.d865bde5.js
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..7f1820f1
--- /dev/null
+++ b/assets/solution_0301-0400_337 - House Robber III.md.d865bde5.js
@@ -0,0 +1,23 @@
+import{_ as s,o as a,c as n,a as l}from"./app.e4604e86.js";const F=JSON.parse('{"title":"337. House Robber III","description":"","frontmatter":{},"headers":[{"level":2,"title":"Problem Statement:","slug":"problem-statement","link":"#problem-statement","children":[{"level":3,"title":"Example 1:","slug":"example-1","link":"#example-1","children":[]},{"level":3,"title":"Example 2:","slug":"example-2","link":"#example-2","children":[]},{"level":3,"title":"Constraints:","slug":"constraints","link":"#constraints","children":[]}]},{"level":2,"title":"Solution:","slug":"solution","link":"#solution","children":[{"level":3,"title":"...","slug":"","link":"#","children":[]}]}],"relativePath":"solution/0301-0400/337 - House Robber III.md","lastUpdated":1671291107000}'),o={name:"solution/0301-0400/337 - House Robber III.md"},e=l(`
The thief has found himself a new place for his thievery again. There is only one entrance to this area, called root.
Besides the root, each house has one and only one parent house. After a tour, the smart thief realized that all houses in this place form a binary tree. It will automatically contact the police if two directly-linked houses were broken into on the same night.
Given the root of the binary tree, return the maximum amount of money the thief can rob without alerting the police.
Given an integer n, return an array ans of length n + 1 such that for each i(0 <= i <= n), ans[i] is the number of 1's in the binary representation of i.
`,20),e=[p];function t(c,r,i,C,y,A){return n(),a("div",null,e)}const u=s(o,[["render",t]]);export{d as __pageData,u as default};
diff --git a/assets/solution_0301-0400_338 - Counting Bits.md.56c698f2.lean.js b/assets/solution_0301-0400_338 - Counting Bits.md.56c698f2.lean.js
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..e89a8081
--- /dev/null
+++ b/assets/solution_0301-0400_338 - Counting Bits.md.56c698f2.lean.js
@@ -0,0 +1 @@
+import{_ as s,o as n,c as a,a as l}from"./app.e4604e86.js";const d=JSON.parse('{"title":"338. Counting Bits","description":"","frontmatter":{},"headers":[{"level":2,"title":"Problem Statement","slug":"problem-statement","link":"#problem-statement","children":[]},{"level":2,"title":"Solution:","slug":"solution","link":"#solution","children":[{"level":3,"title":"...","slug":"","link":"#","children":[]}]}],"relativePath":"solution/0301-0400/338 - Counting Bits.md","lastUpdated":1677201121000}'),o={name:"solution/0301-0400/338 - Counting Bits.md"},p=l("",20),e=[p];function t(c,r,i,C,y,A){return n(),a("div",null,e)}const u=s(o,[["render",t]]);export{d as __pageData,u as default};
diff --git a/assets/solution_0301-0400_342 - Power of Four.md.2f5bf262.js b/assets/solution_0301-0400_342 - Power of Four.md.2f5bf262.js
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..37586bf1
--- /dev/null
+++ b/assets/solution_0301-0400_342 - Power of Four.md.2f5bf262.js
@@ -0,0 +1,23 @@
+import{_ as a,o as n,c as l,f as o,a as s}from"./app.e4604e86.js";const u=JSON.parse('{"title":"342. Power of Four","description":"","frontmatter":{},"headers":[{"level":2,"title":"Problem Statement","slug":"problem-statement","link":"#problem-statement","children":[]},{"level":2,"title":"Solution:","slug":"solution","link":"#solution","children":[{"level":3,"title":"...","slug":"","link":"#","children":[]}]}],"relativePath":"solution/0301-0400/342 - Power of Four.md","lastUpdated":1677201121000}'),p={name:"solution/0301-0400/342 - Power of Four.md"},e=s(`
`,4);function r(c,i,C,A,D,y){return n(),l("div",null,[e,o(" Could you solve it without loops/recursion? "),t])}const F=a(p,[["render",r]]);export{u as __pageData,F as default};
diff --git a/assets/solution_0301-0400_342 - Power of Four.md.2f5bf262.lean.js b/assets/solution_0301-0400_342 - Power of Four.md.2f5bf262.lean.js
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..ed07cf83
--- /dev/null
+++ b/assets/solution_0301-0400_342 - Power of Four.md.2f5bf262.lean.js
@@ -0,0 +1 @@
+import{_ as a,o as n,c as l,f as o,a as s}from"./app.e4604e86.js";const u=JSON.parse('{"title":"342. Power of Four","description":"","frontmatter":{},"headers":[{"level":2,"title":"Problem Statement","slug":"problem-statement","link":"#problem-statement","children":[]},{"level":2,"title":"Solution:","slug":"solution","link":"#solution","children":[{"level":3,"title":"...","slug":"","link":"#","children":[]}]}],"relativePath":"solution/0301-0400/342 - Power of Four.md","lastUpdated":1677201121000}'),p={name:"solution/0301-0400/342 - Power of Four.md"},e=s("",17),t=s("",4);function r(c,i,C,A,D,y){return n(),l("div",null,[e,o(" Could you solve it without loops/recursion? "),t])}const F=a(p,[["render",r]]);export{u as __pageData,F as default};
diff --git a/assets/solution_0301-0400_344 - Reverse String.md.c33e162e.js b/assets/solution_0301-0400_344 - Reverse String.md.c33e162e.js
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..f9db2e8e
--- /dev/null
+++ b/assets/solution_0301-0400_344 - Reverse String.md.c33e162e.js
@@ -0,0 +1,16 @@
+import{_ as s,o as a,c as n,a as l}from"./app.e4604e86.js";const u=JSON.parse('{"title":"344. Reverse String","description":"","frontmatter":{},"headers":[{"level":2,"title":"Problem Statement:","slug":"problem-statement","link":"#problem-statement","children":[{"level":3,"title":"Example 1:","slug":"example-1","link":"#example-1","children":[]},{"level":3,"title":"Example 2:","slug":"example-2","link":"#example-2","children":[]},{"level":3,"title":"Constraints:","slug":"constraints","link":"#constraints","children":[]}]},{"level":2,"title":"Solution:","slug":"solution","link":"#solution","children":[{"level":3,"title":"...","slug":"","link":"#","children":[]}]}],"relativePath":"solution/0301-0400/344 - Reverse String.md","lastUpdated":1671291107000}'),e={name:"solution/0301-0400/344 - Reverse String.md"},o=l(`
`,15),t=[o];function p(r,c,i,D,C,y){return a(),n("div",null,t)}const d=s(e,[["render",p]]);export{u as __pageData,d as default};
diff --git a/assets/solution_0301-0400_344 - Reverse String.md.c33e162e.lean.js b/assets/solution_0301-0400_344 - Reverse String.md.c33e162e.lean.js
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..f1b6708a
--- /dev/null
+++ b/assets/solution_0301-0400_344 - Reverse String.md.c33e162e.lean.js
@@ -0,0 +1 @@
+import{_ as s,o as a,c as n,a as l}from"./app.e4604e86.js";const u=JSON.parse('{"title":"344. Reverse String","description":"","frontmatter":{},"headers":[{"level":2,"title":"Problem Statement:","slug":"problem-statement","link":"#problem-statement","children":[{"level":3,"title":"Example 1:","slug":"example-1","link":"#example-1","children":[]},{"level":3,"title":"Example 2:","slug":"example-2","link":"#example-2","children":[]},{"level":3,"title":"Constraints:","slug":"constraints","link":"#constraints","children":[]}]},{"level":2,"title":"Solution:","slug":"solution","link":"#solution","children":[{"level":3,"title":"...","slug":"","link":"#","children":[]}]}],"relativePath":"solution/0301-0400/344 - Reverse String.md","lastUpdated":1671291107000}'),e={name:"solution/0301-0400/344 - Reverse String.md"},o=l("",15),t=[o];function p(r,c,i,D,C,y){return a(),n("div",null,t)}const d=s(e,[["render",p]]);export{u as __pageData,d as default};
diff --git a/assets/solution_0301-0400_345 - Reverse Vowels of a String.md.b4c01eaf.js b/assets/solution_0301-0400_345 - Reverse Vowels of a String.md.b4c01eaf.js
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..316f1b14
--- /dev/null
+++ b/assets/solution_0301-0400_345 - Reverse Vowels of a String.md.b4c01eaf.js
@@ -0,0 +1,54 @@
+import{_ as s,o as n,c as a,a as l}from"./app.e4604e86.js";const i=JSON.parse('{"title":"345. Reverse Vowels of a String","description":"","frontmatter":{},"headers":[{"level":2,"title":"Problem Statement","slug":"problem-statement","link":"#problem-statement","children":[]},{"level":2,"title":"Solution:","slug":"solution","link":"#solution","children":[{"level":3,"title":"...","slug":"","link":"#","children":[]}]}],"relativePath":"solution/0301-0400/345 - Reverse Vowels of a String.md","lastUpdated":1677201121000}'),p={name:"solution/0301-0400/345 - Reverse Vowels of a String.md"},o=l(`
`,17),e=[o];function t(c,r,D,y,C,F){return n(),a("div",null,e)}const d=s(p,[["render",t]]);export{i as __pageData,d as default};
diff --git a/assets/solution_0301-0400_345 - Reverse Vowels of a String.md.b4c01eaf.lean.js b/assets/solution_0301-0400_345 - Reverse Vowels of a String.md.b4c01eaf.lean.js
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..59e30672
--- /dev/null
+++ b/assets/solution_0301-0400_345 - Reverse Vowels of a String.md.b4c01eaf.lean.js
@@ -0,0 +1 @@
+import{_ as s,o as n,c as a,a as l}from"./app.e4604e86.js";const i=JSON.parse('{"title":"345. Reverse Vowels of a String","description":"","frontmatter":{},"headers":[{"level":2,"title":"Problem Statement","slug":"problem-statement","link":"#problem-statement","children":[]},{"level":2,"title":"Solution:","slug":"solution","link":"#solution","children":[{"level":3,"title":"...","slug":"","link":"#","children":[]}]}],"relativePath":"solution/0301-0400/345 - Reverse Vowels of a String.md","lastUpdated":1677201121000}'),p={name:"solution/0301-0400/345 - Reverse Vowels of a String.md"},o=l("",17),e=[o];function t(c,r,D,y,C,F){return n(),a("div",null,e)}const d=s(p,[["render",t]]);export{i as __pageData,d as default};
diff --git a/assets/solution_0301-0400_349 - Intersection of Two Arrays.md.9ea1c865.js b/assets/solution_0301-0400_349 - Intersection of Two Arrays.md.9ea1c865.js
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..60a84d7e
--- /dev/null
+++ b/assets/solution_0301-0400_349 - Intersection of Two Arrays.md.9ea1c865.js
@@ -0,0 +1,34 @@
+import{_ as s,o as n,c as a,a as l}from"./app.e4604e86.js";const i=JSON.parse('{"title":"349. Intersection of Two Arrays","description":"","frontmatter":{},"headers":[{"level":2,"title":"Problem Statement","slug":"problem-statement","link":"#problem-statement","children":[]},{"level":2,"title":"Solution:","slug":"solution","link":"#solution","children":[{"level":3,"title":"...","slug":"","link":"#","children":[]}]}],"relativePath":"solution/0301-0400/349 - Intersection of Two Arrays.md","lastUpdated":1677287497000}'),p={name:"solution/0301-0400/349 - Intersection of Two Arrays.md"},o=l(`
Given two integer arrays nums1 and nums2, return an array of their intersection. Each element in the result must be unique and you may return the result in any order.
`,16),e=[o];function t(c,r,D,y,C,A){return n(),a("div",null,e)}const u=s(p,[["render",t]]);export{i as __pageData,u as default};
diff --git a/assets/solution_0301-0400_349 - Intersection of Two Arrays.md.9ea1c865.lean.js b/assets/solution_0301-0400_349 - Intersection of Two Arrays.md.9ea1c865.lean.js
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..d9b947bf
--- /dev/null
+++ b/assets/solution_0301-0400_349 - Intersection of Two Arrays.md.9ea1c865.lean.js
@@ -0,0 +1 @@
+import{_ as s,o as n,c as a,a as l}from"./app.e4604e86.js";const i=JSON.parse('{"title":"349. Intersection of Two Arrays","description":"","frontmatter":{},"headers":[{"level":2,"title":"Problem Statement","slug":"problem-statement","link":"#problem-statement","children":[]},{"level":2,"title":"Solution:","slug":"solution","link":"#solution","children":[{"level":3,"title":"...","slug":"","link":"#","children":[]}]}],"relativePath":"solution/0301-0400/349 - Intersection of Two Arrays.md","lastUpdated":1677287497000}'),p={name:"solution/0301-0400/349 - Intersection of Two Arrays.md"},o=l("",16),e=[o];function t(c,r,D,y,C,A){return n(),a("div",null,e)}const u=s(p,[["render",t]]);export{i as __pageData,u as default};
diff --git a/assets/solution_0301-0400_350 - Intersection of Two Arrays II.md.1ee76df3.js b/assets/solution_0301-0400_350 - Intersection of Two Arrays II.md.1ee76df3.js
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..300bb5f7
--- /dev/null
+++ b/assets/solution_0301-0400_350 - Intersection of Two Arrays II.md.1ee76df3.js
@@ -0,0 +1,32 @@
+import{_ as s,o as n,c as a,a as l}from"./app.e4604e86.js";const i=JSON.parse('{"title":"350. Intersection of Two Arrays II","description":"","frontmatter":{},"headers":[{"level":2,"title":"Problem Statement","slug":"problem-statement","link":"#problem-statement","children":[]},{"level":2,"title":"Solution:","slug":"solution","link":"#solution","children":[{"level":3,"title":"...","slug":"","link":"#","children":[]}]}],"relativePath":"solution/0301-0400/350 - Intersection of Two Arrays II.md","lastUpdated":1677374362000}'),o={name:"solution/0301-0400/350 - Intersection of Two Arrays II.md"},p=l(`
Given two integer arrays nums1 and nums2, return an array of their intersection. Each element in the result must appear as many times as it shows in both arrays and you may return the result in any order.
`,19),e=[p];function t(r,c,D,y,C,A){return n(),a("div",null,e)}const d=s(o,[["render",t]]);export{i as __pageData,d as default};
diff --git a/assets/solution_0301-0400_350 - Intersection of Two Arrays II.md.1ee76df3.lean.js b/assets/solution_0301-0400_350 - Intersection of Two Arrays II.md.1ee76df3.lean.js
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..19642e8b
--- /dev/null
+++ b/assets/solution_0301-0400_350 - Intersection of Two Arrays II.md.1ee76df3.lean.js
@@ -0,0 +1 @@
+import{_ as s,o as n,c as a,a as l}from"./app.e4604e86.js";const i=JSON.parse('{"title":"350. Intersection of Two Arrays II","description":"","frontmatter":{},"headers":[{"level":2,"title":"Problem Statement","slug":"problem-statement","link":"#problem-statement","children":[]},{"level":2,"title":"Solution:","slug":"solution","link":"#solution","children":[{"level":3,"title":"...","slug":"","link":"#","children":[]}]}],"relativePath":"solution/0301-0400/350 - Intersection of Two Arrays II.md","lastUpdated":1677374362000}'),o={name:"solution/0301-0400/350 - Intersection of Two Arrays II.md"},p=l("",19),e=[p];function t(r,c,D,y,C,A){return n(),a("div",null,e)}const d=s(o,[["render",t]]);export{i as __pageData,d as default};
diff --git a/assets/solution_0301-0400_367 - Valid Perfect Square.md.b3c76a65.js b/assets/solution_0301-0400_367 - Valid Perfect Square.md.b3c76a65.js
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..a8152408
--- /dev/null
+++ b/assets/solution_0301-0400_367 - Valid Perfect Square.md.b3c76a65.js
@@ -0,0 +1,23 @@
+import{_ as s,o as a,c as n,a as l}from"./app.e4604e86.js";const F=JSON.parse('{"title":"367. Valid Perfect Square","description":"","frontmatter":{},"headers":[{"level":2,"title":"Problem Statement:","slug":"problem-statement","link":"#problem-statement","children":[{"level":3,"title":"Example 1:","slug":"example-1","link":"#example-1","children":[]},{"level":3,"title":"Example 2:","slug":"example-2","link":"#example-2","children":[]},{"level":3,"title":"Constraints:","slug":"constraints","link":"#constraints","children":[]}]},{"level":2,"title":"Solution:","slug":"solution","link":"#solution","children":[{"level":3,"title":"...","slug":"","link":"#","children":[]}]}],"relativePath":"solution/0301-0400/367 - Valid Perfect Square.md","lastUpdated":1671291107000}'),e={name:"solution/0301-0400/367 - Valid Perfect Square.md"},p=l(`
`,15),o=[p];function t(r,c,i,D,C,y){return a(),n("div",null,o)}const d=s(e,[["render",t]]);export{F as __pageData,d as default};
diff --git a/assets/solution_0301-0400_367 - Valid Perfect Square.md.b3c76a65.lean.js b/assets/solution_0301-0400_367 - Valid Perfect Square.md.b3c76a65.lean.js
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..84fa86ab
--- /dev/null
+++ b/assets/solution_0301-0400_367 - Valid Perfect Square.md.b3c76a65.lean.js
@@ -0,0 +1 @@
+import{_ as s,o as a,c as n,a as l}from"./app.e4604e86.js";const F=JSON.parse('{"title":"367. Valid Perfect Square","description":"","frontmatter":{},"headers":[{"level":2,"title":"Problem Statement:","slug":"problem-statement","link":"#problem-statement","children":[{"level":3,"title":"Example 1:","slug":"example-1","link":"#example-1","children":[]},{"level":3,"title":"Example 2:","slug":"example-2","link":"#example-2","children":[]},{"level":3,"title":"Constraints:","slug":"constraints","link":"#constraints","children":[]}]},{"level":2,"title":"Solution:","slug":"solution","link":"#solution","children":[{"level":3,"title":"...","slug":"","link":"#","children":[]}]}],"relativePath":"solution/0301-0400/367 - Valid Perfect Square.md","lastUpdated":1671291107000}'),e={name:"solution/0301-0400/367 - Valid Perfect Square.md"},p=l("",15),o=[p];function t(r,c,i,D,C,y){return a(),n("div",null,o)}const d=s(e,[["render",t]]);export{F as __pageData,d as default};
diff --git a/assets/solution_0301-0400_369 - Plus One Linked List.md.4a3f5d04.js b/assets/solution_0301-0400_369 - Plus One Linked List.md.4a3f5d04.js
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..905d1373
--- /dev/null
+++ b/assets/solution_0301-0400_369 - Plus One Linked List.md.4a3f5d04.js
@@ -0,0 +1,33 @@
+import{_ as s,o as a,c as n,a as l}from"./app.e4604e86.js";const F=JSON.parse('{"title":"369 Plus One Linked List","description":"","frontmatter":{},"headers":[{"level":2,"title":"Problem Statement:","slug":"problem-statement","link":"#problem-statement","children":[{"level":3,"title":"Example 1","slug":"example-1","link":"#example-1","children":[]},{"level":3,"title":"Example 2","slug":"example-2","link":"#example-2","children":[]}]},{"level":2,"title":"Solution:","slug":"solution","link":"#solution","children":[{"level":3,"title":"...","slug":"","link":"#","children":[]}]}],"relativePath":"solution/0301-0400/369 - Plus One Linked List.md","lastUpdated":1671291107000}'),p={name:"solution/0301-0400/369 - Plus One Linked List.md"},e=l(`
`,16),o=[e];function t(r,c,D,C,A,y){return a(),n("div",null,o)}const d=s(p,[["render",t]]);export{F as __pageData,d as default};
diff --git a/assets/solution_0301-0400_369 - Plus One Linked List.md.4a3f5d04.lean.js b/assets/solution_0301-0400_369 - Plus One Linked List.md.4a3f5d04.lean.js
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..393dbb7f
--- /dev/null
+++ b/assets/solution_0301-0400_369 - Plus One Linked List.md.4a3f5d04.lean.js
@@ -0,0 +1 @@
+import{_ as s,o as a,c as n,a as l}from"./app.e4604e86.js";const F=JSON.parse('{"title":"369 Plus One Linked List","description":"","frontmatter":{},"headers":[{"level":2,"title":"Problem Statement:","slug":"problem-statement","link":"#problem-statement","children":[{"level":3,"title":"Example 1","slug":"example-1","link":"#example-1","children":[]},{"level":3,"title":"Example 2","slug":"example-2","link":"#example-2","children":[]}]},{"level":2,"title":"Solution:","slug":"solution","link":"#solution","children":[{"level":3,"title":"...","slug":"","link":"#","children":[]}]}],"relativePath":"solution/0301-0400/369 - Plus One Linked List.md","lastUpdated":1671291107000}'),p={name:"solution/0301-0400/369 - Plus One Linked List.md"},e=l("",16),o=[e];function t(r,c,D,C,A,y){return a(),n("div",null,o)}const d=s(p,[["render",t]]);export{F as __pageData,d as default};
diff --git a/assets/solution_0301-0400_374 - Guess Number Higher or Lower.md.e3e786f3.js b/assets/solution_0301-0400_374 - Guess Number Higher or Lower.md.e3e786f3.js
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..6f7266a9
--- /dev/null
+++ b/assets/solution_0301-0400_374 - Guess Number Higher or Lower.md.e3e786f3.js
@@ -0,0 +1,26 @@
+import{_ as s,o as a,c as n,a as l}from"./app.e4604e86.js";const d=JSON.parse('{"title":"374. Guess Number Higher or Lower","description":"","frontmatter":{},"headers":[{"level":2,"title":"Problem Statement","slug":"problem-statement","link":"#problem-statement","children":[]},{"level":2,"title":"Solution:","slug":"solution","link":"#solution","children":[{"level":3,"title":"...","slug":"","link":"#","children":[]}]}],"relativePath":"solution/0301-0400/374 - Guess Number Higher or Lower.md","lastUpdated":1677374362000}'),e={name:"solution/0301-0400/374 - Guess Number Higher or Lower.md"},p=l(`
`,23),o=[p];function t(r,c,i,C,D,y){return a(),n("div",null,o)}const u=s(e,[["render",t]]);export{d as __pageData,u as default};
diff --git a/assets/solution_0301-0400_374 - Guess Number Higher or Lower.md.e3e786f3.lean.js b/assets/solution_0301-0400_374 - Guess Number Higher or Lower.md.e3e786f3.lean.js
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..409793a5
--- /dev/null
+++ b/assets/solution_0301-0400_374 - Guess Number Higher or Lower.md.e3e786f3.lean.js
@@ -0,0 +1 @@
+import{_ as s,o as a,c as n,a as l}from"./app.e4604e86.js";const d=JSON.parse('{"title":"374. Guess Number Higher or Lower","description":"","frontmatter":{},"headers":[{"level":2,"title":"Problem Statement","slug":"problem-statement","link":"#problem-statement","children":[]},{"level":2,"title":"Solution:","slug":"solution","link":"#solution","children":[{"level":3,"title":"...","slug":"","link":"#","children":[]}]}],"relativePath":"solution/0301-0400/374 - Guess Number Higher or Lower.md","lastUpdated":1677374362000}'),e={name:"solution/0301-0400/374 - Guess Number Higher or Lower.md"},p=l("",23),o=[p];function t(r,c,i,C,D,y){return a(),n("div",null,o)}const u=s(e,[["render",t]]);export{d as __pageData,u as default};
diff --git a/assets/solution_0301-0400_382 - Linked List Random Node.md.4fcba4d4.js b/assets/solution_0301-0400_382 - Linked List Random Node.md.4fcba4d4.js
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..09b62048
--- /dev/null
+++ b/assets/solution_0301-0400_382 - Linked List Random Node.md.4fcba4d4.js
@@ -0,0 +1,52 @@
+import{_ as s,o as n,c as a,a as l}from"./app.e4604e86.js";const A=JSON.parse('{"title":"382. Linked List Random Node","description":"","frontmatter":{},"headers":[{"level":2,"title":"Problem Statement","slug":"problem-statement","link":"#problem-statement","children":[]},{"level":2,"title":"Solution:","slug":"solution","link":"#solution","children":[{"level":3,"title":"...","slug":"","link":"#","children":[]}]}],"relativePath":"solution/0301-0400/382 - Linked List Random Node.md","lastUpdated":1678822270000}'),o={name:"solution/0301-0400/382 - Linked List Random Node.md"},p=l(`
`,20),e=[p];function t(c,r,i,D,y,C){return n(),a("div",null,e)}const F=s(o,[["render",t]]);export{A as __pageData,F as default};
diff --git a/assets/solution_0301-0400_382 - Linked List Random Node.md.4fcba4d4.lean.js b/assets/solution_0301-0400_382 - Linked List Random Node.md.4fcba4d4.lean.js
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..1af83a85
--- /dev/null
+++ b/assets/solution_0301-0400_382 - Linked List Random Node.md.4fcba4d4.lean.js
@@ -0,0 +1 @@
+import{_ as s,o as n,c as a,a as l}from"./app.e4604e86.js";const A=JSON.parse('{"title":"382. Linked List Random Node","description":"","frontmatter":{},"headers":[{"level":2,"title":"Problem Statement","slug":"problem-statement","link":"#problem-statement","children":[]},{"level":2,"title":"Solution:","slug":"solution","link":"#solution","children":[{"level":3,"title":"...","slug":"","link":"#","children":[]}]}],"relativePath":"solution/0301-0400/382 - Linked List Random Node.md","lastUpdated":1678822270000}'),o={name:"solution/0301-0400/382 - Linked List Random Node.md"},p=l("",20),e=[p];function t(c,r,i,D,y,C){return n(),a("div",null,e)}const F=s(o,[["render",t]]);export{A as __pageData,F as default};
diff --git a/assets/solution_0301-0400_383 - Ransom Note.md.5edeca1f.js b/assets/solution_0301-0400_383 - Ransom Note.md.5edeca1f.js
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..53d9430e
--- /dev/null
+++ b/assets/solution_0301-0400_383 - Ransom Note.md.5edeca1f.js
@@ -0,0 +1,70 @@
+import{_ as s,o as a,c as n,a as l}from"./app.e4604e86.js";const F=JSON.parse('{"title":"383. Ransom Note","description":"","frontmatter":{},"headers":[{"level":2,"title":"Problem Statement","slug":"problem-statement","link":"#problem-statement","children":[]},{"level":2,"title":"Solution:","slug":"solution","link":"#solution","children":[{"level":3,"title":"...","slug":"","link":"#","children":[]}]}],"relativePath":"solution/0301-0400/383 - Ransom Note.md","lastUpdated":1677374362000}'),p={name:"solution/0301-0400/383 - Ransom Note.md"},o=l(`
implSolution{
+pubfncan_construct(ransom_note:String, magazine:String)->bool{
+ // Convert the magazine string to a vector of characters
+letmut magazine = magazine.chars().collect::<Vec<char>>();
+
+ // Iterate over the ransom note string
+for c in ransom_note.chars(){
+ // If the magazine contains the character, remove it
+ // Otherwise, return false
+ // position() returns the index of the first element that matches the closure
+ // else returns None
+ifletSome(i)= magazine.iter().position(|&x| x == c){
+ magazine.remove(i);
+}else{
+returnfalse;
+}
+}
+
+true
+}
+}
+
+
go
packagemain
+
+funccanConstruct(ransomNote string, magazine string)bool{
+iflen(ransomNote)>len(magazine){
+returnfalse
+}
+// make a map of the magazine
+ mag :=make(map[rune]int)
+
+// count the number of each character in the magazine
+for _, c :=range magazine {
+ mag[c]++
+}
+
+// check if the ransom note can be made from the magazine
+for _, c :=range ransomNote {
+if mag[c]==0{
+returnfalse
+}
+ mag[c]--
+}
+
+// // make a vector of the magazine
+// magVec := make([]int, 26)
+
+// for _, c := range magazine {
+// magVec[c-'a']++
+// }
+
+// // check if ransomNote can be constructed from magazine
+// for _, c := range ransomNote {
+// if magVec[c-'a'] == 0 {
+// return false
+// }
+// magVec[c-'a']--
+// }
+
+returntrue
+}
+
+
`,19),e=[o];function t(c,r,D,y,C,A){return a(),n("div",null,e)}const d=s(p,[["render",t]]);export{F as __pageData,d as default};
diff --git a/assets/solution_0301-0400_383 - Ransom Note.md.5edeca1f.lean.js b/assets/solution_0301-0400_383 - Ransom Note.md.5edeca1f.lean.js
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..dcfaff51
--- /dev/null
+++ b/assets/solution_0301-0400_383 - Ransom Note.md.5edeca1f.lean.js
@@ -0,0 +1 @@
+import{_ as s,o as a,c as n,a as l}from"./app.e4604e86.js";const F=JSON.parse('{"title":"383. Ransom Note","description":"","frontmatter":{},"headers":[{"level":2,"title":"Problem Statement","slug":"problem-statement","link":"#problem-statement","children":[]},{"level":2,"title":"Solution:","slug":"solution","link":"#solution","children":[{"level":3,"title":"...","slug":"","link":"#","children":[]}]}],"relativePath":"solution/0301-0400/383 - Ransom Note.md","lastUpdated":1677374362000}'),p={name:"solution/0301-0400/383 - Ransom Note.md"},o=l("",19),e=[o];function t(c,r,D,y,C,A){return a(),n("div",null,e)}const d=s(p,[["render",t]]);export{F as __pageData,d as default};
diff --git a/assets/solution_0301-0400_387 - First Unique Character in a String.md.8181902a.js b/assets/solution_0301-0400_387 - First Unique Character in a String.md.8181902a.js
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..50ba2965
--- /dev/null
+++ b/assets/solution_0301-0400_387 - First Unique Character in a String.md.8181902a.js
@@ -0,0 +1,30 @@
+import{_ as s,o as a,c as n,a as l}from"./app.e4604e86.js";const A=JSON.parse('{"title":"387. First Unique Character in a String","description":"","frontmatter":{},"headers":[{"level":2,"title":"Problem Statement","slug":"problem-statement","link":"#problem-statement","children":[]},{"level":2,"title":"Solution:","slug":"solution","link":"#solution","children":[{"level":3,"title":"...","slug":"","link":"#","children":[]}]}],"relativePath":"solution/0301-0400/387 - First Unique Character in a String.md","lastUpdated":1677287497000}'),p={name:"solution/0301-0400/387 - First Unique Character in a String.md"},o=l(`
implSolution{
+pubfnfirst_uniq_char(s:String)->i32{
+letmut map =std::collections::HashMap::new();
+for c in s.chars(){
+ // increase the count of the character if exists
+ // otherwise insert the character w/ default value 0
+ // then increase the count by 1
+*map.entry(c).or_insert(0)+=1;
+}
+
+ // iterate over the string and return the index of the first character
+ // that has a count of 1
+for(i, c)in s.chars().enumerate(){
+if*map.get(&c).unwrap()==1{
+return i asi32;
+}
+}
+
+-1
+}
+}
+
+
`,18),e=[o];function t(c,r,i,C,y,D){return a(),n("div",null,e)}const d=s(p,[["render",t]]);export{A as __pageData,d as default};
diff --git a/assets/solution_0301-0400_387 - First Unique Character in a String.md.8181902a.lean.js b/assets/solution_0301-0400_387 - First Unique Character in a String.md.8181902a.lean.js
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..1374e618
--- /dev/null
+++ b/assets/solution_0301-0400_387 - First Unique Character in a String.md.8181902a.lean.js
@@ -0,0 +1 @@
+import{_ as s,o as a,c as n,a as l}from"./app.e4604e86.js";const A=JSON.parse('{"title":"387. First Unique Character in a String","description":"","frontmatter":{},"headers":[{"level":2,"title":"Problem Statement","slug":"problem-statement","link":"#problem-statement","children":[]},{"level":2,"title":"Solution:","slug":"solution","link":"#solution","children":[{"level":3,"title":"...","slug":"","link":"#","children":[]}]}],"relativePath":"solution/0301-0400/387 - First Unique Character in a String.md","lastUpdated":1677287497000}'),p={name:"solution/0301-0400/387 - First Unique Character in a String.md"},o=l("",18),e=[o];function t(c,r,i,C,y,D){return a(),n("div",null,e)}const d=s(p,[["render",t]]);export{A as __pageData,d as default};
diff --git a/assets/solution_0301-0400_389 - Find the Difference.md.c48692f5.js b/assets/solution_0301-0400_389 - Find the Difference.md.c48692f5.js
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..f1f84bd7
--- /dev/null
+++ b/assets/solution_0301-0400_389 - Find the Difference.md.c48692f5.js
@@ -0,0 +1,15 @@
+import{_ as s,o as a,c as n,a as e}from"./app.e4604e86.js";const A=JSON.parse('{"title":"389. Find the Difference","description":"","frontmatter":{},"headers":[{"level":2,"title":"Problem Statement:","slug":"problem-statement","link":"#problem-statement","children":[{"level":3,"title":"Example 1:","slug":"example-1","link":"#example-1","children":[]},{"level":3,"title":"Example 2:","slug":"example-2","link":"#example-2","children":[]},{"level":3,"title":"Constraints:","slug":"constraints","link":"#constraints","children":[]}]},{"level":2,"title":"Solution:","slug":"solution","link":"#solution","children":[{"level":3,"title":"...","slug":"","link":"#","children":[]}]}],"relativePath":"solution/0301-0400/389 - Find the Difference.md","lastUpdated":1671291107000}'),l={name:"solution/0301-0400/389 - Find the Difference.md"},o=e(`
publiccharfindTheDifference(String s,String t){
+char c =0;
+for(int i =0; i < s.length();++i)
+ c ^= s.charAt(i);
+for(int i =0; i < t.length();++i)
+ c ^= t.charAt(i);
+return c;
+}
+
`,16),t=[o];function p(r,c,i,d,D,C){return a(),n("div",null,t)}const h=s(l,[["render",p]]);export{A as __pageData,h as default};
diff --git a/assets/solution_0301-0400_389 - Find the Difference.md.c48692f5.lean.js b/assets/solution_0301-0400_389 - Find the Difference.md.c48692f5.lean.js
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..c3df2e1d
--- /dev/null
+++ b/assets/solution_0301-0400_389 - Find the Difference.md.c48692f5.lean.js
@@ -0,0 +1 @@
+import{_ as s,o as a,c as n,a as e}from"./app.e4604e86.js";const A=JSON.parse('{"title":"389. Find the Difference","description":"","frontmatter":{},"headers":[{"level":2,"title":"Problem Statement:","slug":"problem-statement","link":"#problem-statement","children":[{"level":3,"title":"Example 1:","slug":"example-1","link":"#example-1","children":[]},{"level":3,"title":"Example 2:","slug":"example-2","link":"#example-2","children":[]},{"level":3,"title":"Constraints:","slug":"constraints","link":"#constraints","children":[]}]},{"level":2,"title":"Solution:","slug":"solution","link":"#solution","children":[{"level":3,"title":"...","slug":"","link":"#","children":[]}]}],"relativePath":"solution/0301-0400/389 - Find the Difference.md","lastUpdated":1671291107000}'),l={name:"solution/0301-0400/389 - Find the Difference.md"},o=e("",16),t=[o];function p(r,c,i,d,D,C){return a(),n("div",null,t)}const h=s(l,[["render",p]]);export{A as __pageData,h as default};
diff --git a/assets/solution_0301-0400_392 - Is Subsequence.md.e5387d7d.js b/assets/solution_0301-0400_392 - Is Subsequence.md.e5387d7d.js
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..441021cb
--- /dev/null
+++ b/assets/solution_0301-0400_392 - Is Subsequence.md.e5387d7d.js
@@ -0,0 +1,21 @@
+import{_ as e,o as l,c as o,f as s,a,b as n}from"./app.e4604e86.js";const _=JSON.parse('{"title":"392. Is Subsequence","description":"","frontmatter":{},"headers":[{"level":2,"title":"Problem Statement","slug":"problem-statement","link":"#problem-statement","children":[]},{"level":2,"title":"Solution:","slug":"solution","link":"#solution","children":[{"level":3,"title":"...","slug":"","link":"#","children":[]}]}],"relativePath":"solution/0301-0400/392 - Is Subsequence.md","lastUpdated":1677374362000}'),p={name:"solution/0301-0400/392 - Is Subsequence.md"},t=a(`
Given two strings s and t, return true if s is a subsequence of t, or false otherwise.
A subsequence of a string is a new string that is formed from the original string by deleting some (can be none) of the characters without disturbing the relative positions of the remaining characters. (i.e., "ace" is a subsequence of "abcde" while "aec" is not).
Example 1:
Input: s = "abc", t = "ahbgdc"
+Output: true
+
Example 2:
Input: s = "axc", t = "ahbgdc"
+Output: false
+
Constraints:
0 <= s.length <= 100
0 <= t.length <= 104
s and t consist only of lowercase English letters.
`,4);function y(A,d,u,F,h,g){return l(),o("div",null,[t,s(" Suppose there are lots of incoming "),c,s(", say "),r,s(" where "),i,s(", and you want to check one by one to see if "),D,s(" has its subsequence. In this scenario, how would you change your code? "),C])}const m=e(p,[["render",y]]);export{_ as __pageData,m as default};
diff --git a/assets/solution_0301-0400_392 - Is Subsequence.md.e5387d7d.lean.js b/assets/solution_0301-0400_392 - Is Subsequence.md.e5387d7d.lean.js
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..75e9f650
--- /dev/null
+++ b/assets/solution_0301-0400_392 - Is Subsequence.md.e5387d7d.lean.js
@@ -0,0 +1 @@
+import{_ as e,o as l,c as o,f as s,a,b as n}from"./app.e4604e86.js";const _=JSON.parse('{"title":"392. Is Subsequence","description":"","frontmatter":{},"headers":[{"level":2,"title":"Problem Statement","slug":"problem-statement","link":"#problem-statement","children":[]},{"level":2,"title":"Solution:","slug":"solution","link":"#solution","children":[{"level":3,"title":"...","slug":"","link":"#","children":[]}]}],"relativePath":"solution/0301-0400/392 - Is Subsequence.md","lastUpdated":1677374362000}'),p={name:"solution/0301-0400/392 - Is Subsequence.md"},t=a("",15),c=n("code",null,"s",-1),r=n("code",null,[s("s"),n("sub",null,"1"),s(", s"),n("sub",null,"2"),s(", ..., s"),n("sub",null,"k")],-1),i=n("code",null,[s("k >= 10"),n("sup",null,"9")],-1),D=n("code",null,"t",-1),C=a("",4);function y(A,d,u,F,h,g){return l(),o("div",null,[t,s(" Suppose there are lots of incoming "),c,s(", say "),r,s(" where "),i,s(", and you want to check one by one to see if "),D,s(" has its subsequence. In this scenario, how would you change your code? "),C])}const m=e(p,[["render",y]]);export{_ as __pageData,m as default};
diff --git a/assets/solution_0401-0500_401 - Binary Watch.md.ae7474be.js b/assets/solution_0401-0500_401 - Binary Watch.md.ae7474be.js
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..d10c87a3
--- /dev/null
+++ b/assets/solution_0401-0500_401 - Binary Watch.md.ae7474be.js
@@ -0,0 +1,27 @@
+import{_ as s,o as n,c as a,a as o}from"./app.e4604e86.js";const d=JSON.parse('{"title":"401. Binary Watch","description":"","frontmatter":{},"headers":[{"level":2,"title":"Problem Statement","slug":"problem-statement","link":"#problem-statement","children":[]},{"level":2,"title":"Solution:","slug":"solution","link":"#solution","children":[{"level":3,"title":"...","slug":"","link":"#","children":[]}]}],"relativePath":"solution/0401-0500/401 - Binary Watch.md","lastUpdated":1677460380000}'),l={name:"solution/0401-0500/401 - Binary Watch.md"},e=o(`
A binary watch has 4 LEDs on the top to represent the hours (0-11), and 6 LEDs on the bottom to represent the minutes (0-59). Each LED represents a zero or one, with the least significant bit on the right.
For example, the below binary watch reads "4:51".
Given an integer turnedOn which represents the number of LEDs that are currently on (ignoring the PM), return all possible times the watch could represent. You may return the answer in any order.
The hour must not contain a leading zero.
For example, "01:00" is not valid. It should be "1:00".
The minute must be consist of two digits and may contain a leading zero.
For example, "10:2" is not valid. It should be "10:02".
implSolution{
+pubfnread_binary_watch(turned_on:i32)->Vec<String>{
+letmut res =Vec::new();
+
+ // 12 hours, 60 minutes
+ // here we use 0_i32 to avoid the warning of type inference
+for i in0_i32..12{
+for j in0_i32..60{
+ // if the sum of the number of 1s in the binary representation
+ // of the hour and minute is equal to turned_on,
+ // then the time is added to the res
+if i.count_ones()+ j.count_ones()== turned_on asu32{
+ res.push(format!("{}:{:02}", i, j));
+}
+}
+}
+
+ res
+}
+}
+
+
`,24),p=[e];function t(r,c,i,y,C,D){return n(),a("div",null,p)}const F=s(l,[["render",t]]);export{d as __pageData,F as default};
diff --git a/assets/solution_0401-0500_401 - Binary Watch.md.ae7474be.lean.js b/assets/solution_0401-0500_401 - Binary Watch.md.ae7474be.lean.js
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..79b7f4ff
--- /dev/null
+++ b/assets/solution_0401-0500_401 - Binary Watch.md.ae7474be.lean.js
@@ -0,0 +1 @@
+import{_ as s,o as n,c as a,a as o}from"./app.e4604e86.js";const d=JSON.parse('{"title":"401. Binary Watch","description":"","frontmatter":{},"headers":[{"level":2,"title":"Problem Statement","slug":"problem-statement","link":"#problem-statement","children":[]},{"level":2,"title":"Solution:","slug":"solution","link":"#solution","children":[{"level":3,"title":"...","slug":"","link":"#","children":[]}]}],"relativePath":"solution/0401-0500/401 - Binary Watch.md","lastUpdated":1677460380000}'),l={name:"solution/0401-0500/401 - Binary Watch.md"},e=o("",24),p=[e];function t(r,c,i,y,C,D){return n(),a("div",null,p)}const F=s(l,[["render",t]]);export{d as __pageData,F as default};
diff --git a/assets/solution_0401-0500_404 - Sum of Left Leaves.md.5332ffa3.js b/assets/solution_0401-0500_404 - Sum of Left Leaves.md.5332ffa3.js
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..e9c0f78d
--- /dev/null
+++ b/assets/solution_0401-0500_404 - Sum of Left Leaves.md.5332ffa3.js
@@ -0,0 +1,61 @@
+import{_ as s,o as n,c as a,a as l}from"./app.e4604e86.js";const i=JSON.parse('{"title":"404. Sum of Left Leaves","description":"","frontmatter":{},"headers":[{"level":2,"title":"Problem Statement","slug":"problem-statement","link":"#problem-statement","children":[]},{"level":2,"title":"Solution:","slug":"solution","link":"#solution","children":[{"level":3,"title":"...","slug":"","link":"#","children":[]}]}],"relativePath":"solution/0401-0500/404 - Sum of Left Leaves.md","lastUpdated":1677418438000}'),p={name:"solution/0401-0500/404 - Sum of Left Leaves.md"},o=l(`
`,18),e=[o];function t(c,r,D,y,A,C){return n(),a("div",null,e)}const d=s(p,[["render",t]]);export{i as __pageData,d as default};
diff --git a/assets/solution_0401-0500_404 - Sum of Left Leaves.md.5332ffa3.lean.js b/assets/solution_0401-0500_404 - Sum of Left Leaves.md.5332ffa3.lean.js
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..a1ff12c9
--- /dev/null
+++ b/assets/solution_0401-0500_404 - Sum of Left Leaves.md.5332ffa3.lean.js
@@ -0,0 +1 @@
+import{_ as s,o as n,c as a,a as l}from"./app.e4604e86.js";const i=JSON.parse('{"title":"404. Sum of Left Leaves","description":"","frontmatter":{},"headers":[{"level":2,"title":"Problem Statement","slug":"problem-statement","link":"#problem-statement","children":[]},{"level":2,"title":"Solution:","slug":"solution","link":"#solution","children":[{"level":3,"title":"...","slug":"","link":"#","children":[]}]}],"relativePath":"solution/0401-0500/404 - Sum of Left Leaves.md","lastUpdated":1677418438000}'),p={name:"solution/0401-0500/404 - Sum of Left Leaves.md"},o=l("",18),e=[o];function t(c,r,D,y,A,C){return n(),a("div",null,e)}const d=s(p,[["render",t]]);export{i as __pageData,d as default};
diff --git a/assets/solution_0401-0500_412 - Fizz Buzz.md.7494f36e.js b/assets/solution_0401-0500_412 - Fizz Buzz.md.7494f36e.js
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..6d6d8659
--- /dev/null
+++ b/assets/solution_0401-0500_412 - Fizz Buzz.md.7494f36e.js
@@ -0,0 +1,29 @@
+import{_ as s,o as n,c as a,a as o}from"./app.e4604e86.js";const A=JSON.parse('{"title":"412. Fizz Buzz","description":"","frontmatter":{},"headers":[{"level":2,"title":"Problem Statement","slug":"problem-statement","link":"#problem-statement","children":[]},{"level":2,"title":"Solution:","slug":"solution","link":"#solution","children":[{"level":3,"title":"...","slug":"","link":"#","children":[]}]}],"relativePath":"solution/0401-0500/412 - Fizz Buzz.md","lastUpdated":1677460380000}'),l={name:"solution/0401-0500/412 - Fizz Buzz.md"},p=o(`
implSolution{
+pubfnfizz_buzz(n:i32)->Vec<String>{
+letmut res =Vec::new();
+
+for i in1..=n {
+ // same as divisible by 3 and 5
+if i %15==0{
+ res.push("FizzBuzz".to_string());
+}elseif i %3==0{
+ res.push("Fizz".to_string());
+}elseif i %5==0{
+ res.push("Buzz".to_string());
+}else{
+ res.push(i.to_string());
+}
+}
+
+ res
+}
+}
+
+
`,19),e=[p];function t(c,r,i,D,F,y){return n(),a("div",null,e)}const u=s(l,[["render",t]]);export{A as __pageData,u as default};
diff --git a/assets/solution_0401-0500_412 - Fizz Buzz.md.7494f36e.lean.js b/assets/solution_0401-0500_412 - Fizz Buzz.md.7494f36e.lean.js
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..44dbfe4c
--- /dev/null
+++ b/assets/solution_0401-0500_412 - Fizz Buzz.md.7494f36e.lean.js
@@ -0,0 +1 @@
+import{_ as s,o as n,c as a,a as o}from"./app.e4604e86.js";const A=JSON.parse('{"title":"412. Fizz Buzz","description":"","frontmatter":{},"headers":[{"level":2,"title":"Problem Statement","slug":"problem-statement","link":"#problem-statement","children":[]},{"level":2,"title":"Solution:","slug":"solution","link":"#solution","children":[{"level":3,"title":"...","slug":"","link":"#","children":[]}]}],"relativePath":"solution/0401-0500/412 - Fizz Buzz.md","lastUpdated":1677460380000}'),l={name:"solution/0401-0500/412 - Fizz Buzz.md"},p=o("",19),e=[p];function t(c,r,i,D,F,y){return n(),a("div",null,e)}const u=s(l,[["render",t]]);export{A as __pageData,u as default};
diff --git a/assets/solution_0401-0500_414 - Third Maximum Number.md.04251e05.js b/assets/solution_0401-0500_414 - Third Maximum Number.md.04251e05.js
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..db73084a
--- /dev/null
+++ b/assets/solution_0401-0500_414 - Third Maximum Number.md.04251e05.js
@@ -0,0 +1,36 @@
+import{_ as a,o as l,c as p,f as s,a as n,b as e}from"./app.e4604e86.js";const F=JSON.parse('{"title":"414. Third Maximum Number","description":"","frontmatter":{},"headers":[{"level":2,"title":"Problem Statement","slug":"problem-statement","link":"#problem-statement","children":[]},{"level":2,"title":"Solution:","slug":"solution","link":"#solution","children":[{"level":3,"title":"...","slug":"","link":"#","children":[]}]}],"relativePath":"solution/0401-0500/414 - Third Maximum Number.md","lastUpdated":1677460380000}'),o={name:"solution/0401-0500/414 - Third Maximum Number.md"},t=n(`
Given an integer array nums, return the third distinct maximum number in this array. If the third maximum does not exist, return the maximum number.
Example 1:
Input: nums = [3,2,1]
+Output: 1
+Explanation:
+The first distinct maximum is 3.
+The second distinct maximum is 2.
+The third distinct maximum is 1.
+
Example 2:
Input: nums = [1,2]
+Output: 2
+Explanation:
+The first distinct maximum is 2.
+The second distinct maximum is 1.
+The third distinct maximum does not exist, so the maximum (2) is returned instead.
+
Example 3:
Input: nums = [2,2,3,1]
+Output: 1
+Explanation:
+The first distinct maximum is 3.
+The second distinct maximum is 2 (both 2's are counted together since they have the same value).
+The third distinct maximum is 1.
+
`,4);function i(C,A,d,y,D,m){return l(),p("div",null,[t,s(" Can you find an "),c,s(" solution? "),r])}const h=a(o,[["render",i]]);export{F as __pageData,h as default};
diff --git a/assets/solution_0401-0500_414 - Third Maximum Number.md.04251e05.lean.js b/assets/solution_0401-0500_414 - Third Maximum Number.md.04251e05.lean.js
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..51c3b1b5
--- /dev/null
+++ b/assets/solution_0401-0500_414 - Third Maximum Number.md.04251e05.lean.js
@@ -0,0 +1 @@
+import{_ as a,o as l,c as p,f as s,a as n,b as e}from"./app.e4604e86.js";const F=JSON.parse('{"title":"414. Third Maximum Number","description":"","frontmatter":{},"headers":[{"level":2,"title":"Problem Statement","slug":"problem-statement","link":"#problem-statement","children":[]},{"level":2,"title":"Solution:","slug":"solution","link":"#solution","children":[{"level":3,"title":"...","slug":"","link":"#","children":[]}]}],"relativePath":"solution/0401-0500/414 - Third Maximum Number.md","lastUpdated":1677460380000}'),o={name:"solution/0401-0500/414 - Third Maximum Number.md"},t=n("",16),c=e("code",null,"O(n)",-1),r=n("",4);function i(C,A,d,y,D,m){return l(),p("div",null,[t,s(" Can you find an "),c,s(" solution? "),r])}const h=a(o,[["render",i]]);export{F as __pageData,h as default};
diff --git a/assets/solution_0401-0500_434 - Number of Segments in a String.md.8dcdd995.js b/assets/solution_0401-0500_434 - Number of Segments in a String.md.8dcdd995.js
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..50beaa16
--- /dev/null
+++ b/assets/solution_0401-0500_434 - Number of Segments in a String.md.8dcdd995.js
@@ -0,0 +1,24 @@
+import{_ as s,o as n,c as a,a as l}from"./app.e4604e86.js";const d=JSON.parse('{"title":"434. Number of Segments in a String","description":"","frontmatter":{},"headers":[{"level":2,"title":"Problem Statement","slug":"problem-statement","link":"#problem-statement","children":[]},{"level":2,"title":"Solution:","slug":"solution","link":"#solution","children":[{"level":3,"title":"...","slug":"","link":"#","children":[]}]}],"relativePath":"solution/0401-0500/434 - Number of Segments in a String.md","lastUpdated":1677645016000}'),e={name:"solution/0401-0500/434 - Number of Segments in a String.md"},o=l(`
`,17),p=[o];function t(c,r,i,C,D,y){return n(),a("div",null,p)}const F=s(e,[["render",t]]);export{d as __pageData,F as default};
diff --git a/assets/solution_0401-0500_434 - Number of Segments in a String.md.8dcdd995.lean.js b/assets/solution_0401-0500_434 - Number of Segments in a String.md.8dcdd995.lean.js
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..c1b898df
--- /dev/null
+++ b/assets/solution_0401-0500_434 - Number of Segments in a String.md.8dcdd995.lean.js
@@ -0,0 +1 @@
+import{_ as s,o as n,c as a,a as l}from"./app.e4604e86.js";const d=JSON.parse('{"title":"434. Number of Segments in a String","description":"","frontmatter":{},"headers":[{"level":2,"title":"Problem Statement","slug":"problem-statement","link":"#problem-statement","children":[]},{"level":2,"title":"Solution:","slug":"solution","link":"#solution","children":[{"level":3,"title":"...","slug":"","link":"#","children":[]}]}],"relativePath":"solution/0401-0500/434 - Number of Segments in a String.md","lastUpdated":1677645016000}'),e={name:"solution/0401-0500/434 - Number of Segments in a String.md"},o=l("",17),p=[o];function t(c,r,i,C,D,y){return n(),a("div",null,p)}const F=s(e,[["render",t]]);export{d as __pageData,F as default};
diff --git a/assets/solution_0401-0500_438 - Find All Anagrams in a String.md.5b3e782c.js b/assets/solution_0401-0500_438 - Find All Anagrams in a String.md.5b3e782c.js
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..67b7b733
--- /dev/null
+++ b/assets/solution_0401-0500_438 - Find All Anagrams in a String.md.5b3e782c.js
@@ -0,0 +1,46 @@
+import{_ as s,o as n,c as a,a as l}from"./app.e4604e86.js";const i=JSON.parse('{"title":"438. Find All Anagrams in a String","description":"","frontmatter":{},"headers":[{"level":2,"title":"Problem Statement","slug":"problem-statement","link":"#problem-statement","children":[]},{"level":2,"title":"Solution:","slug":"solution","link":"#solution","children":[{"level":3,"title":"...","slug":"","link":"#","children":[]}]}],"relativePath":"solution/0401-0500/438 - Find All Anagrams in a String.md","lastUpdated":1676656807000}'),p={name:"solution/0401-0500/438 - Find All Anagrams in a String.md"},o=l(`
Given two strings s and p, return an array of all the start indices of p's anagrams in s. You may return the answer in any order.
An Anagram is a word or phrase formed by rearranging the letters of a different word or phrase, typically using all the original letters exactly once.
Example 1:
Input: s = "cbaebabacd", p = "abc"
+Output: [0,6]
+Explanation:
+The substring with start index = 0 is "cba", which is an anagram of "abc".
+The substring with start index = 6 is "bac", which is an anagram of "abc".
+
Example 2:
Input: s = "abab", p = "ab"
+Output: [0,1,2]
+Explanation:
+The substring with start index = 0 is "ab", which is an anagram of "ab".
+The substring with start index = 1 is "ba", which is an anagram of "ab".
+The substring with start index = 2 is "ab", which is an anagram of "ab".
+
classSolution:
+deffindAnagrams(self,s:str,p:str)-> list[int]:
+ s_len, p_len =len(s),len(p)
+if p_len > s_len:
+return[]
+ p_count, s_count ={},{}
+# increment the count of each character in p and s,
+# for the first p_len characters in s
+# with get() we can set a default value if the key is not found
+for i inrange(p_len):
+ p_count[p[i]]= p_count.get(p[i],0)+1
+ s_count[s[i]]= s_count.get(s[i],0)+1
+
+# if the counts are equal, we found an anagram
+ res =[0]if p_count == s_count else[]
+ l =0
+for r inrange(p_len, s_len):
+# increment the count of the right character
+ s_count[s[r]]= s_count.get(s[r],0)+1
+# decrement the count of the left character
+ s_count[s[l]]-=1
+
+# if the count of the left character is 0,
+# we can remove it from the dictionary
+if s_count[s[l]]==0:
+del s_count[s[l]]
+# increment the left pointer
+ l +=1
+# if the counts are equal, we found an anagram
+if p_count == s_count:
+ res.append(l)
+return res
+
+
`,17),e=[o];function t(c,r,D,A,y,F){return n(),a("div",null,e)}const d=s(p,[["render",t]]);export{i as __pageData,d as default};
diff --git a/assets/solution_0401-0500_438 - Find All Anagrams in a String.md.5b3e782c.lean.js b/assets/solution_0401-0500_438 - Find All Anagrams in a String.md.5b3e782c.lean.js
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..b9b7137d
--- /dev/null
+++ b/assets/solution_0401-0500_438 - Find All Anagrams in a String.md.5b3e782c.lean.js
@@ -0,0 +1 @@
+import{_ as s,o as n,c as a,a as l}from"./app.e4604e86.js";const i=JSON.parse('{"title":"438. Find All Anagrams in a String","description":"","frontmatter":{},"headers":[{"level":2,"title":"Problem Statement","slug":"problem-statement","link":"#problem-statement","children":[]},{"level":2,"title":"Solution:","slug":"solution","link":"#solution","children":[{"level":3,"title":"...","slug":"","link":"#","children":[]}]}],"relativePath":"solution/0401-0500/438 - Find All Anagrams in a String.md","lastUpdated":1676656807000}'),p={name:"solution/0401-0500/438 - Find All Anagrams in a String.md"},o=l("",17),e=[o];function t(c,r,D,A,y,F){return n(),a("div",null,e)}const d=s(p,[["render",t]]);export{i as __pageData,d as default};
diff --git a/assets/solution_0401-0500_441 - Arranging Coins.md.312e9d1b.js b/assets/solution_0401-0500_441 - Arranging Coins.md.312e9d1b.js
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..dfce2a3f
--- /dev/null
+++ b/assets/solution_0401-0500_441 - Arranging Coins.md.312e9d1b.js
@@ -0,0 +1,21 @@
+import{_ as s,o as a,c as n,a as l}from"./app.e4604e86.js";const D=JSON.parse('{"title":"441. Arranging Coins","description":"","frontmatter":{},"headers":[{"level":2,"title":"Problem Statement","slug":"problem-statement","link":"#problem-statement","children":[]},{"level":2,"title":"Solution:","slug":"solution","link":"#solution","children":[{"level":3,"title":"...","slug":"","link":"#","children":[]}]}],"relativePath":"solution/0401-0500/441 - Arranging Coins.md","lastUpdated":1677645016000}'),e={name:"solution/0401-0500/441 - Arranging Coins.md"},o=l(`
You have n coins and you want to build a staircase with these coins. The staircase consists of k rows where the ith row has exactly i coins. The last row of the staircase may be incomplete.
Given the integer n, return the number of complete rows of the staircase you will build.
Example 1:
Input: n = 5
+Output: 2
+Explanation: Because the 3rd row is incomplete, we return 2.
+
Example 2:
Input: n = 8
+Output: 3
+Explanation: Because the 4th row is incomplete, we return 3.
+
`,19),p=[o];function t(c,r,i,C,d,y){return a(),n("div",null,p)}const h=s(e,[["render",t]]);export{D as __pageData,h as default};
diff --git a/assets/solution_0401-0500_441 - Arranging Coins.md.312e9d1b.lean.js b/assets/solution_0401-0500_441 - Arranging Coins.md.312e9d1b.lean.js
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..84cc32d3
--- /dev/null
+++ b/assets/solution_0401-0500_441 - Arranging Coins.md.312e9d1b.lean.js
@@ -0,0 +1 @@
+import{_ as s,o as a,c as n,a as l}from"./app.e4604e86.js";const D=JSON.parse('{"title":"441. Arranging Coins","description":"","frontmatter":{},"headers":[{"level":2,"title":"Problem Statement","slug":"problem-statement","link":"#problem-statement","children":[]},{"level":2,"title":"Solution:","slug":"solution","link":"#solution","children":[{"level":3,"title":"...","slug":"","link":"#","children":[]}]}],"relativePath":"solution/0401-0500/441 - Arranging Coins.md","lastUpdated":1677645016000}'),e={name:"solution/0401-0500/441 - Arranging Coins.md"},o=l("",19),p=[o];function t(c,r,i,C,d,y){return a(),n("div",null,p)}const h=s(e,[["render",t]]);export{D as __pageData,h as default};
diff --git a/assets/solution_0401-0500_442 - Find All Duplicates in an Array.md.f14f98a8.js b/assets/solution_0401-0500_442 - Find All Duplicates in an Array.md.f14f98a8.js
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..a7253385
--- /dev/null
+++ b/assets/solution_0401-0500_442 - Find All Duplicates in an Array.md.f14f98a8.js
@@ -0,0 +1,19 @@
+import{_ as s,o as a,c as n,a as l}from"./app.e4604e86.js";const d=JSON.parse('{"title":"442. Find All Duplicates in an Array","description":"","frontmatter":{},"headers":[{"level":2,"title":"Problem Statement:","slug":"problem-statement","link":"#problem-statement","children":[{"level":3,"title":"Example 1:","slug":"example-1","link":"#example-1","children":[]},{"level":3,"title":"Example 2:","slug":"example-2","link":"#example-2","children":[]},{"level":3,"title":"Example 3:","slug":"example-3","link":"#example-3","children":[]},{"level":3,"title":"Constraints:","slug":"constraints","link":"#constraints","children":[]}]},{"level":2,"title":"Solution:","slug":"solution","link":"#solution","children":[{"level":3,"title":"...","slug":"","link":"#","children":[]}]}],"relativePath":"solution/0401-0500/442 - Find All Duplicates in an Array.md","lastUpdated":1671291107000}'),e={name:"solution/0401-0500/442 - Find All Duplicates in an Array.md"},p=l(`
Given an integer array nums of length n where all the integers of nums are in the range [1, n] and each integer appears once or twice, return an array of all the integers that appears twice.
You must write an algorithm that runs in O(n) time and uses only constant extra space.
`,17),o=[p];function t(r,c,i,D,y,C){return a(),n("div",null,o)}const F=s(e,[["render",t]]);export{d as __pageData,F as default};
diff --git a/assets/solution_0401-0500_442 - Find All Duplicates in an Array.md.f14f98a8.lean.js b/assets/solution_0401-0500_442 - Find All Duplicates in an Array.md.f14f98a8.lean.js
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..5fa999f3
--- /dev/null
+++ b/assets/solution_0401-0500_442 - Find All Duplicates in an Array.md.f14f98a8.lean.js
@@ -0,0 +1 @@
+import{_ as s,o as a,c as n,a as l}from"./app.e4604e86.js";const d=JSON.parse('{"title":"442. Find All Duplicates in an Array","description":"","frontmatter":{},"headers":[{"level":2,"title":"Problem Statement:","slug":"problem-statement","link":"#problem-statement","children":[{"level":3,"title":"Example 1:","slug":"example-1","link":"#example-1","children":[]},{"level":3,"title":"Example 2:","slug":"example-2","link":"#example-2","children":[]},{"level":3,"title":"Example 3:","slug":"example-3","link":"#example-3","children":[]},{"level":3,"title":"Constraints:","slug":"constraints","link":"#constraints","children":[]}]},{"level":2,"title":"Solution:","slug":"solution","link":"#solution","children":[{"level":3,"title":"...","slug":"","link":"#","children":[]}]}],"relativePath":"solution/0401-0500/442 - Find All Duplicates in an Array.md","lastUpdated":1671291107000}'),e={name:"solution/0401-0500/442 - Find All Duplicates in an Array.md"},p=l("",17),o=[p];function t(r,c,i,D,y,C){return a(),n("div",null,o)}const F=s(e,[["render",t]]);export{d as __pageData,F as default};
diff --git a/assets/solution_0401-0500_443 - String Compression.md.fb53fd46.js b/assets/solution_0401-0500_443 - String Compression.md.fb53fd46.js
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..7c8a56f5
--- /dev/null
+++ b/assets/solution_0401-0500_443 - String Compression.md.fb53fd46.js
@@ -0,0 +1,67 @@
+import{_ as s,o as n,c as a,a as e}from"./app.e4604e86.js";const d=JSON.parse('{"title":"443. String Compression","description":"","frontmatter":{},"headers":[{"level":2,"title":"Problem Statement","slug":"problem-statement","link":"#problem-statement","children":[{"level":3,"title":"...","slug":"","link":"#","children":[]}]}],"relativePath":"solution/0401-0500/443 - String Compression.md","lastUpdated":1677762379000}'),t={name:"solution/0401-0500/443 - String Compression.md"},l=e(`
Given an array of characters chars, compress it using the following algorithm:
Begin with an empty string s. For each group of consecutive repeating characters in chars:
If the group's length is 1, append the character to s.
Otherwise, append the character followed by the group's length.
The compressed string sshould not be returned separately, but instead, be stored in the input character array chars. Note that group lengths that are 10 or longer will be split into multiple characters in chars.
After you are done modifying the input array, return the new length of the array.
You must write an algorithm that uses only constant extra space.
Example 1:
Input: chars = ["a","a","b","b","c","c","c"]
+Output: Return 6, and the first 6 characters of the input array should be: ["a","2","b","2","c","3"]
+Explanation: The groups are "aa", "bb", and "ccc". This compresses to "a2b2c3".
+
Example 2:
Input: chars = ["a"]
+Output: Return 1, and the first character of the input array should be: ["a"]
+Explanation: The only group is "a", which remains uncompressed since it's a single character.
+
Example 3:
Input: chars = ["a","b","b","b","b","b","b","b","b","b","b","b","b"]
+Output: Return 4, and the first 4 characters of the input array should be: ["a","b","1","2"].
+Explanation: The groups are "a" and "bbbbbbbbbbbb". This compresses to "ab12".\`\`\`
+
+<p> </p>
+<p><strong>Constraints:</strong></p>
+<ul>
+<li><code>1 <= chars.length <= 2000</code></li>
+<li><code>chars[i]</code> is a lowercase English letter, uppercase English letter, digit, or symbol.</li>
+</ul>
+
+
+::: details _Click to open Hints_
+
+- How do you know if you are at the end of a consecutive group of characters?
+
+:::
+
+## Solution:
+
+::: code-group
+
+\`\`\`rs [Rust]
+impl Solution {
+ pub fn compress(chars: &mut Vec<char>) -> i32 {
+ let (mut i, n) = (0, chars.len());
+ let mut new_len = 0;
+
+ while i < n {
+ let mut j = i;
+
+ // increment j until we find a different character or reach the end
+ while j < n && chars[j] == chars[i] {
+ j += 1;
+ }
+
+ // place the character at the new position
+ // e.g. if we have aabbccc, we place a at the start of the array
+ chars[new_len] = chars[i];
+ new_len += 1;
+
+ // if the length of the group of characters is greater than 1
+ // i.e. suppose if new_len is 12, we need to place 12 as characters [..., '1','2', ...]
+ if j - i > 1 {
+ for c in (j - i).to_string().chars() {
+ chars[new_len] = c;
+ new_len += 1;
+ }
+ }
+
+ // place i at same position as j,
+ // i.e. the start of the next group of characters
+ i = j;
+ }
+
+ new_len as i32
+ }
+}
+
+
You are given two non-empty linked lists representing two non-negative integers. The most significant digit comes first and each of their nodes contains a single digit. Add the two numbers and return the sum as a linked list.
You may assume the two numbers do not contain any leading zero, except the number 0 itself.
`,19),e=[o];function t(r,c,D,A,y,C){return a(),n("div",null,e)}const d=s(p,[["render",t]]);export{F as __pageData,d as default};
diff --git a/assets/solution_0401-0500_445 - Add Two Numbers II.md.f824629e.lean.js b/assets/solution_0401-0500_445 - Add Two Numbers II.md.f824629e.lean.js
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..80517a5f
--- /dev/null
+++ b/assets/solution_0401-0500_445 - Add Two Numbers II.md.f824629e.lean.js
@@ -0,0 +1 @@
+import{_ as s,o as a,c as n,a as l}from"./app.e4604e86.js";const F=JSON.parse('{"title":"445. Add Two Numbers II","description":"","frontmatter":{},"headers":[{"level":2,"title":"Problem Statement:","slug":"problem-statement","link":"#problem-statement","children":[{"level":3,"title":"Example 1:","slug":"example-1","link":"#example-1","children":[]},{"level":3,"title":"Example 2:","slug":"example-2","link":"#example-2","children":[]},{"level":3,"title":"Example 3:","slug":"example-3","link":"#example-3","children":[]},{"level":3,"title":"Constraints:","slug":"constraints","link":"#constraints","children":[]}]},{"level":2,"title":"Solution:","slug":"solution","link":"#solution","children":[{"level":3,"title":"...","slug":"","link":"#","children":[]}]}],"relativePath":"solution/0401-0500/445 - Add Two Numbers II.md","lastUpdated":1671291107000}'),p={name:"solution/0401-0500/445 - Add Two Numbers II.md"},o=l("",19),e=[o];function t(r,c,D,A,y,C){return a(),n("div",null,e)}const d=s(p,[["render",t]]);export{F as __pageData,d as default};
diff --git a/assets/solution_0401-0500_448 - Find All Numbers Disappeared in an Array.md.84c610eb.js b/assets/solution_0401-0500_448 - Find All Numbers Disappeared in an Array.md.84c610eb.js
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..fac7baae
--- /dev/null
+++ b/assets/solution_0401-0500_448 - Find All Numbers Disappeared in an Array.md.84c610eb.js
@@ -0,0 +1,25 @@
+import{_ as s,o as a,c as n,a as l}from"./app.e4604e86.js";const d=JSON.parse('{"title":"448. Find All Numbers Disappeared in an Array","description":"","frontmatter":{},"headers":[{"level":2,"title":"Problem Statement","slug":"problem-statement","link":"#problem-statement","children":[]},{"level":2,"title":"Solution:","slug":"solution","link":"#solution","children":[{"level":3,"title":"...","slug":"","link":"#","children":[]}]}],"relativePath":"solution/0401-0500/448 - Find All Numbers Disappeared in an Array.md","lastUpdated":1677645016000}'),e={name:"solution/0401-0500/448 - Find All Numbers Disappeared in an Array.md"},o=l(`
Given an array nums of n integers where nums[i] is in the range [1, n], return an array of all the integers in the range[1, n]that do not appear innums.
Example 1:
Input: nums = [4,3,2,7,8,2,3,1]
+Output: [5,6]
+
Example 2:
Input: nums = [1,1]
+Output: [2]
+
Constraints:
n == nums.length
1 <= n <= 105
1 <= nums[i] <= n
Follow up: Could you do it without extra space and in O(n) runtime? You may assume the returned list does not count as extra space.
Click to open Hints
This is a really easy problem if you decide to use additional memory. For those trying to write an initial solution using additional memory, think counters!
However, the trick really is to not use any additional space than what is already available to use. Sometimes, multiple passes over the input array help find the solution. However, there's an interesting piece of information in this problem that makes it easy to re-use the input array itself for the solution.
The problem specifies that the numbers in the array will be in the range [1, n] where n is the number of elements in the array. Can we use this information and modify the array in-place somehow to find what we need?
`,19),p=[o];function t(r,c,i,y,C,D){return a(),n("div",null,p)}const A=s(e,[["render",t]]);export{d as __pageData,A as default};
diff --git a/assets/solution_0401-0500_448 - Find All Numbers Disappeared in an Array.md.84c610eb.lean.js b/assets/solution_0401-0500_448 - Find All Numbers Disappeared in an Array.md.84c610eb.lean.js
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..22ca8f8a
--- /dev/null
+++ b/assets/solution_0401-0500_448 - Find All Numbers Disappeared in an Array.md.84c610eb.lean.js
@@ -0,0 +1 @@
+import{_ as s,o as a,c as n,a as l}from"./app.e4604e86.js";const d=JSON.parse('{"title":"448. Find All Numbers Disappeared in an Array","description":"","frontmatter":{},"headers":[{"level":2,"title":"Problem Statement","slug":"problem-statement","link":"#problem-statement","children":[]},{"level":2,"title":"Solution:","slug":"solution","link":"#solution","children":[{"level":3,"title":"...","slug":"","link":"#","children":[]}]}],"relativePath":"solution/0401-0500/448 - Find All Numbers Disappeared in an Array.md","lastUpdated":1677645016000}'),e={name:"solution/0401-0500/448 - Find All Numbers Disappeared in an Array.md"},o=l("",19),p=[o];function t(r,c,i,y,C,D){return a(),n("div",null,p)}const A=s(e,[["render",t]]);export{d as __pageData,A as default};
diff --git a/assets/solution_0401-0500_461 - Hamming Distance.md.2603ff11.js b/assets/solution_0401-0500_461 - Hamming Distance.md.2603ff11.js
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..da9b93b9
--- /dev/null
+++ b/assets/solution_0401-0500_461 - Hamming Distance.md.2603ff11.js
@@ -0,0 +1,28 @@
+import{_ as s,o as a,c as n,a as l}from"./app.e4604e86.js";const F=JSON.parse('{"title":"461. Hamming Distance","description":"","frontmatter":{},"headers":[{"level":2,"title":"Problem Statement","slug":"problem-statement","link":"#problem-statement","children":[]},{"level":2,"title":"Solution:","slug":"solution","link":"#solution","children":[{"level":3,"title":"...","slug":"","link":"#","children":[]}]}],"relativePath":"solution/0401-0500/461 - Hamming Distance.md","lastUpdated":1677645016000}'),p={name:"solution/0401-0500/461 - Hamming Distance.md"},o=l(`
`,17),e=[o];function t(c,r,i,C,D,y){return a(),n("div",null,e)}const d=s(p,[["render",t]]);export{F as __pageData,d as default};
diff --git a/assets/solution_0401-0500_461 - Hamming Distance.md.2603ff11.lean.js b/assets/solution_0401-0500_461 - Hamming Distance.md.2603ff11.lean.js
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..df23151b
--- /dev/null
+++ b/assets/solution_0401-0500_461 - Hamming Distance.md.2603ff11.lean.js
@@ -0,0 +1 @@
+import{_ as s,o as a,c as n,a as l}from"./app.e4604e86.js";const F=JSON.parse('{"title":"461. Hamming Distance","description":"","frontmatter":{},"headers":[{"level":2,"title":"Problem Statement","slug":"problem-statement","link":"#problem-statement","children":[]},{"level":2,"title":"Solution:","slug":"solution","link":"#solution","children":[{"level":3,"title":"...","slug":"","link":"#","children":[]}]}],"relativePath":"solution/0401-0500/461 - Hamming Distance.md","lastUpdated":1677645016000}'),p={name:"solution/0401-0500/461 - Hamming Distance.md"},o=l("",17),e=[o];function t(c,r,i,C,D,y){return a(),n("div",null,e)}const d=s(p,[["render",t]]);export{F as __pageData,d as default};
diff --git a/assets/solution_0401-0500_463 - Island Perimeter.md.13bee12f.js b/assets/solution_0401-0500_463 - Island Perimeter.md.13bee12f.js
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..21f00933
--- /dev/null
+++ b/assets/solution_0401-0500_463 - Island Perimeter.md.13bee12f.js
@@ -0,0 +1,32 @@
+import{_ as s,o as a,c as n,a as l}from"./app.e4604e86.js";const d=JSON.parse('{"title":"463. Island Perimeter","description":"","frontmatter":{},"headers":[{"level":2,"title":"Problem Statement","slug":"problem-statement","link":"#problem-statement","children":[]},{"level":2,"title":"Solution:","slug":"solution","link":"#solution","children":[{"level":3,"title":"...","slug":"","link":"#","children":[]}]}],"relativePath":"solution/0401-0500/463 - Island Perimeter.md","lastUpdated":1680513503000}'),p={name:"solution/0401-0500/463 - Island Perimeter.md"},e=l(`
You are given row x colgrid representing a map where grid[i][j] = 1 represents land and grid[i][j] = 0 represents water.
Grid cells are connected horizontally/vertically (not diagonally). The grid is completely surrounded by water, and there is exactly one island (i.e., one or more connected land cells).
The island doesn't have "lakes", meaning the water inside isn't connected to the water around the island. One cell is a square with side length 1. The grid is rectangular, width and height don't exceed 100. Determine the perimeter of the island.
Example 1:
Input: grid = [[0,1,0,0],[1,1,1,0],[0,1,0,0],[1,1,0,0]]
+Output: 16
+Explanation: The perimeter is the 16 yellow stripes in the image above.
+
`,21),o=[e];function t(r,c,i,C,D,y){return a(),n("div",null,o)}const F=s(p,[["render",t]]);export{d as __pageData,F as default};
diff --git a/assets/solution_0401-0500_463 - Island Perimeter.md.13bee12f.lean.js b/assets/solution_0401-0500_463 - Island Perimeter.md.13bee12f.lean.js
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..fc543aae
--- /dev/null
+++ b/assets/solution_0401-0500_463 - Island Perimeter.md.13bee12f.lean.js
@@ -0,0 +1 @@
+import{_ as s,o as a,c as n,a as l}from"./app.e4604e86.js";const d=JSON.parse('{"title":"463. Island Perimeter","description":"","frontmatter":{},"headers":[{"level":2,"title":"Problem Statement","slug":"problem-statement","link":"#problem-statement","children":[]},{"level":2,"title":"Solution:","slug":"solution","link":"#solution","children":[{"level":3,"title":"...","slug":"","link":"#","children":[]}]}],"relativePath":"solution/0401-0500/463 - Island Perimeter.md","lastUpdated":1680513503000}'),p={name:"solution/0401-0500/463 - Island Perimeter.md"},e=l("",21),o=[e];function t(r,c,i,C,D,y){return a(),n("div",null,o)}const F=s(p,[["render",t]]);export{d as __pageData,F as default};
diff --git a/assets/solution_0401-0500_476 - Number Complement.md.71b7487d.js b/assets/solution_0401-0500_476 - Number Complement.md.71b7487d.js
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..367ee896
--- /dev/null
+++ b/assets/solution_0401-0500_476 - Number Complement.md.71b7487d.js
@@ -0,0 +1,24 @@
+import{_ as s,o as n,c as a,a as l}from"./app.e4604e86.js";const A=JSON.parse('{"title":"476. Number Complement","description":"","frontmatter":{},"headers":[{"level":2,"title":"Problem Statement","slug":"problem-statement","link":"#problem-statement","children":[]},{"level":2,"title":"Solution:","slug":"solution","link":"#solution","children":[{"level":3,"title":"...","slug":"","link":"#","children":[]}]}],"relativePath":"solution/0401-0500/476 - Number Complement.md","lastUpdated":1677645016000}'),e={name:"solution/0401-0500/476 - Number Complement.md"},o=l(`
The complement of an integer is the integer you get when you flip all the 0's to 1's and all the 1's to 0's in its binary representation.
For example, The integer 5 is "101" in binary and its complement is "010" which is the integer 2.
Given an integer num, return its complement.
Example 1:
Input: num = 5
+Output: 2
+Explanation: The binary representation of 5 is 101 (no leading zero bits), and its complement is 010. So you need to output 2.
+
Example 2:
Input: num = 1
+Output: 0
+Explanation: The binary representation of 1 is 1 (no leading zero bits), and its complement is 0. So you need to output 0.
+
You are given a license key represented as a string s that consists of only alphanumeric characters and dashes. The string is separated into n + 1 groups by n dashes. You are also given an integer k.
We want to reformat the string s such that each group contains exactly k characters, except for the first group, which could be shorter than k but still must contain at least one character. Furthermore, there must be a dash inserted between two groups, and you should convert all lowercase letters to uppercase.
Return the reformatted license key.
Example 1:
Input: s = "5F3Z-2e-9-w", k = 4
+Output: "5F3Z-2E9W"
+Explanation: The string s has been split into two parts, each part has 4 characters.
+Note that the two extra dashes are not needed and can be removed.
+
Example 2:
Input: s = "2-5g-3-J", k = 2
+Output: "2-5G-3J"
+Explanation: The string s has been split into three parts, each part has 2 characters except the first part as it could be shorter as mentioned above.
+
Constraints:
1 <= s.length <= 105
s consists of English letters, digits, and dashes '-'.
Given a binary array nums, return the maximum number of consecutive 1's in the array.
Example 1:
Input: nums = [1,1,0,1,1,1]
+Output: 3
+Explanation: The first two digits or the last three digits are consecutive 1s. The maximum number of consecutive 1s is 3.
+
Example 2:
Input: nums = [1,0,1,1,0,1]
+Output: 2
+
Constraints:
1 <= nums.length <= 105
nums[i] is either 0 or 1.
Click to open Hints
You need to think about two things as far as any window is concerned. One is the starting point for the window. How do you detect that a new window of 1s has started? The next part is detecting the ending point for this window.
How do you detect the ending point for an existing window? If you figure these two things out, you will be able to detect the windows of consecutive ones. All that remains afterward is to find the longest such window and return the size.
`,17),p=[o];function t(c,r,i,C,D,y){return n(),a("div",null,p)}const F=s(e,[["render",t]]);export{d as __pageData,F as default};
diff --git a/assets/solution_0401-0500_485 - Max Consecutive Ones.md.7b21de3a.lean.js b/assets/solution_0401-0500_485 - Max Consecutive Ones.md.7b21de3a.lean.js
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..915c858d
--- /dev/null
+++ b/assets/solution_0401-0500_485 - Max Consecutive Ones.md.7b21de3a.lean.js
@@ -0,0 +1 @@
+import{_ as s,o as n,c as a,a as l}from"./app.e4604e86.js";const d=JSON.parse('{"title":"485. Max Consecutive Ones","description":"","frontmatter":{},"headers":[{"level":2,"title":"Problem Statement","slug":"problem-statement","link":"#problem-statement","children":[]},{"level":2,"title":"Solution:","slug":"solution","link":"#solution","children":[{"level":3,"title":"...","slug":"","link":"#","children":[]}]}],"relativePath":"solution/0401-0500/485 - Max Consecutive Ones.md","lastUpdated":1677645016000}'),e={name:"solution/0401-0500/485 - Max Consecutive Ones.md"},o=l("",17),p=[o];function t(c,r,i,C,D,y){return n(),a("div",null,p)}const F=s(e,[["render",t]]);export{d as __pageData,F as default};
diff --git a/assets/solution_0401-0500_492 - Construct the Rectangle.md.8f462143.js b/assets/solution_0401-0500_492 - Construct the Rectangle.md.8f462143.js
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..202244f6
--- /dev/null
+++ b/assets/solution_0401-0500_492 - Construct the Rectangle.md.8f462143.js
@@ -0,0 +1,25 @@
+import{_ as s,o as a,c as n,a as e}from"./app.e4604e86.js";const h=JSON.parse('{"title":"492. Construct the Rectangle","description":"","frontmatter":{},"headers":[{"level":2,"title":"Problem Statement","slug":"problem-statement","link":"#problem-statement","children":[]},{"level":2,"title":"Solution:","slug":"solution","link":"#solution","children":[{"level":3,"title":"...","slug":"","link":"#","children":[]}]}],"relativePath":"solution/0401-0500/492 - Construct the Rectangle.md","lastUpdated":1677645016000}'),l={name:"solution/0401-0500/492 - Construct the Rectangle.md"},o=e(`
A web developer needs to know how to design a web page's size. So, given a specific rectangular web page’s area, your job by now is to design a rectangular web page, whose length L and width W satisfy the following requirements:
The area of the rectangular web page you designed must equal to the given target area.
The width W should not be larger than the length L, which means L >= W.
The difference between length L and width W should be as small as possible.
Return an array [L, W] where L and W are the length and width of the web page you designed in sequence.
Example 1:
Input: area = 4
+Output: [2,2]
+Explanation: The target area is 4, and all the possible ways to construct it are [1,4], [2,2], [4,1].
+But according to requirement 2, [1,4] is illegal; according to requirement 3, [4,1] is not optimal compared to [2,2]. So the length L is 2, and the width W is 2.
+
Example 2:
Input: area = 37
+Output: [37,1]
+
Example 3:
Input: area = 122122
+Output: [427,286]
+
Constraints:
1 <= area <= 107
Click to open Hints
The W is always less than or equal to the square root of the area, so we start searching at sqrt(area) till we find the result.
implSolution{
+pubfnconstruct_rectangle(area:i32)->Vec<i32>{
+letmut w =(area asf64).sqrt()asi32;
+
+ // until the remainder is 0, decrement w
+ // this will find the largest w that is a factor of area
+while area % w !=0{
+ w -=1;
+}
+
+ // return the result
+vec![area / w, w]
+}
+}
+
+
packagemain
+
+typeDirectionint
+
+const(
+ Up Direction =iota
+ Down
+)
+
+funcfindDiagonalOrder(mat [][]int)[]int{
+ direction := Up
+ row, col :=0,0
+ row_len, col_len :=len(mat),len(mat[0])
+ res :=make([]int, row_len*col_len)
+
+for i :=0; i < row_len*col_len; i++{
+ res[i]= mat[row][col]
+
+if direction == Up {
+if row ==0|| col == col_len-1{
+ direction = Down
+
+if col == col_len-1{
+ row++
+}else{
+ col++
+}
+
+}else{
+ row--
+ col++
+}
+}else{
+if col ==0|| row == row_len-1{
+ direction = Up
+
+if row == row_len-1{
+ col++
+}else{
+ row++
+}
+
+}else{
+ row++
+ col--
+}
+}
+}
+
+return res
+}
+
+
rs
enumDirection{
+Up,
+Down,
+}
+
+implSolution{
+pubfnfind_diagonal_order(mat:Vec<Vec<i32>>)->Vec<i32>{
+letmut result =vec![];
+letmut direction =Direction::Up;
+let(mut row,mut col)=(0,0);
+let(row_len, col_len)=(mat.len(), mat[0].len());
+
+while row < row_len && col < col_len {
+ // push the current element to the result vector
+ result.push(mat[row][col]);
+
+match direction {
+Direction::Up=>{
+if row ==0|| col == col_len -1{
+ // if we are at the top row or the rightmost column, change direction to "Down"
+ direction =Direction::Down;
+
+if col == col_len -1{
+ // if at the rightmost column, move to the next row
+ row +=1;
+}else{
+ // otherwise, move to the next column
+ col +=1;
+}
+}else{
+ // move diagonally upward
+ row -=1;
+ col +=1;
+}
+}
+Direction::Down=>{
+if col ==0|| row == row_len -1{
+ // if we are at the leftmost column or the bottom row, change direction to "Up"
+ direction =Direction::Up;
+
+if row == row_len -1{
+ // if at the bottom row, move to the next column
+ col +=1;
+}else{
+ // otherwise, move to the next row
+ row +=1;
+}
+}else{
+ // move diagonally downward
+ row +=1;
+ col -=1;
+}
+}
+}
+}
+
+ result
+}
+}
+
+
Suppose LeetCode will start its IPO soon. In order to sell a good price of its shares to Venture Capital, LeetCode would like to work on some projects to increase its capital before the IPO. Since it has limited resources, it can only finish at most k distinct projects before the IPO. Help LeetCode design the best way to maximize its total capital after finishing at most k distinct projects.
You are given n projects where the ith project has a pure profit profits[i] and a minimum capital of capital[i] is needed to start it.
Initially, you have w capital. When you finish a project, you will obtain its pure profit and the profit will be added to your total capital.
Pick a list of at mostk distinct projects from given projects to maximize your final capital, and return the final maximized capital.
The answer is guaranteed to fit in a 32-bit signed integer.
Example 1:
Input: k = 2, w = 0, profits = [1,2,3], capital = [0,1,1]
+Output: 4
+Explanation: Since your initial capital is 0, you can only start the project indexed 0.
+After finishing it you will obtain profit 1 and your capital becomes 1.
+With capital 1, you can either start the project indexed 1 or the project indexed 2.
+Since you can choose at most 2 projects, you need to finish the project indexed 2 to get the maximum capital.
+Therefore, output the final maximized capital, which is 0 + 1 + 3 = 4.
+
Example 2:
Input: k = 3, w = 0, profits = [1,2,3], capital = [0,1,2]
+Output: 6
+
`,20),e=[o];function t(c,r,D,i,C,y){return a(),n("div",null,e)}const d=s(p,[["render",t]]);export{F as __pageData,d as default};
diff --git a/assets/solution_0501-0600_502 - IPO.md.4354a877.lean.js b/assets/solution_0501-0600_502 - IPO.md.4354a877.lean.js
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..d221bdf3
--- /dev/null
+++ b/assets/solution_0501-0600_502 - IPO.md.4354a877.lean.js
@@ -0,0 +1 @@
+import{_ as s,o as a,c as n,a as l}from"./app.e4604e86.js";const F=JSON.parse('{"title":"502. IPO","description":"","frontmatter":{},"headers":[{"level":2,"title":"Problem Statement","slug":"problem-statement","link":"#problem-statement","children":[]},{"level":2,"title":"Solution:","slug":"solution","link":"#solution","children":[{"level":3,"title":"...","slug":"","link":"#","children":[]}]}],"relativePath":"solution/0501-0600/502 - IPO.md","lastUpdated":1677201121000}'),p={name:"solution/0501-0600/502 - IPO.md"},o=l("",20),e=[o];function t(c,r,D,i,C,y){return a(),n("div",null,e)}const d=s(p,[["render",t]]);export{F as __pageData,d as default};
diff --git a/assets/solution_0501-0600_504 - Base 7.md.9103810c.js b/assets/solution_0501-0600_504 - Base 7.md.9103810c.js
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..bd899956
--- /dev/null
+++ b/assets/solution_0501-0600_504 - Base 7.md.9103810c.js
@@ -0,0 +1,30 @@
+import{_ as s,o as a,c as n,a as l}from"./app.e4604e86.js";const F=JSON.parse('{"title":"504. Base 7","description":"","frontmatter":{},"headers":[{"level":2,"title":"Problem Statement","slug":"problem-statement","link":"#problem-statement","children":[]},{"level":2,"title":"Solution:","slug":"solution","link":"#solution","children":[{"level":3,"title":"...","slug":"","link":"#","children":[]}]}],"relativePath":"solution/0501-0600/504 - Base 7.md","lastUpdated":1677645016000}'),p={name:"solution/0501-0600/504 - Base 7.md"},o=l(`
`,16),e=[o];function t(c,r,D,C,y,A){return a(),n("div",null,e)}const u=s(p,[["render",t]]);export{F as __pageData,u as default};
diff --git a/assets/solution_0501-0600_504 - Base 7.md.9103810c.lean.js b/assets/solution_0501-0600_504 - Base 7.md.9103810c.lean.js
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..41f83c10
--- /dev/null
+++ b/assets/solution_0501-0600_504 - Base 7.md.9103810c.lean.js
@@ -0,0 +1 @@
+import{_ as s,o as a,c as n,a as l}from"./app.e4604e86.js";const F=JSON.parse('{"title":"504. Base 7","description":"","frontmatter":{},"headers":[{"level":2,"title":"Problem Statement","slug":"problem-statement","link":"#problem-statement","children":[]},{"level":2,"title":"Solution:","slug":"solution","link":"#solution","children":[{"level":3,"title":"...","slug":"","link":"#","children":[]}]}],"relativePath":"solution/0501-0600/504 - Base 7.md","lastUpdated":1677645016000}'),p={name:"solution/0501-0600/504 - Base 7.md"},o=l("",16),e=[o];function t(c,r,D,C,y,A){return a(),n("div",null,e)}const u=s(p,[["render",t]]);export{F as __pageData,u as default};
diff --git a/assets/solution_0501-0600_506 - Relative Ranks.md.f3d9e740.js b/assets/solution_0501-0600_506 - Relative Ranks.md.f3d9e740.js
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..75c8694b
--- /dev/null
+++ b/assets/solution_0501-0600_506 - Relative Ranks.md.f3d9e740.js
@@ -0,0 +1,27 @@
+import{_ as s,o as a,c as n,a as l}from"./app.e4604e86.js";const A=JSON.parse('{"title":"506. Relative Ranks","description":"","frontmatter":{},"headers":[{"level":2,"title":"Problem Statement:","slug":"problem-statement","link":"#problem-statement","children":[{"level":3,"title":"Example 1:","slug":"example-1","link":"#example-1","children":[]},{"level":3,"title":"Example 2:","slug":"example-2","link":"#example-2","children":[]},{"level":3,"title":"Constraints:","slug":"constraints","link":"#constraints","children":[]}]},{"level":2,"title":"Solution:","slug":"solution","link":"#solution","children":[{"level":3,"title":"...","slug":"","link":"#","children":[]}]}],"relativePath":"solution/0501-0600/506 - Relative Ranks.md","lastUpdated":1671291107000}'),o={name:"solution/0501-0600/506 - Relative Ranks.md"},e=l(`
You are given an integer array score of size n, where score[i] is the score of the ith athlete in a competition. All the scores are guaranteed to be unique.
The athletes are placed based on their scores, where the 1st place athlete has the highest score, the 2nd place athlete has the 2nd highest score, and so on. The placement of each athlete determines their rank:
The 1st place athlete's rank is "Gold Medal".
The 2nd place athlete's rank is "Silver Medal".
The 3rd place athlete's rank is "Bronze Medal".
For the 4th place to the nth place athlete, their rank is their placement number (i.e., the xth place athlete's rank is "x").
Return an array answer of size n where answer[i] is the rank of the ith athlete.
A perfect number is a positive integer that is equal to the sum of its positive divisors, excluding the number itself. A divisor of an integer x is an integer that can divide x evenly.
Given an integer n, return true if n is a perfect number, otherwise return false.
Example 1:
Input: num = 28
+Output: true
+Explanation: 28 = 1 + 2 + 4 + 7 + 14
+1, 2, 4, 7, and 14 are all divisors of 28.
+
implSolution{
+pubfncheck_perfect_number(num:i32)->bool{
+if num ==1{
+returnfalse;
+}
+
+let(mut sum,mut i)=(1,2);
+
+while i * i <= num {
+ // if i is a factor of num, add i and num / i to sum
+if num % i ==0{
+ sum += i;
+if i * i != num {
+ sum += num / i;
+}
+}
+ i +=1;
+}
+
+ sum == num
+}
+}
+
+
The Fibonacci numbers, commonly denoted F(n) form a sequence, called the Fibonacci sequence, such that each number is the sum of the two preceding ones, starting from 0 and 1. That is,
F(0) = 0, F(1) = 1
+F(n) = F(n - 1) + F(n - 2), for n > 1.
+Given n, calculate F(n).
+
Given a string s, find the longest palindromic subsequence's length in s.
A subsequence is a sequence that can be derived from another sequence by deleting some or no elements without changing the order of the remaining elements.
`,20),o=[e];function t(c,r,i,D,A,y){return n(),a("div",null,o)}const d=s(p,[["render",t]]);export{F as __pageData,d as default};
diff --git a/assets/solution_0501-0600_530 - Minimum Absolute Difference in BST.md.fec8d767.lean.js b/assets/solution_0501-0600_530 - Minimum Absolute Difference in BST.md.fec8d767.lean.js
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..ddb30989
--- /dev/null
+++ b/assets/solution_0501-0600_530 - Minimum Absolute Difference in BST.md.fec8d767.lean.js
@@ -0,0 +1 @@
+import{_ as s,o as n,c as a,a as l}from"./app.e4604e86.js";const F=JSON.parse('{"title":"530. Minimum Absolute Difference in BST","description":"","frontmatter":{},"headers":[{"level":2,"title":"Problem Statement","slug":"problem-statement","link":"#problem-statement","children":[]},{"level":2,"title":"Solution:","slug":"solution","link":"#solution","children":[{"level":3,"title":"...","slug":"","link":"#","children":[]}]}],"relativePath":"solution/0501-0600/530 - Minimum Absolute Difference in BST.md","lastUpdated":1676656807000}'),p={name:"solution/0501-0600/530 - Minimum Absolute Difference in BST.md"},e=l("",20),o=[e];function t(c,r,i,D,A,y){return n(),a("div",null,o)}const d=s(p,[["render",t]]);export{F as __pageData,d as default};
diff --git a/assets/solution_0501-0600_540 - Single Element in a Sorted Array.md.5c58c806.js b/assets/solution_0501-0600_540 - Single Element in a Sorted Array.md.5c58c806.js
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..f6f25e44
--- /dev/null
+++ b/assets/solution_0501-0600_540 - Single Element in a Sorted Array.md.5c58c806.js
@@ -0,0 +1,38 @@
+import{_ as s,o as n,c as a,a as l}from"./app.e4604e86.js";const d=JSON.parse('{"title":"540. Single Element in a Sorted Array","description":"","frontmatter":{},"headers":[{"level":2,"title":"Problem Statement","slug":"problem-statement","link":"#problem-statement","children":[]},{"level":2,"title":"Solution:","slug":"solution","link":"#solution","children":[{"level":3,"title":"...","slug":"","link":"#","children":[]}]}],"relativePath":"solution/0501-0600/540 - Single Element in a Sorted Array.md","lastUpdated":1677028205000}'),e={name:"solution/0501-0600/540 - Single Element in a Sorted Array.md"},p=l(`
packagemain
+
+funcsingleNonDuplicate(nums []int)int{
+ res :=0
+
+for _, num :=range nums {
+// a ^ a = 0
+// a ^ a ^ a = a
+// a ^ a ^ b = b
+// also position of a and b doesn't matter
+ res ^= num
+}
+
+return res
+}
+
+
rs
implSolution{
+pubfnsingle_non_duplicate(nums:Vec<i32>)->i32{
+letmut res =0;
+
+for num in nums {
+ // a ^ a = 0
+ // a ^ a ^ a = a
+ // a ^ a ^ b = b
+ // also position of a and b doesn't matter
+ res ^= num;
+}
+
+ res
+}
+}
+
+
`,18),o=[p];function t(c,r,i,y,C,D){return n(),a("div",null,o)}const F=s(e,[["render",t]]);export{d as __pageData,F as default};
diff --git a/assets/solution_0501-0600_540 - Single Element in a Sorted Array.md.5c58c806.lean.js b/assets/solution_0501-0600_540 - Single Element in a Sorted Array.md.5c58c806.lean.js
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..37e3f638
--- /dev/null
+++ b/assets/solution_0501-0600_540 - Single Element in a Sorted Array.md.5c58c806.lean.js
@@ -0,0 +1 @@
+import{_ as s,o as n,c as a,a as l}from"./app.e4604e86.js";const d=JSON.parse('{"title":"540. Single Element in a Sorted Array","description":"","frontmatter":{},"headers":[{"level":2,"title":"Problem Statement","slug":"problem-statement","link":"#problem-statement","children":[]},{"level":2,"title":"Solution:","slug":"solution","link":"#solution","children":[{"level":3,"title":"...","slug":"","link":"#","children":[]}]}],"relativePath":"solution/0501-0600/540 - Single Element in a Sorted Array.md","lastUpdated":1677028205000}'),e={name:"solution/0501-0600/540 - Single Element in a Sorted Array.md"},p=l("",18),o=[p];function t(c,r,i,y,C,D){return n(),a("div",null,o)}const F=s(e,[["render",t]]);export{d as __pageData,F as default};
diff --git a/assets/solution_0501-0600_541 - Reverse String II.md.436195ea.js b/assets/solution_0501-0600_541 - Reverse String II.md.436195ea.js
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..d0fa3635
--- /dev/null
+++ b/assets/solution_0501-0600_541 - Reverse String II.md.436195ea.js
@@ -0,0 +1,18 @@
+import{_ as s,o as a,c as n,a as e}from"./app.e4604e86.js";const d=JSON.parse('{"title":"541. Reverse String II","description":"","frontmatter":{},"headers":[{"level":2,"title":"Problem Statement:","slug":"problem-statement","link":"#problem-statement","children":[{"level":3,"title":"Example 1:","slug":"example-1","link":"#example-1","children":[]},{"level":3,"title":"Example 2:","slug":"example-2","link":"#example-2","children":[]},{"level":3,"title":"Constraints:","slug":"constraints","link":"#constraints","children":[]}]},{"level":2,"title":"Solution:","slug":"solution","link":"#solution","children":[{"level":3,"title":"...","slug":"","link":"#","children":[]}]}],"relativePath":"solution/0501-0600/541 - Reverse String II.md","lastUpdated":1671291107000}'),l={name:"solution/0501-0600/541 - Reverse String II.md"},o=e(`
Given a string s and an integer k, reverse the first k characters for every 2k characters counting from the start of the string.
If there are fewer than k characters left, reverse all of them. If there are less than 2k but greater than or equal to k characters, then reverse the first k characters and leave the other as original.
publicStringreverseStr(String s,int k){
+String res ="";
+int index =0,
+ flag =0,
+ len = s.length();
+while(index < len){
+StringBuilder sb =newStringBuilder(s.substring(index,(index + k > len)? len : index + k));
+ res +=(flag++%2==0)? sb.reverse(): sb;
+ index += k;
+}
+return res;
+}
+
`,17),e=[o];function t(r,c,D,y,A,C){return a(),n("div",null,e)}const h=s(p,[["render",t]]);export{i as __pageData,h as default};
diff --git a/assets/solution_0501-0600_543 - Diameter of Binary Tree.md.f7974f63.lean.js b/assets/solution_0501-0600_543 - Diameter of Binary Tree.md.f7974f63.lean.js
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..afab0198
--- /dev/null
+++ b/assets/solution_0501-0600_543 - Diameter of Binary Tree.md.f7974f63.lean.js
@@ -0,0 +1 @@
+import{_ as s,o as a,c as n,a as l}from"./app.e4604e86.js";const i=JSON.parse('{"title":"543. Diameter of Binary Tree","description":"","frontmatter":{},"headers":[{"level":2,"title":"Problem Statement:","slug":"problem-statement","link":"#problem-statement","children":[{"level":3,"title":"Example 1:","slug":"example-1","link":"#example-1","children":[]},{"level":3,"title":"Example 2:","slug":"example-2","link":"#example-2","children":[]},{"level":3,"title":"Constraints:","slug":"constraints","link":"#constraints","children":[]}]},{"level":2,"title":"Solution:","slug":"solution","link":"#solution","children":[{"level":3,"title":"...","slug":"","link":"#","children":[]}]}],"relativePath":"solution/0501-0600/543 - Diameter of Binary Tree.md","lastUpdated":1671291107000}'),p={name:"solution/0501-0600/543 - Diameter of Binary Tree.md"},o=l("",17),e=[o];function t(r,c,D,y,A,C){return a(),n("div",null,e)}const h=s(p,[["render",t]]);export{i as __pageData,h as default};
diff --git a/assets/solution_0601-0700_605 - Can Place Flowers.md.8c88c122.js b/assets/solution_0601-0700_605 - Can Place Flowers.md.8c88c122.js
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..a602ca72
--- /dev/null
+++ b/assets/solution_0601-0700_605 - Can Place Flowers.md.8c88c122.js
@@ -0,0 +1,59 @@
+import{_ as s,o as n,c as a,a as l}from"./app.e4604e86.js";const i=JSON.parse('{"title":"605. Can Place Flowers","description":"","frontmatter":{},"headers":[{"level":2,"title":"Problem Statement","slug":"problem-statement","link":"#problem-statement","children":[]},{"level":2,"title":"Solution:","slug":"solution","link":"#solution","children":[{"level":3,"title":"...","slug":"","link":"#","children":[]}]}],"relativePath":"solution/0601-0700/605 - Can Place Flowers.md","lastUpdated":1689264763000}'),p={name:"solution/0601-0700/605 - Can Place Flowers.md"},o=l(`
You have a long flowerbed in which some of the plots are planted, and some are not. However, flowers cannot be planted in adjacent plots.
Given an integer array flowerbed containing 0's and 1's, where 0 means empty and 1 means not empty, and an integer n, return trueifnnew flowers can be planted in theflowerbedwithout violating the no-adjacent-flowers rule andfalseotherwise.
Example 1:
Input: flowerbed = [1,0,0,0,1], n = 1
+Output: true
+
Example 2:
Input: flowerbed = [1,0,0,0,1], n = 2
+Output: false
+
`,17),e=[o];function t(c,r,C,D,y,F){return n(),a("div",null,e)}const d=s(p,[["render",t]]);export{i as __pageData,d as default};
diff --git a/assets/solution_0601-0700_605 - Can Place Flowers.md.8c88c122.lean.js b/assets/solution_0601-0700_605 - Can Place Flowers.md.8c88c122.lean.js
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..c61d9122
--- /dev/null
+++ b/assets/solution_0601-0700_605 - Can Place Flowers.md.8c88c122.lean.js
@@ -0,0 +1 @@
+import{_ as s,o as n,c as a,a as l}from"./app.e4604e86.js";const i=JSON.parse('{"title":"605. Can Place Flowers","description":"","frontmatter":{},"headers":[{"level":2,"title":"Problem Statement","slug":"problem-statement","link":"#problem-statement","children":[]},{"level":2,"title":"Solution:","slug":"solution","link":"#solution","children":[{"level":3,"title":"...","slug":"","link":"#","children":[]}]}],"relativePath":"solution/0601-0700/605 - Can Place Flowers.md","lastUpdated":1689264763000}'),p={name:"solution/0601-0700/605 - Can Place Flowers.md"},o=l("",17),e=[o];function t(c,r,C,D,y,F){return n(),a("div",null,e)}const d=s(p,[["render",t]]);export{i as __pageData,d as default};
diff --git a/assets/solution_0601-0700_652 - Find Duplicate Subtrees.md.3c293139.js b/assets/solution_0601-0700_652 - Find Duplicate Subtrees.md.3c293139.js
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..ab84a1dd
--- /dev/null
+++ b/assets/solution_0601-0700_652 - Find Duplicate Subtrees.md.3c293139.js
@@ -0,0 +1,49 @@
+import{_ as s,o as a,c as n,a as l}from"./app.e4604e86.js";const F=JSON.parse('{"title":"652. Find Duplicate Subtrees","description":"","frontmatter":{},"headers":[{"level":2,"title":"Problem Statement","slug":"problem-statement","link":"#problem-statement","children":[]},{"level":2,"title":"Solution:","slug":"solution","link":"#solution","children":[{"level":3,"title":"...","slug":"","link":"#","children":[]}]}],"relativePath":"solution/0601-0700/652 - Find Duplicate Subtrees.md","lastUpdated":1677645016000}'),p={name:"solution/0601-0700/652 - Find Duplicate Subtrees.md"},o=l(`
packagemain
+
+import"strconv"
+
+// Definition for a binary tree node.
+typeTreeNodestruct{
+ Val int
+ Left *TreeNode
+ Right *TreeNode
+}
+
+funcfindDuplicateSubtrees(root *TreeNode)[]*TreeNode {
+// to store the hash value of subtrees
+ hashMap :=make(map[string]int)
+// to store the result
+ res :=make([]*TreeNode,0)
+// traverse the tree
+traverse(root, hashMap,&res)
+return res
+}
+
+// traverse the tree
+functraverse(root *TreeNode, hashMap map[string]int, res *[]*TreeNode)string{
+// if the root is nil, return "#"
+if root ==nil{
+return"#"
+}
+// traverse the left and right subtree
+ left :=traverse(root.Left, hashMap, res)
+ right :=traverse(root.Right, hashMap, res)
+// get the hash value of the subtree
+ subTree := left +","+ right +","+ strconv.Itoa(root.Val)
+// if the hash value of the subtree is 1, it means that the subtree is duplicated
+if hashMap[subTree]==1{
+*res =append(*res, root)
+}
+// add the hash value of the subtree to the hashMap
+ hashMap[subTree]++
+return subTree
+}
+
+
`,23),e=[o];function t(r,c,D,y,C,A){return a(),n("div",null,e)}const d=s(p,[["render",t]]);export{F as __pageData,d as default};
diff --git a/assets/solution_0601-0700_652 - Find Duplicate Subtrees.md.3c293139.lean.js b/assets/solution_0601-0700_652 - Find Duplicate Subtrees.md.3c293139.lean.js
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..de38fa9b
--- /dev/null
+++ b/assets/solution_0601-0700_652 - Find Duplicate Subtrees.md.3c293139.lean.js
@@ -0,0 +1 @@
+import{_ as s,o as a,c as n,a as l}from"./app.e4604e86.js";const F=JSON.parse('{"title":"652. Find Duplicate Subtrees","description":"","frontmatter":{},"headers":[{"level":2,"title":"Problem Statement","slug":"problem-statement","link":"#problem-statement","children":[]},{"level":2,"title":"Solution:","slug":"solution","link":"#solution","children":[{"level":3,"title":"...","slug":"","link":"#","children":[]}]}],"relativePath":"solution/0601-0700/652 - Find Duplicate Subtrees.md","lastUpdated":1677645016000}'),p={name:"solution/0601-0700/652 - Find Duplicate Subtrees.md"},o=l("",23),e=[o];function t(r,c,D,y,C,A){return a(),n("div",null,e)}const d=s(p,[["render",t]]);export{F as __pageData,d as default};
diff --git a/assets/solution_0601-0700_653 - Two Sum IV - Input is a BST.md.f2c07c17.js b/assets/solution_0601-0700_653 - Two Sum IV - Input is a BST.md.f2c07c17.js
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..d132a18d
--- /dev/null
+++ b/assets/solution_0601-0700_653 - Two Sum IV - Input is a BST.md.f2c07c17.js
@@ -0,0 +1,24 @@
+import{_ as s,o as a,c as n,a as l}from"./app.e4604e86.js";const F=JSON.parse('{"title":"653. Two Sum IV - Input is a BST","description":"","frontmatter":{},"headers":[{"level":2,"title":"Problem Statement:","slug":"problem-statement","link":"#problem-statement","children":[{"level":3,"title":"Example 1:","slug":"example-1","link":"#example-1","children":[]},{"level":3,"title":"Example 2:","slug":"example-2","link":"#example-2","children":[]},{"level":3,"title":"Constraints:","slug":"constraints","link":"#constraints","children":[]}]},{"level":2,"title":"Solution:","slug":"solution","link":"#solution","children":[{"level":3,"title":"...","slug":"","link":"#","children":[]}]}],"relativePath":"solution/0601-0700/653 - Two Sum IV - Input is a BST.md","lastUpdated":1671291107000}'),e={name:"solution/0601-0700/653 - Two Sum IV - Input is a BST.md"},o=l(`
Given the root of a Binary Search Tree and a target number k, return true if there exist two elements in the BST such that their sum is equal to the given target.
`,16),p=[o];function t(r,c,D,i,A,C){return a(),n("div",null,p)}const d=s(e,[["render",t]]);export{F as __pageData,d as default};
diff --git a/assets/solution_0601-0700_653 - Two Sum IV - Input is a BST.md.f2c07c17.lean.js b/assets/solution_0601-0700_653 - Two Sum IV - Input is a BST.md.f2c07c17.lean.js
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..6e01e1cf
--- /dev/null
+++ b/assets/solution_0601-0700_653 - Two Sum IV - Input is a BST.md.f2c07c17.lean.js
@@ -0,0 +1 @@
+import{_ as s,o as a,c as n,a as l}from"./app.e4604e86.js";const F=JSON.parse('{"title":"653. Two Sum IV - Input is a BST","description":"","frontmatter":{},"headers":[{"level":2,"title":"Problem Statement:","slug":"problem-statement","link":"#problem-statement","children":[{"level":3,"title":"Example 1:","slug":"example-1","link":"#example-1","children":[]},{"level":3,"title":"Example 2:","slug":"example-2","link":"#example-2","children":[]},{"level":3,"title":"Constraints:","slug":"constraints","link":"#constraints","children":[]}]},{"level":2,"title":"Solution:","slug":"solution","link":"#solution","children":[{"level":3,"title":"...","slug":"","link":"#","children":[]}]}],"relativePath":"solution/0601-0700/653 - Two Sum IV - Input is a BST.md","lastUpdated":1671291107000}'),e={name:"solution/0601-0700/653 - Two Sum IV - Input is a BST.md"},o=l("",16),p=[o];function t(r,c,D,i,A,C){return a(),n("div",null,p)}const d=s(e,[["render",t]]);export{F as __pageData,d as default};
diff --git a/assets/solution_0601-0700_695 - Max Area of Island.md.04d7865e.js b/assets/solution_0601-0700_695 - Max Area of Island.md.04d7865e.js
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..18fff95b
--- /dev/null
+++ b/assets/solution_0601-0700_695 - Max Area of Island.md.04d7865e.js
@@ -0,0 +1,38 @@
+import{_ as s,o as a,c as n,a as l}from"./app.e4604e86.js";const i=JSON.parse('{"title":"695. Max Area of Island","description":"","frontmatter":{},"headers":[{"level":2,"title":"Problem Statement","slug":"problem-statement","link":"#problem-statement","children":[]},{"level":2,"title":"Solution:","slug":"solution","link":"#solution","children":[{"level":3,"title":"...","slug":"","link":"#","children":[]}]}],"relativePath":"solution/0601-0700/695 - Max Area of Island.md","lastUpdated":1678822270000}'),o={name:"solution/0601-0700/695 - Max Area of Island.md"},p=l(`
You are given an m x n binary matrix grid. An island is a group of 1's (representing land) connected 4-directionally (horizontal or vertical.) You may assume all four edges of the grid are surrounded by water.
The area of an island is the number of cells with a value 1 in the island.
Return the maximum area of an island in grid. If there is no island, return 0.
Example 1:
Input: grid = [[0,0,1,0,0,0,0,1,0,0,0,0,0],[0,0,0,0,0,0,0,1,1,1,0,0,0],[0,1,1,0,1,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0],[0,1,0,0,1,1,0,0,1,0,1,0,0],[0,1,0,0,1,1,0,0,1,1,1,0,0],[0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,1,0,0],[0,0,0,0,0,0,0,1,1,1,0,0,0],[0,0,0,0,0,0,0,1,1,0,0,0,0]]
+Output: 6
+Explanation: The answer is not 11, because the island must be connected 4-directionally.
+
`,19),e=[p];function t(r,c,D,C,y,F){return a(),n("div",null,e)}const d=s(o,[["render",t]]);export{i as __pageData,d as default};
diff --git a/assets/solution_0601-0700_695 - Max Area of Island.md.04d7865e.lean.js b/assets/solution_0601-0700_695 - Max Area of Island.md.04d7865e.lean.js
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..36d763b5
--- /dev/null
+++ b/assets/solution_0601-0700_695 - Max Area of Island.md.04d7865e.lean.js
@@ -0,0 +1 @@
+import{_ as s,o as a,c as n,a as l}from"./app.e4604e86.js";const i=JSON.parse('{"title":"695. Max Area of Island","description":"","frontmatter":{},"headers":[{"level":2,"title":"Problem Statement","slug":"problem-statement","link":"#problem-statement","children":[]},{"level":2,"title":"Solution:","slug":"solution","link":"#solution","children":[{"level":3,"title":"...","slug":"","link":"#","children":[]}]}],"relativePath":"solution/0601-0700/695 - Max Area of Island.md","lastUpdated":1678822270000}'),o={name:"solution/0601-0700/695 - Max Area of Island.md"},p=l("",19),e=[p];function t(r,c,D,C,y,F){return a(),n("div",null,e)}const d=s(o,[["render",t]]);export{i as __pageData,d as default};
diff --git a/assets/solution_0701-0800_704 - Binary Search.md.6403df35.js b/assets/solution_0701-0800_704 - Binary Search.md.6403df35.js
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..618ffbd1
--- /dev/null
+++ b/assets/solution_0701-0800_704 - Binary Search.md.6403df35.js
@@ -0,0 +1,23 @@
+import{_ as s,o as a,c as n,a as l}from"./app.e4604e86.js";const d=JSON.parse('{"title":"704. Binary Search","description":"","frontmatter":{},"headers":[{"level":2,"title":"Problem Statement:","slug":"problem-statement","link":"#problem-statement","children":[{"level":3,"title":"Example 1:","slug":"example-1","link":"#example-1","children":[]},{"level":3,"title":"Example 2:","slug":"example-2","link":"#example-2","children":[]},{"level":3,"title":"Constraints:","slug":"constraints","link":"#constraints","children":[]}]},{"level":2,"title":"Solution:","slug":"solution","link":"#solution","children":[{"level":3,"title":"...","slug":"","link":"#","children":[]}]}],"relativePath":"solution/0701-0800/704 - Binary Search.md","lastUpdated":1671291107000}'),e={name:"solution/0701-0800/704 - Binary Search.md"},p=l(`
Given an array of integers nums which is sorted in ascending order, and an integer target, write a function to search target in nums. If target exists, then return its index. Otherwise, return -1.
You must write an algorithm with O(log n) runtime complexity.
Given an array of integers temperatures represents the daily temperatures, return an array answer such that answer[i] is the number of days you have to wait after the ith day to get a warmer temperature. If there is no future day for which this is possible, keep answer[i] == 0 instead.
You're given strings jewels representing the types of stones that are jewels, and stones representing the stones you have. Each character in stones is a type of stone you have. You want to know how many of the stones you have are also jewels.
Letters are case sensitive, so "a" is considered a different type of stone from "A".
`,15),t=[o];function p(r,c,i,d,y,h){return a(),e("div",null,t)}const D=s(l,[["render",p]]);export{C as __pageData,D as default};
diff --git a/assets/solution_0701-0800_771 - Jewels and Stones.md.ec1795d8.lean.js b/assets/solution_0701-0800_771 - Jewels and Stones.md.ec1795d8.lean.js
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..c26f07a2
--- /dev/null
+++ b/assets/solution_0701-0800_771 - Jewels and Stones.md.ec1795d8.lean.js
@@ -0,0 +1 @@
+import{_ as s,o as a,c as e,a as n}from"./app.e4604e86.js";const C=JSON.parse('{"title":"771. Jewels and Stones","description":"","frontmatter":{},"headers":[{"level":2,"title":"Problem Statement:","slug":"problem-statement","link":"#problem-statement","children":[{"level":3,"title":"Example 1:","slug":"example-1","link":"#example-1","children":[]},{"level":3,"title":"Example 2:","slug":"example-2","link":"#example-2","children":[]},{"level":3,"title":"Constraints:","slug":"constraints","link":"#constraints","children":[]}]},{"level":2,"title":"Solution:","slug":"solution","link":"#solution","children":[{"level":3,"title":"...","slug":"","link":"#","children":[]}]}],"relativePath":"solution/0701-0800/771 - Jewels and Stones.md","lastUpdated":1671291107000}'),l={name:"solution/0701-0800/771 - Jewels and Stones.md"},o=n("",15),t=[o];function p(r,c,i,d,y,h){return a(),e("div",null,t)}const D=s(l,[["render",p]]);export{C as __pageData,D as default};
diff --git a/assets/solution_0701-0800_783 - Minimum Distance Between BST Nodes.md.81c07254.js b/assets/solution_0701-0800_783 - Minimum Distance Between BST Nodes.md.81c07254.js
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..3f2140fe
--- /dev/null
+++ b/assets/solution_0701-0800_783 - Minimum Distance Between BST Nodes.md.81c07254.js
@@ -0,0 +1,44 @@
+import{_ as s,o as n,c as a,a as l}from"./app.e4604e86.js";const F=JSON.parse('{"title":"783. Minimum Distance Between BST Nodes","description":"","frontmatter":{},"headers":[{"level":2,"title":"Problem Statement","slug":"problem-statement","link":"#problem-statement","children":[]},{"level":2,"title":"Solution:","slug":"solution","link":"#solution","children":[{"level":3,"title":"...","slug":"","link":"#","children":[]}]}],"relativePath":"solution/0701-0800/783 - Minimum Distance Between BST Nodes.md","lastUpdated":1676656807000}'),p={name:"solution/0701-0800/783 - Minimum Distance Between BST Nodes.md"},e=l(`
`,20),o=[e];function t(c,r,D,i,y,A){return n(),a("div",null,o)}const d=s(p,[["render",t]]);export{F as __pageData,d as default};
diff --git a/assets/solution_0701-0800_783 - Minimum Distance Between BST Nodes.md.81c07254.lean.js b/assets/solution_0701-0800_783 - Minimum Distance Between BST Nodes.md.81c07254.lean.js
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..b6d0486b
--- /dev/null
+++ b/assets/solution_0701-0800_783 - Minimum Distance Between BST Nodes.md.81c07254.lean.js
@@ -0,0 +1 @@
+import{_ as s,o as n,c as a,a as l}from"./app.e4604e86.js";const F=JSON.parse('{"title":"783. Minimum Distance Between BST Nodes","description":"","frontmatter":{},"headers":[{"level":2,"title":"Problem Statement","slug":"problem-statement","link":"#problem-statement","children":[]},{"level":2,"title":"Solution:","slug":"solution","link":"#solution","children":[{"level":3,"title":"...","slug":"","link":"#","children":[]}]}],"relativePath":"solution/0701-0800/783 - Minimum Distance Between BST Nodes.md","lastUpdated":1676656807000}'),p={name:"solution/0701-0800/783 - Minimum Distance Between BST Nodes.md"},e=l("",20),o=[e];function t(c,r,D,i,y,A){return n(),a("div",null,o)}const d=s(p,[["render",t]]);export{F as __pageData,d as default};
diff --git a/assets/solution_0801-0900_875 - Koko Eating Bananas.md.21b969d9.js b/assets/solution_0801-0900_875 - Koko Eating Bananas.md.21b969d9.js
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..d417891d
--- /dev/null
+++ b/assets/solution_0801-0900_875 - Koko Eating Bananas.md.21b969d9.js
@@ -0,0 +1,48 @@
+import{_ as s,o as a,c as n,a as l}from"./app.e4604e86.js";const i=JSON.parse('{"title":"875. Koko Eating Bananas","description":"","frontmatter":{},"headers":[{"level":2,"title":"Problem Statement","slug":"problem-statement","link":"#problem-statement","children":[]},{"level":2,"title":"Solution:","slug":"solution","link":"#solution","children":[{"level":3,"title":"...","slug":"","link":"#","children":[]}]}],"relativePath":"solution/0801-0900/875 - Koko Eating Bananas.md","lastUpdated":1678822270000}'),p={name:"solution/0801-0900/875 - Koko Eating Bananas.md"},o=l(`
Koko loves to eat bananas. There are n piles of bananas, the ith pile has piles[i] bananas. The guards have gone and will come back in h hours.
Koko can decide her bananas-per-hour eating speed of k. Each hour, she chooses some pile of bananas and eats k bananas from that pile. If the pile has less than k bananas, she eats all of them instead and will not eat any more bananas during this hour.
Koko likes to eat slowly but still wants to finish eating all the bananas before the guards return.
Return the minimum integerksuch that she can eat all the bananas withinhhours.
Example 1:
Input: piles = [3,6,7,11], h = 8
+Output: 4
+
Example 2:
Input: piles = [30,11,23,4,20], h = 5
+Output: 30
+
Example 3:
Input: piles = [30,11,23,4,20], h = 6
+Output: 23
+
import math
+
+
+classSolution:
+defminEatingSpeed(self,p: list[int],h:int)->int:
+ left, right =1,max(p)
+
+while left <= right:
+ m =(left+right)//2
+# t = sum((i+m-1)//m for i in p)
+# t = sum(-(-i//m) for i in p)
+ t =sum(math.ceil(i/m)for i in p)
+if t > h:
+ left = m+1
+else:
+ right = m-1
+return left
+
+
`,21),e=[o];function t(c,r,D,y,C,F){return a(),n("div",null,e)}const d=s(p,[["render",t]]);export{i as __pageData,d as default};
diff --git a/assets/solution_0801-0900_875 - Koko Eating Bananas.md.21b969d9.lean.js b/assets/solution_0801-0900_875 - Koko Eating Bananas.md.21b969d9.lean.js
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..fda187a7
--- /dev/null
+++ b/assets/solution_0801-0900_875 - Koko Eating Bananas.md.21b969d9.lean.js
@@ -0,0 +1 @@
+import{_ as s,o as a,c as n,a as l}from"./app.e4604e86.js";const i=JSON.parse('{"title":"875. Koko Eating Bananas","description":"","frontmatter":{},"headers":[{"level":2,"title":"Problem Statement","slug":"problem-statement","link":"#problem-statement","children":[]},{"level":2,"title":"Solution:","slug":"solution","link":"#solution","children":[{"level":3,"title":"...","slug":"","link":"#","children":[]}]}],"relativePath":"solution/0801-0900/875 - Koko Eating Bananas.md","lastUpdated":1678822270000}'),p={name:"solution/0801-0900/875 - Koko Eating Bananas.md"},o=l("",21),e=[o];function t(c,r,D,y,C,F){return a(),n("div",null,e)}const d=s(p,[["render",t]]);export{i as __pageData,d as default};
diff --git a/assets/solution_0801-0900_876 - Middle of the Linked List.md.937594a8.js b/assets/solution_0801-0900_876 - Middle of the Linked List.md.937594a8.js
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..4cb85ff8
--- /dev/null
+++ b/assets/solution_0801-0900_876 - Middle of the Linked List.md.937594a8.js
@@ -0,0 +1,17 @@
+import{_ as s,o as a,c as e,a as n}from"./app.e4604e86.js";const A=JSON.parse('{"title":"876. Middle of the Linked List","description":"","frontmatter":{},"headers":[{"level":2,"title":"Problem Statement:","slug":"problem-statement","link":"#problem-statement","children":[{"level":3,"title":"Example 1:","slug":"example-1","link":"#example-1","children":[]},{"level":3,"title":"Example 2:","slug":"example-2","link":"#example-2","children":[]},{"level":3,"title":"Constraints:","slug":"constraints","link":"#constraints","children":[]}]},{"level":2,"title":"Solution:","slug":"solution","link":"#solution","children":[{"level":3,"title":"...","slug":"","link":"#","children":[]}]}],"relativePath":"solution/0801-0900/876 - Middle of the Linked List.md","lastUpdated":1671291107000}'),l={name:"solution/0801-0900/876 - Middle of the Linked List.md"},t=n(`
`,17),o=[t];function p(r,c,i,d,h,D){return a(),e("div",null,o)}const y=s(l,[["render",p]]);export{A as __pageData,y as default};
diff --git a/assets/solution_0801-0900_876 - Middle of the Linked List.md.937594a8.lean.js b/assets/solution_0801-0900_876 - Middle of the Linked List.md.937594a8.lean.js
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..74df96e8
--- /dev/null
+++ b/assets/solution_0801-0900_876 - Middle of the Linked List.md.937594a8.lean.js
@@ -0,0 +1 @@
+import{_ as s,o as a,c as e,a as n}from"./app.e4604e86.js";const A=JSON.parse('{"title":"876. Middle of the Linked List","description":"","frontmatter":{},"headers":[{"level":2,"title":"Problem Statement:","slug":"problem-statement","link":"#problem-statement","children":[{"level":3,"title":"Example 1:","slug":"example-1","link":"#example-1","children":[]},{"level":3,"title":"Example 2:","slug":"example-2","link":"#example-2","children":[]},{"level":3,"title":"Constraints:","slug":"constraints","link":"#constraints","children":[]}]},{"level":2,"title":"Solution:","slug":"solution","link":"#solution","children":[{"level":3,"title":"...","slug":"","link":"#","children":[]}]}],"relativePath":"solution/0801-0900/876 - Middle of the Linked List.md","lastUpdated":1671291107000}'),l={name:"solution/0801-0900/876 - Middle of the Linked List.md"},t=n("",17),o=[t];function p(r,c,i,d,h,D){return a(),e("div",null,o)}const y=s(l,[["render",p]]);export{A as __pageData,y as default};
diff --git a/assets/solution_0801-0900_888 - Fair Candy Swap.md.53ce1729.js b/assets/solution_0801-0900_888 - Fair Candy Swap.md.53ce1729.js
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..982f600a
--- /dev/null
+++ b/assets/solution_0801-0900_888 - Fair Candy Swap.md.53ce1729.js
@@ -0,0 +1,37 @@
+import{_ as s,o as a,c as n,a as l}from"./app.e4604e86.js";const F=JSON.parse('{"title":"888. Fair Candy Swap","description":"","frontmatter":{},"headers":[{"level":2,"title":"Problem Statement:","slug":"problem-statement","link":"#problem-statement","children":[{"level":3,"title":"Example 1:","slug":"example-1","link":"#example-1","children":[]},{"level":3,"title":"Example 2:","slug":"example-2","link":"#example-2","children":[]},{"level":3,"title":"Example 3:","slug":"example-3","link":"#example-3","children":[]},{"level":3,"title":"Constraints:","slug":"constraints","link":"#constraints","children":[]}]},{"level":2,"title":"Solution:","slug":"solution","link":"#solution","children":[{"level":3,"title":"...","slug":"","link":"#","children":[]}]}],"relativePath":"solution/0801-0900/888 - Fair Candy Swap.md","lastUpdated":1671291107000}'),e={name:"solution/0801-0900/888 - Fair Candy Swap.md"},o=l(`
Alice and Bob have a different total number of candies. You are given two integer arrays aliceSizes and bobSizes where aliceSizes[i] is the number of candies of the ith box of candy that Alice has and bobSizes[j] is the number of candies of the jth box of candy that Bob has.
Since they are friends, they would like to exchange one candy box each so that after the exchange, they both have the same total amount of candy. The total amount of candy a person has is the sum of the number of candies in each box they have.
Return an integer array answer where answer[0] is the number of candies in the box that Alice must exchange, and answer[1] is the number of candies in the box that Bob must exchange. If there are multiple answers, you may return any one of them. It is guaranteed that at least one answer exists.
Given an array of integers nums, sort the array in ascending order and return it.
You must solve the problem without using any built-in functions in O(nlog(n)) time complexity and with the smallest space complexity possible.
Example 1:
Input: nums = [5,2,3,1]
+Output: [1,2,3,5]
+Explanation: After sorting the array, the positions of some numbers are not changed (for example, 2 and 3), while the positions of other numbers are changed (for example, 1 and 5).
+
Example 2:
Input: nums = [5,1,1,2,0,0]
+Output: [0,0,1,1,2,5]
+Explanation: Note that the values of nums are not necessairly unique.
+
`,17),e=[o];function t(c,r,D,C,y,F){return n(),a("div",null,e)}const u=s(p,[["render",t]]);export{i as __pageData,u as default};
diff --git a/assets/solution_0901-1000_912 - Sort an Array.md.c7062b3f.lean.js b/assets/solution_0901-1000_912 - Sort an Array.md.c7062b3f.lean.js
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..0b41f4bc
--- /dev/null
+++ b/assets/solution_0901-1000_912 - Sort an Array.md.c7062b3f.lean.js
@@ -0,0 +1 @@
+import{_ as s,o as n,c as a,a as l}from"./app.e4604e86.js";const i=JSON.parse('{"title":"912. Sort an Array","description":"","frontmatter":{},"headers":[{"level":2,"title":"Problem Statement","slug":"problem-statement","link":"#problem-statement","children":[]},{"level":2,"title":"Solution:","slug":"solution","link":"#solution","children":[{"level":3,"title":"...","slug":"","link":"#","children":[]}]}],"relativePath":"solution/0901-1000/912 - Sort an Array.md","lastUpdated":1677762379000}'),p={name:"solution/0901-1000/912 - Sort an Array.md"},o=l("",17),e=[o];function t(c,r,D,C,y,F){return n(),a("div",null,e)}const u=s(p,[["render",t]]);export{i as __pageData,u as default};
diff --git a/assets/solution_0901-1000_944 - Delete Columns to Make Sorted.md.793056e7.js b/assets/solution_0901-1000_944 - Delete Columns to Make Sorted.md.793056e7.js
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..470fca09
--- /dev/null
+++ b/assets/solution_0901-1000_944 - Delete Columns to Make Sorted.md.793056e7.js
@@ -0,0 +1,47 @@
+import{_ as s,o as n,c as a,a as o}from"./app.e4604e86.js";const F=JSON.parse('{"title":"944. Delete Columns to Make Sorted","description":"","frontmatter":{},"headers":[{"level":2,"title":"Problem Statement","slug":"problem-statement","link":"#problem-statement","children":[]},{"level":2,"title":"Solution:","slug":"solution","link":"#solution","children":[{"level":3,"title":"...","slug":"","link":"#","children":[]}]}],"relativePath":"solution/0901-1000/944 - Delete Columns to Make Sorted.md","lastUpdated":1674028147000}'),l={name:"solution/0901-1000/944 - Delete Columns to Make Sorted.md"},e=o(`
You are given an array of n strings strs, all of the same length.
The strings can be arranged such that there is one on each line, making a grid.
For example, strs = ["abc", "bce", "cae"] can be arranged as follows:
abc
+bce
+cae
+
You want to delete the columns that are not sorted lexicographically. In the above example (0-indexed), columns 0 ('a', 'b', 'c') and 2 ('c', 'e', 'e') are sorted, while column 1 ('b', 'c', 'a') is not, so you would delete column 1.
Return the number of columns that you will delete.
Example 1:
Input: strs = ["cba","daf","ghi"]
+Output: 1
+Explanation: The grid looks as follows:
+ cba
+ daf
+ ghi
+Columns 0 and 2 are sorted, but column 1 is not, so you only need to delete 1 column.
+
Example 2:
Input: strs = ["a","b"]
+Output: 0
+Explanation: The grid looks as follows:
+ a
+ b
+Column 0 is the only column and is sorted, so you will not delete any columns.
+
Example 3:
Input: strs = ["zyx","wvu","tsr"]
+Output: 3
+Explanation: The grid looks as follows:
+ zyx
+ wvu
+ tsr
+All 3 columns are not sorted, so you will delete all 3.
+
`,23),p=[e];function t(r,c,D,y,C,i){return n(),a("div",null,p)}const d=s(l,[["render",t]]);export{F as __pageData,d as default};
diff --git a/assets/solution_0901-1000_944 - Delete Columns to Make Sorted.md.793056e7.lean.js b/assets/solution_0901-1000_944 - Delete Columns to Make Sorted.md.793056e7.lean.js
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..3360f601
--- /dev/null
+++ b/assets/solution_0901-1000_944 - Delete Columns to Make Sorted.md.793056e7.lean.js
@@ -0,0 +1 @@
+import{_ as s,o as n,c as a,a as o}from"./app.e4604e86.js";const F=JSON.parse('{"title":"944. Delete Columns to Make Sorted","description":"","frontmatter":{},"headers":[{"level":2,"title":"Problem Statement","slug":"problem-statement","link":"#problem-statement","children":[]},{"level":2,"title":"Solution:","slug":"solution","link":"#solution","children":[{"level":3,"title":"...","slug":"","link":"#","children":[]}]}],"relativePath":"solution/0901-1000/944 - Delete Columns to Make Sorted.md","lastUpdated":1674028147000}'),l={name:"solution/0901-1000/944 - Delete Columns to Make Sorted.md"},e=o("",23),p=[e];function t(r,c,D,y,C,i){return n(),a("div",null,p)}const d=s(l,[["render",t]]);export{F as __pageData,d as default};
diff --git a/assets/solution_0901-1000_958 - Check Completeness of a Binary Tree.md.f4c7668c.js b/assets/solution_0901-1000_958 - Check Completeness of a Binary Tree.md.f4c7668c.js
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..ea5bc314
--- /dev/null
+++ b/assets/solution_0901-1000_958 - Check Completeness of a Binary Tree.md.f4c7668c.js
@@ -0,0 +1,38 @@
+import{_ as s,o as a,c as n,a as e}from"./app.e4604e86.js";const F=JSON.parse('{"title":"958. Check Completeness of a Binary Tree","description":"","frontmatter":{},"headers":[{"level":2,"title":"Problem Statement","slug":"problem-statement","link":"#problem-statement","children":[]},{"level":2,"title":"Solution:","slug":"solution","link":"#solution","children":[{"level":3,"title":"...","slug":"","link":"#","children":[]}]}],"relativePath":"solution/0901-1000/958 - Check Completeness of a Binary Tree.md","lastUpdated":1680513503000}'),l={name:"solution/0901-1000/958 - Check Completeness of a Binary Tree.md"},p=e(`
Given the root of a binary tree, determine if it is a complete binary tree.
In a complete binary tree, every level, except possibly the last, is completely filled, and all nodes in the last level are as far left as possible. It can have between 1 and 2h nodes inclusive at the last level h.
Example 1:
Input: root = [1,2,3,4,5,6]
+Output: true
+Explanation: Every level before the last is full (ie. levels with node-values {1} and {2, 3}), and all nodes in the last level ({4, 5, 6}) are as far left as possible.
+
Example 2:
Input: root = [1,2,3,4,5,null,7]
+Output: false
+Explanation: The node with value 7 isn't as far left as possible.
+
Constraints:
The number of nodes in the tree is in the range [1, 100].
`,19),o=[p];function t(c,r,i,D,y,C){return a(),n("div",null,o)}const d=s(l,[["render",t]]);export{F as __pageData,d as default};
diff --git a/assets/solution_0901-1000_958 - Check Completeness of a Binary Tree.md.f4c7668c.lean.js b/assets/solution_0901-1000_958 - Check Completeness of a Binary Tree.md.f4c7668c.lean.js
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..7416badb
--- /dev/null
+++ b/assets/solution_0901-1000_958 - Check Completeness of a Binary Tree.md.f4c7668c.lean.js
@@ -0,0 +1 @@
+import{_ as s,o as a,c as n,a as e}from"./app.e4604e86.js";const F=JSON.parse('{"title":"958. Check Completeness of a Binary Tree","description":"","frontmatter":{},"headers":[{"level":2,"title":"Problem Statement","slug":"problem-statement","link":"#problem-statement","children":[]},{"level":2,"title":"Solution:","slug":"solution","link":"#solution","children":[{"level":3,"title":"...","slug":"","link":"#","children":[]}]}],"relativePath":"solution/0901-1000/958 - Check Completeness of a Binary Tree.md","lastUpdated":1680513503000}'),l={name:"solution/0901-1000/958 - Check Completeness of a Binary Tree.md"},p=e("",19),o=[p];function t(c,r,i,D,y,C){return a(),n("div",null,o)}const d=s(l,[["render",t]]);export{F as __pageData,d as default};
diff --git a/assets/solution_0901-1000_997 - Find the Town Judge.md.694eeaa4.js b/assets/solution_0901-1000_997 - Find the Town Judge.md.694eeaa4.js
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..a9197ee8
--- /dev/null
+++ b/assets/solution_0901-1000_997 - Find the Town Judge.md.694eeaa4.js
@@ -0,0 +1,21 @@
+import{_ as s,o as n,c as a,a as l}from"./app.e4604e86.js";const A=JSON.parse('{"title":"997. Find the Town Judge","description":"","frontmatter":{},"headers":[{"level":2,"title":"Problem Statement","slug":"problem-statement","link":"#problem-statement","children":[]},{"level":2,"title":"Solution:","slug":"solution","link":"#solution","children":[{"level":3,"title":"...","slug":"","link":"#","children":[]}]}],"relativePath":"solution/0901-1000/997 - Find the Town Judge.md","lastUpdated":1674542557000}'),e={name:"solution/0901-1000/997 - Find the Town Judge.md"},o=l(`
`,22),p=[o];function t(c,r,i,C,D,d){return n(),a("div",null,p)}const F=s(e,[["render",t]]);export{A as __pageData,F as default};
diff --git a/assets/solution_0901-1000_997 - Find the Town Judge.md.694eeaa4.lean.js b/assets/solution_0901-1000_997 - Find the Town Judge.md.694eeaa4.lean.js
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..00888a99
--- /dev/null
+++ b/assets/solution_0901-1000_997 - Find the Town Judge.md.694eeaa4.lean.js
@@ -0,0 +1 @@
+import{_ as s,o as n,c as a,a as l}from"./app.e4604e86.js";const A=JSON.parse('{"title":"997. Find the Town Judge","description":"","frontmatter":{},"headers":[{"level":2,"title":"Problem Statement","slug":"problem-statement","link":"#problem-statement","children":[]},{"level":2,"title":"Solution:","slug":"solution","link":"#solution","children":[{"level":3,"title":"...","slug":"","link":"#","children":[]}]}],"relativePath":"solution/0901-1000/997 - Find the Town Judge.md","lastUpdated":1674542557000}'),e={name:"solution/0901-1000/997 - Find the Town Judge.md"},o=l("",22),p=[o];function t(c,r,i,C,D,d){return n(),a("div",null,p)}const F=s(e,[["render",t]]);export{A as __pageData,F as default};
diff --git a/assets/solution_1001-1100_1011 - Capacity To Ship Packages Within D Days.md.504fac7a.js b/assets/solution_1001-1100_1011 - Capacity To Ship Packages Within D Days.md.504fac7a.js
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..d0ccd80c
--- /dev/null
+++ b/assets/solution_1001-1100_1011 - Capacity To Ship Packages Within D Days.md.504fac7a.js
@@ -0,0 +1,69 @@
+import{_ as s,o as a,c as n,a as l}from"./app.e4604e86.js";const d=JSON.parse('{"title":"1011. Capacity To Ship Packages Within D Days","description":"","frontmatter":{},"headers":[{"level":2,"title":"Problem Statement","slug":"problem-statement","link":"#problem-statement","children":[]},{"level":2,"title":"Solution:","slug":"solution","link":"#solution","children":[{"level":3,"title":"...","slug":"","link":"#","children":[]}]}],"relativePath":"solution/1001-1100/1011 - Capacity To Ship Packages Within D Days.md","lastUpdated":1677114573000}'),p={name:"solution/1001-1100/1011 - Capacity To Ship Packages Within D Days.md"},o=l(`
A conveyor belt has packages that must be shipped from one port to another within days days.
The ith package on the conveyor belt has a weight of weights[i]. Each day, we load the ship with packages on the conveyor belt (in the order given by weights). We may not load more weight than the maximum weight capacity of the ship.
Return the least weight capacity of the ship that will result in all the packages on the conveyor belt being shipped within days days.
Example 1:
+Input: weights = [1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10], days = 5
+Output: 15
+Explanation: A ship capacity of 15 is the minimum to ship all the packages in 5 days like this:
+1st day: 1, 2, 3, 4, 5
+2nd day: 6, 7
+3rd day: 8
+4th day: 9
+5th day: 10
+
+Note that the cargo must be shipped in the order given, so using a ship of capacity 14 and splitting the packages into parts like (2, 3, 4, 5), (1, 6, 7), (8), (9), (10) is not allowed.
+
Example 2:
+Input: weights = [3,2,2,4,1,4], days = 3
+Output: 6
+Explanation: A ship capacity of 6 is the minimum to ship all the packages in 3 days like this:
+1st day: 3, 2
+2nd day: 2, 4
+3rd day: 1, 4
+
implSolution{
+pubfnship_within_days(weights:Vec<i32>, days:i32)->i32{
+letmut min_cap =0; // it is the max of all weights
+letmut max_cap =0; // sum of all weights
+
+for w in weights.iter(){
+ // assign the max of all weights to min_cap
+ min_cap = min_cap.max(*w);
+ // add all the weights to right
+ max_cap += w;
+}
+
+ // binary search
+while min_cap < max_cap {
+let mid =(min_cap + max_cap)/2;
+letmut days_used =1;
+letmut cur_cap =0;
+
+ // for each weight, if the current capacity + weight is greater than mid,
+ // then we need to use another day
+ // otherwise, we can use the current day
+for w in weights.iter(){
+if cur_cap + w > mid {
+ days_used +=1;
+ cur_cap =0;
+}
+ cur_cap += w;
+}
+
+ // if days_used is greater than days, then we need to increase the capacity
+if days_used > days {
+ min_cap = mid +1;
+}else{
+ max_cap = mid;
+}
+}
+
+ min_cap
+}
+}
+
+
`,21),e=[o];function t(c,r,i,y,C,D){return a(),n("div",null,e)}const F=s(p,[["render",t]]);export{d as __pageData,F as default};
diff --git a/assets/solution_1001-1100_1011 - Capacity To Ship Packages Within D Days.md.504fac7a.lean.js b/assets/solution_1001-1100_1011 - Capacity To Ship Packages Within D Days.md.504fac7a.lean.js
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..ab4e91b9
--- /dev/null
+++ b/assets/solution_1001-1100_1011 - Capacity To Ship Packages Within D Days.md.504fac7a.lean.js
@@ -0,0 +1 @@
+import{_ as s,o as a,c as n,a as l}from"./app.e4604e86.js";const d=JSON.parse('{"title":"1011. Capacity To Ship Packages Within D Days","description":"","frontmatter":{},"headers":[{"level":2,"title":"Problem Statement","slug":"problem-statement","link":"#problem-statement","children":[]},{"level":2,"title":"Solution:","slug":"solution","link":"#solution","children":[{"level":3,"title":"...","slug":"","link":"#","children":[]}]}],"relativePath":"solution/1001-1100/1011 - Capacity To Ship Packages Within D Days.md","lastUpdated":1677114573000}'),p={name:"solution/1001-1100/1011 - Capacity To Ship Packages Within D Days.md"},o=l("",21),e=[o];function t(c,r,i,y,C,D){return a(),n("div",null,e)}const F=s(p,[["render",t]]);export{d as __pageData,F as default};
diff --git a/assets/solution_1001-1100_1029 - Two City Scheduling.md.c22c31a1.js b/assets/solution_1001-1100_1029 - Two City Scheduling.md.c22c31a1.js
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..45d813db
--- /dev/null
+++ b/assets/solution_1001-1100_1029 - Two City Scheduling.md.c22c31a1.js
@@ -0,0 +1,37 @@
+import{_ as s,o as n,c as a,a as l}from"./app.e4604e86.js";const F=JSON.parse('{"title":"1029. Two City Scheduling","description":"","frontmatter":{},"headers":[{"level":2,"title":"Problem Statement","slug":"problem-statement","link":"#problem-statement","children":[]},{"level":2,"title":"Solution:","slug":"solution","link":"#solution","children":[{"level":3,"title":"...","slug":"","link":"#","children":[]}]}],"relativePath":"solution/1001-1100/1029 - Two City Scheduling.md","lastUpdated":1689264763000}'),o={name:"solution/1001-1100/1029 - Two City Scheduling.md"},p=l(`
A company is planning to interview 2n people. Given the array costs where costs[i] = [aCosti, bCosti], the cost of flying the ith person to city a is aCosti, and the cost of flying the ith person to city b is bCosti.
Return the minimum cost to fly every person to a city such that exactly n people arrive in each city.
Example 1:
Input: costs = [[10,20],[30,200],[400,50],[30,20]]
+Output: 110
+Explanation:
+The first person goes to city A for a cost of 10.
+The second person goes to city A for a cost of 30.
+The third person goes to city B for a cost of 50.
+The fourth person goes to city B for a cost of 20.
+
+The total minimum cost is 10 + 30 + 50 + 20 = 110 to have half the people interviewing in each city.
+
implSolution{
+pubfntwo_city_sched_cost(costs:Vec<Vec<i32>>)->i32{
+letmut costs = costs;
+
+letmut total =0;
+let n = costs.len()/2;
+
+ // sort by a gain which company has
+ // by sending a person to city A and not to city B
+ costs.sort_by(|a, b|(a[0]- a[1]).cmp(&(b[0]- b[1])));
+
+ // to optimize the company expenses,
+ // send the first n persons to the city A
+ // and the others to the city B
+for i in0..n {
+ total += costs[i][0]+ costs[i + n][1]; // city A + city B
+}
+
+ total
+}
+}
+
+
`,19),e=[p];function t(c,r,i,y,C,D){return n(),a("div",null,e)}const d=s(o,[["render",t]]);export{F as __pageData,d as default};
diff --git a/assets/solution_1001-1100_1029 - Two City Scheduling.md.c22c31a1.lean.js b/assets/solution_1001-1100_1029 - Two City Scheduling.md.c22c31a1.lean.js
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..46fb5db0
--- /dev/null
+++ b/assets/solution_1001-1100_1029 - Two City Scheduling.md.c22c31a1.lean.js
@@ -0,0 +1 @@
+import{_ as s,o as n,c as a,a as l}from"./app.e4604e86.js";const F=JSON.parse('{"title":"1029. Two City Scheduling","description":"","frontmatter":{},"headers":[{"level":2,"title":"Problem Statement","slug":"problem-statement","link":"#problem-statement","children":[]},{"level":2,"title":"Solution:","slug":"solution","link":"#solution","children":[{"level":3,"title":"...","slug":"","link":"#","children":[]}]}],"relativePath":"solution/1001-1100/1029 - Two City Scheduling.md","lastUpdated":1689264763000}'),o={name:"solution/1001-1100/1029 - Two City Scheduling.md"},p=l("",19),e=[p];function t(c,r,i,y,C,D){return n(),a("div",null,e)}const d=s(o,[["render",t]]);export{F as __pageData,d as default};
diff --git a/assets/solution_1001-1100_1047 - Remove All Adjacent Duplicates In String.md.31288eef.js b/assets/solution_1001-1100_1047 - Remove All Adjacent Duplicates In String.md.31288eef.js
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..8d5c7269
--- /dev/null
+++ b/assets/solution_1001-1100_1047 - Remove All Adjacent Duplicates In String.md.31288eef.js
@@ -0,0 +1,27 @@
+import{_ as s,o as a,c as n,a as l}from"./app.e4604e86.js";const F=JSON.parse('{"title":"1047. Remove All Adjacent Duplicates In String","description":"","frontmatter":{},"headers":[{"level":2,"title":"Problem Statement:","slug":"problem-statement","link":"#problem-statement","children":[{"level":3,"title":"Example 1:","slug":"example-1","link":"#example-1","children":[]},{"level":3,"title":"Explanation:","slug":"explanation","link":"#explanation","children":[]},{"level":3,"title":"Example 2:","slug":"example-2","link":"#example-2","children":[]},{"level":3,"title":"Constraints:","slug":"constraints","link":"#constraints","children":[]}]},{"level":2,"title":"Solution:","slug":"solution","link":"#solution","children":[{"level":3,"title":"...","slug":"","link":"#","children":[]}]}],"relativePath":"solution/1001-1100/1047 - Remove All Adjacent Duplicates In String.md","lastUpdated":1671697454000}'),e={name:"solution/1001-1100/1047 - Remove All Adjacent Duplicates In String.md"},o=l(`
You are given a string s consisting of lowercase English letters. A duplicate removal consists of choosing two adjacent and equal letters and removing them.
We repeatedly make duplicate removals on s until we no longer can.
Return the final string after all such duplicate removals have been made. It can be proven that the answer is unique.
For example, in "abbaca" we could remove "bb" since the letters are adjacent and equal, and this is the only possible move. The result of this move is that the string is "aaca", of which only "aa" is possible, so the final string is "ca".
+
`,18),p=[o];function t(c,r,i,D,A,y){return a(),n("div",null,p)}const d=s(e,[["render",t]]);export{F as __pageData,d as default};
diff --git a/assets/solution_1001-1100_1047 - Remove All Adjacent Duplicates In String.md.31288eef.lean.js b/assets/solution_1001-1100_1047 - Remove All Adjacent Duplicates In String.md.31288eef.lean.js
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..b45ab6ca
--- /dev/null
+++ b/assets/solution_1001-1100_1047 - Remove All Adjacent Duplicates In String.md.31288eef.lean.js
@@ -0,0 +1 @@
+import{_ as s,o as a,c as n,a as l}from"./app.e4604e86.js";const F=JSON.parse('{"title":"1047. Remove All Adjacent Duplicates In String","description":"","frontmatter":{},"headers":[{"level":2,"title":"Problem Statement:","slug":"problem-statement","link":"#problem-statement","children":[{"level":3,"title":"Example 1:","slug":"example-1","link":"#example-1","children":[]},{"level":3,"title":"Explanation:","slug":"explanation","link":"#explanation","children":[]},{"level":3,"title":"Example 2:","slug":"example-2","link":"#example-2","children":[]},{"level":3,"title":"Constraints:","slug":"constraints","link":"#constraints","children":[]}]},{"level":2,"title":"Solution:","slug":"solution","link":"#solution","children":[{"level":3,"title":"...","slug":"","link":"#","children":[]}]}],"relativePath":"solution/1001-1100/1047 - Remove All Adjacent Duplicates In String.md","lastUpdated":1671697454000}'),e={name:"solution/1001-1100/1047 - Remove All Adjacent Duplicates In String.md"},o=l("",18),p=[o];function t(c,r,i,D,A,y){return a(),n("div",null,p)}const d=s(e,[["render",t]]);export{F as __pageData,d as default};
diff --git a/assets/solution_1001-1100_1092 - Shortest Common Supersequence.md.edf11803.js b/assets/solution_1001-1100_1092 - Shortest Common Supersequence.md.edf11803.js
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..229a6c31
--- /dev/null
+++ b/assets/solution_1001-1100_1092 - Shortest Common Supersequence.md.edf11803.js
@@ -0,0 +1,51 @@
+import{_ as s,o as a,c as n,a as l}from"./app.e4604e86.js";const i=JSON.parse('{"title":"1092. Shortest Common Supersequence","description":"","frontmatter":{},"headers":[{"level":2,"title":"Problem Statement:","slug":"problem-statement","link":"#problem-statement","children":[{"level":3,"title":"Example 1:","slug":"example-1","link":"#example-1","children":[]},{"level":3,"title":"Example 2:","slug":"example-2","link":"#example-2","children":[]},{"level":3,"title":"Constraints:","slug":"constraints","link":"#constraints","children":[]}]},{"level":2,"title":"Solution:","slug":"solution","link":"#solution","children":[{"level":3,"title":"...","slug":"","link":"#","children":[]}]}],"relativePath":"solution/1001-1100/1092 - Shortest Common Supersequence.md","lastUpdated":1671291107000}'),p={name:"solution/1001-1100/1092 - Shortest Common Supersequence.md"},o=l(`
Given two strings str1 and str2, return the shortest string that has both str1 and str2 as subsequences. If there are multiple valid strings, return any of them.
A string s is a subsequence of string t if deleting some number of characters from t (possibly 0) results in the string s.
Input: str1 = "abac", str2 = "cab"
+Output: "cabac"
+Explanation:
+str1 = "abac" is a subsequence of "cabac" because we can delete the first "c".
+str2 = "cab" is a subsequence of "cabac" because we can delete the last "ac".
+The answer provided is the shortest such string that satisfies these properties.
+
`,15),e=[o];function t(c,r,D,C,y,F){return a(),n("div",null,e)}const d=s(p,[["render",t]]);export{i as __pageData,d as default};
diff --git a/assets/solution_1001-1100_1092 - Shortest Common Supersequence.md.edf11803.lean.js b/assets/solution_1001-1100_1092 - Shortest Common Supersequence.md.edf11803.lean.js
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..56906b87
--- /dev/null
+++ b/assets/solution_1001-1100_1092 - Shortest Common Supersequence.md.edf11803.lean.js
@@ -0,0 +1 @@
+import{_ as s,o as a,c as n,a as l}from"./app.e4604e86.js";const i=JSON.parse('{"title":"1092. Shortest Common Supersequence","description":"","frontmatter":{},"headers":[{"level":2,"title":"Problem Statement:","slug":"problem-statement","link":"#problem-statement","children":[{"level":3,"title":"Example 1:","slug":"example-1","link":"#example-1","children":[]},{"level":3,"title":"Example 2:","slug":"example-2","link":"#example-2","children":[]},{"level":3,"title":"Constraints:","slug":"constraints","link":"#constraints","children":[]}]},{"level":2,"title":"Solution:","slug":"solution","link":"#solution","children":[{"level":3,"title":"...","slug":"","link":"#","children":[]}]}],"relativePath":"solution/1001-1100/1092 - Shortest Common Supersequence.md","lastUpdated":1671291107000}'),p={name:"solution/1001-1100/1092 - Shortest Common Supersequence.md"},o=l("",15),e=[o];function t(c,r,D,C,y,F){return a(),n("div",null,e)}const d=s(p,[["render",t]]);export{i as __pageData,d as default};
diff --git a/assets/solution_1101-1200_1108 - Defanging an IP Address.md.947c6073.js b/assets/solution_1101-1200_1108 - Defanging an IP Address.md.947c6073.js
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..1962d4c3
--- /dev/null
+++ b/assets/solution_1101-1200_1108 - Defanging an IP Address.md.947c6073.js
@@ -0,0 +1,22 @@
+import{_ as s,o as a,c as n,a as l}from"./app.e4604e86.js";const y=JSON.parse('{"title":"1108. Defanging an IP Address","description":"","frontmatter":{},"headers":[{"level":2,"title":"Problem Statement","slug":"problem-statement","link":"#problem-statement","children":[]},{"level":2,"title":"Solution:","slug":"solution","link":"#solution","children":[{"level":3,"title":"...","slug":"","link":"#","children":[]}]}],"relativePath":"solution/1101-1200/1108 - Defanging an IP Address.md","lastUpdated":1677762379000}'),e={name:"solution/1101-1200/1108 - Defanging an IP Address.md"},p=l(`
`,17),o=[p];function t(r,c,i,d,D,C){return a(),n("div",null,o)}const F=s(e,[["render",t]]);export{y as __pageData,F as default};
diff --git a/assets/solution_1101-1200_1108 - Defanging an IP Address.md.947c6073.lean.js b/assets/solution_1101-1200_1108 - Defanging an IP Address.md.947c6073.lean.js
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..eeced96e
--- /dev/null
+++ b/assets/solution_1101-1200_1108 - Defanging an IP Address.md.947c6073.lean.js
@@ -0,0 +1 @@
+import{_ as s,o as a,c as n,a as l}from"./app.e4604e86.js";const y=JSON.parse('{"title":"1108. Defanging an IP Address","description":"","frontmatter":{},"headers":[{"level":2,"title":"Problem Statement","slug":"problem-statement","link":"#problem-statement","children":[]},{"level":2,"title":"Solution:","slug":"solution","link":"#solution","children":[{"level":3,"title":"...","slug":"","link":"#","children":[]}]}],"relativePath":"solution/1101-1200/1108 - Defanging an IP Address.md","lastUpdated":1677762379000}'),e={name:"solution/1101-1200/1108 - Defanging an IP Address.md"},p=l("",17),o=[p];function t(r,c,i,d,D,C){return a(),n("div",null,o)}const F=s(e,[["render",t]]);export{y as __pageData,F as default};
diff --git a/assets/solution_1101-1200_1143 - Longest Common Subsequence.md.301e9543.js b/assets/solution_1101-1200_1143 - Longest Common Subsequence.md.301e9543.js
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..c5c411a8
--- /dev/null
+++ b/assets/solution_1101-1200_1143 - Longest Common Subsequence.md.301e9543.js
@@ -0,0 +1,26 @@
+import{_ as s,o as n,c as a,a as l}from"./app.e4604e86.js";const F=JSON.parse('{"title":"1143. Longest Common Subsequence","description":"","frontmatter":{},"headers":[{"level":2,"title":"Problem Statement:","slug":"problem-statement","link":"#problem-statement","children":[{"level":3,"title":"Example 1:","slug":"example-1","link":"#example-1","children":[]},{"level":3,"title":"Example 2:","slug":"example-2","link":"#example-2","children":[]},{"level":3,"title":"Example 3:","slug":"example-3","link":"#example-3","children":[]},{"level":3,"title":"Constraints:","slug":"constraints","link":"#constraints","children":[]}]},{"level":2,"title":"Solution:","slug":"solution","link":"#solution","children":[{"level":3,"title":"...","slug":"","link":"#","children":[]}]}],"relativePath":"solution/1101-1200/1143 - Longest Common Subsequence.md","lastUpdated":1671291107000}'),o={name:"solution/1101-1200/1143 - Longest Common Subsequence.md"},e=l(`
Given two strings text1 and text2, return the length of their longest common subsequence. If there is no common subsequence, return 0.
A subsequence of a string is a new string generated from the original string with some characters (can be none) deleted without changing the relative order of the remaining characters.
For example, "ace" is a subsequence of "abcde". A common subsequence of two strings is a subsequence that is common to both strings.
`,18),p=[e];function t(c,r,D,C,y,A){return n(),a("div",null,p)}const d=s(o,[["render",t]]);export{F as __pageData,d as default};
diff --git a/assets/solution_1101-1200_1143 - Longest Common Subsequence.md.301e9543.lean.js b/assets/solution_1101-1200_1143 - Longest Common Subsequence.md.301e9543.lean.js
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..ad2030a7
--- /dev/null
+++ b/assets/solution_1101-1200_1143 - Longest Common Subsequence.md.301e9543.lean.js
@@ -0,0 +1 @@
+import{_ as s,o as n,c as a,a as l}from"./app.e4604e86.js";const F=JSON.parse('{"title":"1143. Longest Common Subsequence","description":"","frontmatter":{},"headers":[{"level":2,"title":"Problem Statement:","slug":"problem-statement","link":"#problem-statement","children":[{"level":3,"title":"Example 1:","slug":"example-1","link":"#example-1","children":[]},{"level":3,"title":"Example 2:","slug":"example-2","link":"#example-2","children":[]},{"level":3,"title":"Example 3:","slug":"example-3","link":"#example-3","children":[]},{"level":3,"title":"Constraints:","slug":"constraints","link":"#constraints","children":[]}]},{"level":2,"title":"Solution:","slug":"solution","link":"#solution","children":[{"level":3,"title":"...","slug":"","link":"#","children":[]}]}],"relativePath":"solution/1101-1200/1143 - Longest Common Subsequence.md","lastUpdated":1671291107000}'),o={name:"solution/1101-1200/1143 - Longest Common Subsequence.md"},e=l("",18),p=[e];function t(c,r,D,C,y,A){return n(),a("div",null,p)}const d=s(o,[["render",t]]);export{F as __pageData,d as default};
diff --git a/assets/solution_1201-1300_1232 - Check If It Is a Straight Line.md.e1add48e.js b/assets/solution_1201-1300_1232 - Check If It Is a Straight Line.md.e1add48e.js
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..d4ec293f
--- /dev/null
+++ b/assets/solution_1201-1300_1232 - Check If It Is a Straight Line.md.e1add48e.js
@@ -0,0 +1,27 @@
+import{_ as s,o as a,c as n,a as l}from"./app.e4604e86.js";const A=JSON.parse('{"title":"1232. Check If It Is a Straight Line","description":"","frontmatter":{},"headers":[{"level":2,"title":"Problem Statement:","slug":"problem-statement","link":"#problem-statement","children":[{"level":3,"title":"Example 1:","slug":"example-1","link":"#example-1","children":[]},{"level":3,"title":"Example 2:","slug":"example-2","link":"#example-2","children":[]},{"level":3,"title":"Constraints:","slug":"constraints","link":"#constraints","children":[]}]},{"level":2,"title":"Solution:","slug":"solution","link":"#solution","children":[{"level":3,"title":"...","slug":"","link":"#","children":[]}]}],"relativePath":"solution/1201-1300/1232 - Check If It Is a Straight Line.md","lastUpdated":1671291107000}'),e={name:"solution/1201-1300/1232 - Check If It Is a Straight Line.md"},o=l(`
You are given an array coordinates, coordinates[i] = [x, y], where [x, y] represents the coordinate of a point. Check if these points make a straight line in the XY plane.
`,16),p=[o];function t(c,r,i,D,y,C){return a(),n("div",null,p)}const d=s(e,[["render",t]]);export{A as __pageData,d as default};
diff --git a/assets/solution_1201-1300_1232 - Check If It Is a Straight Line.md.e1add48e.lean.js b/assets/solution_1201-1300_1232 - Check If It Is a Straight Line.md.e1add48e.lean.js
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..3bdfb7c9
--- /dev/null
+++ b/assets/solution_1201-1300_1232 - Check If It Is a Straight Line.md.e1add48e.lean.js
@@ -0,0 +1 @@
+import{_ as s,o as a,c as n,a as l}from"./app.e4604e86.js";const A=JSON.parse('{"title":"1232. Check If It Is a Straight Line","description":"","frontmatter":{},"headers":[{"level":2,"title":"Problem Statement:","slug":"problem-statement","link":"#problem-statement","children":[{"level":3,"title":"Example 1:","slug":"example-1","link":"#example-1","children":[]},{"level":3,"title":"Example 2:","slug":"example-2","link":"#example-2","children":[]},{"level":3,"title":"Constraints:","slug":"constraints","link":"#constraints","children":[]}]},{"level":2,"title":"Solution:","slug":"solution","link":"#solution","children":[{"level":3,"title":"...","slug":"","link":"#","children":[]}]}],"relativePath":"solution/1201-1300/1232 - Check If It Is a Straight Line.md","lastUpdated":1671291107000}'),e={name:"solution/1201-1300/1232 - Check If It Is a Straight Line.md"},o=l("",16),p=[o];function t(c,r,i,D,y,C){return a(),n("div",null,p)}const d=s(e,[["render",t]]);export{A as __pageData,d as default};
diff --git a/assets/solution_1301-1400_1345 - Jump Game IV.md.99cd0bd2.js b/assets/solution_1301-1400_1345 - Jump Game IV.md.99cd0bd2.js
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..3030df94
--- /dev/null
+++ b/assets/solution_1301-1400_1345 - Jump Game IV.md.99cd0bd2.js
@@ -0,0 +1,58 @@
+import{_ as s,o as a,c as n,a as l}from"./app.e4604e86.js";const i=JSON.parse('{"title":"1345. Jump Game IV","description":"","frontmatter":{},"headers":[{"level":2,"title":"Problem Statement","slug":"problem-statement","link":"#problem-statement","children":[]},{"level":2,"title":"Solution:","slug":"solution","link":"#solution","children":[{"level":3,"title":"...","slug":"","link":"#","children":[]}]}],"relativePath":"solution/1301-1400/1345 - Jump Game IV.md","lastUpdated":1678822270000}'),p={name:"solution/1301-1400/1345 - Jump Game IV.md"},o=l(`
Given an array of integers arr, you are initially positioned at the first index of the array.
In one step you can jump from index i to index:
i + 1 where: i + 1 < arr.length.
i - 1 where: i - 1 >= 0.
j where: arr[i] == arr[j] and i != j.
Return the minimum number of steps to reach the last index of the array.
Notice that you can not jump outside of the array at any time.
Example 1:
Input: arr = [100,-23,-23,404,100,23,23,23,3,404]
+Output: 3
+Explanation: You need three jumps from index 0 --> 4 --> 3 --> 9. Note that index 9 is the last index of the array.
+
Example 2:
Input: arr = [7]
+Output: 0
+Explanation: Start index is the last index. You do not need to jump.
+
Example 3:
Input: arr = [7,6,9,6,9,6,9,7]
+Output: 1
+Explanation: You can jump directly from index 0 to index 7 which is last index of the array.
+
Constraints:
1 <= arr.length <= 5 * 104
-108 <= arr[i] <= 108
Click to open Hints
Build a graph of n nodes where nodes are the indices of the array and edges for node i are nodes i+1, i-1, j where arr[i] == arr[j].
Start bfs from node 0 and keep distance. The answer is the distance when you reach node n-1.
`,23),e=[o];function t(c,r,D,y,C,F){return a(),n("div",null,e)}const d=s(p,[["render",t]]);export{i as __pageData,d as default};
diff --git a/assets/solution_1301-1400_1345 - Jump Game IV.md.99cd0bd2.lean.js b/assets/solution_1301-1400_1345 - Jump Game IV.md.99cd0bd2.lean.js
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..a9250dbd
--- /dev/null
+++ b/assets/solution_1301-1400_1345 - Jump Game IV.md.99cd0bd2.lean.js
@@ -0,0 +1 @@
+import{_ as s,o as a,c as n,a as l}from"./app.e4604e86.js";const i=JSON.parse('{"title":"1345. Jump Game IV","description":"","frontmatter":{},"headers":[{"level":2,"title":"Problem Statement","slug":"problem-statement","link":"#problem-statement","children":[]},{"level":2,"title":"Solution:","slug":"solution","link":"#solution","children":[{"level":3,"title":"...","slug":"","link":"#","children":[]}]}],"relativePath":"solution/1301-1400/1345 - Jump Game IV.md","lastUpdated":1678822270000}'),p={name:"solution/1301-1400/1345 - Jump Game IV.md"},o=l("",23),e=[o];function t(c,r,D,y,C,F){return a(),n("div",null,e)}const d=s(p,[["render",t]]);export{i as __pageData,d as default};
diff --git a/assets/solution_1401-1500_1431 - Kids With the Greatest Number of Candies.md.6ccb0bd0.js b/assets/solution_1401-1500_1431 - Kids With the Greatest Number of Candies.md.6ccb0bd0.js
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..2b9da07d
--- /dev/null
+++ b/assets/solution_1401-1500_1431 - Kids With the Greatest Number of Candies.md.6ccb0bd0.js
@@ -0,0 +1,88 @@
+import{_ as s,o as a,c as n,a as l}from"./app.e4604e86.js";const F=JSON.parse('{"title":"1431. Kids With the Greatest Number of Candies","description":"","frontmatter":{},"headers":[{"level":2,"title":"Problem Statement","slug":"problem-statement","link":"#problem-statement","children":[]},{"level":2,"title":"Solution:","slug":"solution","link":"#solution","children":[{"level":3,"title":"...","slug":"","link":"#","children":[]}]}],"relativePath":"solution/1401-1500/1431 - Kids With the Greatest Number of Candies.md","lastUpdated":1689264763000}'),p={name:"solution/1401-1500/1431 - Kids With the Greatest Number of Candies.md"},o=l(`
There are n kids with candies. You are given an integer array candies, where each candies[i] represents the number of candies the ith kid has, and an integer extraCandies, denoting the number of extra candies that you have.
Return a boolean array result of length n, where result[i] is true if, after giving the ith kid all the extraCandies, they will have the greatest number of candies among all the kids, or false otherwise.
Note that multiple kids can have the greatest number of candies.
Example 1:
Input: candies = [2,3,5,1,3], extraCandies = 3
+Output: [true,true,true,false,true]
+Explanation: If you give all extraCandies to:
+- Kid 1, they will have 2 + 3 = 5 candies, which is the greatest among the kids.
+- Kid 2, they will have 3 + 3 = 6 candies, which is the greatest among the kids.
+- Kid 3, they will have 5 + 3 = 8 candies, which is the greatest among the kids.
+- Kid 4, they will have 1 + 3 = 4 candies, which is not the greatest among the kids.
+- Kid 5, they will have 3 + 3 = 6 candies, which is the greatest among the kids.
+
Example 2:
Input: candies = [4,2,1,1,2], extraCandies = 1
+Output: [true,false,false,false,false]
+Explanation: There is only 1 extra candy.
+Kid 1 will always have the greatest number of candies, even if a different kid is given the extra candy.
+
`,21),e=[o];function t(c,r,D,C,y,A){return a(),n("div",null,e)}const d=s(p,[["render",t]]);export{F as __pageData,d as default};
diff --git a/assets/solution_1401-1500_1431 - Kids With the Greatest Number of Candies.md.6ccb0bd0.lean.js b/assets/solution_1401-1500_1431 - Kids With the Greatest Number of Candies.md.6ccb0bd0.lean.js
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..3ef881d2
--- /dev/null
+++ b/assets/solution_1401-1500_1431 - Kids With the Greatest Number of Candies.md.6ccb0bd0.lean.js
@@ -0,0 +1 @@
+import{_ as s,o as a,c as n,a as l}from"./app.e4604e86.js";const F=JSON.parse('{"title":"1431. Kids With the Greatest Number of Candies","description":"","frontmatter":{},"headers":[{"level":2,"title":"Problem Statement","slug":"problem-statement","link":"#problem-statement","children":[]},{"level":2,"title":"Solution:","slug":"solution","link":"#solution","children":[{"level":3,"title":"...","slug":"","link":"#","children":[]}]}],"relativePath":"solution/1401-1500/1431 - Kids With the Greatest Number of Candies.md","lastUpdated":1689264763000}'),p={name:"solution/1401-1500/1431 - Kids With the Greatest Number of Candies.md"},o=l("",21),e=[o];function t(c,r,D,C,y,A){return a(),n("div",null,e)}const d=s(p,[["render",t]]);export{F as __pageData,d as default};
diff --git a/assets/solution_1401-1500_1461 - Check If a String Contains All Binary Codes of Size K.md.fa1d7f44.js b/assets/solution_1401-1500_1461 - Check If a String Contains All Binary Codes of Size K.md.fa1d7f44.js
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..4de004f9
--- /dev/null
+++ b/assets/solution_1401-1500_1461 - Check If a String Contains All Binary Codes of Size K.md.fa1d7f44.js
@@ -0,0 +1,31 @@
+import{_ as s,o as a,c as n,a as l}from"./app.e4604e86.js";const d=JSON.parse('{"title":"1461. Check If a String Contains All Binary Codes of Size K","description":"","frontmatter":{},"headers":[{"level":2,"title":"Problem Statement:","slug":"problem-statement","link":"#problem-statement","children":[{"level":3,"title":"Example 1:","slug":"example-1","link":"#example-1","children":[]},{"level":3,"title":"Explanation:","slug":"explanation","link":"#explanation","children":[]},{"level":3,"title":"Example 2:","slug":"example-2","link":"#example-2","children":[]},{"level":3,"title":"Explanation:","slug":"explanation-1","link":"#explanation-1","children":[]},{"level":3,"title":"Example 3:","slug":"example-3","link":"#example-3","children":[]},{"level":3,"title":"Explanation:","slug":"explanation-2","link":"#explanation-2","children":[]},{"level":3,"title":"Constraints:","slug":"constraints","link":"#constraints","children":[]}]},{"level":2,"title":"Solution:","slug":"solution","link":"#solution","children":[{"level":3,"title":"...","slug":"","link":"#","children":[]}]}],"relativePath":"solution/1401-1500/1461 - Check If a String Contains All Binary Codes of Size K.md","lastUpdated":1671291107000}'),e={name:"solution/1401-1500/1461 - Check If a String Contains All Binary Codes of Size K.md"},o=l(`
1461. Check If a String Contains All Binary Codes of Size K #
`,22),p=[o];function t(c,r,i,C,y,A){return a(),n("div",null,p)}const F=s(e,[["render",t]]);export{d as __pageData,F as default};
diff --git a/assets/solution_1401-1500_1461 - Check If a String Contains All Binary Codes of Size K.md.fa1d7f44.lean.js b/assets/solution_1401-1500_1461 - Check If a String Contains All Binary Codes of Size K.md.fa1d7f44.lean.js
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..4d91ccb0
--- /dev/null
+++ b/assets/solution_1401-1500_1461 - Check If a String Contains All Binary Codes of Size K.md.fa1d7f44.lean.js
@@ -0,0 +1 @@
+import{_ as s,o as a,c as n,a as l}from"./app.e4604e86.js";const d=JSON.parse('{"title":"1461. Check If a String Contains All Binary Codes of Size K","description":"","frontmatter":{},"headers":[{"level":2,"title":"Problem Statement:","slug":"problem-statement","link":"#problem-statement","children":[{"level":3,"title":"Example 1:","slug":"example-1","link":"#example-1","children":[]},{"level":3,"title":"Explanation:","slug":"explanation","link":"#explanation","children":[]},{"level":3,"title":"Example 2:","slug":"example-2","link":"#example-2","children":[]},{"level":3,"title":"Explanation:","slug":"explanation-1","link":"#explanation-1","children":[]},{"level":3,"title":"Example 3:","slug":"example-3","link":"#example-3","children":[]},{"level":3,"title":"Explanation:","slug":"explanation-2","link":"#explanation-2","children":[]},{"level":3,"title":"Constraints:","slug":"constraints","link":"#constraints","children":[]}]},{"level":2,"title":"Solution:","slug":"solution","link":"#solution","children":[{"level":3,"title":"...","slug":"","link":"#","children":[]}]}],"relativePath":"solution/1401-1500/1461 - Check If a String Contains All Binary Codes of Size K.md","lastUpdated":1671291107000}'),e={name:"solution/1401-1500/1461 - Check If a String Contains All Binary Codes of Size K.md"},o=l("",22),p=[o];function t(c,r,i,C,y,A){return a(),n("div",null,p)}const F=s(e,[["render",t]]);export{d as __pageData,F as default};
diff --git a/assets/solution_1401-1500_1470 - Shuffle the Array.md.498e516b.js b/assets/solution_1401-1500_1470 - Shuffle the Array.md.498e516b.js
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..54364222
--- /dev/null
+++ b/assets/solution_1401-1500_1470 - Shuffle the Array.md.498e516b.js
@@ -0,0 +1,27 @@
+import{_ as s,o as n,c as a,a as l}from"./app.e4604e86.js";const u=JSON.parse('{"title":"1470. Shuffle the Array","description":"","frontmatter":{},"headers":[{"level":2,"title":"Problem Statement","slug":"problem-statement","link":"#problem-statement","children":[]},{"level":2,"title":"Solution:","slug":"solution","link":"#solution","children":[{"level":3,"title":"...","slug":"","link":"#","children":[]}]}],"relativePath":"solution/1401-1500/1470 - Shuffle the Array.md","lastUpdated":1676656807000}'),e={name:"solution/1401-1500/1470 - Shuffle the Array.md"},p=l(`
Given the array nums consisting of 2n elements in the form [x1,x2,...,xn,y1,y2,...,yn].
Return the array in the form[x1,y1,x2,y2,...,xn,yn].
Example 1:
+Input: nums = [2,5,1,3,4,7], n = 3
+Output: [2,3,5,4,1,7]
+Explanation: Since x1=2, x2=5, x3=1, y1=3, y2=4, y3=7 then the answer is [2,3,5,4,1,7].
+
Example 2:
+Input: nums = [1,2,3,4,4,3,2,1], n = 4
+Output: [1,4,2,3,3,2,4,1]
+
Example 3:
+Input: nums = [1,1,2,2], n = 2
+Output: [1,2,1,2]
+
Constraints:
1 <= n <= 500
nums.length == 2n
1 <= nums[i] <= 10^3
Click to open Hints
Use two pointers to create the new array of 2n elements. The first starting at the beginning and the other starting at (n+1)th position. Alternate between them and create the new array.
packagemain
+
+funcshuffle(nums []int, n int)[]int{
+ res :=make([]int, n*2)
+
+for i :=0; i < n; i++{
+// at even indices, put the slice of the array from 0 to n
+ res[i*2]= nums[i]
+// at odd indices, put the slice of the array from n to the end
+ res[i*2+1]= nums[n+i]
+}
+
+return res
+}
+
+
You have a browser of one tab where you start on the homepage and you can visit another url, get back in the history number of steps or move forward in the history number of steps.
Implement the BrowserHistory class:
BrowserHistory(string homepage) Initializes the object with the homepage of the browser.
void visit(string url) Visits url from the current page. It clears up all the forward history.
string back(int steps) Move steps back in history. If you can only return x steps in the history and steps > x, you will return only x steps. Return the current url after moving back in history at moststeps.
string forward(int steps) Move steps forward in history. If you can only forward x steps in the history and steps > x, you will forward only x steps. Return the current url after forwarding in history at moststeps.
Example:
Input:
+["BrowserHistory","visit","visit","visit","back","back","forward","visit","forward","back","back"]
+[["leetcode.com"],["google.com"],["facebook.com"],["youtube.com"],[1],[1],[1],["linkedin.com"],[2],[2],[7]]
+Output:
+[null,null,null,null,"facebook.com","google.com","facebook.com",null,"linkedin.com","google.com","leetcode.com"]
+
+Explanation:
+BrowserHistory browserHistory = new BrowserHistory("leetcode.com");
+browserHistory.visit("google.com"); // You are in "leetcode.com". Visit "google.com"
+browserHistory.visit("facebook.com"); // You are in "google.com". Visit "facebook.com"
+browserHistory.visit("youtube.com"); // You are in "facebook.com". Visit "youtube.com"
+browserHistory.back(1); // You are in "youtube.com", move back to "facebook.com" return "facebook.com"
+browserHistory.back(1); // You are in "facebook.com", move back to "google.com" return "google.com"
+browserHistory.forward(1); // You are in "google.com", move forward to "facebook.com" return "facebook.com"
+browserHistory.visit("linkedin.com"); // You are in "facebook.com". Visit "linkedin.com"
+browserHistory.forward(2); // You are in "linkedin.com", you cannot move forward any steps.
+browserHistory.back(2); // You are in "linkedin.com", move back two steps to "facebook.com" then to "google.com". return "google.com"
+browserHistory.back(7); // You are in "google.com", you can move back only one step to "leetcode.com". return "leetcode.com"
+
Constraints:
1 <= homepage.length <= 20
1 <= url.length <= 20
1 <= steps <= 100
homepage and url consist of '.' or lower case English letters.
At most 5000 calls will be made to visit, back, and forward.
Click to open Hints
Use two stacks: one for back history, and one for forward history. You can simulate the functions by popping an element from one stack and pushing it into the other.
Can you improve program runtime by using a different data structure?
`,17),p=[e];function t(r,c,D,i,y,C){return o(),n("div",null,p)}const u=s(l,[["render",t]]);export{F as __pageData,u as default};
diff --git a/assets/solution_1401-1500_1472 - Design Browser History.md.fd8d7d2f.lean.js b/assets/solution_1401-1500_1472 - Design Browser History.md.fd8d7d2f.lean.js
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..2fa9b1f6
--- /dev/null
+++ b/assets/solution_1401-1500_1472 - Design Browser History.md.fd8d7d2f.lean.js
@@ -0,0 +1 @@
+import{_ as s,o,c as n,a}from"./app.e4604e86.js";const F=JSON.parse('{"title":"1472. Design Browser History","description":"","frontmatter":{},"headers":[{"level":2,"title":"Problem Statement","slug":"problem-statement","link":"#problem-statement","children":[]},{"level":2,"title":"Solution:","slug":"solution","link":"#solution","children":[{"level":3,"title":"...","slug":"","link":"#","children":[]}]}],"relativePath":"solution/1401-1500/1472 - Design Browser History.md","lastUpdated":1680513503000}'),l={name:"solution/1401-1500/1472 - Design Browser History.md"},e=a("",17),p=[e];function t(r,c,D,i,y,C){return o(),n("div",null,p)}const u=s(l,[["render",t]]);export{F as __pageData,u as default};
diff --git a/assets/solution_1401-1500_1480 - Running Sum of 1d Array.md.67f66fb0.js b/assets/solution_1401-1500_1480 - Running Sum of 1d Array.md.67f66fb0.js
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..b3f47080
--- /dev/null
+++ b/assets/solution_1401-1500_1480 - Running Sum of 1d Array.md.67f66fb0.js
@@ -0,0 +1,26 @@
+import{_ as s,o as a,c as n,a as l}from"./app.e4604e86.js";const d=JSON.parse('{"title":"1480. Running Sum of 1d Array","description":"","frontmatter":{},"headers":[{"level":2,"title":"Problem Statement:","slug":"problem-statement","link":"#problem-statement","children":[{"level":3,"title":"Example 1:","slug":"example-1","link":"#example-1","children":[]},{"level":3,"title":"Explanation:","slug":"explanation","link":"#explanation","children":[]},{"level":3,"title":"Example 2:","slug":"example-2","link":"#example-2","children":[]},{"level":3,"title":"Explanation:","slug":"explanation-1","link":"#explanation-1","children":[]},{"level":3,"title":"Example 3:","slug":"example-3","link":"#example-3","children":[]},{"level":3,"title":"Constraints:","slug":"constraints","link":"#constraints","children":[]}]},{"level":2,"title":"Solution:","slug":"solution","link":"#solution","children":[{"level":3,"title":"...","slug":"","link":"#","children":[]}]}],"relativePath":"solution/1401-1500/1480 - Running Sum of 1d Array.md","lastUpdated":1671291107000}'),p={name:"solution/1401-1500/1480 - Running Sum of 1d Array.md"},e=l(`
`,21),o=[e];function t(r,c,i,C,D,y){return a(),n("div",null,o)}const u=s(p,[["render",t]]);export{d as __pageData,u as default};
diff --git a/assets/solution_1401-1500_1480 - Running Sum of 1d Array.md.67f66fb0.lean.js b/assets/solution_1401-1500_1480 - Running Sum of 1d Array.md.67f66fb0.lean.js
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..7f71c44e
--- /dev/null
+++ b/assets/solution_1401-1500_1480 - Running Sum of 1d Array.md.67f66fb0.lean.js
@@ -0,0 +1 @@
+import{_ as s,o as a,c as n,a as l}from"./app.e4604e86.js";const d=JSON.parse('{"title":"1480. Running Sum of 1d Array","description":"","frontmatter":{},"headers":[{"level":2,"title":"Problem Statement:","slug":"problem-statement","link":"#problem-statement","children":[{"level":3,"title":"Example 1:","slug":"example-1","link":"#example-1","children":[]},{"level":3,"title":"Explanation:","slug":"explanation","link":"#explanation","children":[]},{"level":3,"title":"Example 2:","slug":"example-2","link":"#example-2","children":[]},{"level":3,"title":"Explanation:","slug":"explanation-1","link":"#explanation-1","children":[]},{"level":3,"title":"Example 3:","slug":"example-3","link":"#example-3","children":[]},{"level":3,"title":"Constraints:","slug":"constraints","link":"#constraints","children":[]}]},{"level":2,"title":"Solution:","slug":"solution","link":"#solution","children":[{"level":3,"title":"...","slug":"","link":"#","children":[]}]}],"relativePath":"solution/1401-1500/1480 - Running Sum of 1d Array.md","lastUpdated":1671291107000}'),p={name:"solution/1401-1500/1480 - Running Sum of 1d Array.md"},e=l("",21),o=[e];function t(r,c,i,C,D,y){return a(),n("div",null,o)}const u=s(p,[["render",t]]);export{d as __pageData,u as default};
diff --git a/assets/solution_1401-1500_1491 - Average Salary Excluding the Minimum and Maximum Salary.md.80cb080a.js b/assets/solution_1401-1500_1491 - Average Salary Excluding the Minimum and Maximum Salary.md.80cb080a.js
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..2d0fa59b
--- /dev/null
+++ b/assets/solution_1401-1500_1491 - Average Salary Excluding the Minimum and Maximum Salary.md.80cb080a.js
@@ -0,0 +1,18 @@
+import{_ as a,o as s,c as n,a as l}from"./app.e4604e86.js";const C=JSON.parse('{"title":"1491. Average Salary Excluding the Minimum and Maximum Salary","description":"","frontmatter":{},"headers":[{"level":2,"title":"Problem Statement:","slug":"problem-statement","link":"#problem-statement","children":[{"level":3,"title":"Example 1:","slug":"example-1","link":"#example-1","children":[]},{"level":3,"title":"Example 2:","slug":"example-2","link":"#example-2","children":[]},{"level":3,"title":"Constraints:","slug":"constraints","link":"#constraints","children":[]}]},{"level":2,"title":"Solution:","slug":"solution","link":"#solution","children":[{"level":3,"title":"...","slug":"","link":"#","children":[]}]}],"relativePath":"solution/1401-1500/1491 - Average Salary Excluding the Minimum and Maximum Salary.md","lastUpdated":1671291107000}'),e={name:"solution/1401-1500/1491 - Average Salary Excluding the Minimum and Maximum Salary.md"},p=l(`
1491. Average Salary Excluding the Minimum and Maximum Salary #
Input: salary = [4000,3000,1000,2000]
+Output: 2500.00000
+Explanation: Minimum salary and maximum salary are 1000 and 4000 respectively.
+Average salary excluding minimum and maximum salary is (2000+3000) / 2 = 2500
+
Input: salary = [1000,2000,3000]
+Output: 2000.00000
+Explanation: Minimum salary and maximum salary are 1000 and 3000 respectively.
+Average salary excluding minimum and maximum salary is (2000) / 1 = 2000
+
publicdoubleaverage(int[] salary){
+ Arrays.sort(salary);
+int len = salary.length;
+double res =0;
+for(int i =1; i < len -1; i++)
+ res += salary[i];
+return res /(len -2);
+}
+
`,15),o=[p];function t(r,c,i,y,d,m){return s(),n("div",null,o)}const A=a(e,[["render",t]]);export{C as __pageData,A as default};
diff --git a/assets/solution_1401-1500_1491 - Average Salary Excluding the Minimum and Maximum Salary.md.80cb080a.lean.js b/assets/solution_1401-1500_1491 - Average Salary Excluding the Minimum and Maximum Salary.md.80cb080a.lean.js
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..f9e24a58
--- /dev/null
+++ b/assets/solution_1401-1500_1491 - Average Salary Excluding the Minimum and Maximum Salary.md.80cb080a.lean.js
@@ -0,0 +1 @@
+import{_ as a,o as s,c as n,a as l}from"./app.e4604e86.js";const C=JSON.parse('{"title":"1491. Average Salary Excluding the Minimum and Maximum Salary","description":"","frontmatter":{},"headers":[{"level":2,"title":"Problem Statement:","slug":"problem-statement","link":"#problem-statement","children":[{"level":3,"title":"Example 1:","slug":"example-1","link":"#example-1","children":[]},{"level":3,"title":"Example 2:","slug":"example-2","link":"#example-2","children":[]},{"level":3,"title":"Constraints:","slug":"constraints","link":"#constraints","children":[]}]},{"level":2,"title":"Solution:","slug":"solution","link":"#solution","children":[{"level":3,"title":"...","slug":"","link":"#","children":[]}]}],"relativePath":"solution/1401-1500/1491 - Average Salary Excluding the Minimum and Maximum Salary.md","lastUpdated":1671291107000}'),e={name:"solution/1401-1500/1491 - Average Salary Excluding the Minimum and Maximum Salary.md"},p=l("",15),o=[p];function t(r,c,i,y,d,m){return s(),n("div",null,o)}const A=a(e,[["render",t]]);export{C as __pageData,A as default};
diff --git a/assets/solution_1401-1500_1498 - Number of Subsequences That Satisfy the Given Sum Condition.md.318f6205.js b/assets/solution_1401-1500_1498 - Number of Subsequences That Satisfy the Given Sum Condition.md.318f6205.js
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..17ab7f05
--- /dev/null
+++ b/assets/solution_1401-1500_1498 - Number of Subsequences That Satisfy the Given Sum Condition.md.318f6205.js
@@ -0,0 +1,37 @@
+import{_ as s,o as n,c as a,a as l}from"./app.e4604e86.js";const F=JSON.parse('{"title":"1498. Number of Subsequences That Satisfy the Given Sum Condition","description":"","frontmatter":{},"headers":[{"level":2,"title":"Problem Statement:","slug":"problem-statement","link":"#problem-statement","children":[{"level":3,"title":"Example 1:","slug":"example-1","link":"#example-1","children":[]},{"level":3,"title":"Example 2:","slug":"example-2","link":"#example-2","children":[]},{"level":3,"title":"Example 3:","slug":"example-3","link":"#example-3","children":[]},{"level":3,"title":"Constraints:","slug":"constraints","link":"#constraints","children":[]}]},{"level":2,"title":"Solution:","slug":"solution","link":"#solution","children":[{"level":3,"title":"...","slug":"","link":"#","children":[]}]}],"relativePath":"solution/1401-1500/1498 - Number of Subsequences That Satisfy the Given Sum Condition.md","lastUpdated":1671291107000}'),e={name:"solution/1401-1500/1498 - Number of Subsequences That Satisfy the Given Sum Condition.md"},p=l(`
1498. Number of Subsequences That Satisfy the Given Sum Condition #
You are given an array of integers nums and an integer target.
Return the number of non-empty subsequences of nums such that the sum of the minimum and maximum element on it is less or equal to target. Since the answer may be too large, return it modulo 109 + 7.
Input: nums = [2,3,3,4,6,7], target = 12
+Output: 61
+Explanation: There are 63 non-empty subsequences, two of them do not satisfy the condition ([6,7], [7]).
+Number of valid subsequences (63 - 2 = 61).
+
`,17),o=[p];function t(c,r,i,D,C,y){return n(),a("div",null,o)}const u=s(e,[["render",t]]);export{F as __pageData,u as default};
diff --git a/assets/solution_1401-1500_1498 - Number of Subsequences That Satisfy the Given Sum Condition.md.318f6205.lean.js b/assets/solution_1401-1500_1498 - Number of Subsequences That Satisfy the Given Sum Condition.md.318f6205.lean.js
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..1c206588
--- /dev/null
+++ b/assets/solution_1401-1500_1498 - Number of Subsequences That Satisfy the Given Sum Condition.md.318f6205.lean.js
@@ -0,0 +1 @@
+import{_ as s,o as n,c as a,a as l}from"./app.e4604e86.js";const F=JSON.parse('{"title":"1498. Number of Subsequences That Satisfy the Given Sum Condition","description":"","frontmatter":{},"headers":[{"level":2,"title":"Problem Statement:","slug":"problem-statement","link":"#problem-statement","children":[{"level":3,"title":"Example 1:","slug":"example-1","link":"#example-1","children":[]},{"level":3,"title":"Example 2:","slug":"example-2","link":"#example-2","children":[]},{"level":3,"title":"Example 3:","slug":"example-3","link":"#example-3","children":[]},{"level":3,"title":"Constraints:","slug":"constraints","link":"#constraints","children":[]}]},{"level":2,"title":"Solution:","slug":"solution","link":"#solution","children":[{"level":3,"title":"...","slug":"","link":"#","children":[]}]}],"relativePath":"solution/1401-1500/1498 - Number of Subsequences That Satisfy the Given Sum Condition.md","lastUpdated":1671291107000}'),e={name:"solution/1401-1500/1498 - Number of Subsequences That Satisfy the Given Sum Condition.md"},p=l("",17),o=[p];function t(c,r,i,D,C,y){return n(),a("div",null,o)}const u=s(e,[["render",t]]);export{F as __pageData,u as default};
diff --git a/assets/solution_1501-1600_1512 - Number of Good Pairs.md.f54c2eec.js b/assets/solution_1501-1600_1512 - Number of Good Pairs.md.f54c2eec.js
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..7dc02f4f
--- /dev/null
+++ b/assets/solution_1501-1600_1512 - Number of Good Pairs.md.f54c2eec.js
@@ -0,0 +1,25 @@
+import{_ as s,o as a,c as n,a as l}from"./app.e4604e86.js";const D=JSON.parse('{"title":"1512. Number of Good Pairs","description":"","frontmatter":{},"headers":[{"level":2,"title":"Problem Statement","slug":"problem-statement","link":"#problem-statement","children":[]},{"level":2,"title":"Solution:","slug":"solution","link":"#solution","children":[{"level":3,"title":"...","slug":"","link":"#","children":[]}]}],"relativePath":"solution/1501-1600/1512 - Number of Good Pairs.md","lastUpdated":1677958804000}'),o={name:"solution/1501-1600/1512 - Number of Good Pairs.md"},p=l(`
`,20),e=[p];function t(c,r,i,C,y,d){return a(),n("div",null,e)}const F=s(o,[["render",t]]);export{D as __pageData,F as default};
diff --git a/assets/solution_1501-1600_1512 - Number of Good Pairs.md.f54c2eec.lean.js b/assets/solution_1501-1600_1512 - Number of Good Pairs.md.f54c2eec.lean.js
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..53a5e92a
--- /dev/null
+++ b/assets/solution_1501-1600_1512 - Number of Good Pairs.md.f54c2eec.lean.js
@@ -0,0 +1 @@
+import{_ as s,o as a,c as n,a as l}from"./app.e4604e86.js";const D=JSON.parse('{"title":"1512. Number of Good Pairs","description":"","frontmatter":{},"headers":[{"level":2,"title":"Problem Statement","slug":"problem-statement","link":"#problem-statement","children":[]},{"level":2,"title":"Solution:","slug":"solution","link":"#solution","children":[{"level":3,"title":"...","slug":"","link":"#","children":[]}]}],"relativePath":"solution/1501-1600/1512 - Number of Good Pairs.md","lastUpdated":1677958804000}'),o={name:"solution/1501-1600/1512 - Number of Good Pairs.md"},p=l("",20),e=[p];function t(c,r,i,C,y,d){return a(),n("div",null,e)}const F=s(o,[["render",t]]);export{D as __pageData,F as default};
diff --git a/assets/solution_1501-1600_1523. Count Odd Numbers in an Interval Range.md.4cc92523.js b/assets/solution_1501-1600_1523. Count Odd Numbers in an Interval Range.md.4cc92523.js
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..cca31cc2
--- /dev/null
+++ b/assets/solution_1501-1600_1523. Count Odd Numbers in an Interval Range.md.4cc92523.js
@@ -0,0 +1,15 @@
+import{_ as t,r as p,o as r,c,b as s,f as n,e,w as l,a as o}from"./app.e4604e86.js";const k=JSON.parse('{"title":"1523. Count Odd Numbers in an Interval Range","description":"","frontmatter":{},"headers":[{"level":2,"title":"Problem Statement","slug":"problem-statement","link":"#problem-statement","children":[]},{"level":2,"title":"Solution:","slug":"solution","link":"#solution","children":[{"level":3,"title":"...","slug":"","link":"#","children":[]}]}],"relativePath":"solution/1501-1600/1523. Count Odd Numbers in an Interval Range.md","lastUpdated":1676656807000}'),i={name:"solution/1501-1600/1523. Count Odd Numbers in an Interval Range.md"},d=o('
',3),u=s("code",null,"low",-1),h=s("em",null,"count of odd numbers between ",-1),C=s("code",null,"low",-1),_=s("em",null," and ",-1),D=s("em",null," (inclusive)",-1),y=o(`
Example 1:
+Input: low = 3, high = 7
+Output: 3
+Explanation: The odd numbers between 3 and 7 are [3,5,7].\`\`\`
+
+<p><strong class="example">Example 2:</strong></p>
+
+
Input: low = 8, high = 10 Output: 1 Explanation: The odd numbers between 8 and 10 are [9].\`\`\`
Constraints:
0 <= low <= high <= 10^9
Click to open Hints
If the range (high - low + 1) is even, the number of even and odd numbers in this range will be the same.
If the range (high - low + 1) is odd, the solution will depend on the parity of high and low.
`,12);function A(g,m,b,F,v,f){const a=p("font");return r(),c("div",null,[d,s("p",null,[n("Given two non-negative integers "),u,n(" and "),s("code",null,[e(a,{face:"monospace"},{default:l(()=>[n("high")]),_:1})]),n(". Return the "),h,C,_,s("code",null,[e(a,{face:"monospace"},{default:l(()=>[n("high")]),_:1})]),D,n(".")]),y])}const x=t(i,[["render",A]]);export{k as __pageData,x as default};
diff --git a/assets/solution_1501-1600_1523. Count Odd Numbers in an Interval Range.md.4cc92523.lean.js b/assets/solution_1501-1600_1523. Count Odd Numbers in an Interval Range.md.4cc92523.lean.js
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..8fcfcbe9
--- /dev/null
+++ b/assets/solution_1501-1600_1523. Count Odd Numbers in an Interval Range.md.4cc92523.lean.js
@@ -0,0 +1 @@
+import{_ as t,r as p,o as r,c,b as s,f as n,e,w as l,a as o}from"./app.e4604e86.js";const k=JSON.parse('{"title":"1523. Count Odd Numbers in an Interval Range","description":"","frontmatter":{},"headers":[{"level":2,"title":"Problem Statement","slug":"problem-statement","link":"#problem-statement","children":[]},{"level":2,"title":"Solution:","slug":"solution","link":"#solution","children":[{"level":3,"title":"...","slug":"","link":"#","children":[]}]}],"relativePath":"solution/1501-1600/1523. Count Odd Numbers in an Interval Range.md","lastUpdated":1676656807000}'),i={name:"solution/1501-1600/1523. Count Odd Numbers in an Interval Range.md"},d=o("",3),u=s("code",null,"low",-1),h=s("em",null,"count of odd numbers between ",-1),C=s("code",null,"low",-1),_=s("em",null," and ",-1),D=s("em",null," (inclusive)",-1),y=o("",12);function A(g,m,b,F,v,f){const a=p("font");return r(),c("div",null,[d,s("p",null,[n("Given two non-negative integers "),u,n(" and "),s("code",null,[e(a,{face:"monospace"},{default:l(()=>[n("high")]),_:1})]),n(". Return the "),h,C,_,s("code",null,[e(a,{face:"monospace"},{default:l(()=>[n("high")]),_:1})]),D,n(".")]),y])}const x=t(i,[["render",A]]);export{k as __pageData,x as default};
diff --git a/assets/solution_1501-1600_1537 - Get the Maximum Score.md.73e65486.js b/assets/solution_1501-1600_1537 - Get the Maximum Score.md.73e65486.js
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..cff96768
--- /dev/null
+++ b/assets/solution_1501-1600_1537 - Get the Maximum Score.md.73e65486.js
@@ -0,0 +1,61 @@
+import{_ as s,o as n,c as a,a as l}from"./app.e4604e86.js";const F=JSON.parse('{"title":"1537. Get the Maximum Score","description":"","frontmatter":{},"headers":[{"level":2,"title":"Problem Statement:","slug":"problem-statement","link":"#problem-statement","children":[{"level":3,"title":"Example 1:","slug":"example-1","link":"#example-1","children":[]},{"level":3,"title":"Example 2:","slug":"example-2","link":"#example-2","children":[]},{"level":3,"title":"Example 3:","slug":"example-3","link":"#example-3","children":[]},{"level":3,"title":"Constraints:","slug":"constraints","link":"#constraints","children":[]}]},{"level":2,"title":"Solution:","slug":"solution","link":"#solution","children":[{"level":3,"title":"...","slug":"","link":"#","children":[]}]}],"relativePath":"solution/1501-1600/1537 - Get the Maximum Score.md","lastUpdated":1671291107000}'),e={name:"solution/1501-1600/1537 - Get the Maximum Score.md"},p=l(`
You are given two sorted arrays of distinct integers nums1 and nums2.
A valid path is defined as follows:
Choose array nums1 or nums2 to traverse (from index-0).
Traverse the current array from left to right.
If you are reading any value that is present in nums1 and nums2 you are allowed to change your path to the other array. (Only one repeated value is considered in the valid path).
The score is defined as the sum of uniques values in a valid path.
Return the maximum score you can obtain of all possible valid paths. Since the answer may be too large, return it modulo 109 + 7.
Input: nums1 = [2,4,5,8,10], nums2 = [4,6,8,9]
+Output: 30
+Explanation: Valid paths:
+[2,4,5,8,10], [2,4,5,8,9], [2,4,6,8,9], [2,4,6,8,10], (starting from nums1)
+[4,6,8,9], [4,5,8,10], [4,5,8,9], [4,6,8,10] (starting from nums2)
+The maximum is obtained with the path in green [2,4,6,8,10].
+
Input: nums1 = [1,2,3,4,5], nums2 = [6,7,8,9,10]
+Output: 40
+Explanation: There are no common elements between nums1 and nums2.
+Maximum sum is obtained with the path [6,7,8,9,10].
+
publicclassGetTheMaxScore{
+
+/* Two Pointer Approach */
+publicintmaxSum(int[]nums1,int[]nums2){
+// initializing two pointer vars
+int i =0, j =0;
+int len1 = nums1.length, len2 = nums2.length;
+
+// taking the vars of long type to avoid integer overflow or runtime error
+long upperSum =0, lowerSum =0;
+
+// traverse till one of the arrays length
+while(i < len1 && j < len2){
+
+// adding the element to the upperSum until element of first array is >=
+// the element of second array & then increamenting the pointer var by 1
+if(nums1[i]< nums2[j])
+ upperSum += nums1[i++];
+
+// adding the element to the lowerSum until element of second array is >=
+// the element of first array & then increamenting the pointer var by 1
+elseif(nums1[i]> nums2[j])
+ lowerSum += nums2[j++];
+
+// when the element of both arrays are equal,
+// assign the value of max of upperSum & lowerSum and adding the element itself
+else{
+ upperSum = lowerSum = Math.max(upperSum, lowerSum)+ nums1[i];
+// increasing both pointer by 1, as the value at both the pointers is same,
+// avoiding the repetition of element in the sum
+ i++;
+ j++;
+}
+}
+
+// adding the remaining element from first array
+while(i < len1)
+ upperSum += nums1[i++];
+
+// adding the remaining element from second array
+while(j < len2)
+ lowerSum += nums2[j++];
+
+return(int)(Math.max(upperSum, lowerSum)%1000000007);
+}
+}
+
`,21),o=[p];function t(r,c,i,D,y,C){return n(),a("div",null,o)}const m=s(e,[["render",t]]);export{F as __pageData,m as default};
diff --git a/assets/solution_1501-1600_1537 - Get the Maximum Score.md.73e65486.lean.js b/assets/solution_1501-1600_1537 - Get the Maximum Score.md.73e65486.lean.js
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..f103bc37
--- /dev/null
+++ b/assets/solution_1501-1600_1537 - Get the Maximum Score.md.73e65486.lean.js
@@ -0,0 +1 @@
+import{_ as s,o as n,c as a,a as l}from"./app.e4604e86.js";const F=JSON.parse('{"title":"1537. Get the Maximum Score","description":"","frontmatter":{},"headers":[{"level":2,"title":"Problem Statement:","slug":"problem-statement","link":"#problem-statement","children":[{"level":3,"title":"Example 1:","slug":"example-1","link":"#example-1","children":[]},{"level":3,"title":"Example 2:","slug":"example-2","link":"#example-2","children":[]},{"level":3,"title":"Example 3:","slug":"example-3","link":"#example-3","children":[]},{"level":3,"title":"Constraints:","slug":"constraints","link":"#constraints","children":[]}]},{"level":2,"title":"Solution:","slug":"solution","link":"#solution","children":[{"level":3,"title":"...","slug":"","link":"#","children":[]}]}],"relativePath":"solution/1501-1600/1537 - Get the Maximum Score.md","lastUpdated":1671291107000}'),e={name:"solution/1501-1600/1537 - Get the Maximum Score.md"},p=l("",21),o=[p];function t(r,c,i,D,y,C){return n(),a("div",null,o)}const m=s(e,[["render",t]]);export{F as __pageData,m as default};
diff --git a/assets/solution_1501-1600_1539 - Kth Missing Positive Number.md.ee787093.js b/assets/solution_1501-1600_1539 - Kth Missing Positive Number.md.ee787093.js
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..8abd56d8
--- /dev/null
+++ b/assets/solution_1501-1600_1539 - Kth Missing Positive Number.md.ee787093.js
@@ -0,0 +1,26 @@
+import{_ as s,o as a,c as n,a as l}from"./app.e4604e86.js";const F=JSON.parse('{"title":"1539. Kth Missing Positive Number","description":"","frontmatter":{},"headers":[{"level":2,"title":"Problem Statement","slug":"problem-statement","link":"#problem-statement","children":[]},{"level":2,"title":"Solution:","slug":"solution","link":"#solution","children":[{"level":3,"title":"...","slug":"","link":"#","children":[]}]}],"relativePath":"solution/1501-1600/1539 - Kth Missing Positive Number.md","lastUpdated":1678822270000}'),p={name:"solution/1501-1600/1539 - Kth Missing Positive Number.md"},o=l(`
Given an array arr of positive integers sorted in a strictly increasing order, and an integer k.
Return thekthpositive integer that is missing from this array.
Example 1:
Input: arr = [2,3,4,7,11], k = 5
+Output: 9
+Explanation: The missing positive integers are [1,5,6,8,9,10,12,13,...]. The 5th missing positive integer is 9.
+
Example 2:
Input: arr = [1,2,3,4], k = 2
+Output: 6
+Explanation: The missing positive integers are [5,6,7,...]. The 2nd missing positive integer is 6.
+
Constraints:
1 <= arr.length <= 1000
1 <= arr[i] <= 1000
1 <= k <= 1000
arr[i] < arr[j] for 1 <= i < j <= arr.length
Follow up:
Could you solve this problem in less than O(n) complexity?
Click to open Hints
Keep track of how many positive numbers are missing as you scan the array.
You are given an m x n integer grid accounts where accounts[i][j] is the amount of money the ith customer has in the jth bank. Return the wealth that the richest customer has.
A customer's wealth is the amount of money they have in all their bank accounts. The richest customer is the customer that has the maximum wealth.
Example 1:
Input: accounts = [[1,2,3],[3,2,1]]
+Output: 6
+Explanation:
+1st customer has wealth = 1 + 2 + 3 = 6
+2nd customer has wealth = 3 + 2 + 1 = 6
+Both customers are considered the richest with a wealth of 6 each, so return 6.
+
Example 2:
Input: accounts = [[1,5],[7,3],[3,5]]
+Output: 10
+Explanation:
+1st customer has wealth = 6
+2nd customer has wealth = 10
+3rd customer has wealth = 8
+The 2nd customer is the richest with a wealth of 10.\`\`\`
+
+<p><strong class="example">Example 3:</strong></p>
+
+
+<p> </p>
+<p><strong>Constraints:</strong></p>
+<ul>
+<li><code>m == accounts.length</code></li>
+<li><code>n == accounts[i].length</code></li>
+<li><code>1 <= m, n <= 50</code></li>
+<li><code>1 <= accounts[i][j] <= 100</code></li>
+</ul>
+
+
+::: details _Click to open Hints_
+
+- Calculate the wealth of each customer
+- Find the maximum element in array.
+
+:::
+
+## Solution:
+
+::: code-group
+
+\`\`\`rs [Rust]
+impl Solution {
+ pub fn maximum_wealth(accounts: Vec<Vec<i32>>) -> i32 {
+ let mut max = 0;
+
+ for account in accounts {
+ let mut sum = 0;
+ for money in account {
+ sum += money;
+ }
+ if sum > max {
+ max = sum;
+ }
+ }
+ max
+ }
+}
+
+
`,15),p=[t];function o(c,r,i,C,A,h){return n(),a("div",null,p)}const d=s(e,[["render",o]]);export{m as __pageData,d as default};
diff --git a/assets/solution_1601-1700_1672 - Richest Customer Wealth.md.0aef5bd3.lean.js b/assets/solution_1601-1700_1672 - Richest Customer Wealth.md.0aef5bd3.lean.js
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..71d4d611
--- /dev/null
+++ b/assets/solution_1601-1700_1672 - Richest Customer Wealth.md.0aef5bd3.lean.js
@@ -0,0 +1 @@
+import{_ as s,o as n,c as a,a as l}from"./app.e4604e86.js";const m=JSON.parse('{"title":"1672. Richest Customer Wealth","description":"","frontmatter":{},"headers":[{"level":2,"title":"Problem Statement","slug":"problem-statement","link":"#problem-statement","children":[{"level":3,"title":"...","slug":"","link":"#","children":[]}]}],"relativePath":"solution/1601-1700/1672 - Richest Customer Wealth.md","lastUpdated":1677958804000}'),e={name:"solution/1601-1700/1672 - Richest Customer Wealth.md"},t=l("",15),p=[t];function o(c,r,i,C,A,h){return n(),a("div",null,p)}const d=s(e,[["render",o]]);export{m as __pageData,d as default};
diff --git a/assets/solution_1601-1700_1689 - Partitioning Into Minimum Number Of Deci-Binary Numbers.md.289724ac.js b/assets/solution_1601-1700_1689 - Partitioning Into Minimum Number Of Deci-Binary Numbers.md.289724ac.js
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..a46e81e7
--- /dev/null
+++ b/assets/solution_1601-1700_1689 - Partitioning Into Minimum Number Of Deci-Binary Numbers.md.289724ac.js
@@ -0,0 +1,20 @@
+import{_ as s,o as n,c as a,a as e}from"./app.e4604e86.js";const C=JSON.parse('{"title":"1689. Partitioning Into Minimum Number Of Deci-Binary Numbers","description":"","frontmatter":{},"headers":[{"level":2,"title":"Problem Statement","slug":"problem-statement","link":"#problem-statement","children":[]},{"level":2,"title":"Solution:","slug":"solution","link":"#solution","children":[{"level":3,"title":"...","slug":"","link":"#","children":[]}]}],"relativePath":"solution/1601-1700/1689 - Partitioning Into Minimum Number Of Deci-Binary Numbers.md","lastUpdated":1677958804000}'),l={name:"solution/1601-1700/1689 - Partitioning Into Minimum Number Of Deci-Binary Numbers.md"},o=e(`
1689. Partitioning Into Minimum Number Of Deci-Binary Numbers #
A decimal number is called deci-binary if each of its digits is either 0 or 1 without any leading zeros. For example, 101 and 1100 are deci-binary, while 112 and 3001 are not.
Given a string n that represents a positive decimal integer, return the minimum number of positive deci-binary numbers needed so that they sum up to n.
implSolution{
+pubfnmin_partitions(n:String)->i32{
+ // this will be slightly faster as it doesn't need to convert the char to a digit
+ // as the max() function will return the max char value (in ASCII) which is the same as the max digit value
+
+ // n.chars().max().unwrap().to_digit(10).unwrap() as i32
+
+ n.chars().map(|c| c.to_digit(10).unwrap()).max().unwrap()asi32
+}
+}
+
+
`,20),t=[o];function p(i,r,c,d,u,m){return n(),a("div",null,t)}const h=s(l,[["render",p]]);export{C as __pageData,h as default};
diff --git a/assets/solution_1601-1700_1689 - Partitioning Into Minimum Number Of Deci-Binary Numbers.md.289724ac.lean.js b/assets/solution_1601-1700_1689 - Partitioning Into Minimum Number Of Deci-Binary Numbers.md.289724ac.lean.js
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..0df58f4c
--- /dev/null
+++ b/assets/solution_1601-1700_1689 - Partitioning Into Minimum Number Of Deci-Binary Numbers.md.289724ac.lean.js
@@ -0,0 +1 @@
+import{_ as s,o as n,c as a,a as e}from"./app.e4604e86.js";const C=JSON.parse('{"title":"1689. Partitioning Into Minimum Number Of Deci-Binary Numbers","description":"","frontmatter":{},"headers":[{"level":2,"title":"Problem Statement","slug":"problem-statement","link":"#problem-statement","children":[]},{"level":2,"title":"Solution:","slug":"solution","link":"#solution","children":[{"level":3,"title":"...","slug":"","link":"#","children":[]}]}],"relativePath":"solution/1601-1700/1689 - Partitioning Into Minimum Number Of Deci-Binary Numbers.md","lastUpdated":1677958804000}'),l={name:"solution/1601-1700/1689 - Partitioning Into Minimum Number Of Deci-Binary Numbers.md"},o=e("",20),t=[o];function p(i,r,c,d,u,m){return n(),a("div",null,t)}const h=s(l,[["render",p]]);export{C as __pageData,h as default};
diff --git a/assets/solution_1901-2000_1920 - Build Array from Permutation.md.d4764baf.js b/assets/solution_1901-2000_1920 - Build Array from Permutation.md.d4764baf.js
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..d04edace
--- /dev/null
+++ b/assets/solution_1901-2000_1920 - Build Array from Permutation.md.d4764baf.js
@@ -0,0 +1,26 @@
+import{_ as s,o as n,c as a,a as l}from"./app.e4604e86.js";const d=JSON.parse('{"title":"1920. Build Array from Permutation","description":"","frontmatter":{},"headers":[{"level":2,"title":"Problem Statement","slug":"problem-statement","link":"#problem-statement","children":[]},{"level":2,"title":"Solution:","slug":"solution","link":"#solution","children":[{"level":3,"title":"...","slug":"","link":"#","children":[]}]}],"relativePath":"solution/1901-2000/1920 - Build Array from Permutation.md","lastUpdated":1677958804000}'),e={name:"solution/1901-2000/1920 - Build Array from Permutation.md"},o=l(`
Given a zero-based permutationnums (0-indexed), build an array ans of the same length where ans[i] = nums[nums[i]] for each 0 <= i < nums.length and return it.
A zero-based permutationnums is an array of distinct integers from 0 to nums.length - 1 (inclusive).
Example 1:
Input: nums = [0,2,1,5,3,4]
+Output: [0,1,2,4,5,3]
+Explanation: The array ans is built as follows:
+ans = [nums[nums[0]], nums[nums[1]], nums[nums[2]], nums[nums[3]], nums[nums[4]], nums[nums[5]]]
+ = [nums[0], nums[2], nums[1], nums[5], nums[3], nums[4]]
+ = [0,1,2,4,5,3]
+
Example 2:
Input: nums = [5,0,1,2,3,4]
+Output: [4,5,0,1,2,3]
+Explanation: The array ans is built as follows:
+ans = [nums[nums[0]], nums[nums[1]], nums[nums[2]], nums[nums[3]], nums[nums[4]], nums[nums[5]]]
+ = [nums[5], nums[0], nums[1], nums[2], nums[3], nums[4]]
+ = [4,5,0,1,2,3]
+
Constraints:
1 <= nums.length <= 1000
0 <= nums[i] < nums.length
The elements in nums are distinct.
Follow-up: Can you solve it without using an extra space (i.e., O(1) memory)?
Click to open Hints
Just apply what's said in the statement.
Notice that you can't apply it on the same array directly since some elements will change after application
`,20),p=[o];function t(r,c,i,u,m,y){return n(),a("div",null,p)}const A=s(e,[["render",t]]);export{d as __pageData,A as default};
diff --git a/assets/solution_1901-2000_1920 - Build Array from Permutation.md.d4764baf.lean.js b/assets/solution_1901-2000_1920 - Build Array from Permutation.md.d4764baf.lean.js
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..5d519986
--- /dev/null
+++ b/assets/solution_1901-2000_1920 - Build Array from Permutation.md.d4764baf.lean.js
@@ -0,0 +1 @@
+import{_ as s,o as n,c as a,a as l}from"./app.e4604e86.js";const d=JSON.parse('{"title":"1920. Build Array from Permutation","description":"","frontmatter":{},"headers":[{"level":2,"title":"Problem Statement","slug":"problem-statement","link":"#problem-statement","children":[]},{"level":2,"title":"Solution:","slug":"solution","link":"#solution","children":[{"level":3,"title":"...","slug":"","link":"#","children":[]}]}],"relativePath":"solution/1901-2000/1920 - Build Array from Permutation.md","lastUpdated":1677958804000}'),e={name:"solution/1901-2000/1920 - Build Array from Permutation.md"},o=l("",20),p=[o];function t(r,c,i,u,m,y){return n(),a("div",null,p)}const A=s(e,[["render",t]]);export{d as __pageData,A as default};
diff --git a/assets/solution_1901-2000_1929 - Concatenation of Array.md.f1106b2b.js b/assets/solution_1901-2000_1929 - Concatenation of Array.md.f1106b2b.js
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..85058c78
--- /dev/null
+++ b/assets/solution_1901-2000_1929 - Concatenation of Array.md.f1106b2b.js
@@ -0,0 +1,41 @@
+import{_ as s,o as n,c as a,a as l}from"./app.e4604e86.js";const y=JSON.parse('{"title":"1929. Concatenation of Array","description":"","frontmatter":{},"headers":[{"level":2,"title":"Problem Statement","slug":"problem-statement","link":"#problem-statement","children":[{"level":3,"title":"...","slug":"","link":"#","children":[]}]}],"relativePath":"solution/1901-2000/1929 - Concatenation of Array.md","lastUpdated":1677762379000}'),e={name:"solution/1901-2000/1929 - Concatenation of Array.md"},t=l(`
Given an integer array nums of length n, you want to create an array ans of length 2n where ans[i] == nums[i] and ans[i + n] == nums[i] for 0 <= i < n (0-indexed).
Specifically, ans is the concatenation of two nums arrays.
Return the array ans.
Example 1:
Input: nums = [1,2,1]
+Output: [1,2,1,1,2,1]
+Explanation: The array ans is formed as follows:
+- ans = [nums[0],nums[1],nums[2],nums[0],nums[1],nums[2]]
+- ans = [1,2,1,1,2,1]\`\`\`
+
+<p><strong class="example">Example 2:</strong></p>
+
+
Input: nums = [1,3,2,1] Output: [1,3,2,1,1,3,2,1] Explanation: The array ans is formed as follows:
ans = [nums[0],nums[1],nums[2],nums[3],nums[0],nums[1],nums[2],nums[3]]
ans = [1,3,2,1,1,3,2,1]
+<p> </p>
+<p><strong>Constraints:</strong></p>
+<ul>
+<li><code>n == nums.length</code></li>
+<li><code>1 <= n <= 1000</code></li>
+<li><code>1 <= nums[i] <= 1000</code></li>
+</ul>
+
+
+::: details _Click to open Hints_
+
+- Build an array of size 2 * n and assign num[i] to ans[i] and ans[i + n]
+
+:::
+
+## Solution:
+
+::: code-group
+
+\`\`\`rs [Rust]
+impl Solution {
+ pub fn get_concatenation(nums: Vec<i32>) -> Vec<i32> {
+ let mut result = nums.clone();
+
+ result.extend(nums);
+
+ result
+ }
+}
+
+
`,15),p=[t];function o(c,r,i,C,A,d){return n(),a("div",null,p)}const m=s(e,[["render",o]]);export{y as __pageData,m as default};
diff --git a/assets/solution_1901-2000_1929 - Concatenation of Array.md.f1106b2b.lean.js b/assets/solution_1901-2000_1929 - Concatenation of Array.md.f1106b2b.lean.js
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..2ea8d534
--- /dev/null
+++ b/assets/solution_1901-2000_1929 - Concatenation of Array.md.f1106b2b.lean.js
@@ -0,0 +1 @@
+import{_ as s,o as n,c as a,a as l}from"./app.e4604e86.js";const y=JSON.parse('{"title":"1929. Concatenation of Array","description":"","frontmatter":{},"headers":[{"level":2,"title":"Problem Statement","slug":"problem-statement","link":"#problem-statement","children":[{"level":3,"title":"...","slug":"","link":"#","children":[]}]}],"relativePath":"solution/1901-2000/1929 - Concatenation of Array.md","lastUpdated":1677762379000}'),e={name:"solution/1901-2000/1929 - Concatenation of Array.md"},t=l("",15),p=[t];function o(c,r,i,C,A,d){return n(),a("div",null,p)}const m=s(e,[["render",o]]);export{y as __pageData,m as default};
diff --git a/assets/solution_1901-2000_1957 - Delete Characters to Make Fancy String.md.c16dbb86.js b/assets/solution_1901-2000_1957 - Delete Characters to Make Fancy String.md.c16dbb86.js
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..a1abe3e7
--- /dev/null
+++ b/assets/solution_1901-2000_1957 - Delete Characters to Make Fancy String.md.c16dbb86.js
@@ -0,0 +1,32 @@
+import{_ as s,o as a,c as n,a as o}from"./app.e4604e86.js";const C=JSON.parse('{"title":"1957. Delete Characters to Make Fancy String","description":"","frontmatter":{},"headers":[{"level":2,"title":"Problem Statement","slug":"problem-statement","link":"#problem-statement","children":[]},{"level":2,"title":"Solution:","slug":"solution","link":"#solution","children":[{"level":3,"title":"...","slug":"","link":"#","children":[]}]}],"relativePath":"solution/1901-2000/1957 - Delete Characters to Make Fancy String.md","lastUpdated":1674119766000}'),e={name:"solution/1901-2000/1957 - Delete Characters to Make Fancy String.md"},l=o(`
A fancy string is a string where no threeconsecutive characters are equal.
Given a string s, delete the minimum possible number of characters from s to make it fancy.
Return the final string after the deletion. It can be shown that the answer will always be unique.
Example 1:
Input: s = "leeetcode"
+Output: "leetcode"
+Explanation:
+Remove an 'e' from the first group of 'e's to create "leetcode".
+No three consecutive characters are equal, so return "leetcode".
+
Example 2:
Input: s = "aaabaaaa"
+Output: "aabaa"
+Explanation:
+Remove an 'a' from the first group of 'a's to create "aabaaaa".
+Remove two 'a's from the second group of 'a's to create "aabaa".
+No three consecutive characters are equal, so return "aabaa".
+
Example 3:
Input: s = "aab"
+Output: "aab"
+Explanation: No three consecutive characters are equal, so return "aab".
+
Constraints:
1 <= s.length <= 105
s consists only of lowercase English letters.
Click to open Hints
What's the optimal way to delete characters if three or more consecutive characters are equal?
If three or more consecutive characters are equal, keep two of them and delete the rest.
`,21),t=[l];function p(r,c,D,i,y,F){return a(),n("div",null,t)}const u=s(e,[["render",p]]);export{C as __pageData,u as default};
diff --git a/assets/solution_1901-2000_1957 - Delete Characters to Make Fancy String.md.c16dbb86.lean.js b/assets/solution_1901-2000_1957 - Delete Characters to Make Fancy String.md.c16dbb86.lean.js
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..18c83236
--- /dev/null
+++ b/assets/solution_1901-2000_1957 - Delete Characters to Make Fancy String.md.c16dbb86.lean.js
@@ -0,0 +1 @@
+import{_ as s,o as a,c as n,a as o}from"./app.e4604e86.js";const C=JSON.parse('{"title":"1957. Delete Characters to Make Fancy String","description":"","frontmatter":{},"headers":[{"level":2,"title":"Problem Statement","slug":"problem-statement","link":"#problem-statement","children":[]},{"level":2,"title":"Solution:","slug":"solution","link":"#solution","children":[{"level":3,"title":"...","slug":"","link":"#","children":[]}]}],"relativePath":"solution/1901-2000/1957 - Delete Characters to Make Fancy String.md","lastUpdated":1674119766000}'),e={name:"solution/1901-2000/1957 - Delete Characters to Make Fancy String.md"},l=o("",21),t=[l];function p(r,c,D,i,y,F){return a(),n("div",null,t)}const u=s(e,[["render",p]]);export{C as __pageData,u as default};
diff --git a/assets/solution_2101-2200_2011 - Final Value of Variable After Performing Operations.md.7ad7e527.js b/assets/solution_2101-2200_2011 - Final Value of Variable After Performing Operations.md.7ad7e527.js
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..9c5105dc
--- /dev/null
+++ b/assets/solution_2101-2200_2011 - Final Value of Variable After Performing Operations.md.7ad7e527.js
@@ -0,0 +1,44 @@
+import{_ as s,o as a,c as n,a as l}from"./app.e4604e86.js";const D=JSON.parse('{"title":"2011. Final Value of Variable After Performing Operations","description":"","frontmatter":{},"headers":[{"level":2,"title":"Problem Statement","slug":"problem-statement","link":"#problem-statement","children":[]},{"level":2,"title":"Solution:","slug":"solution","link":"#solution","children":[{"level":3,"title":"...","slug":"","link":"#","children":[]}]}],"relativePath":"solution/2101-2200/2011 - Final Value of Variable After Performing Operations.md","lastUpdated":1677958804000}'),e={name:"solution/2101-2200/2011 - Final Value of Variable After Performing Operations.md"},o=l(`
2011. Final Value of Variable After Performing Operations #
There is a programming language with only four operations and one variable X:
++X and X++increments the value of the variable X by 1.
--X and X--decrements the value of the variable X by 1.
Initially, the value of X is 0.
Given an array of strings operations containing a list of operations, return the final value of Xafter performing all the operations.
Example 1:
Input: operations = ["--X","X++","X++"]
+Output: 1
+Explanation: The operations are performed as follows:
+Initially, X = 0.
+--X: X is decremented by 1, X = 0 - 1 = -1.
+X++: X is incremented by 1, X = -1 + 1 = 0.
+X++: X is incremented by 1, X = 0 + 1 = 1.
+
Example 2:
Input: operations = ["++X","++X","X++"]
+Output: 3
+Explanation: The operations are performed as follows:
+Initially, X = 0.
+++X: X is incremented by 1, X = 0 + 1 = 1.
+++X: X is incremented by 1, X = 1 + 1 = 2.
+X++: X is incremented by 1, X = 2 + 1 = 3.
+
Example 3:
Input: operations = ["X++","++X","--X","X--"]
+Output: 0
+Explanation: The operations are performed as follows:
+Initially, X = 0.
+X++: X is incremented by 1, X = 0 + 1 = 1.
+++X: X is incremented by 1, X = 1 + 1 = 2.
+--X: X is decremented by 1, X = 2 - 1 = 1.
+X--: X is decremented by 1, X = 1 - 1 = 0.
+
Constraints:
1 <= operations.length <= 100
operations[i] will be either "++X", "X++", "--X", or "X--".
Click to open Hints
There are only two operations to keep track of.
Use a variable to store the value after each operation.
`,22),p=[o];function t(r,c,i,C,y,d){return a(),n("div",null,p)}const u=s(e,[["render",t]]);export{D as __pageData,u as default};
diff --git a/assets/solution_2101-2200_2011 - Final Value of Variable After Performing Operations.md.7ad7e527.lean.js b/assets/solution_2101-2200_2011 - Final Value of Variable After Performing Operations.md.7ad7e527.lean.js
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..42efc85e
--- /dev/null
+++ b/assets/solution_2101-2200_2011 - Final Value of Variable After Performing Operations.md.7ad7e527.lean.js
@@ -0,0 +1 @@
+import{_ as s,o as a,c as n,a as l}from"./app.e4604e86.js";const D=JSON.parse('{"title":"2011. Final Value of Variable After Performing Operations","description":"","frontmatter":{},"headers":[{"level":2,"title":"Problem Statement","slug":"problem-statement","link":"#problem-statement","children":[]},{"level":2,"title":"Solution:","slug":"solution","link":"#solution","children":[{"level":3,"title":"...","slug":"","link":"#","children":[]}]}],"relativePath":"solution/2101-2200/2011 - Final Value of Variable After Performing Operations.md","lastUpdated":1677958804000}'),e={name:"solution/2101-2200/2011 - Final Value of Variable After Performing Operations.md"},o=l("",22),p=[o];function t(r,c,i,C,y,d){return a(),n("div",null,p)}const u=s(e,[["render",t]]);export{D as __pageData,u as default};
diff --git a/assets/solution_2101-2200_2114 - Maximum Number of Words Found in Sentences.md.9727b95e.js b/assets/solution_2101-2200_2114 - Maximum Number of Words Found in Sentences.md.9727b95e.js
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..25c32667
--- /dev/null
+++ b/assets/solution_2101-2200_2114 - Maximum Number of Words Found in Sentences.md.9727b95e.js
@@ -0,0 +1,28 @@
+import{_ as s,o as n,c as e,a}from"./app.e4604e86.js";const A=JSON.parse('{"title":"2114. Maximum Number of Words Found in Sentences","description":"","frontmatter":{},"headers":[{"level":2,"title":"Problem Statement","slug":"problem-statement","link":"#problem-statement","children":[]},{"level":2,"title":"Solution:","slug":"solution","link":"#solution","children":[{"level":3,"title":"...","slug":"","link":"#","children":[]}]}],"relativePath":"solution/2101-2200/2114 - Maximum Number of Words Found in Sentences.md","lastUpdated":1677958804000}'),o={name:"solution/2101-2200/2114 - Maximum Number of Words Found in Sentences.md"},l=a(`
2114. Maximum Number of Words Found in Sentences #
A sentence is a list of words that are separated by a single space with no leading or trailing spaces.
You are given an array of strings sentences, where each sentences[i] represents a single sentence.
Return the maximum number of words that appear in a single sentence.
Example 1:
Input: sentences = ["alice and bob love leetcode", "i think so too", "this is great thanks very much"]
+Output: 6
+Explanation:
+- The first sentence, "alice and bob love leetcode", has 5 words in total.
+- The second sentence, "i think so too", has 4 words in total.
+- The third sentence, "this is great thanks very much", has 6 words in total.
+Thus, the maximum number of words in a single sentence comes from the third sentence, which has 6 words.
+
Example 2:
Input: sentences = ["please wait", "continue to fight", "continue to win"]
+Output: 3
+Explanation: It is possible that multiple sentences contain the same number of words.
+In this example, the second and third sentences (underlined) have the same number of words.
+
Constraints:
1 <= sentences.length <= 100
1 <= sentences[i].length <= 100
sentences[i] consists only of lowercase English letters and ' ' only.
sentences[i] does not have leading or trailing spaces.
All the words in sentences[i] are separated by a single space.
Click to open Hints
Process each sentence separately and count the number of words by looking for the number of space characters in the sentence and adding it by 1.
`,19),t=[l];function p(c,r,i,d,C,u){return n(),e("div",null,t)}const D=s(o,[["render",p]]);export{A as __pageData,D as default};
diff --git a/assets/solution_2101-2200_2114 - Maximum Number of Words Found in Sentences.md.9727b95e.lean.js b/assets/solution_2101-2200_2114 - Maximum Number of Words Found in Sentences.md.9727b95e.lean.js
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..a9751de2
--- /dev/null
+++ b/assets/solution_2101-2200_2114 - Maximum Number of Words Found in Sentences.md.9727b95e.lean.js
@@ -0,0 +1 @@
+import{_ as s,o as n,c as e,a}from"./app.e4604e86.js";const A=JSON.parse('{"title":"2114. Maximum Number of Words Found in Sentences","description":"","frontmatter":{},"headers":[{"level":2,"title":"Problem Statement","slug":"problem-statement","link":"#problem-statement","children":[]},{"level":2,"title":"Solution:","slug":"solution","link":"#solution","children":[{"level":3,"title":"...","slug":"","link":"#","children":[]}]}],"relativePath":"solution/2101-2200/2114 - Maximum Number of Words Found in Sentences.md","lastUpdated":1677958804000}'),o={name:"solution/2101-2200/2114 - Maximum Number of Words Found in Sentences.md"},l=a("",19),t=[l];function p(c,r,i,d,C,u){return n(),e("div",null,t)}const D=s(o,[["render",p]]);export{A as __pageData,D as default};
diff --git a/assets/solution_2101-2200_2160 - Minimum Sum of Four Digit Number After Splitting Digits.md.8944b3ee.js b/assets/solution_2101-2200_2160 - Minimum Sum of Four Digit Number After Splitting Digits.md.8944b3ee.js
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..232f450e
--- /dev/null
+++ b/assets/solution_2101-2200_2160 - Minimum Sum of Four Digit Number After Splitting Digits.md.8944b3ee.js
@@ -0,0 +1,27 @@
+import{_ as s,o as n,c as a,a as l}from"./app.e4604e86.js";const A=JSON.parse('{"title":"2160. Minimum Sum of Four Digit Number After Splitting Digits","description":"","frontmatter":{},"headers":[{"level":2,"title":"Problem Statement","slug":"problem-statement","link":"#problem-statement","children":[]},{"level":2,"title":"Solution:","slug":"solution","link":"#solution","children":[{"level":3,"title":"...","slug":"","link":"#","children":[]}]}],"relativePath":"solution/2101-2200/2160 - Minimum Sum of Four Digit Number After Splitting Digits.md","lastUpdated":1678822270000}'),o={name:"solution/2101-2200/2160 - Minimum Sum of Four Digit Number After Splitting Digits.md"},e=l(`
2160. Minimum Sum of Four Digit Number After Splitting Digits #
You are given a positive integer num consisting of exactly four digits. Split num into two new integers new1 and new2 by using the digits found in num. Leading zeros are allowed in new1 and new2, and all the digits found in num must be used.
For example, given num = 2932, you have the following digits: two 2's, one 9 and one 3. Some of the possible pairs [new1, new2] are [22, 93], [23, 92], [223, 9] and [2, 329].
Return the minimum possible sum of new1 and new2.
Example 1:
Input: num = 2932
+Output: 52
+Explanation: Some possible pairs [new1, new2] are [29, 23], [223, 9], etc.
+The minimum sum can be obtained by the pair [29, 23]: 29 + 23 = 52.
+
Example 2:
Input: num = 4009
+Output: 13
+Explanation: Some possible pairs [new1, new2] are [0, 49], [490, 0], etc.
+The minimum sum can be obtained by the pair [4, 9]: 4 + 9 = 13.
+
Constraints:
1000 <= num <= 9999
Click to open Hints
Notice that the most optimal way to obtain the minimum possible sum using 4 digits is by summing up two 2-digit numbers.
We can use the two smallest digits out of the four as the digits found in the tens place respectively.
Similarly, we use the final 2 larger digits as the digits found in the ones place.
`,19),p=[e];function t(c,r,i,D,y,F){return n(),a("div",null,p)}const C=s(o,[["render",t]]);export{A as __pageData,C as default};
diff --git a/assets/solution_2101-2200_2160 - Minimum Sum of Four Digit Number After Splitting Digits.md.8944b3ee.lean.js b/assets/solution_2101-2200_2160 - Minimum Sum of Four Digit Number After Splitting Digits.md.8944b3ee.lean.js
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..3afa75f4
--- /dev/null
+++ b/assets/solution_2101-2200_2160 - Minimum Sum of Four Digit Number After Splitting Digits.md.8944b3ee.lean.js
@@ -0,0 +1 @@
+import{_ as s,o as n,c as a,a as l}from"./app.e4604e86.js";const A=JSON.parse('{"title":"2160. Minimum Sum of Four Digit Number After Splitting Digits","description":"","frontmatter":{},"headers":[{"level":2,"title":"Problem Statement","slug":"problem-statement","link":"#problem-statement","children":[]},{"level":2,"title":"Solution:","slug":"solution","link":"#solution","children":[{"level":3,"title":"...","slug":"","link":"#","children":[]}]}],"relativePath":"solution/2101-2200/2160 - Minimum Sum of Four Digit Number After Splitting Digits.md","lastUpdated":1678822270000}'),o={name:"solution/2101-2200/2160 - Minimum Sum of Four Digit Number After Splitting Digits.md"},e=l("",19),p=[e];function t(c,r,i,D,y,F){return n(),a("div",null,p)}const C=s(o,[["render",t]]);export{A as __pageData,C as default};
diff --git a/assets/solution_2101-2200_2176 - Count Equal and Divisible Pairs in an Array.md.43e7bbc1.js b/assets/solution_2101-2200_2176 - Count Equal and Divisible Pairs in an Array.md.43e7bbc1.js
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..76dd89b1
--- /dev/null
+++ b/assets/solution_2101-2200_2176 - Count Equal and Divisible Pairs in an Array.md.43e7bbc1.js
@@ -0,0 +1,29 @@
+import{_ as s,o as n,c as a,a as l}from"./app.e4604e86.js";const d=JSON.parse('{"title":"2176. Count Equal and Divisible Pairs in an Array","description":"","frontmatter":{},"headers":[{"level":2,"title":"Problem Statement","slug":"problem-statement","link":"#problem-statement","children":[]},{"level":2,"title":"Solution:","slug":"solution","link":"#solution","children":[{"level":3,"title":"...","slug":"","link":"#","children":[]}]}],"relativePath":"solution/2101-2200/2176 - Count Equal and Divisible Pairs in an Array.md","lastUpdated":1677460380000}'),p={name:"solution/2101-2200/2176 - Count Equal and Divisible Pairs in an Array.md"},e=l(`
2176. Count Equal and Divisible Pairs in an Array #
Given a 0-indexed integer array nums of length n and an integer k, return the number of pairs(i, j)where0 <= i < j < n, such thatnums[i] == nums[j]and(i * j)is divisible byk.
Example 1:
Input: nums = [3,1,2,2,2,1,3], k = 2
+Output: 4
+Explanation:
+There are 4 pairs that meet all the requirements:
+- nums[0] == nums[6], and 0 * 6 == 0, which is divisible by 2.
+- nums[2] == nums[3], and 2 * 3 == 6, which is divisible by 2.
+- nums[2] == nums[4], and 2 * 4 == 8, which is divisible by 2.
+- nums[3] == nums[4], and 3 * 4 == 12, which is divisible by 2.
+
Example 2:
Input: nums = [1,2,3,4], k = 1
+Output: 0
+Explanation: Since no value in nums is repeated, there are no pairs (i,j) that meet all the requirements.
+
Constraints:
1 <= nums.length <= 100
1 <= nums[i], k <= 100
Click to open Hints
For every possible pair of indices (i, j) where i < j, check if it satisfies the given conditions.
implSolution{
+pubfncount_pairs(nums:Vec<i32>, k:i32)->i32{
+letmut ans =0;
+
+for i in0..nums.len(){
+for j in i +1..nums.len(){
+if nums[i]== nums[j]&&(i * j)% k asusize==0{
+ ans +=1;
+}
+}
+}
+
+ ans
+}
+}
+
+
`,17),o=[e];function t(c,r,i,C,y,D){return n(),a("div",null,o)}const F=s(p,[["render",t]]);export{d as __pageData,F as default};
diff --git a/assets/solution_2101-2200_2176 - Count Equal and Divisible Pairs in an Array.md.43e7bbc1.lean.js b/assets/solution_2101-2200_2176 - Count Equal and Divisible Pairs in an Array.md.43e7bbc1.lean.js
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..275786d0
--- /dev/null
+++ b/assets/solution_2101-2200_2176 - Count Equal and Divisible Pairs in an Array.md.43e7bbc1.lean.js
@@ -0,0 +1 @@
+import{_ as s,o as n,c as a,a as l}from"./app.e4604e86.js";const d=JSON.parse('{"title":"2176. Count Equal and Divisible Pairs in an Array","description":"","frontmatter":{},"headers":[{"level":2,"title":"Problem Statement","slug":"problem-statement","link":"#problem-statement","children":[]},{"level":2,"title":"Solution:","slug":"solution","link":"#solution","children":[{"level":3,"title":"...","slug":"","link":"#","children":[]}]}],"relativePath":"solution/2101-2200/2176 - Count Equal and Divisible Pairs in an Array.md","lastUpdated":1677460380000}'),p={name:"solution/2101-2200/2176 - Count Equal and Divisible Pairs in an Array.md"},e=l("",17),o=[e];function t(c,r,i,C,y,D){return n(),a("div",null,o)}const F=s(p,[["render",t]]);export{d as __pageData,F as default};
diff --git a/assets/solution_2101-2200_2187 - Minimum Time to Complete Trips.md.5a37b03e.js b/assets/solution_2101-2200_2187 - Minimum Time to Complete Trips.md.5a37b03e.js
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..e17e7e3d
--- /dev/null
+++ b/assets/solution_2101-2200_2187 - Minimum Time to Complete Trips.md.5a37b03e.js
@@ -0,0 +1,44 @@
+import{_ as s,o as n,c as a,a as l}from"./app.e4604e86.js";const F=JSON.parse('{"title":"2187. Minimum Time to Complete Trips","description":"","frontmatter":{},"headers":[{"level":2,"title":"Problem Statement","slug":"problem-statement","link":"#problem-statement","children":[]},{"level":2,"title":"Solution:","slug":"solution","link":"#solution","children":[{"level":3,"title":"...","slug":"","link":"#","children":[]}]}],"relativePath":"solution/2101-2200/2187 - Minimum Time to Complete Trips.md","lastUpdated":1678822270000}'),p={name:"solution/2101-2200/2187 - Minimum Time to Complete Trips.md"},o=l(`
You are given an array time where time[i] denotes the time taken by the ith bus to complete one trip.
Each bus can make multiple trips successively; that is, the next trip can start immediately after completing the current trip. Also, each bus operates independently; that is, the trips of one bus do not influence the trips of any other bus.
You are also given an integer totalTrips, which denotes the number of trips all buses should make in total. Return the minimum time required for all buses to complete at leasttotalTrips trips.
Example 1:
Input: time = [1,2,3], totalTrips = 5
+Output: 3
+Explanation:
+- At time t = 1, the number of trips completed by each bus are [1,0,0].
+ The total number of trips completed is 1 + 0 + 0 = 1.
+- At time t = 2, the number of trips completed by each bus are [2,1,0].
+ The total number of trips completed is 2 + 1 + 0 = 3.
+- At time t = 3, the number of trips completed by each bus are [3,1,1].
+ The total number of trips completed is 3 + 1 + 1 = 5.
+So the minimum time needed for all buses to complete at least 5 trips is 3.
+
Example 2:
Input: time = [2], totalTrips = 1
+Output: 2
+Explanation:
+There is only one bus, and it will complete its first trip at t = 2.
+So the minimum time needed to complete 1 trip is 2.
+
Constraints:
1 <= time.length <= 105
1 <= time[i], totalTrips <= 107
Click to open Hints
For a given amount of time, how can we count the total number of trips completed by all buses within that time?
`,19),e=[o];function t(r,c,i,C,D,A){return n(),a("div",null,e)}const m=s(p,[["render",t]]);export{F as __pageData,m as default};
diff --git a/assets/solution_2101-2200_2187 - Minimum Time to Complete Trips.md.5a37b03e.lean.js b/assets/solution_2101-2200_2187 - Minimum Time to Complete Trips.md.5a37b03e.lean.js
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..4b5b2278
--- /dev/null
+++ b/assets/solution_2101-2200_2187 - Minimum Time to Complete Trips.md.5a37b03e.lean.js
@@ -0,0 +1 @@
+import{_ as s,o as n,c as a,a as l}from"./app.e4604e86.js";const F=JSON.parse('{"title":"2187. Minimum Time to Complete Trips","description":"","frontmatter":{},"headers":[{"level":2,"title":"Problem Statement","slug":"problem-statement","link":"#problem-statement","children":[]},{"level":2,"title":"Solution:","slug":"solution","link":"#solution","children":[{"level":3,"title":"...","slug":"","link":"#","children":[]}]}],"relativePath":"solution/2101-2200/2187 - Minimum Time to Complete Trips.md","lastUpdated":1678822270000}'),p={name:"solution/2101-2200/2187 - Minimum Time to Complete Trips.md"},o=l("",19),e=[o];function t(r,c,i,C,D,A){return n(),a("div",null,e)}const m=s(p,[["render",t]]);export{F as __pageData,m as default};
diff --git a/assets/solution_2101-2200_2413 - Smallest Even Multiple.md.45b7de05.js b/assets/solution_2101-2200_2413 - Smallest Even Multiple.md.45b7de05.js
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..7195fa6d
--- /dev/null
+++ b/assets/solution_2101-2200_2413 - Smallest Even Multiple.md.45b7de05.js
@@ -0,0 +1,18 @@
+import{_ as s,o as a,c as n,a as l}from"./app.e4604e86.js";const A=JSON.parse('{"title":"2413. Smallest Even Multiple","description":"","frontmatter":{},"headers":[{"level":2,"title":"Problem Statement","slug":"problem-statement","link":"#problem-statement","children":[]},{"level":2,"title":"Solution:","slug":"solution","link":"#solution","children":[{"level":3,"title":"...","slug":"","link":"#","children":[]}]}],"relativePath":"solution/2101-2200/2413 - Smallest Even Multiple.md","lastUpdated":1677958804000}'),e={name:"solution/2101-2200/2413 - Smallest Even Multiple.md"},p=l(`
`,17),t=[p];function o(r,c,i,C,d,y){return a(),n("div",null,t)}const u=s(e,[["render",o]]);export{A as __pageData,u as default};
diff --git a/assets/solution_2101-2200_2413 - Smallest Even Multiple.md.45b7de05.lean.js b/assets/solution_2101-2200_2413 - Smallest Even Multiple.md.45b7de05.lean.js
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..2dbc9801
--- /dev/null
+++ b/assets/solution_2101-2200_2413 - Smallest Even Multiple.md.45b7de05.lean.js
@@ -0,0 +1 @@
+import{_ as s,o as a,c as n,a as l}from"./app.e4604e86.js";const A=JSON.parse('{"title":"2413. Smallest Even Multiple","description":"","frontmatter":{},"headers":[{"level":2,"title":"Problem Statement","slug":"problem-statement","link":"#problem-statement","children":[]},{"level":2,"title":"Solution:","slug":"solution","link":"#solution","children":[{"level":3,"title":"...","slug":"","link":"#","children":[]}]}],"relativePath":"solution/2101-2200/2413 - Smallest Even Multiple.md","lastUpdated":1677958804000}'),e={name:"solution/2101-2200/2413 - Smallest Even Multiple.md"},p=l("",17),t=[p];function o(r,c,i,C,d,y){return a(),n("div",null,t)}const u=s(e,[["render",o]]);export{A as __pageData,u as default};
diff --git a/assets/solution_2201-2300_2235 - Add Two Integers.md.21a42abe.js b/assets/solution_2201-2300_2235 - Add Two Integers.md.21a42abe.js
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..393be531
--- /dev/null
+++ b/assets/solution_2201-2300_2235 - Add Two Integers.md.21a42abe.js
@@ -0,0 +1,14 @@
+import{_ as s,o as n,c as a,a as e}from"./app.e4604e86.js";const y=JSON.parse('{"title":"2235. Add Two Integers","description":"","frontmatter":{},"headers":[{"level":2,"title":"Problem Statement","slug":"problem-statement","link":"#problem-statement","children":[]},{"level":2,"title":"Solution:","slug":"solution","link":"#solution","children":[{"level":3,"title":"...","slug":"","link":"#","children":[]}]}],"relativePath":"solution/2201-2300/2235 - Add Two Integers.md","lastUpdated":1677958804000}'),l={name:"solution/2201-2300/2235 - Add Two Integers.md"},o=e(`
`,16),t=[o];function p(r,c,i,d,C,u){return n(),a("div",null,t)}const m=s(l,[["render",p]]);export{y as __pageData,m as default};
diff --git a/assets/solution_2201-2300_2235 - Add Two Integers.md.21a42abe.lean.js b/assets/solution_2201-2300_2235 - Add Two Integers.md.21a42abe.lean.js
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..f5815203
--- /dev/null
+++ b/assets/solution_2201-2300_2235 - Add Two Integers.md.21a42abe.lean.js
@@ -0,0 +1 @@
+import{_ as s,o as n,c as a,a as e}from"./app.e4604e86.js";const y=JSON.parse('{"title":"2235. Add Two Integers","description":"","frontmatter":{},"headers":[{"level":2,"title":"Problem Statement","slug":"problem-statement","link":"#problem-statement","children":[]},{"level":2,"title":"Solution:","slug":"solution","link":"#solution","children":[{"level":3,"title":"...","slug":"","link":"#","children":[]}]}],"relativePath":"solution/2201-2300/2235 - Add Two Integers.md","lastUpdated":1677958804000}'),l={name:"solution/2201-2300/2235 - Add Two Integers.md"},o=e("",16),t=[o];function p(r,c,i,d,C,u){return n(),a("div",null,t)}const m=s(l,[["render",p]]);export{y as __pageData,m as default};
diff --git a/assets/solution_2201-2300_2236 - Root Equals Sum of Children.md.2e414e5e.js b/assets/solution_2201-2300_2236 - Root Equals Sum of Children.md.2e414e5e.js
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..14d96faf
--- /dev/null
+++ b/assets/solution_2201-2300_2236 - Root Equals Sum of Children.md.2e414e5e.js
@@ -0,0 +1,15 @@
+import{_ as a,o as s,c as e,a as l}from"./app.e4604e86.js";const A=JSON.parse('{"title":"2236. Root Equals Sum of Children","description":"","frontmatter":{},"headers":[{"level":2,"title":"Problem Statement:","slug":"problem-statement","link":"#problem-statement","children":[{"level":3,"title":"Example 1:","slug":"example-1","link":"#example-1","children":[]},{"level":3,"title":"Explanation:","slug":"explanation","link":"#explanation","children":[]},{"level":3,"title":"Example 2:","slug":"example-2","link":"#example-2","children":[]},{"level":3,"title":"Explanation:","slug":"explanation-1","link":"#explanation-1","children":[]},{"level":3,"title":"Constraints:","slug":"constraints","link":"#constraints","children":[]}]},{"level":2,"title":"Solution:","slug":"solution","link":"#solution","children":[{"level":3,"title":"...","slug":"","link":"#","children":[]}]}],"relativePath":"solution/2201-2300/2236 - Root Equals Sum of Children.md","lastUpdated":1671291107000}'),n={name:"solution/2201-2300/2236 - Root Equals Sum of Children.md"},o=l(`
`,21),t=[o];function p(r,i,c,d,h,u){return s(),e("div",null,t)}const y=a(n,[["render",p]]);export{A as __pageData,y as default};
diff --git a/assets/solution_2201-2300_2236 - Root Equals Sum of Children.md.2e414e5e.lean.js b/assets/solution_2201-2300_2236 - Root Equals Sum of Children.md.2e414e5e.lean.js
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..1ca6ef0c
--- /dev/null
+++ b/assets/solution_2201-2300_2236 - Root Equals Sum of Children.md.2e414e5e.lean.js
@@ -0,0 +1 @@
+import{_ as a,o as s,c as e,a as l}from"./app.e4604e86.js";const A=JSON.parse('{"title":"2236. Root Equals Sum of Children","description":"","frontmatter":{},"headers":[{"level":2,"title":"Problem Statement:","slug":"problem-statement","link":"#problem-statement","children":[{"level":3,"title":"Example 1:","slug":"example-1","link":"#example-1","children":[]},{"level":3,"title":"Explanation:","slug":"explanation","link":"#explanation","children":[]},{"level":3,"title":"Example 2:","slug":"example-2","link":"#example-2","children":[]},{"level":3,"title":"Explanation:","slug":"explanation-1","link":"#explanation-1","children":[]},{"level":3,"title":"Constraints:","slug":"constraints","link":"#constraints","children":[]}]},{"level":2,"title":"Solution:","slug":"solution","link":"#solution","children":[{"level":3,"title":"...","slug":"","link":"#","children":[]}]}],"relativePath":"solution/2201-2300/2236 - Root Equals Sum of Children.md","lastUpdated":1671291107000}'),n={name:"solution/2201-2300/2236 - Root Equals Sum of Children.md"},o=l("",21),t=[o];function p(r,i,c,d,h,u){return s(),e("div",null,t)}const y=a(n,[["render",p]]);export{A as __pageData,y as default};
diff --git a/assets/solution_2301-2400_2348 - Number of Zero-Filled Subarrays.md.a6743e9b.js b/assets/solution_2301-2400_2348 - Number of Zero-Filled Subarrays.md.a6743e9b.js
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..8eebdfd4
--- /dev/null
+++ b/assets/solution_2301-2400_2348 - Number of Zero-Filled Subarrays.md.a6743e9b.js
@@ -0,0 +1,54 @@
+import{_ as s,o as n,c as a,a as e}from"./app.e4604e86.js";const d=JSON.parse('{"title":"2348. Number of Zero-Filled Subarrays","description":"","frontmatter":{},"headers":[{"level":2,"title":"Problem Statement","slug":"problem-statement","link":"#problem-statement","children":[{"level":3,"title":"...","slug":"","link":"#","children":[]}]}],"relativePath":"solution/2301-2400/2348 - Number of Zero-Filled Subarrays.md","lastUpdated":1680513503000}'),l={name:"solution/2301-2400/2348 - Number of Zero-Filled Subarrays.md"},p=e(`
Given an integer array nums, return the number of subarrays filled with 0.
A subarray is a contiguous non-empty sequence of elements within an array.
Example 1:
Input: nums = [1,3,0,0,2,0,0,4]
+Output: 6
+Explanation:
+There are 4 occurrences of [0] as a subarray.
+There are 2 occurrences of [0,0] as a subarray.
+There is no occurrence of a subarray with a size more than 2 filled with 0. Therefore, we return 6.\`\`\`
+
+<p><strong class="example">Example 2:</strong></p>
+
+
Input: nums = [0,0,0,2,0,0] Output: 9 Explanation: There are 5 occurrences of [0] as a subarray. There are 3 occurrences of [0,0] as a subarray. There is 1 occurrence of [0,0,0] as a subarray. There is no occurrence of a subarray with a size more than 3 filled with 0. Therefore, we return 9.
Input: nums = [2,10,2019] Output: 0 Explanation: There is no subarray filled with 0. Therefore, we return 0.
+<p> </p>
+<p><strong>Constraints:</strong></p>
+<ul>
+<li><code>1 <= nums.length <= 10<sup>5</sup></code></li>
+<li><code>-10<sup>9</sup> <= nums[i] <= 10<sup>9</sup></code></li>
+</ul>
+
+
+::: details _Click to open Hints_
+
+- For each zero, you can calculate the number of zero-filled subarrays that end on that index, which is the number of consecutive zeros behind the current element + 1.
+- Maintain the number of consecutive zeros behind the current element, count the number of zero-filled subarrays that end on each index, sum it up to get the answer.
+
+:::
+
+## Solution:
+
+::: code-group
+
+\`\`\`rs [Rust]
+impl Solution {
+ pub fn zero_filled_subarray(nums: Vec<i32>) -> i64 {
+ let mut nums = nums;
+ nums.push(1);
+
+ let (mut res, mut count) = (0, 0);
+ for num in nums {
+ if num == 0 {
+ count += 1;
+ } else {
+ res += count * (count + 1) / 2;
+ count = 0;
+ }
+ }
+
+ res
+ }
+}
+
+
`,15),t=[p];function o(r,c,i,u,C,A){return n(),a("div",null,t)}const m=s(l,[["render",o]]);export{d as __pageData,m as default};
diff --git a/assets/solution_2301-2400_2348 - Number of Zero-Filled Subarrays.md.a6743e9b.lean.js b/assets/solution_2301-2400_2348 - Number of Zero-Filled Subarrays.md.a6743e9b.lean.js
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..45ebd180
--- /dev/null
+++ b/assets/solution_2301-2400_2348 - Number of Zero-Filled Subarrays.md.a6743e9b.lean.js
@@ -0,0 +1 @@
+import{_ as s,o as n,c as a,a as e}from"./app.e4604e86.js";const d=JSON.parse('{"title":"2348. Number of Zero-Filled Subarrays","description":"","frontmatter":{},"headers":[{"level":2,"title":"Problem Statement","slug":"problem-statement","link":"#problem-statement","children":[{"level":3,"title":"...","slug":"","link":"#","children":[]}]}],"relativePath":"solution/2301-2400/2348 - Number of Zero-Filled Subarrays.md","lastUpdated":1680513503000}'),l={name:"solution/2301-2400/2348 - Number of Zero-Filled Subarrays.md"},p=e("",15),t=[p];function o(r,c,i,u,C,A){return n(),a("div",null,t)}const m=s(l,[["render",o]]);export{d as __pageData,m as default};
diff --git a/assets/solution_2301-2400_2396 - Strictly Palindromic Number.md.b6902872.js b/assets/solution_2301-2400_2396 - Strictly Palindromic Number.md.b6902872.js
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..546b5a39
--- /dev/null
+++ b/assets/solution_2301-2400_2396 - Strictly Palindromic Number.md.b6902872.js
@@ -0,0 +1,27 @@
+import{_ as s,o as n,c as a,a as l}from"./app.e4604e86.js";const D=JSON.parse('{"title":"2396. Strictly Palindromic Number","description":"","frontmatter":{},"headers":[{"level":2,"title":"Problem Statement","slug":"problem-statement","link":"#problem-statement","children":[]},{"level":2,"title":"Solution:","slug":"solution","link":"#solution","children":[{"level":3,"title":"...","slug":"","link":"#","children":[]}]}],"relativePath":"solution/2301-2400/2396 - Strictly Palindromic Number.md","lastUpdated":1677958804000}'),e={name:"solution/2301-2400/2396 - Strictly Palindromic Number.md"},o=l(`
An integer n is strictly palindromic if, for every base b between 2 and n - 2 (inclusive), the string representation of the integer n in base b is palindromic.
Given an integer n, return trueif n is strictly palindromic and false otherwise.
A string is palindromic if it reads the same forward and backward.
Example 1:
Input: n = 9
+Output: false
+Explanation: In base 2: 9 = 1001 (base 2), which is palindromic.
+In base 3: 9 = 100 (base 3), which is not palindromic.
+Therefore, 9 is not strictly palindromic so we return false.
+Note that in bases 4, 5, 6, and 7, n = 9 is also not palindromic.
+
Example 2:
Input: n = 4
+Output: false
+Explanation: We only consider base 2: 4 = 100 (base 2), which is not palindromic.
+Therefore, we return false.
+
+
Constraints:
4 <= n <= 105
Click to open Hints
Consider the representation of the given number in the base n - 2.
The number n in base (n - 2) is always 12, which is not palindromic.
`,19),p=[o];function t(r,c,i,C,d,y){return n(),a("div",null,p)}const m=s(e,[["render",t]]);export{D as __pageData,m as default};
diff --git a/assets/solution_2301-2400_2396 - Strictly Palindromic Number.md.b6902872.lean.js b/assets/solution_2301-2400_2396 - Strictly Palindromic Number.md.b6902872.lean.js
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..b30d7a16
--- /dev/null
+++ b/assets/solution_2301-2400_2396 - Strictly Palindromic Number.md.b6902872.lean.js
@@ -0,0 +1 @@
+import{_ as s,o as n,c as a,a as l}from"./app.e4604e86.js";const D=JSON.parse('{"title":"2396. Strictly Palindromic Number","description":"","frontmatter":{},"headers":[{"level":2,"title":"Problem Statement","slug":"problem-statement","link":"#problem-statement","children":[]},{"level":2,"title":"Solution:","slug":"solution","link":"#solution","children":[{"level":3,"title":"...","slug":"","link":"#","children":[]}]}],"relativePath":"solution/2301-2400/2396 - Strictly Palindromic Number.md","lastUpdated":1677958804000}'),e={name:"solution/2301-2400/2396 - Strictly Palindromic Number.md"},o=l("",19),p=[o];function t(r,c,i,C,d,y){return n(),a("div",null,p)}const m=s(e,[["render",t]]);export{D as __pageData,m as default};
diff --git a/assets/solution_2401-2500_2427 - Number of Common Factors.md.7e6bc604.js b/assets/solution_2401-2500_2427 - Number of Common Factors.md.7e6bc604.js
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..82f60afd
--- /dev/null
+++ b/assets/solution_2401-2500_2427 - Number of Common Factors.md.7e6bc604.js
@@ -0,0 +1,23 @@
+import{_ as s,o as a,c as n,a as o}from"./app.e4604e86.js";const d=JSON.parse('{"title":"2427. Number of Common Factors","description":"","frontmatter":{},"headers":[{"level":2,"title":"Problem Statement","slug":"problem-statement","link":"#problem-statement","children":[]},{"level":2,"title":"Solution:","slug":"solution","link":"#solution","children":[{"level":3,"title":"...","slug":"","link":"#","children":[]}]}],"relativePath":"solution/2401-2500/2427 - Number of Common Factors.md","lastUpdated":1677460380000}'),l={name:"solution/2401-2500/2427 - Number of Common Factors.md"},e=o(`
`,18),p=[e];function t(c,r,i,C,y,D){return a(),n("div",null,p)}const F=s(l,[["render",t]]);export{d as __pageData,F as default};
diff --git a/assets/solution_2401-2500_2427 - Number of Common Factors.md.7e6bc604.lean.js b/assets/solution_2401-2500_2427 - Number of Common Factors.md.7e6bc604.lean.js
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..4a935e45
--- /dev/null
+++ b/assets/solution_2401-2500_2427 - Number of Common Factors.md.7e6bc604.lean.js
@@ -0,0 +1 @@
+import{_ as s,o as a,c as n,a as o}from"./app.e4604e86.js";const d=JSON.parse('{"title":"2427. Number of Common Factors","description":"","frontmatter":{},"headers":[{"level":2,"title":"Problem Statement","slug":"problem-statement","link":"#problem-statement","children":[]},{"level":2,"title":"Solution:","slug":"solution","link":"#solution","children":[{"level":3,"title":"...","slug":"","link":"#","children":[]}]}],"relativePath":"solution/2401-2500/2427 - Number of Common Factors.md","lastUpdated":1677460380000}'),l={name:"solution/2401-2500/2427 - Number of Common Factors.md"},e=o("",18),p=[e];function t(c,r,i,C,y,D){return a(),n("div",null,p)}const F=s(l,[["render",t]]);export{d as __pageData,F as default};
diff --git a/assets/solution_2401-2500_2444 - Count Subarrays With Fixed Bounds.md.f7164976.js b/assets/solution_2401-2500_2444 - Count Subarrays With Fixed Bounds.md.f7164976.js
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..30565243
--- /dev/null
+++ b/assets/solution_2401-2500_2444 - Count Subarrays With Fixed Bounds.md.f7164976.js
@@ -0,0 +1,42 @@
+import{_ as s,o as a,c as n,a as l}from"./app.e4604e86.js";const F=JSON.parse('{"title":"2444. Count Subarrays With Fixed Bounds","description":"","frontmatter":{},"headers":[{"level":2,"title":"Problem Statement","slug":"problem-statement","link":"#problem-statement","children":[]},{"level":2,"title":"Solution:","slug":"solution","link":"#solution","children":[{"level":3,"title":"...","slug":"","link":"#","children":[]}]}],"relativePath":"solution/2401-2500/2444 - Count Subarrays With Fixed Bounds.md","lastUpdated":1677958804000}'),o={name:"solution/2401-2500/2444 - Count Subarrays With Fixed Bounds.md"},p=l(`
You are given an integer array nums and two integers minK and maxK.
A fixed-bound subarray of nums is a subarray that satisfies the following conditions:
The minimum value in the subarray is equal to minK.
The maximum value in the subarray is equal to maxK.
Return the number of fixed-bound subarrays.
A subarray is a contiguous part of an array.
Example 1:
Input: nums = [1,3,5,2,7,5], minK = 1, maxK = 5
+Output: 2
+Explanation: The fixed-bound subarrays are [1,3,5] and [1,3,5,2].
+
Example 2:
Input: nums = [1,1,1,1], minK = 1, maxK = 1
+Output: 10
+Explanation: Every subarray of nums is a fixed-bound subarray. There are 10 possible subarrays.
+
Constraints:
2 <= nums.length <= 105
1 <= nums[i], minK, maxK <= 106
Click to open Hints
Can you solve the problem if all the numbers in the array were between minK and maxK inclusive?
Think of the inclusion-exclusion principle.
Divide the array into multiple subarrays such that each number in each subarray is between minK and maxK inclusive, solve the previous problem for each subarray, and sum all the answers.
implSolution{
+pubfncount_subarrays(nums:Vec<i32>, min_k:i32, max_k:i32)->i64{
+let(mut bad,mut min,mut max)=(-1,-1,-1);
+ // bad is the index of the first number that is not in the range [min_k, max_k]
+letmut res =0;
+
+for(i,&num)in nums.iter().enumerate(){
+let i = i asi64;
+
+ // set i to bad index if it is not in the range [min_k, max_k]
+if!(min_k <= num && num <= max_k){
+ bad = i;
+}
+
+ // set i to min index if num is equal to min_k
+if min_k == num {
+ min = i;
+}
+ // set i to max index if num is equal to max_k
+if max_k == num {
+ max = i;
+}
+
+ // it is the last starting point for the subarray
+let start = min.min(max);
+if start > bad {
+ res += start - bad; // add the number of subarrays b/w [bad + 1, start]
+}
+}
+
+ res
+}
+}
+
+
`,21),e=[p];function t(r,c,i,D,y,C){return a(),n("div",null,e)}const u=s(o,[["render",t]]);export{F as __pageData,u as default};
diff --git a/assets/solution_2401-2500_2444 - Count Subarrays With Fixed Bounds.md.f7164976.lean.js b/assets/solution_2401-2500_2444 - Count Subarrays With Fixed Bounds.md.f7164976.lean.js
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..7e702423
--- /dev/null
+++ b/assets/solution_2401-2500_2444 - Count Subarrays With Fixed Bounds.md.f7164976.lean.js
@@ -0,0 +1 @@
+import{_ as s,o as a,c as n,a as l}from"./app.e4604e86.js";const F=JSON.parse('{"title":"2444. Count Subarrays With Fixed Bounds","description":"","frontmatter":{},"headers":[{"level":2,"title":"Problem Statement","slug":"problem-statement","link":"#problem-statement","children":[]},{"level":2,"title":"Solution:","slug":"solution","link":"#solution","children":[{"level":3,"title":"...","slug":"","link":"#","children":[]}]}],"relativePath":"solution/2401-2500/2444 - Count Subarrays With Fixed Bounds.md","lastUpdated":1677958804000}'),o={name:"solution/2401-2500/2444 - Count Subarrays With Fixed Bounds.md"},p=l("",21),e=[p];function t(r,c,i,D,y,C){return a(),n("div",null,e)}const u=s(o,[["render",t]]);export{F as __pageData,u as default};
diff --git a/assets/solution_2401-2500_2469 - Convert the Temperature.md.539adef9.js b/assets/solution_2401-2500_2469 - Convert the Temperature.md.539adef9.js
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..a08027b0
--- /dev/null
+++ b/assets/solution_2401-2500_2469 - Convert the Temperature.md.539adef9.js
@@ -0,0 +1,18 @@
+import{_ as s,o as a,c as e,a as n}from"./app.e4604e86.js";const D=JSON.parse('{"title":"2469. Convert the Temperature","description":"","frontmatter":{},"headers":[{"level":2,"title":"Problem Statement","slug":"problem-statement","link":"#problem-statement","children":[]},{"level":2,"title":"Solution:","slug":"solution","link":"#solution","children":[{"level":3,"title":"...","slug":"","link":"#","children":[]}]}],"relativePath":"solution/2401-2500/2469 - Convert the Temperature.md","lastUpdated":1677762379000}'),l={name:"solution/2401-2500/2469 - Convert the Temperature.md"},t=n(`
You are given a non-negative floating point number rounded to two decimal places celsius, that denotes the temperature in Celsius.
You should convert Celsius into Kelvin and Fahrenheit and return it as an array ans = [kelvin, fahrenheit].
Return the array ans. Answers within 10-5 of the actual answer will be accepted.
Note that:
Kelvin = Celsius + 273.15
Fahrenheit = Celsius * 1.80 + 32.00
Example 1:
Input: celsius = 36.50
+Output: [309.65000,97.70000]
+Explanation: Temperature at 36.50 Celsius converted in Kelvin is 309.65 and converted in Fahrenheit is 97.70.
+
Example 2:
Input: celsius = 122.11
+Output: [395.26000,251.79800]
+Explanation: Temperature at 122.11 Celsius converted in Kelvin is 395.26 and converted in Fahrenheit is 251.798.
+
Constraints:
0 <= celsius <= 1000
Click to open Hints
Implement formulas that are given in the statement.
`,21),o=[t];function p(r,c,i,C,d,u){return a(),e("div",null,o)}const h=s(l,[["render",p]]);export{D as __pageData,h as default};
diff --git a/assets/solution_2401-2500_2469 - Convert the Temperature.md.539adef9.lean.js b/assets/solution_2401-2500_2469 - Convert the Temperature.md.539adef9.lean.js
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..019eeb14
--- /dev/null
+++ b/assets/solution_2401-2500_2469 - Convert the Temperature.md.539adef9.lean.js
@@ -0,0 +1 @@
+import{_ as s,o as a,c as e,a as n}from"./app.e4604e86.js";const D=JSON.parse('{"title":"2469. Convert the Temperature","description":"","frontmatter":{},"headers":[{"level":2,"title":"Problem Statement","slug":"problem-statement","link":"#problem-statement","children":[]},{"level":2,"title":"Solution:","slug":"solution","link":"#solution","children":[{"level":3,"title":"...","slug":"","link":"#","children":[]}]}],"relativePath":"solution/2401-2500/2469 - Convert the Temperature.md","lastUpdated":1677762379000}'),l={name:"solution/2401-2500/2469 - Convert the Temperature.md"},t=n("",21),o=[t];function p(r,c,i,C,d,u){return a(),e("div",null,o)}const h=s(l,[["render",p]]);export{D as __pageData,h as default};
diff --git a/assets/solution_2401-2500_2574 - Left and Right Sum Differences.md.98c97f87.js b/assets/solution_2401-2500_2574 - Left and Right Sum Differences.md.98c97f87.js
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..0da7e7d5
--- /dev/null
+++ b/assets/solution_2401-2500_2574 - Left and Right Sum Differences.md.98c97f87.js
@@ -0,0 +1,27 @@
+import{_ as s,o as n,c as a,a as l}from"./app.e4604e86.js";const A=JSON.parse('{"title":"2574. Left and Right Sum Differences","description":"","frontmatter":{},"headers":[{"level":2,"title":"Problem Statement","slug":"problem-statement","link":"#problem-statement","children":[]},{"level":2,"title":"Solution:","slug":"solution","link":"#solution","children":[{"level":3,"title":"...","slug":"","link":"#","children":[]}]}],"relativePath":"solution/2401-2500/2574 - Left and Right Sum Differences.md","lastUpdated":1677958804000}'),e={name:"solution/2401-2500/2574 - Left and Right Sum Differences.md"},o=l(`
Given a 0-indexed integer array nums, find a 0-indexed integer array answer where:
answer.length == nums.length.
answer[i] = |leftSum[i] - rightSum[i]|.
Where:
leftSum[i] is the sum of elements to the left of the index i in the array nums. If there is no such element, leftSum[i] = 0.
rightSum[i] is the sum of elements to the right of the index i in the array nums. If there is no such element, rightSum[i] = 0.
Return the arrayanswer.
Example 1:
Input: nums = [10,4,8,3]
+Output: [15,1,11,22]
+Explanation: The array leftSum is [0,10,14,22] and the array rightSum is [15,11,3,0].
+The array answer is [|0 - 15|,|10 - 11|,|14 - 3|,|22 - 0|] = [15,1,11,22].
+
Example 2:
Input: nums = [1]
+Output: [0]
+Explanation: The array leftSum is [0] and the array rightSum is [0].
+The array answer is [|0 - 0|] = [0].
+
Constraints:
1 <= nums.length <= 1000
1 <= nums[i] <= 105
Click to open Hints
For each index i, maintain two variables leftSum and rightSum.
Iterate on the range j: [0 … i - 1] and add nums[j] to the leftSum and similarly iterate on the range j: [i + 1 … nums.length - 1] and add nums[j] to the rightSum.
`,21),p=[o];function t(r,c,i,y,C,D){return n(),a("div",null,p)}const u=s(e,[["render",t]]);export{A as __pageData,u as default};
diff --git a/assets/solution_2401-2500_2574 - Left and Right Sum Differences.md.98c97f87.lean.js b/assets/solution_2401-2500_2574 - Left and Right Sum Differences.md.98c97f87.lean.js
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..0b2c22d1
--- /dev/null
+++ b/assets/solution_2401-2500_2574 - Left and Right Sum Differences.md.98c97f87.lean.js
@@ -0,0 +1 @@
+import{_ as s,o as n,c as a,a as l}from"./app.e4604e86.js";const A=JSON.parse('{"title":"2574. Left and Right Sum Differences","description":"","frontmatter":{},"headers":[{"level":2,"title":"Problem Statement","slug":"problem-statement","link":"#problem-statement","children":[]},{"level":2,"title":"Solution:","slug":"solution","link":"#solution","children":[{"level":3,"title":"...","slug":"","link":"#","children":[]}]}],"relativePath":"solution/2401-2500/2574 - Left and Right Sum Differences.md","lastUpdated":1677958804000}'),e={name:"solution/2401-2500/2574 - Left and Right Sum Differences.md"},o=l("",21),p=[o];function t(r,c,i,y,C,D){return n(),a("div",null,p)}const u=s(e,[["render",t]]);export{A as __pageData,u as default};
diff --git a/assets/solution_2501-2600_2551 - Put Marbles in Bags.md.50c1a855.js b/assets/solution_2501-2600_2551 - Put Marbles in Bags.md.50c1a855.js
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..ca7502de
--- /dev/null
+++ b/assets/solution_2501-2600_2551 - Put Marbles in Bags.md.50c1a855.js
@@ -0,0 +1,28 @@
+import{_ as s,o as a,c as n,a as l}from"./app.e4604e86.js";const F=JSON.parse('{"title":"2551. Put Marbles in Bags","description":"","frontmatter":{},"headers":[{"level":2,"title":"Problem Statement","slug":"problem-statement","link":"#problem-statement","children":[]},{"level":2,"title":"Solution:","slug":"solution","link":"#solution","children":[{"level":3,"title":"...","slug":"","link":"#","children":[]}]}],"relativePath":"solution/2501-2600/2551 - Put Marbles in Bags.md","lastUpdated":1689264763000}'),e={name:"solution/2501-2600/2551 - Put Marbles in Bags.md"},o=l(`
You have k bags. You are given a 0-indexed integer array weights where weights[i] is the weight of the ith marble. You are also given the integer k.
Divide the marbles into the k bags according to the following rules:
No bag is empty.
If the ith marble and jth marble are in a bag, then all marbles with an index between the ith and jth indices should also be in that same bag.
If a bag consists of all the marbles with an index from i to j inclusively, then the cost of the bag is weights[i] + weights[j].
The score after distributing the marbles is the sum of the costs of all the k bags.
Return the difference between the maximum and minimum scores among marble distributions.
Example 1:
Input: weights = [1,3,5,1], k = 2
+Output: 4
+Explanation:
+The distribution [1],[3,5,1] results in the minimal score of (1+1) + (3+1) = 6.
+The distribution [1,3],[5,1], results in the maximal score of (1+3) + (5+1) = 10.
+Thus, we return their difference 10 - 6 = 4.
+
Example 2:
Input: weights = [1, 3], k = 2
+Output: 0
+Explanation: The only distribution possible is [1],[3].
+Since both the maximal and minimal score are the same, we return 0.
+
-
-
-
-[contributors]: https://contrib.rocks/image?repo=rajput-hemant/leetcode&max=500
-[contributors-graph]: https://github.com/rajput-hemant/leetcode/graphs/contributors
-
-
-
-[leetcode]: https://github.com/rajput-hemant/leetcode
-[topicwise]: ./TOPICWISE.md
-[serialwise]: ./SERIALWISE.md
-
-
-
-[array]: ./TOPICWISE.md#array
-[string]: ./TOPICWISE.md#string
-[hash table]: ./TOPICWISE.md#hash-table
-[dynamic programming]: ./TOPICWISE.md#dynamic-programming
-[math]: ./TOPICWISE.md#math
-[sorting]: ./TOPICWISE.md#sorting
-[greedy]: ./TOPICWISE.md#greedy
-[depth-first search]: ./TOPICWISE.md#depth-first-search
-[database]: ./TOPICWISE.md#database
-[breadth-first search]: ./TOPICWISE.md#breadth-first-search
-[tree]: ./TOPICWISE.md#tree
-[binary search]: ./TOPICWISE.md#binary-search
-[matrix]: ./TOPICWISE.md#matrix
-[binary tree]: ./TOPICWISE.md#binary-tree
-[two pointers]: ./TOPICWISE.md#two-pointers
-[bit manipulation]: ./TOPICWISE.md#bit-manipulation
-[stack]: ./TOPICWISE.md#stack
-[heap ]: ./TOPICWISE.md#heap-priority-queue
-[design]: ./TOPICWISE.md#design
-[graph]: ./TOPICWISE.md#graph
-[prefix sum]: ./TOPICWISE.md#prefix-sum
-[simulation]: ./TOPICWISE.md#simulation
-[backtracking]: ./TOPICWISE.md#backtracking
-[counting]: ./TOPICWISE.md#counting
-[sliding window]: ./TOPICWISE.md#sliding-window
-[union find]: ./TOPICWISE.md#union-find
-[linked list]: ./TOPICWISE.md#linked-list
-[ordered set]: ./TOPICWISE.md#ordered-set
-[monotonic stack]: ./TOPICWISE.md#monotonic-stack
-[enumeration]: ./TOPICWISE.md#enumeration
-[recursion]: ./TOPICWISE.md#recursion
-[trie]: ./TOPICWISE.md#trie
-[divide and conquer]: ./TOPICWISE.md#divide-and-conquer
-[binary search tree]: ./TOPICWISE.md#binary-search-tree
-[bitmask]: ./TOPICWISE.md#bitmask
-[queue]: ./TOPICWISE.md#queue
-[memoization]: ./TOPICWISE.md#memoization
-[topological sort]: ./TOPICWISE.md#topological-sort
-[geometry]: ./TOPICWISE.md#geometry
-[segment tree]: ./TOPICWISE.md#segment-tree
-[hash function]: ./TOPICWISE.md#hash-function
-[game theory]: ./TOPICWISE.md#game-theory
-[binary indexed tree]: ./TOPICWISE.md#binary-indexed-tree
-[number theory]: ./TOPICWISE.md#number-theory
-[interactive]: ./TOPICWISE.md#interactive
-[string matching]: ./TOPICWISE.md#string-matching
-[rolling hash]: ./TOPICWISE.md#rolling-hash
-[data stream]: ./TOPICWISE.md#data-stream
-[shortest path]: ./TOPICWISE.md#shortest-path
-[combinatorics]: ./TOPICWISE.md#combinatorics
-[randomized]: ./TOPICWISE.md#randomized
-[monotonic queue]: ./TOPICWISE.md#monotonic-queue
-[brainteaser]: ./TOPICWISE.md#brainteaser
-[merge sort]: ./TOPICWISE.md#merge-sort
-[iterator]: ./TOPICWISE.md#iterator
-[concurrency]: ./TOPICWISE.md#concurrency
-[doubly-linked list]: ./TOPICWISE.md#doubly-linked-list
-[probability and statistics]: ./TOPICWISE.md#probability-and-statistics
-[quickselect]: ./TOPICWISE.md#quickselect
-[bucket sort]: ./TOPICWISE.md#bucket-sort
-[suffix array]: ./TOPICWISE.md#suffix-array
-[minimum spanning tree]: ./TOPICWISE.md#minimum-spanning-tree
-[counting sort]: ./TOPICWISE.md#counting-sort
-[shell]: ./TOPICWISE.md#shell
-[line sweep]: ./TOPICWISE.md#line-sweep
-[reservoir sampling]: ./TOPICWISE.md#reservoir-sampling
-[eulerian circuit]: ./TOPICWISE.md#eulerian-circuit
-[radix sort]: ./TOPICWISE.md#radix-sort
-[strongly connected component]: ./TOPICWISE.md#strongly-connected-component
-[rejection sampling]: ./TOPICWISE.md#rejection-sampling
-[biconnected component]: ./TOPICWISE.md#biconnected-component
diff --git a/docs/solution/0001-0100/001 - Two Sum.md b/docs/solution/0001-0100/001 - Two Sum.md
deleted file mode 100644
index 19f66bfb..00000000
--- a/docs/solution/0001-0100/001 - Two Sum.md
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,90 +0,0 @@
-# 1. Two Sum [![][share]](https://leetcode.com/problems/two-sum)
-
-![][easy]
-
-## Problem Statement:
-
-Given an array of integers nums and an integer `target`, return indices of the two numbers such that they add up to `target`.
-
-You may assume that each input would have **exactly one solution**, and you may not use the same element twice.
-
-You can return the answer in any order.
-
-### Example 1:
-
-```
-Input: nums = [2,7,11,15], target = 9
-Output: [0,1]
-Explanation: Because nums[0] + nums[1] == 9, we return [0, 1].
-```
-
-### Example 2:
-
-```
-Input: nums = [3,2,4], target = 6
-Output: [1,2]
-```
-
-### Example 3:
-
-```
-Input: nums = [3,3], target = 6
-Output: [0,1]
-```
-
-### Constraints:
-
-- 2 <= nums.length <= 104
-- -109 <= nums[i] <= 109
-- -109 <= target <= 109
-- **Only one valid answer exists.**
-
-**Follow-up:** Can you come up with an algorithm that is less than O(n2) time complexity?
-
-## Solution:
-
-::: code-group
-
-```java
-public static int[] twoSum(int nums[], int target) {
- int[] sum = new int[2];
- for (int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++)
- for (int j = i + 1; j < nums.length; j++) {
- if (i == j)
- continue;
- if (nums[i] + nums[j] == target) {
- sum[0] = i;
- sum[1] = j;
- }
- }
- return sum;
-}
-
-public static int[] twoSum2(int nums[], int target) {
- Map map = new HashMap<>();
- for (int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) {
- int complement = target - nums[i];
- if (map.containsKey(complement))
- return new int[] { map.get(complement), i };
- else {
- map.put(nums[i], i);
- }
- }
- throw new IllegalArgumentException();
-}
-```
-
-:::
-
-### [_..._](#)
-
-```
-
-```
-
-
-
-[share]: https://img.icons8.com/external-anggara-blue-anggara-putra/20/000000/external-share-user-interface-basic-anggara-blue-anggara-putra-2.png
-[easy]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Easy-bright.svg
-[medium]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Medium-yellow.svg
-[hard]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Hard-red.svg
diff --git a/docs/solution/0001-0100/002 - Add Two Numbers.md b/docs/solution/0001-0100/002 - Add Two Numbers.md
deleted file mode 100644
index 4b711e99..00000000
--- a/docs/solution/0001-0100/002 - Add Two Numbers.md
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,81 +0,0 @@
-# 2. Add Two Numbers [![][share]](https://leetcode.com/problems/add-two-numbers)
-
-![][medium]
-
-## Problem Statement:
-
-You are given two **non-empty** linked lists representing two non-negative integers. The digits are stored in **reverse order**, and each of their nodes contains a single digit. Add the two numbers and return the sum as a linked list.
-
-You may assume the two numbers do not contain any leading zero, except the number 0 itself.
-
-### Example 1:
-
-
-
-```
-Input: l1 = [2,4,3], l2 = [5,6,4]
-Output: [7,0,8]
-Explanation: 342 + 465 = 807.
-```
-
-### Example 2:
-
-```
-Input: l1 = [0], l2 = [0]
-Output: [0]
-```
-
-### Example 3:
-
-```
-Input: l1 = [9,9,9,9,9,9,9], l2 = [9,9,9,9]
-Output: [8,9,9,9,0,0,0,1]
-```
-
-### Constraints:
-
-- The number of nodes in each linked list is in the range `[1, 100]`.
-- `0 <= Node.val <= 9`
-- It is guaranteed that the list represents a number that does not have leading zeros.
-
-## Solution:
-
-::: code-group
-
-```java
-public ListNode addTwoNumbers(ListNode a, ListNode b) {
- ListNode dummy = new ListNode(0),
- tail = dummy;
- int carry = 0;
- while (a != null || b != null) {
- int x = (a != null) ? a.val : 0,
- y = (b != null) ? b.val : 0,
- sum = carry + x + y;
- carry = sum / 10;
- tail.next = new ListNode(sum % 10);
- tail = tail.next;
- if (a != null)
- a = a.next;
- if (b != null)
- b = b.next;
- }
- if (carry > 0)
- tail.next = new ListNode(carry);
- return dummy.next;
-}
-```
-
-:::
-
-### [_..._](#)
-
-```
-
-```
-
-
-
-[share]: https://img.icons8.com/external-anggara-blue-anggara-putra/20/000000/external-share-user-interface-basic-anggara-blue-anggara-putra-2.png
-[easy]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Easy-bright.svg
-[medium]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Medium-yellow.svg
-[hard]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Hard-red.svg
diff --git a/docs/solution/0001-0100/004 - Median of Two Sorted Arrays.md b/docs/solution/0001-0100/004 - Median of Two Sorted Arrays.md
deleted file mode 100644
index b66dd96f..00000000
--- a/docs/solution/0001-0100/004 - Median of Two Sorted Arrays.md
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,77 +0,0 @@
-# 4. Median of Two Sorted Arrays [![share]](https://leetcode.com/problems/median-of-two-sorted-arrays)
-
-![][hard]
-
-## Problem Statement:
-
-Given two sorted arrays `nums1` and `nums2` of size `m` and `n` respectively, return **the median** of the two sorted arrays.
-
-The overall run time complexity should be `O(log (m+n))`.
-
-### Example 1:
-
-```
-Input: nums1 = [1,3], nums2 = [2]
-Output: 2.00000
-Explanation: merged array = [1,2,3] and median is 2.
-```
-
-### Example 2:
-
-```
-Input: nums1 = [1,2], nums2 = [3,4]
-Output: 2.50000
-Explanation: merged array = [1,2,3,4] and median is (2 + 3) / 2 = 2.5.
-```
-
-### Constraints:
-
-- nums1.length == m
-- nums2.length == n
-- 0 <= m <= 1000
-- 0 <= n <= 1000
-- 1 <= m + n <= 2000
-- -106 <= nums1[i], nums2[i] <= 106
-
-## Solution:
-
-::: code-group
-
-```java
-public class MedianOfTwoSortedArrays {
- public static double findMedianSortedArrays(int[] nums1, int[] nums2) {
- int[] merged = new int[nums1.length + nums2.length];
- int startnums1 = 0, startnums2 = 0, i = 0;
- while (startnums1 < nums1.length && startnums2 < nums2.length) {
- if (nums1[startnums1] < nums2[startnums2])
- merged[i++] = nums1[startnums1++];
- else
- merged[i++] = nums2[startnums2++];
- }
- while (startnums1 < nums1.length)
- merged[i++] = nums1[startnums1++];
- while (startnums2 < nums2.length)
- merged[i++] = nums2[startnums2++];
- double median = 0;
- int mid = merged.length / 2;
- if (merged.length % 2 == 0)
- median = (double) (merged[mid] + merged[mid - 1]) / 2;
- else
- median = (double) merged[mid];
- return median;
- }
-}
-```
-
-:::
-
-### [_..._](#)
-
-```
-
-```
-
-
-
-[share]: https://img.icons8.com/external-anggara-blue-anggara-putra/20/000000/external-share-user-interface-basic-anggara-blue-anggara-putra-2.png
-[hard]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Hard-red.svg
diff --git a/docs/solution/0001-0100/007 - Reverse Integer.md b/docs/solution/0001-0100/007 - Reverse Integer.md
deleted file mode 100644
index 3d4c89d1..00000000
--- a/docs/solution/0001-0100/007 - Reverse Integer.md
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,64 +0,0 @@
-# 7. Reverse Integer [![share]](https://leetcode.com/problems/reverse-integer)
-
-![][medium]
-
-## Problem Statement:
-
-Given a signed 32-bit integer `x`, return x with its digits reversed. If reversing `x` causes the value to go outside the signed 32-bit integer range [-231, 231 - 1], then return `0`.
-
-Assume the environment does not allow you to store 64-bit integers (signed or unsigned).
-
-### Example 1:
-
-```
-Input: x = 123
-Output: 321
-```
-
-### Example 2:
-
-```
-Input: x = -123
-Output: -321
-```
-
-### Example 3:
-
-```
-Input: x = 120
-Output: 21
-```
-
-### Constraints:
-
-- -231 <= x <= 231 -
-
-## Solution:
-
-::: code-group
-
-```java
-public static int reverse(int x) {
- String reversed = new StringBuilder().append(Math.abs(x)).reverse().toString();
- try {
- return x < 0 ? Integer.parseInt(reversed) * -1 : Integer.parseInt(reversed);
- } catch (Exception e) {
- return 0;
- }
-}
-```
-
-:::
-
-### [_..._](#)
-
-```
-
-```
-
-
-
-[share]: https://img.icons8.com/external-anggara-blue-anggara-putra/20/000000/external-share-user-interface-basic-anggara-blue-anggara-putra-2.png
-[easy]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Easy-bright.svg
-[medium]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Medium-yellow.svg
-[hard]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Hard-red.svg
diff --git a/docs/solution/0001-0100/009 - Palindrome Number.md b/docs/solution/0001-0100/009 - Palindrome Number.md
deleted file mode 100644
index d6940555..00000000
--- a/docs/solution/0001-0100/009 - Palindrome Number.md
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,73 +0,0 @@
-# 9. Palindrome Number [![share]](https://leetcode.com/problems/palindrome-number)
-
-![][easy]
-
-## Problem Statement:
-
-Given an integer `x`, return `true` if `x` is palindrome integer.
-
-An integer is a **palindrome** when it reads the same backward as forward.
-
-- For example, `121` is a palindrome while `123` is not.
-
-### Example 1:
-
-```
-Input: x = 121
-Output: true
-Explanation: 121 reads as 121 from left to right and from right to left.
-```
-
-### Example 2:
-
-```
-Input: x = -121
-Output: false
-Explanation: From left to right, it reads -121. From right to left, it becomes 121-. Therefore it is not a palindrome.
-```
-
-### Example 3:
-
-```
-Input: x = 10
-Output: false
-Explanation: Reads 01 from right to left. Therefore it is not a palindrome.
-```
-
-### Constraints:
-
-- -231 <= x <= 231 - 1
-
-**Follow up**: Could you solve it without converting the integer to a string?
-
-## Solution:
-
-::: code-group
-
-```java
-public static boolean isPalindrome(int x) {
- if (x < 0 || x % 10 == 0 && x != 0)
- return false;
- int reverseNum = 0;
- while (x > reverseNum) {
- reverseNum = reverseNum * 10 + x % 10;
- x /= 10;
- }
- return x == reverseNum || x == reverseNum / 10;
-}
-```
-
-:::
-
-### [_..._](#)
-
-```
-
-```
-
-
-
-[share]: https://img.icons8.com/external-anggara-blue-anggara-putra/20/000000/external-share-user-interface-basic-anggara-blue-anggara-putra-2.png
-[easy]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Easy-bright.svg
-[medium]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Medium-yellow.svg
-[hard]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Hard-red.svg
diff --git a/docs/solution/0001-0100/013 - Roman to Integer.md b/docs/solution/0001-0100/013 - Roman to Integer.md
deleted file mode 100644
index 975e4dbe..00000000
--- a/docs/solution/0001-0100/013 - Roman to Integer.md
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,99 +0,0 @@
-# 13. Roman to Integer [![share]](https://leetcode.com/problems/roman-to-integer/)
-
-![][easy]
-
-## Problem Statement:
-
-Roman numerals are represented by seven different symbols: `I`, `V`, `X`, `L`, `C`, `D` and `M`.
-
-```
-Symbol Value
-I 1
-V 5
-X 10
-L 50
-C 100
-D 500
-M 1000
-```
-
-For example, `2` is written as `II` in Roman numeral, just two ones added together. `12` is written as `XII`, which is simply `X + II`. The number `27` is written as `XXVII`, which is `XX + V + II`.
-
-Roman numerals are usually written largest to smallest from left to right. However, the numeral for four is not `IIII`. Instead, the number four is written as `IV`. Because the one is before the five we subtract it making four. The same principle applies to the number nine, which is written as `IX`. There are six instances where subtraction is used:
-
-- I can be placed before `V` (5) and `X` (10) to make 4 and 9.
-- X can be placed before `L` (50) and `C` (100) to make 40 and 90.
-- C can be placed before `D` (500) and `M` (1000) to make 400 and 900.
- Given a roman numeral, convert it to an integer.
-
-### Example 1:
-
-```
-Input: s = "III"
-Output: 3
-Explanation: III = 3.
-```
-
-### Example 2:
-
-```
-Input: s = "LVIII"
-Output: 58
-Explanation: L = 50, V= 5, III = 3.
-```
-
-### Example 3:
-
-```
-Input: s = "MCMXCIV"
-Output: 1994
-Explanation: M = 1000, CM = 900, XC = 90 and IV = 4.
-```
-
-### Constraints:
-
-```
-- 1 <= s.length <= 15
-- s contains only the characters `('I', 'V', 'X', 'L', 'C', 'D', 'M')`.
-- It is guaranteed that s is a valid roman numeral in the range [`1, 3999]`.
-```
-
-## Solution:
-
-::: code-group
-
-```java
-public int romanToInt(String s) {
- Map map = Map.of(
- 'I', 1,
- 'V', 5,
- 'X', 10,
- 'L', 50,
- 'C', 100,
- 'D', 500,
- 'M', 1000);
- int res = map.get(s.charAt(s.length() - 1));
- for (int i = s.length() - 2; i >= 0; i--) {
- if (map.get(s.charAt(i)) < map.get(s.charAt(i + 1)))
- res -= map.get(s.charAt(i));
- else
- res += map.get(s.charAt(i));
- }
- return res;
-}
-```
-
-:::
-
-### [_..._](#)
-
-```
-
-```
-
-
-
-[share]: https://img.icons8.com/external-anggara-blue-anggara-putra/20/000000/external-share-user-interface-basic-anggara-blue-anggara-putra-2.png
-[easy]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Easy-bright.svg
-[medium]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Medium-yellow.svg
-[hard]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Hard-red.svg
diff --git a/docs/solution/0001-0100/014 - Longest Common Prefix.md b/docs/solution/0001-0100/014 - Longest Common Prefix.md
deleted file mode 100644
index ab588490..00000000
--- a/docs/solution/0001-0100/014 - Longest Common Prefix.md
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,68 +0,0 @@
-# 14. Longest Common Prefix [![share]](https://leetcode.com/problems/longest-common-prefix/)
-
-![][easy]
-
-## Problem Statement
-
-
Write a function to find the longest common prefix string amongst an array of strings.
-
-
If there is no common prefix, return an empty string "".
Given n pairs of parentheses, write a function to generate all combinations of well-formed parentheses.
-
-
-
Example 1:
-
Input: n = 3
-Output: ["((()))","(()())","(())()","()(())","()()()"]
-
Example 2:
-
Input: n = 1
-Output: ["()"]
-
-
-
Constraints:
-
-
-
1 <= n <= 8
-
-
-## Solution:
-
-::: code-group
-
-```java
-import java.util.ArrayList;
-import java.util.List;
-
-class Solution {
- public List generateParenthesis(int n) {
- List ans = new ArrayList<>();
- backtrack(ans, "", 0, 0, n);
- return ans;
- }
-
- private void backtrack(List ans, String str, int open, int close, int n) {
- if (str.length() == n * 2) {
- ans.add(str);
- return;
- }
-
- if (open < n)
- backtrack(ans, str + "(", open + 1, close, n);
-
- if (close < open)
- backtrack(ans, str + ")", open, close + 1, n);
- }
-}
-```
-
-:::
-
-### [_..._](#)
-
-```
-
-```
-
-
-
-[share]: https://graph.org/file/3ea5234dda646b71c574a.png
-[easy]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Easy-bright.svg
-[medium]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Medium-yellow.svg
-[hard]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Hard-red.svg
diff --git a/docs/solution/0001-0100/024 - Swap Nodes in Pairs.md b/docs/solution/0001-0100/024 - Swap Nodes in Pairs.md
deleted file mode 100644
index 2f069aa8..00000000
--- a/docs/solution/0001-0100/024 - Swap Nodes in Pairs.md
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,81 +0,0 @@
-# 24. Swap Nodes in Pairs [![share]](https://leetcode.com/problems/swap-nodes-in-pairs)
-
-![][medium]
-
-## Problem Statement:
-
-Given a linked list, swap every two adjacent nodes and return its head. You must solve the problem without modifying the values in the list's nodes (i.e., only nodes themselves may be changed.)
-
-
-
-### Example 1:
-
-```
-Input: head = [1,2,3,4]
-Output: [2,1,4,3]
-```
-
-### Example 2:
-
-```
-Input: head = []
-Output: []
-```
-
-### Example 3:
-
-```
-Input: head = [1]
-Output: [1]
-```
-
-### Constraints:
-
-- The number of nodes in the list is in the range `[0, 100]`.
-- 0 <= Node.val <= 100
-
-## Solution:
-
-::: code-group
-
-```java
-public ListNode swapPairs(ListNode head) {
- ListNode p1 = null,
- p2 = null,
- p3 = null;
- if (head == null || head.next == null)
- return head;
- p1 = head;
- p2 = head.next;
- p3 = p2.next;
- p1.next = p3;
- p2.next = p1;
- if (p3 != null)
- p1.next = swapPairs(p3);
- return p2;
-}
-
-public ListNode swapPairs1(ListNode head) {
- ListNode newNode = head;
- while (newNode != null && newNode.next != null) {
- int temp = newNode.val;
- newNode.val = newNode.next.val;
- newNode.next.val = temp;
- newNode = newNode.next.next;
- }
- return head;
-}
-```
-
-:::
-
-### [_..._](#)
-
-```
-
-```
-
-
-
-[share]: https://img.icons8.com/external-anggara-blue-anggara-putra/20/000000/external-share-user-interface-basic-anggara-blue-anggara-putra-2.png
-[medium]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Medium-yellow.svg
diff --git a/docs/solution/0001-0100/026 - Remove Duplicates from Sorted Array.md b/docs/solution/0001-0100/026 - Remove Duplicates from Sorted Array.md
deleted file mode 100644
index a2654985..00000000
--- a/docs/solution/0001-0100/026 - Remove Duplicates from Sorted Array.md
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,101 +0,0 @@
-# 26. Remove Duplicates from Sorted Array [![share]](https://leetcode.com/problems/remove-duplicates-from-sorted-array/)
-
-![][easy]
-
-## Problem Statement:
-
-Given an integer array `nums` sorted in **non-decreasing order**, remove the duplicates in-place such that each unique element appears only once. The **relative order** of the elements should be kept the **same**.
-
-Since it is impossible to change the length of the array in some languages, you must instead have the result be placed in the **first part** of the array `nums`. More formally, if there are `k` elements after removing the duplicates, then the first `k` elements of `nums` should hold the final result. It does not matter what you leave beyond the first `k` elements.
-
-Return `k` after placing the final result in the first `k` slots of `nums`.
-
-Do **not** allocate extra space for another array. You must do this by **modifying the input array** in-place with O(1) extra memory.
-
-### Custom Judge:
-
-```
-The judge will test your solution with the following code:
-
-int[] nums = [...]; // Input array
-int[] expectedNums = [...]; // The expected answer with correct length
-
-int k = removeDuplicates(nums); // Calls your implementation
-
-assert k == expectedNums.length;
-for (int i = 0; i < k; i++) {
- assert nums[i] == expectedNums[i];
-}
-```
-
-If all assertions pass, then your solution will be **accepted**.
-
-### Example 1:
-
-```
-Input: nums = [1,1,2]
-Output: 2, nums = [1,2,_]
-Explanation: Your function should return k = 2, with the first two elements of nums being 1 and 2 respectively.
-It does not matter what you leave beyond the returned k (hence they are underscores).
-```
-
-### Example 2:
-
-```
-Input: nums = [0,0,1,1,1,2,2,3,3,4]
-Output: 5, nums = [0,1,2,3,4,_,_,_,_,_]
-Explanation: Your function should return k = 5, with the first five elements of nums being 0, 1, 2, 3, and 4 respectively.
-It does not matter what you leave beyond the returned k (hence they are underscores).
-```
-
-### Constraints:
-
-- 1 <= nums.length <= 3 \* 104
-- -100 <= nums[i] <= 100
-- nums is sorted in non-decreasing order.
-
-## Solution:
-
-::: code-group
-
-```py [Python]
-def removeDuplicates(nums: list[int]) -> int:
- k = 0
- for i, item in enumerate(nums):
- if i < len(nums) - 1 and item == nums[i + 1]:
- continue
- nums[k] = item
- k += 1
- return k
-
-```
-
-```go [Go]
-package main
-
-func removeDuplicates(nums []int) int {
- k := 0
- for i := 1; i < len(nums); i++ {
- if nums[i] != nums[k] {
- k++
- nums[k] = nums[i]
- }
- }
-
- return k + 1
-}
-
-```
-
-:::
-
-### [_..._](#)
-
-```
-
-```
-
-
-
-[share]: https://img.icons8.com/external-anggara-blue-anggara-putra/20/000000/external-share-user-interface-basic-anggara-blue-anggara-putra-2.png
-[easy]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Easy-green.svg
diff --git a/docs/solution/0001-0100/027 - Remove Element.md b/docs/solution/0001-0100/027 - Remove Element.md
deleted file mode 100644
index 52de9b95..00000000
--- a/docs/solution/0001-0100/027 - Remove Element.md
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,89 +0,0 @@
-# 27. Remove Element [![share]](https://leetcode.com/problems/remove-element)
-
-![][easy]
-
-## Problem Statement:
-
-Given an integer array `nums` and an integer `val`, remove all occurrences of `val` in `nums` in-place. The relative order of the elements may be changed.
-
-Since it is impossible to change the length of the array in some languages, you must instead have the result be placed in the **first part** of the array `nums`. More formally, if there are k elements after removing the duplicates, then the first `k` elements of `nums` should hold the final result. It does not matter what you leave beyond the first `k` elements.
-
-Return `k` after placing the final result in the first `k` slots of `nums`.
-
-Do **not** allocate extra space for another array. You must do this by **modifying the input arra**y in-place with O(1) extra memory.
-
-### Custom Judge:
-
-```
-The judge will test your solution with the following code:
-
-int[] nums = [...]; // Input array
-int val = ...; // Value to remove
-int[] expectedNums = [...]; // The expected answer with correct length.
-// It is sorted with no values equaling val.
-
-int k = removeElement(nums, val); // Calls your implementation
-
-assert k == expectedNums.length;
-sort(nums, 0, k); // Sort the first k elements of nums
-for (int i = 0; i < actualLength; i++) {
-assert nums[i] == expectedNums[i];
-}
-```
-
-If all assertions pass, then your solution will be **accepted**.
-
-### Example 1:
-
-```
-Input: nums = [3,2,2,3], val = 3
-Output: 2, nums = [2,2,_,_]
-Explanation: Your function should return k = 2, with the first two elements of nums being 2.
-It does not matter what you leave beyond the returned k (hence they are underscores).
-```
-
-### Example 2:
-
-```
-Input: nums = [0,1,2,2,3,0,4,2], val = 2
-Output: 5, nums = [0,1,4,0,3,_,_,_]
-Explanation: Your function should return k = 5, with the first five elements of nums containing 0, 0, 1, 3, and 4.
-Note that the five elements can be returned in any order.
-It does not matter what you leave beyond the returned k (hence they are underscores).
-```
-
-### Constraints:
-
-- 0 <= nums.length <= 100
-- 0 <= nums[i] <= 50
-- 0 <= val <= 100
-
-## Solution:
-
-::: code-group
-
-```java
-public int removeElement(int[] nums, int val) {
- int count = 0;
- for (int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++)
- if (nums[i] != val) {
- nums[count] = nums[i];
- }
- return count;
-}
-```
-
-:::
-
-### [_..._](#)
-
-```
-
-```
-
-
-
-[share]: https://img.icons8.com/external-anggara-blue-anggara-putra/20/000000/external-share-user-interface-basic-anggara-blue-anggara-putra-2.png
-[easy]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Easy-bright.svg
-[medium]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Medium-yellow.svg
-[hard]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Hard-red.svg
diff --git a/docs/solution/0001-0100/028 - Find the Index of the First Occurrence in a String.md b/docs/solution/0001-0100/028 - Find the Index of the First Occurrence in a String.md
deleted file mode 100644
index 54c2a2ae..00000000
--- a/docs/solution/0001-0100/028 - Find the Index of the First Occurrence in a String.md
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,73 +0,0 @@
-# 28. Find the Index of the First Occurrence in a String [![share]](https://leetcode.com/problems/find-the-index-of-the-first-occurrence-in-a-string/)
-
-![][medium]
-
-## Problem Statement
-
-
Given two strings needle and haystack, return the index of the first occurrence of needle in haystack, or -1 if needle is not part of haystack.
-
-
Example 1:
-
-```
-Input: haystack = "sadbutsad", needle = "sad"
-Output: 0
-Explanation: "sad" occurs at index 0 and 6.
-The first occurrence is at index 0, so we return 0.
-```
-
-
Example 2:
-
-```
-Input: haystack = "leetcode", needle = "leeto"
-Output: -1
-Explanation: "leeto" did not occur in "leetcode", so we return -1.
-```
-
-
-
Constraints:
-
-
1 <= haystack.length, needle.length <= 104
-
haystack and needle consist of only lowercase English characters.
-
-
-## Solution:
-
-::: code-group
-
-```rs [Rust]
-impl Solution {
- pub fn str_str(haystack: String, needle: String) -> i32 {
- let (m, n) = (haystack.len(), needle.len());
-
- if m < n {
- return -1;
- }
-
- // iterate over the haystack from 0 to m - n
- // because the needle can't be longer than the haystack
- for i in 0..=m - n {
- if haystack[i..i + n] == needle {
- return i as i32;
- }
- }
-
- -1
- }
-}
-
-```
-
-:::
-
-### [_..._](#)
-
-```
-
-```
-
-
-
-[share]: https://graph.org/file/3ea5234dda646b71c574a.png
-[easy]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Easy-bright.svg
-[medium]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Medium-yellow.svg
-[hard]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Hard-red.svg
diff --git a/docs/solution/0001-0100/035 - Search Insert Position.md b/docs/solution/0001-0100/035 - Search Insert Position.md
deleted file mode 100644
index 6d1385f6..00000000
--- a/docs/solution/0001-0100/035 - Search Insert Position.md
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,97 +0,0 @@
-# 35. Search Insert Position [![share]](https://leetcode.com/problems/search-insert-position/)
-
-![][easy]
-
-## Problem Statement
-
-
Given a sorted array of distinct integers and a target value, return the index if the target is found. If not, return the index where it would be if it were inserted in order.
-
You must write an algorithm with O(log n) runtime complexity.
nums contains distinct values sorted in ascending order.
-
-104 <= target <= 104
-
-
-## Solution:
-
-::: code-group
-
-```py [Python]
-class Solution:
- def searchInsert(self, nums: list[int], target: int) -> int:
- if target in nums:
- return nums.index(target)
- else:
- nums.append(target)
- nums.sort()
- return nums.index(target)
-
- # Using binary search
- # start = 0
- # end = len(nums) - 1
- # while start <= end:
- # mid = (start + end) // 2
- # if nums[mid] == target:
- # return mid
- # elif nums[mid] < target:
- # start = mid + 1
- # else:
- # end = mid - 1
- # return start
-
-```
-
-```rs [Rust]
-impl Solution {
- pub fn search_insert(nums: Vec, target: i32) -> i32 {
- for (idx, val) in nums.iter().enumerate() {
- if target <= *val {
- return idx as i32;
- }
- }
-
- nums.len() as i32
- }
-}
-
-```
-
-:::
-
-### [_..._](#)
-
-```
-
-```
-
-
-
-[share]: https://graph.org/file/3ea5234dda646b71c574a.png
-[easy]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Easy-bright.svg
-[medium]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Medium-yellow.svg
-[hard]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Hard-red.svg
diff --git a/docs/solution/0001-0100/037 - Sudoku Solver.md b/docs/solution/0001-0100/037 - Sudoku Solver.md
deleted file mode 100644
index 30c10e19..00000000
--- a/docs/solution/0001-0100/037 - Sudoku Solver.md
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,158 +0,0 @@
-# 37. Sudoku Solver [![share]](https://leetcode.com/problems/sudoku-solver/)
-
-![][hard]
-
-## Problem Statement:
-
-Write a program to solve a Sudoku puzzle by filling the empty cells.
-
-A sudoku solution must satisfy **all of the following rules:**
-
-- Each of the digits `1-9` must occur exactly once in each row.
-- Each of the digits `1-9` must occur exactly once in each column.
-- Each of the digits `1-9` must occur exactly once in each of the 9 `3x3` sub-boxes of the grid.
-- The '.' character indicates empty cells.
-
-### Example 1:
-
-
-
-```
-Input: board =
-[["5","3",".",".","7",".",".",".","."],
-["6",".",".","1","9","5",".",".","."],
-[".","9","8",".",".",".",".","6","."],
-["8",".",".",".","6",".",".",".","3"],
-["4",".",".","8",".","3",".",".","1"],
-["7",".",".",".","2",".",".",".","6"],
-[".","6",".",".",".",".","2","8","."],
-[".",".",".","4","1","9",".",".","5"],
-[".",".",".",".","8",".",".","7","9"]]
-
-Output:
-[["5","3","4","6","7","8","9","1","2"],
-["6","7","2","1","9","5","3","4","8"],
-["1","9","8","3","4","2","5","6","7"],
-["8","5","9","7","6","1","4","2","3"],
-["4","2","6","8","5","3","7","9","1"],
-["7","1","3","9","2","4","8","5","6"],
-["9","6","1","5","3","7","2","8","4"],
-["2","8","7","4","1","9","6","3","5"],
-["3","4","5","2","8","6","1","7","9"]]
-```
-
-**Explanation**: The input board is shown above and the only valid solution is shown below:
-
-
-
-### Constraints:
-
-- board.length == 9
-- board[i].length == 9
-- board[i][j] is a digit or '.'.
-- It is **guaranteed** that the input board has only one solution.
-
-## Solution:
-
-::: code-group
-
-```java
-/*
-A sudoku solution must satisfy all of the following rules:
--> Each of the digits 1-9 must occur exactly once in each row.
--> Each of the digits 1-9 must occur exactly once in each column.
--> Each of the digits 1-9 must occur exactly once in each of the 9 3x3 sub-boxes of the grid.
-The "." character indicates empty cells.
-*/
-
-public class SudokuSolver2 {
- public void solveSudoku(char[][] board) {
- helper(board, 0, 0);
- }
-
- // a utility function to solve the board
- boolean helper(char[][] board, int row, int col) {
- // base case -> recursion stops at the 10th row
- if (row == board.length)
- return true;
- int newRow = 0, newCol = 0;
- // when its the last col of the board, goto next row & first col
- if (col == board.length - 1) {
- newRow = row + 1;
- newCol = 0;
- }
- // else, keep increasing the col by one & the row remains the same
- else {
- newRow = row;
- newCol = col + 1;
- }
- // if the cell isn't empty, i.e. there is a number present in that cell
- if (board[row][col] != '.') {
- // do a recursive call, if the fn returns true, i.e. the board is solved,
- // we'll also return true
- if (helper(board, newRow, newCol))
- return true;
- }
- // if cell is empty
- else {
- for (int i = 1; i <= 9; i++) {
- // if it's safe to place 'i' at that cell
- if (isValidPlacement(board, row, col, i)) {
- board[row][col] = (char) (i + '0');
- // after placing the number, do a recursive call,
- // if the fn returns true, we'll also return true
- if (helper(board, newRow, newCol))
- return true;
- // if the recursive call returns false, i.e. it wasn't safe to place 'i',
- // we'll empty the cell & and will try for the next value of 'i' (backtracking)
- else
- board[row][col] = '.';
- }
- }
- }
- // return false if it isn't posssible to place a number in the cell
- return false;
- }
-
- // a utility fn to check for valid placement of a number in cell of Sudoku Board
- boolean isValidPlacement(char[][] board, int row, int col, int number) {
- // to check if 'number' is present in the row or the col
- for (int i = 0; i < board.length; i++) {
- // return false if 'number' is present in the col
- if (board[i][col] == (char) (number + '0'))
- return false;
- // return false if 'number' is present in the row
- if (board[row][i] == (char) (number + '0'))
- return false;
- }
- // to check if the 'number' is present in the 3X3 grid
- // There are two ways to get the initial row and column of 3X3 grid
- // 1
- int startingRow = (row / 3) * 3;
- int startingCol = (col / 3) * 3;
- // 2
- // int startingRow = (row % 3) - row;
- // int startingCol = (col % 3) - col;
- for (int i = startingRow; i < startingRow + 3; i++)
- for (int j = startingCol; j < startingCol + 3; j++)
- // return false if 'number' is present in the 3X3 grid or matrix
- if (board[i][j] == (char) (number + '0'))
- return false;
- // return true if 'number' isn't present in row, col & grid
- return true;
- }
-}
-```
-
-:::
-
-### [_..._](#)
-
-```
-
-```
-
-
-
-[share]: https://img.icons8.com/external-anggara-blue-anggara-putra/20/000000/external-share-user-interface-basic-anggara-blue-anggara-putra-2.png
-[hard]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Hard-red.svg
diff --git a/docs/solution/0001-0100/041 - First Missing Positive.md b/docs/solution/0001-0100/041 - First Missing Positive.md
deleted file mode 100644
index be4594ea..00000000
--- a/docs/solution/0001-0100/041 - First Missing Positive.md
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,121 +0,0 @@
-# 41. First Missing Positive [![share]](https://leetcode.com/problems/first-missing-positive/)
-
-![][hard]
-
-## Problem Statement
-
-
Given an unsorted integer array nums, return the smallest missing positive integer.
-
You must implement an algorithm that runs in O(n) time and uses O(1) auxiliary space.
-
-
Example 1:
-
-```
-Input: nums = [1,2,0]
-Output: 3
-Explanation: The numbers in the range [1,2] are all in the array.
-```
-
-
Example 2:
-
-```
-Input: nums = [3,4,-1,1]
-Output: 2
-Explanation: 1 is in the array but 2 is missing.
-```
-
-
Example 3:
-
-```
-Input: nums = [7,8,9,11,12]
-Output: 1
-Explanation: The smallest positive integer 1 is missing.
-```
-
-
-
Constraints:
-
-
1 <= nums.length <= 105
-
-231 <= nums[i] <= 231 - 1
-
-
-::: details _Click to open Hints_
-
-- Think about how you would solve the problem in non-constant space. Can you apply that logic to the existing space?
-- We don't care about duplicates or non-positive integers
-- Remember that O(2n) = O(n)
-
-:::
-
-## Solution:
-
-::: code-group
-
-```go [Go]
-package main
-
-func firstMissingPositive(nums []int) int {
- i := 0
-
- for i < len(nums) {
- if nums[i] > 0 && nums[i] <= len(nums) && nums[nums[i]-1] != nums[i] {
- nums[nums[i]-1], nums[i] = nums[i], nums[nums[i]-1]
- } else {
- i++
- }
- }
-
- for i, num := range nums {
- if num != i+1 {
- return i + 1
- }
- }
-
- return len(nums) + 1
-}
-
-```
-
-```rs [Rust]
-impl Solution {
- pub fn first_missing_positive(nums: Vec) -> i32 {
- let (mut nums, mut i) = (nums, 0);
-
- while i < nums.len() {
- let num = nums[i];
-
- // if the number is in the range [1, nums.len()] and not in the right position
- // swap it with the number at the right position
- if num > 0 && num <= nums.len() as i32 && num != nums[num as usize - 1] {
- nums.swap(i, num as usize - 1);
- } else {
- i += 1;
- }
- }
-
- // find the first missing positive number
- for (i, num) in nums.iter().enumerate() {
- if num != &(i as i32 + 1) {
- return i as i32 + 1;
- }
- }
-
- nums.len() as i32 + 1
- }
-}
-
-```
-
-:::
-
-### [_..._](#)
-
-```
-
-```
-
-
-
-[share]: https://graph.org/file/3ea5234dda646b71c574a.png
-[easy]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Easy-bright.svg
-[medium]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Medium-yellow.svg
-[hard]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Hard-red.svg
diff --git a/docs/solution/0001-0100/042 - Trapping Rain Water.md b/docs/solution/0001-0100/042 - Trapping Rain Water.md
deleted file mode 100644
index 6275c5c0..00000000
--- a/docs/solution/0001-0100/042 - Trapping Rain Water.md
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,88 +0,0 @@
-# 42. Trapping Rain Water [![share]](https://leetcode.com/problems/trapping-rain-water/)
-
-![][hard]
-
-## Problem Statement
-
-
Given n non-negative integers representing an elevation map where the width of each bar is 1, compute how much water it can trap after raining.
-
-
Example 1:
-
-
-```
-Input: height = [0,1,0,2,1,0,1,3,2,1,2,1]
-Output: 6
-Explanation: The above elevation map (black section) is represented by array [0,1,0,2,1,0,1,3,2,1,2,1]. In this case, 6 units of rain water (blue section) are being trapped.
-```
-
-
-
-## Solution:
-
-::: code-group
-
-```rs [Rust]
-impl Solution {
- pub fn trap(height: Vec) -> i32 {
- let (mut left, mut right) = (0, height.len() - 1);
- let (mut left_max, mut right_max) = (0, 0);
- let mut ans = 0;
-
- // iterate from both sides to the middle
- while left < right {
- // if left is lower than right, then the water level depends on left
- // else the water level depends on right
- if height[left] < height[right] {
- // if left height is higher than left_max, then update left_max
- // else add the difference between left_max and left height to ans
- if height[left] >= left_max {
- left_max = height[left];
- } else {
- ans += left_max - height[left];
- }
- left += 1;
- } else {
- // if right height is higher than right_max, then update right_max
- // else add the difference between right_max and right height to ans
- if height[right] >= right_max {
- right_max = height[right];
- } else {
- ans += right_max - height[right];
- }
- right -= 1;
- }
- }
-
- ans
- }
-}
-
-```
-
-:::
-
-### [_..._](#)
-
-```
-
-```
-
-
-
-[share]: https://graph.org/file/3ea5234dda646b71c574a.png
-[easy]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Easy-bright.svg
-[medium]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Medium-yellow.svg
-[hard]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Hard-red.svg
diff --git a/docs/solution/0001-0100/048 - Rotate Image.md b/docs/solution/0001-0100/048 - Rotate Image.md
deleted file mode 100644
index 3d09be1e..00000000
--- a/docs/solution/0001-0100/048 - Rotate Image.md
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,70 +0,0 @@
-# 48. Rotate Image [![share]](https://leetcode.com/problems/rotate-image/)
-
-![][medium]
-
-## Problem Statement
-
-
You are given an n x n 2D matrix representing an image, rotate the image by 90 degrees (clockwise).
-
You have to rotate the image in-place, which means you have to modify the input 2D matrix directly. DO NOT allocate another 2D matrix and do the rotation.
-
-## Solution:
-
-::: code-group
-
-```rs [Rust]
-impl Solution {
- pub fn rotate(matrix: &mut Vec>) {
- let n = matrix.len();
-
- for i in 0..n {
- for j in i..n {
- let temp = matrix[i][j];
- matrix[i][j] = matrix[j][i];
- matrix[j][i] = temp;
- }
-
- matrix[i].reverse();
- }
- }
-}
-
-```
-
-:::
-
-### [_..._](#)
-
-```
-
-```
-
-
-
-[share]: https://graph.org/file/3ea5234dda646b71c574a.png
-[easy]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Easy-bright.svg
-[medium]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Medium-yellow.svg
-[hard]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Hard-red.svg
diff --git a/docs/solution/0001-0100/051 - N-Queens.md b/docs/solution/0001-0100/051 - N-Queens.md
deleted file mode 100644
index a809b118..00000000
--- a/docs/solution/0001-0100/051 - N-Queens.md
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,140 +0,0 @@
-# 51. N-Queens [![share]](https://leetcode.com/problems/n-queens/)
-
-![][hard]
-
-## Problem Statement:
-
-The **n-queens** puzzle is the problem of placing `n` queens on an `n x n` chessboard such that no two queens attack each other.
-
-Given an integer `n`, return all distinct solutions to the `n-queens puzzle`. You may return the answer in `any order`.
-
-Each solution contains a distinct board configuration of the n-queens' placement, where `'Q'` and `'.'` both indicate a queen and an empty space, respectively.
-
-### Example 1:
-
-
-
-```
-Input: n = 4
-Output: [[".Q..","...Q","Q...","..Q."],["..Q.","Q...","...Q",".Q.."]]
-```
-
-**Explanation**: There exist two distinct solutions to the 4-queens puzzle as shown above
-
-### Example 2:
-
-```
-Input: n = 1
-Output: [["Q"]]
-```
-
-### Constraints:
-
-- 1 <= n <= 9
-
-## Solution:
-
-::: code-group
-
-```java
-public class NQueens2 {
-
- public static List> nQueens(int n) {
- // List of Lists of boards
- List> allBoards = new ArrayList<>();
- char[][] board = new char[n][n];
- helper(board, allBoards, 0);
- return allBoards;
- }
-
- static void helper(char[][] board, List> allBoards, int col) {
- // save board to allBoards after placing Queens on all possible cols
- if (col == board.length) {
- saveBoard(board, allBoards);
- return;
- }
- for (int row = 0; row < board.length; row++) {
- // if it's safe, place queen at row
- if (isSafe(row, col, board)) {
- board[row][col] = 'Q';
- helper(board, allBoards, col + 1);
- // backtracking
- board[row][col] = '.';
- }
- }
- }
-
- // Fn to check if it's safe to place Queen
- static boolean isSafe(int row, int col, char[][] board) {
- int len = board.length;
- // traverse in all cols to check if a queen is already present or not
- for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) {
- if (board[row][i] == 'Q')
- return false;
- }
- // traverse in all rows to check if a queen is already present or not
- for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) {
- if (board[i][col] == 'Q')
- return false;
- }
- // traverse through upper left diagonal to check if queen is present
- int r = row;
- for (int c = col; c >= 0 && r >= 0; r--, c--) {
- if (board[r][c] == 'Q')
- return false;
- }
- // traverse through upper right diagonal to check if queen is present
- r = row;
- for (int c = col; c < len && r >= 0; r--, c++) {
- if (board[r][c] == 'Q')
- return false;
- }
- // traverse through lower left diagonal to check if queen is present
- r = row;
- for (int c = col; c >= 0 && r < len; r++, c--) {
- if (board[r][c] == 'Q')
- return false;
- }
- // traverse through lower right diagonal to check if queen is present
- r = row;
- for (int c = col; c < len && r < len; r++, c++) {
- if (board[r][c] == 'Q')
- return false;
- }
- return true;
- }
-
- // Fn to save a board to List of Boards
- static void saveBoard(char[][] board, List> allBoards) {
- int len = board.length;
- String row = "";
- List newBoard = new ArrayList<>();
- for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) {
- row = "";
- for (int j = 0; j < len; j++) {
- if (board[i][j] == 'Q')
- row += 'Q';
- else
- row += '.';
- }
- // this adds the row to the newBoards -> "Q..." or "..Q."
- newBoard.add(row);
- }
- // this add the board to the list of boards -> [[..Q., Q..., ...Q, .Q..],...]
- allBoards.add(newBoard);
- }
-}
-```
-
-:::
-
-### [_..._](#)
-
-```
-
-```
-
-
-
-[share]: https://img.icons8.com/external-anggara-blue-anggara-putra/20/000000/external-share-user-interface-basic-anggara-blue-anggara-putra-2.png
-[hard]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Hard-red.svg
diff --git a/docs/solution/0001-0100/053 - Maximum Subarray.md b/docs/solution/0001-0100/053 - Maximum Subarray.md
deleted file mode 100644
index ed3446c6..00000000
--- a/docs/solution/0001-0100/053 - Maximum Subarray.md
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,80 +0,0 @@
-# 53. Maximum Subarray [![share]](https://leetcode.com/problems/maximum-subarray/)
-
-![][medium]
-
-## Problem Statement
-
-
Given an integer array nums, find the subarray with the largest sum, and return its sum.
-
-
Example 1:
-
-```
-Input: nums = [-2,1,-3,4,-1,2,1,-5,4]
-Output: 6
-Explanation: The subarray [4,-1,2,1] has the largest sum 6.
-```
-
-
Example 2:
-
-```
-Input: nums = [1]
-Output: 1
-Explanation: The subarray [1] has the largest sum 1.
-```
-
-
Example 3:
-
-```
-Input: nums = [5,4,-1,7,8]
-Output: 23
-Explanation: The subarray [5,4,-1,7,8] has the largest sum 23.
-```
-
-
-
Constraints:
-
-
1 <= nums.length <= 105
-
-104 <= nums[i] <= 104
-
-
-
Follow up: If you have figured out the O(n) solution, try coding another solution using the divide and conquer approach, which is more subtle.
-
-## Solution:
-
-::: code-group
-
-```go [Go]
-package main
-
-import "math"
-
-func maxSubArray(nums []int) int {
- currSum, maxSum := 0, math.MinInt
-
- for _, num := range nums {
- currSum += num
- maxSum = int(math.Max(float64(maxSum), float64(currSum)))
- if currSum < 0 {
- currSum = 0
- }
- }
-
- return maxSum
-}
-
-```
-
-:::
-
-### [_..._](#)
-
-```
-
-```
-
-
-
-[share]: https://graph.org/file/3ea5234dda646b71c574a.png
-[easy]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Easy-bright.svg
-[medium]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Medium-yellow.svg
-[hard]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Hard-red.svg
diff --git a/docs/solution/0001-0100/055 - Jump Game.md b/docs/solution/0001-0100/055 - Jump Game.md
deleted file mode 100644
index 0431fde8..00000000
--- a/docs/solution/0001-0100/055 - Jump Game.md
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,65 +0,0 @@
-# 55. Jump Game [![share]](https://leetcode.com/problems/jump-game)
-
-![][medium]
-
-## Problem Statement:
-
-You are given an integer array `nums`. You are initially positioned at the array's **first index**, and each element in the array represents your maximum jump length at that position.
-
-Return `true` if you can reach the last index, or `false` otherwise.
-
-### Example 1:
-
-```
-Input: nums = [2,3,1,1,4]
-Output: true
-Explanation: Jump 1 step from index 0 to 1, then 3 steps to the last index.
-```
-
-### Example 2:
-
-```
-Input: nums = [3,2,1,0,4]
-Output: false
-Explanation: You will always arrive at index 3 no matter what. Its maximum jump length is 0, which makes it impossible to reach the last index.
-```
-
-### Constraints:
-
-- 1 <= nums.length <= 104
-- 0 <= nums[i] <= 105
-
-## Solution:
-
-::: code-group
-
-```java
-public boolean canJump(int[] nums) {
- int n = nums.length,
- max = 0;
- if (n == 1)
- return true;
- for (int i = 0; i < n - 1 && max >= i; i++) {
- if (max < i + nums[i])
- max = i + nums[i];
- if (max >= n - 1)
- return true;
- }
- return false;
-}
-```
-
-:::
-
-### [_..._](#)
-
-```
-
-```
-
-
-
-[share]: https://img.icons8.com/external-anggara-blue-anggara-putra/20/000000/external-share-user-interface-basic-anggara-blue-anggara-putra-2.png
-[easy]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Easy-bright.svg
-[medium]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Medium-yellow.svg
-[hard]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Hard-red.svg
diff --git a/docs/solution/0001-0100/058 - Length of Last Word.md b/docs/solution/0001-0100/058 - Length of Last Word.md
deleted file mode 100644
index 879bff44..00000000
--- a/docs/solution/0001-0100/058 - Length of Last Word.md
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,69 +0,0 @@
-# 58. Length of Last Word [![share]](https://leetcode.com/problems/length-of-last-word)
-
-![][easy]
-
-## Problem Statement:
-
-Given a string `s` consisting of words and spaces, return the length of the **last** word in the string.
-
-- A **word** is a maximal substring consisting of non-space characters only.
-
-### Example 1:
-
-```
-Input: s = "Hello World"
-Output: 5
-Explanation: The last word is "World" with length 5.
-```
-
-### Example 2:
-
-```
-Input: s = " fly me to the moon "
-Output: 4
-Explanation: The last word is "moon" with length 4.
-```
-
-### Example 3:
-
-```
-Input: s = "luffy is still joyboy"
-Output: 6
-Explanation: The last word is "joyboy" with length 6.
-```
-
-### Constraints:
-
-- 1 <= s.length <= 105
-- s consists of only English letters and spaces ' '.
-- There will be at least one word in s.
-
-## Solution:
-
-::: code-group
-
-```java
-public int lengthOfLastWord(String s) {
- int count = 0;
- for (int i = s.length() - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
- if (s.charAt(i) != ' ')
- count++;
- else if (count > 0)
- return count;
- }
- return count;
-}
-```
-
-:::
-
-### [_..._](#)
-
-```
-
-```
-
-
-
-[share]: https://img.icons8.com/external-anggara-blue-anggara-putra/20/000000/external-share-user-interface-basic-anggara-blue-anggara-putra-2.png
-[easy]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Easy-green.svg
diff --git a/docs/solution/0001-0100/061 - Rotate List .md b/docs/solution/0001-0100/061 - Rotate List .md
deleted file mode 100644
index fada7825..00000000
--- a/docs/solution/0001-0100/061 - Rotate List .md
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,77 +0,0 @@
-# 61. Rotate List [![][share]](https://leetcode.com/problems/rotate-list/)
-
-![][medium]
-
-## Problem Statement:
-
-Given the `head` of a linked list, rotate the list to the right by `k` places.
-
-### Example 1:
-
-
-
-```
-Input: head = [1,2,3,4,5], k = 2
-Output: [4,5,1,2,3]
-```
-
-### Example 2:
-
-
-
-```
-Input: head = [0,1,2], k = 4
-Output: [2,0,1]
-```
-
-### Constraints:
-
-- The number of nodes in the list is in the range `[0, 500]`.
-- -100 <= Node.val <= 100
-- 0 <= k <= 2 \* 109
-
-## Solution:
-
-::: code-group
-
-```java
-public ListNode rotateRight(ListNode head, int k) {
- if (head == null)
- return null;
- int size = 0;
- ListNode temp = head,
- newHead = null,
- p1 = head,
- p2 = head;
- while (temp != null) {
- size++;
- temp = temp.next;
- }
- k %= size;
- for (int i = 0; i < k; i++)
- p2 = p2.next;
- while (p2.next != null) {
- p1 = p1.next;
- p2 = p2.next;
- }
- p2.next = head;
- newHead = p1.next;
- p1.next = null;
- return newHead;
-}
-```
-
-:::
-
-### [_..._](#)
-
-```
-
-```
-
-
-
-[share]: https://img.icons8.com/external-anggara-blue-anggara-putra/20/000000/external-share-user-interface-basic-anggara-blue-anggara-putra-2.png
-[easy]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Easy-bright.svg
-[medium]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Medium-yellow.svg
-[hard]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Hard-red.svg
diff --git a/docs/solution/0001-0100/066 - Plus One.md b/docs/solution/0001-0100/066 - Plus One.md
deleted file mode 100644
index 2fcf386c..00000000
--- a/docs/solution/0001-0100/066 - Plus One.md
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,83 +0,0 @@
-# 66. Plus One [![share]](https://leetcode.com/problems/plus-one/)
-
-![][easy]
-
-## Problem Statement
-
-
You are given a large integer represented as an integer array digits, where each digits[i] is the ith digit of the integer. The digits are ordered from most significant to least significant in left-to-right order. The large integer does not contain any leading 0's.
-
Increment the large integer by one and return the resulting array of digits.
-
-
Example 1:
-
-```
-Input: digits = [1,2,3]
-Output: [1,2,4]
-Explanation: The array represents the integer 123.
-Incrementing by one gives 123 + 1 = 124.
-Thus, the result should be [1,2,4].
-```
-
-
Example 2:
-
-```
-Input: digits = [4,3,2,1]
-Output: [4,3,2,2]
-Explanation: The array represents the integer 4321.
-Incrementing by one gives 4321 + 1 = 4322.
-Thus, the result should be [4,3,2,2].
-```
-
-
Example 3:
-
-```
-Input: digits = [9]
-Output: [1,0]
-Explanation: The array represents the integer 9.
-Incrementing by one gives 9 + 1 = 10.
-Thus, the result should be [1,0].
-```
-
-
Given a non-negative integer x, return the square root of x rounded down to the nearest integer. The returned integer should be non-negative as well.
-
You must not use any built-in exponent function or operator.
-
-
For example, do not use pow(x, 0.5) in c++ or x ** 0.5 in python.
-
-
-
Example 1:
-
-```
-Input: x = 4
-Output: 2
-Explanation: The square root of 4 is 2, so we return 2.
-```
-
-
Example 2:
-
-```
-Input: x = 8
-Output: 2
-Explanation: The square root of 8 is 2.82842..., and since we round it down to the nearest integer, 2 is returned.
-```
-
-
-
Constraints:
-
-
0 <= x <= 231 - 1
-
-
-::: details _Click to open Hints_
-
-- Try exploring all integers. (Credits: @annujoshi)
-- Use the sorted property of integers to reduced the search space. (Credits: @annujoshi)
-
-:::
-
-## Solution:
-
-::: code-group
-
-```go [Go]
-package main
-
-func mySqrt(x int) int {
- start := 0
- end := x
-
- for start < end {
- // this is to floor the mid value
- // mid of 8 will be 4 , (8+1)/2 = 4.5
- // mid of 9 will be 5 , (9+1)/2 = 5
- mid := start + (end-start+1)/2
- if mid*mid > x {
- end = mid - 1
- } else {
- start = mid
- }
- }
-
- return end
-}
-
-```
-
-:::
-
-### [_..._](#)
-
-```
-
-```
-
-
-
-[share]: https://graph.org/file/3ea5234dda646b71c574a.png
-[easy]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Easy-bright.svg
-[medium]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Medium-yellow.svg
-[hard]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Hard-red.svg
diff --git a/docs/solution/0001-0100/070 - Climbing Stairs.md b/docs/solution/0001-0100/070 - Climbing Stairs.md
deleted file mode 100644
index e21e77e9..00000000
--- a/docs/solution/0001-0100/070 - Climbing Stairs.md
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,62 +0,0 @@
-# 70. Climbing Stairs [![share]](https://leetcode.com/problems/climbing-stairs)
-
-![][easy]
-
-## Problem Statement:
-
-You are climbing a staircase. It takes `n` steps to reach the top.
-
-Each time you can either climb `1` or `2` steps. In how many distinct ways can you climb to the top?
-
-### Example 1:
-
-```
-Input: n = 2
-Output: 2
-Explanation: There are two ways to climb to the top.
-1. 1 step + 1 step
-2. 2 steps
-```
-
-### Example 2:
-
-```
-Input: n = 3
-Output: 3
-Explanation: There are three ways to climb to the top.
-1. 1 step + 1 step + 1 step
-2. 1 step + 2 steps
-3. 2 steps + 1 step
-```
-
-### Constraints:
-
-- 1 <= n <= 45
-
-## Solution:
-
-::: code-group
-
-```java
-public int climbStairs(int n) {
- int[] dp = new int[n + 1];
- dp[0] = 1;
- dp[1] = 1;
- for (int i = 2; i <= n; i++)
- dp[i] = dp[i - 1] + dp[i - 2];
- return dp[n];
-}
-```
-
-:::
-
-### [_..._](#)
-
-```
-
-```
-
-
-
-[share]: https://img.icons8.com/external-anggara-blue-anggara-putra/20/000000/external-share-user-interface-basic-anggara-blue-anggara-putra-2.png
-[easy]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Easy-green.svg
diff --git a/docs/solution/0001-0100/072 - Edit Distance.md b/docs/solution/0001-0100/072 - Edit Distance.md
deleted file mode 100644
index ac0788c2..00000000
--- a/docs/solution/0001-0100/072 - Edit Distance.md
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,214 +0,0 @@
-# 72. Edit Distance [![share]](https://leetcode.com/problems/edit-distance/)
-
-![][hard]
-
-## Problem Statement:
-
-Given two strings `word1` and `word2`, return the minimum number of operations required to convert `word1` to `word2`.
-
-You have the following three operations permitted on a word:
-
-- Insert a character
-- Delete a character
-- Replace a character
-
-### Example 1:
-
-```
-Input: word1 = "horse", word2 = "ros"
-Output: 3
-Explanation:
-horse -> rorse (replace 'h' with 'r')
-rorse -> rose (remove 'r')
-rose -> ros (remove 'e')
-```
-
-### Example 2:
-
-```
-Input: word1 = "intention", word2 = "execution"
-Output: 5
-Explanation:
-intention -> inention (remove 't')
-inention -> enention (replace 'i' with 'e')
-enention -> exention (replace 'n' with 'x')
-exention -> exection (replace 'n' with 'c')
-exection -> execution (insert 'u')
-```
-
-### Constraints:
-
-- 0 <= word1.length, word2.length <= 500
-- word1 and word2 consist of lowercase English letters.
-
-## Solution:
-
-::: code-group
-
-```rs [Rust]
-impl Solution {
- fn min_distance(word1: String, word2: String) -> i32 {
- let (m, n) = (word1.len(), word2.len());
- let (word1, word2) = (word1.as_bytes(), word2.as_bytes());
- let mut dp = vec![vec![0; n + 1]; m + 1];
-
- for i in 0..=m {
- for j in 0..=n {
- if i == 0 {
- dp[i][j] = j as i32;
- } else if j == 0 {
- dp[i][j] = i as i32;
- } else if word1[i - 1] == word2[j - 1] {
- dp[i][j] = dp[i - 1][j - 1];
- } else {
- dp[i][j] = 1 + dp[i - 1][j - 1].min(dp[i - 1][j].min(dp[i][j - 1]));
- }
- }
- }
-
- dp[m][n]
- }
-}
-
-```
-
-```cpp [C++]
-#include
-using namespace std;
-
-int minDistance(string word1, string word2)
-{
- int m = word1.length(),
- n = word2.length();
- vector> dp(m + 1, vector(n + 1));
- for (int i = 0; i < m + 1; i++)
- for (int j = 0; j < n + 1; j++)
- {
- if (i == 0)
- dp[i][j] = j;
- else if (j == 0)
- dp[i][j] = i;
- else if (word1[i - 1] == word2[j - 1])
- dp[i][j] = dp[i - 1][j - 1];
- else
- dp[i][j] = 1 + min(dp[i - 1][j - 1], min(dp[i - 1][j], dp[i][j - 1]));
- }
- return dp[m][n];
-}
-
-// int main()
-// {
-// cout << getMinConversions("intention", "execution") << endl;
-// }
-```
-
-```py [Python]
-def minDistance(word1: str, word2: str) -> int:
- m, n = len(word1), len(word2)
- dp = [[None] * (n + 1) for _ in range(m + 1)]
- for i in range(m + 1):
- for j in range(n + 1):
- if i == 0:
- dp[i][j] = j
- elif j == 0:
- dp[i][j] = i
- elif word1[i - 1] == word2[j - 1]:
- dp[i][j] = dp[i - 1][j - 1]
- else:
- dp[i][j] = 1 + min(dp[i - 1][j - 1], min(dp[i - 1][j], dp[i][j - 1]))
- return dp[m][n]
-
-
-if __name__ == "__main__":
- print(minDistance("intention", "execution"))
-
-```
-
-```go [Go]
-package main
-
-func minDistance(word1 string, word2 string) int {
- m, n := len(word1), len(word2)
-
- dp := make([][]int, m+1)
-
- for i := 0; i <= m; i++ {
- dp[i] = make([]int, n+1)
- }
-
- for i := 0; i <= m; i++ {
- for j := 0; j <= n; j++ {
- if i == 0 {
- dp[i][j] = j
- } else if j == 0 {
- dp[i][j] = i
- } else if word1[i-1] == word2[j-1] {
- dp[i][j] = dp[i-1][j-1]
- } else {
- dp[i][j] = 1 + min(dp[i-1][j-1], min(dp[i-1][j], dp[i][j-1]))
- }
- }
- }
-
- return dp[m][n]
-}
-
-func min(a, b int) int {
- if a < b {
- return a
- }
- return b
-}
-
-```
-
-```java [Java]
-public class EditDistance {
-
- /**
- * Time Complexity => O(n^2)
- *
- * @param str1 String
- * @param str2 String
- * @return the minimum number of operations required to convert {@code str1} to
- * {@code str2}
- */
- public int minDistance(String word1, String word2) {
- int m = word1.length(),
- n = word2.length();
- int[][] dp = new int[m + 1][n + 1];
- for (int i = 0; i < m + 1; i++)
- for (int j = 0; j < n + 1; j++) {
- if (i == 0)
- dp[i][j] = j;
- else if (j == 0)
- dp[i][j] = i;
- else if (word1.charAt(i - 1) == word2.charAt(j - 1))
- dp[i][j] = dp[i - 1][j - 1];
- else
- dp[i][j] = 1 + Math.min(dp[i - 1][j - 1], Math.min(dp[i - 1][j], dp[i][j - 1]));
- }
- return dp[m][n];
- }
-
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- EditDistance ob = new EditDistance();
- System.out.println(ob.minDistance("intention", "execution"));
- }
-}
-```
-
-:::
-
-### [_..._](#)
-
-```
-
-```
-
-
-
-[share]: https://img.icons8.com/external-anggara-blue-anggara-putra/20/000000/external-share-user-interface-basic-anggara-blue-anggara-putra-2.png
-[easy]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Easy-bright.svg
-[medium]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Medium-yellow.svg
-[hard]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Hard-red.svg
diff --git a/docs/solution/0001-0100/074 - Search a 2D Matrix.md b/docs/solution/0001-0100/074 - Search a 2D Matrix.md
deleted file mode 100644
index df497f99..00000000
--- a/docs/solution/0001-0100/074 - Search a 2D Matrix.md
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,78 +0,0 @@
-# 74. Search a 2D Matrix [![share]](https://leetcode.com/problems/search-a-2d-matrix/)
-
-![][medium]
-
-## Problem Statement
-
-
You are given an m x n integer matrix matrix with the following two properties:
-
-
Each row is sorted in non-decreasing order.
-
The first integer of each row is greater than the last integer of the previous row.
-
-
Given an integer target, return trueiftargetis inmatrixorfalseotherwise.
-
You must write a solution in O(log(m * n)) time complexity.
The number of nodes in the list is in the range [0, 300].
-
-100 <= Node.val <= 100
-
The list is guaranteed to be sorted in ascending order.
-
-
-## Solution:
-
-::: code-group
-
-```go [Go]
-package main
-
-// Definition for singly-linked list.
-type ListNode struct {
- Val int
- Next *ListNode
-}
-
-func deleteDuplicates(head *ListNode) *ListNode {
- if head == nil {
- return head
- }
- current := head
- for current != nil && current.Next != nil {
- if current.Val == current.Next.Val {
- current.Next = current.Next.Next
- } else {
- current = current.Next
- }
- }
-
- return head
-}
-
-```
-
-:::
-
-### [_..._](#)
-
-```
-
-```
-
-
-
-[share]: https://graph.org/file/3ea5234dda646b71c574a.png
-[easy]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Easy-bright.svg
-[medium]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Medium-yellow.svg
-[hard]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Hard-red.svg
diff --git a/docs/solution/0001-0100/088 - Merge Sorted Array.md b/docs/solution/0001-0100/088 - Merge Sorted Array.md
deleted file mode 100644
index b8ea6e9c..00000000
--- a/docs/solution/0001-0100/088 - Merge Sorted Array.md
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,95 +0,0 @@
-# 88. Merge Sorted Array [![share]](https://leetcode.com/problems/merge-sorted-array/)
-
-![][easy]
-
-## Problem Statement
-
-
You are given two integer arrays nums1 and nums2, sorted in non-decreasing order, and two integers m and n, representing the number of elements in nums1 and nums2 respectively.
-
Mergenums1 and nums2 into a single array sorted in non-decreasing order.
-
The final sorted array should not be returned by the function, but instead be stored inside the array nums1. To accommodate this, nums1 has a length of m + n, where the first m elements denote the elements that should be merged, and the last n elements are set to 0 and should be ignored. nums2 has a length of n.
-
-
Example 1:
-
-```
-Input: nums1 = [1,2,3,0,0,0], m = 3, nums2 = [2,5,6], n = 3
-Output: [1,2,2,3,5,6]
-Explanation: The arrays we are merging are [1,2,3] and [2,5,6].
-The result of the merge is [1,2,2,3,5,6] with the underlined elements coming from nums1.
-```
-
-
Example 2:
-
-```
-Input: nums1 = [1], m = 1, nums2 = [], n = 0
-Output: [1]
-Explanation: The arrays we are merging are [1] and [].
-The result of the merge is [1].
-```
-
-
Example 3:
-
-```
-Input: nums1 = [0], m = 0, nums2 = [1], n = 1
-Output: [1]
-Explanation: The arrays we are merging are [] and [1].
-The result of the merge is [1].
-Note that because m = 0, there are no elements in nums1. The 0 is only there to ensure the merge result can fit in nums1.
-```
-
-
-
Constraints:
-
-
nums1.length == m + n
-
nums2.length == n
-
0 <= m, n <= 200
-
1 <= m + n <= 200
-
-109 <= nums1[i], nums2[j] <= 109
-
-
-
Follow up: Can you come up with an algorithm that runs in O(m + n) time?
-
-::: details _Click to open Hints_
-
-- You can easily solve this problem if you simply think about two elements at a time rather than two arrays. We know that each of the individual arrays is sorted. What we don't know is how they will intertwine. Can we take a local decision and arrive at an optimal solution?
-- If you simply consider one element each at a time from the two arrays and make a decision and proceed accordingly, you will arrive at the optimal solution.
-
-:::
-
-## Solution:
-
-::: code-group
-
-```go [Go]
-package main
-
-func merge(nums1 []int, m int, nums2 []int, n int) {
- i, j, k := m-1, n-1, m+n-1
-
- for j >= 0 {
- if i >= 0 && nums1[i] > nums2[j] {
- nums1[k] = nums1[i]
- i--
- } else {
- nums1[k] = nums2[j]
- j--
- }
- k--
- }
-}
-
-```
-
-:::
-
-### [_..._](#)
-
-```
-
-```
-
-
-
-[share]: https://graph.org/file/3ea5234dda646b71c574a.png
-[easy]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Easy-bright.svg
-[medium]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Medium-yellow.svg
-[hard]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Hard-red.svg
diff --git a/docs/solution/0001-0100/094 - Binary Tree Inorder Traversal.md b/docs/solution/0001-0100/094 - Binary Tree Inorder Traversal.md
deleted file mode 100644
index d1ab5aef..00000000
--- a/docs/solution/0001-0100/094 - Binary Tree Inorder Traversal.md
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,69 +0,0 @@
-# 94. Binary Tree Inorder Traversal [![share]](https://leetcode.com/problems/binary-tree-inorder-traversal/)
-
-![][easy]
-
-## Problem Statement:
-
-Given the root of a binary tree, return the inorder traversal of its nodes' values.
-
-### Example 1:
-
-
-
-```
-Input: root = [1,null,2,3]
-Output: [1,3,2]
-```
-
-### Example 2:
-
-```
-Input: root = []
-Output: []
-```
-
-### Example 3:
-
-```
-Input: root = [1]
-Output: [1]
-```
-
-### Constraints:
-
-- The number of nodes in the tree is in the range [0, 100].
-- -100 <= Node.val <= 100
-
-**Follow up:** Recursive solution is trivial, could you do it iteratively?
-
-## Solution:
-
-::: code-group
-
-```java
-public class BinaryTreeInorderTraversal {
- List list = new ArrayList<>();
-
- public List inorderTraversal(TreeNode root) {
- if (root == null)
- return list;
- inorderTraversal(root.left);
- list.add(root.val);
- inorderTraversal(root.right);
- return list;
- }
-}
-```
-
-:::
-
-### [_..._](#)
-
-```
-
-```
-
-
-
-[share]: https://img.icons8.com/external-anggara-blue-anggara-putra/20/000000/external-share-user-interface-basic-anggara-blue-anggara-putra-2.png
-[easy]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Easy-green.svg
diff --git a/docs/solution/0001-0100/098 - Validate Binary Search Tree.md b/docs/solution/0001-0100/098 - Validate Binary Search Tree.md
deleted file mode 100644
index 8ec69154..00000000
--- a/docs/solution/0001-0100/098 - Validate Binary Search Tree.md
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,72 +0,0 @@
-# 98. Validate Binary Search Tree [![share]](https://leetcode.com/problems/validate-binary-search-tree/)
-
-![][medium]
-
-## Problem Statement:
-
-Given the `root` of a binary tree, determine if it is a valid binary search tree (BST).
-
-A **valid BST** is defined as follows:
-
-- The left subtree of a node contains only nodes with keys **less than** the node's key.
-- The right subtree of a node contains only nodes with keys **greater than** the node's key.
-- Both the left and right subtrees must also be binary search trees.
-
-### Example 1:
-
-
-
-```
-Input: root = [2,1,3]
-Output: true
-```
-
-### Example 2:
-
-
-
-```
-Input: root = [5,1,4,null,null,3,6]
-Output: false
-```
-
-**Explanation**: The root node's value is 5 but its right child's value is 4.
-
-### Constraints:
-
-- The number of nodes in the tree is in the range [1, 104].
-- -231 <= Node.val <= 231 - 1
-
-## Solution:
-
-::: code-group
-
-```java
-public class ValidateBinarySearchTree {
- public boolean isValidBST(TreeNode root) {
- return isValidBST(root, Long.MIN_VALUE, Long.MAX_VALUE);
- }
-
- private boolean isValidBST(TreeNode root, long min, long max) {
- if (root == null)
- return true;
- return (root.val > min &&
- root.val < max &&
- isValidBST(root.left, min, root.val) &&
- isValidBST(root.right, root.val, max));
- }
-}
-```
-
-:::
-
-### [_..._](#)
-
-```
-
-```
-
-
-
-[share]: https://img.icons8.com/external-anggara-blue-anggara-putra/20/000000/external-share-user-interface-basic-anggara-blue-anggara-putra-2.png
-[medium]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Medium-yellow.svg
diff --git a/docs/solution/0001-0100/100 - Same Tree.md b/docs/solution/0001-0100/100 - Same Tree.md
deleted file mode 100644
index 3e1283e5..00000000
--- a/docs/solution/0001-0100/100 - Same Tree.md
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,74 +0,0 @@
-# 100. Same Tree [![][share]](https://leetcode.com/problems/same-tree/)
-
-![][easy]
-
-## Problem Statement:
-
-Given the roots of two binary trees `p` and `q`, write a function to check if they are the same or not.
-
-Two binary trees are considered the same if they are structurally identical, and the nodes have the same value.
-
-### Example 1:
-
-
-
-```
-Input: p = [1,2,3], q = [1,2,3]
-Output: true
-```
-
-### Example 2:
-
-
-
-```
-Input: p = [1,2], q = [1,null,2]
-Output: false
-```
-
-### Example 3:
-
-
-
-```
-Input: p = [1,2,1], q = [1,1,2]
-Output: false
-```
-
-### Constraints:
-
-- The number of nodes in both trees is in the range `[0, 100]`.
-- -104 <= Node.val <= 104
-
-## Solution:
-
-::: code-group
-
-```java
-public boolean isSameTree(TreeNode p, TreeNode q) {
- if (p == null && q == null)
- return true;
- if (q == null || p == null)
- return false;
- if (p.val != q.val)
- return false;
- boolean left = isSameTree(p.left, q.left);
- boolean right = isSameTree(p.right, q.right);
- return left && right;
-}
-```
-
-:::
-
-### [_..._](#)
-
-```
-
-```
-
-
-
-[share]: https://img.icons8.com/external-anggara-blue-anggara-putra/20/000000/external-share-user-interface-basic-anggara-blue-anggara-putra-2.png
-[easy]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Easy-bright.svg
-[medium]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Medium-yellow.svg
-[hard]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Hard-red.svg
diff --git a/docs/solution/0101-0200/101 - Symmetric Tree.md b/docs/solution/0101-0200/101 - Symmetric Tree.md
deleted file mode 100644
index 00388dc9..00000000
--- a/docs/solution/0101-0200/101 - Symmetric Tree.md
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,100 +0,0 @@
-# 101. Symmetric Tree [![share]](https://leetcode.com/problems/symmetric-tree/)
-
-![][easy]
-
-## Problem Statement
-
-
Given the root of a binary tree, check whether it is a mirror of itself (i.e., symmetric around its center).
The number of nodes in the tree is in the range [1, 1000].
-
-100 <= Node.val <= 100
-
-
-Follow up: Could you solve it both recursively and iteratively?
-
-## Solution:
-
-::: code-group
-
-```go [Go]
-package main
-
-// Definition for a binary tree node.
-type TreeNode struct {
- Val int
- Left *TreeNode
- Right *TreeNode
-}
-
-func isSymmetric(root *TreeNode) bool {
- return isMirror(root, root)
-}
-
-func isMirror(t1, t2 *TreeNode) bool {
- if t1 == nil && t2 == nil {
- return true
- }
-
- if t1 == nil || t2 == nil {
- return false
- }
-
- return (t1.Val == t2.Val) && isMirror(t1.Left, t2.Right) && isMirror(t1.Right, t2.Left)
-}
-
-```
-
-```py [Python]
-
-from out.definitions.treenode import TreeNode
-
-
-class Solution:
- def isSymmetric(self, root: TreeNode) -> bool:
- return self._is_mirror(root, root)
-
- def _is_mirror(self, t1: TreeNode, t2: TreeNode) -> bool:
- if not t1 and not t2:
- return True
- if not t1 or not t2:
- return False
-
- return ((t1.val == t2.val) and
- self._is_mirror(t1.right, t2.left) and
- self._is_mirror(t1.left, t2.right))
-
-```
-
-:::
-
-### [_..._](#)
-
-```
-
-```
-
-
-
-[share]: https://graph.org/file/3ea5234dda646b71c574a.png
-[easy]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Easy-bright.svg
-[medium]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Medium-yellow.svg
-[hard]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Hard-red.svg
diff --git a/docs/solution/0101-0200/103 - Binary Tree Zigzag Level Order Traversal.md b/docs/solution/0101-0200/103 - Binary Tree Zigzag Level Order Traversal.md
deleted file mode 100644
index e14640f8..00000000
--- a/docs/solution/0101-0200/103 - Binary Tree Zigzag Level Order Traversal.md
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,161 +0,0 @@
-# 103. Binary Tree Zigzag Level Order Traversal [![share]](https://leetcode.com/problems/binary-tree-zigzag-level-order-traversal/)
-
-![][medium]
-
-## Problem Statement:
-
-Given the root of a binary tree, return the zigzag level order traversal of its nodes' values. (i.e., from left to right, then right to left for the next level and alternate between).
-
-### Example 1:
-
-
-
-```
-Input: root = [3,9,20,null,null,15,7]
-Output: [[3],[20,9],[15,7]]
-```
-
-### Example 2:
-
-```
-Input: root = [1]
-Output: [[1]]
-```
-
-### Example 3:
-
-```
-Input: root = []
-Output: []
-```
-
-### Constraints:
-
-- The number of nodes in the tree is in the range [0, 2000].
-- -100 <= Node.val <= 100
-
-## Solution:
-
-::: code-group
-
-```java [Java]
-import java.util.LinkedList;
-import java.util.List;
-import java.util.Stack;
-import definitions.TreeNode;
-
-public class BinaryTreeZigzagLevelOrderTraversal {
- public static List> zigzagLevelOrder(TreeNode root) {
- List> result = new LinkedList<>();
- if (root == null)
- return result;
- Stack stk1 = new Stack<>(), stk2 = new Stack<>();
- stk1.push(root);
- while (!stk1.isEmpty() || !stk2.isEmpty()) {
- List list1 = new LinkedList<>();
- while (!stk1.isEmpty()) {
- TreeNode currentNode = stk1.pop();
- list1.add(currentNode.val);
- if (currentNode.left != null)
- stk2.push(currentNode.left);
- if (currentNode.right != null)
- stk2.push(currentNode.right);
- }
- if (!list1.isEmpty())
- result.add(list1);
- List list2 = new LinkedList<>();
- while (!stk2.isEmpty()) {
- TreeNode currentNode = stk2.pop();
- list2.add(currentNode.val);
- if (currentNode.right != null)
- stk1.push(currentNode.right);
- if (currentNode.left != null)
- stk1.push(currentNode.left);
- }
- if (!list2.isEmpty())
- result.add(list2);
- }
- return result;
- }
-}
-
-```
-
-```go [Go]
-package main
-
-// Definition for a binary tree node.
-type TreeNode struct {
- Val int
- Left *TreeNode
- Right *TreeNode
-}
-
-func zigzagLevelOrder(root *TreeNode) [][]int {
- if root == nil {
- return nil
- }
-
- var res [][]int
- var stk1 []*TreeNode
- var stk2 []*TreeNode
-
- stk1 = append(stk1, root)
-
- for len(stk1) > 0 || len(stk2) > 0 {
- var list1 []int
- for len(stk1) > 0 {
- // pop
- node := stk1[len(stk1)-1]
- stk1 = stk1[:len(stk1)-1]
-
- list1 = append(list1, node.Val)
- if node.Left != nil {
- stk2 = append(stk2, node.Left)
- }
- if node.Right != nil {
- stk2 = append(stk2, node.Right)
- }
- }
-
- if len(list1) > 0 {
- res = append(res, list1)
- }
-
- var list2 []int
- for len(stk2) > 0 {
- // pop
- node := stk2[len(stk2)-1]
- stk2 = stk2[:len(stk2)-1]
-
- list2 = append(list2, node.Val)
- if node.Right != nil {
- stk1 = append(stk1, node.Right)
- }
- if node.Left != nil {
- stk1 = append(stk1, node.Left)
- }
- }
-
- if len(list2) > 0 {
- res = append(res, list2)
- }
- }
-
- return res
-}
-
-```
-
-:::
-
-### [_..._](#)
-
-```
-
-```
-
-
-
-[share]: https://img.icons8.com/external-anggara-blue-anggara-putra/20/000000/external-share-user-interface-basic-anggara-blue-anggara-putra-2.png
-[medium]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Medium-yellow.svg
diff --git a/docs/solution/0101-0200/104 - Maximum Depth of Binary Tree.md b/docs/solution/0101-0200/104 - Maximum Depth of Binary Tree.md
deleted file mode 100644
index 64bb3171..00000000
--- a/docs/solution/0101-0200/104 - Maximum Depth of Binary Tree.md
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,59 +0,0 @@
-# 104. Maximum Depth of Binary Tree [![share]](https://leetcode.com/problems/maximum-depth-of-binary-tree/)
-
-![][easy]
-
-## Problem Statement:
-
-Given the root of a binary tree, return its maximum depth.
-
-A binary tree's **maximum depth** is the number of nodes along the longest path from the root node down to the farthest leaf node.
-
-### Example 1:
-
-
-
-```
-Input: root = [3,9,20,null,null,15,7]
-Output: 3
-```
-
-### Example 2:
-
-```
-Input: root = [1,null,2]
-Output: 2
-```
-
-### Constraints:
-
-- The number of nodes in the tree is in the range [0, 104].
-- -100 <= Node.val <= 100
-
-## Solution:
-
-::: code-group
-
-```java
-public class MaximumDepthOfBinaryTree {
-
- public static int maxDepth(TreeNode root) {
- if (root == null)
- return 0;
- int depth = Math.max(maxDepth(root.left), maxDepth(root.right)) + 1;
- return depth;
- }
-}
-```
-
-:::
-
-### [_..._](#)
-
-```
-
-```
-
-
-
-[share]: https://img.icons8.com/external-anggara-blue-anggara-putra/20/000000/external-share-user-interface-basic-anggara-blue-anggara-putra-2.png
-[easy]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Easy-green.svg
diff --git a/docs/solution/0101-0200/106 - Construct Binary Tree from Inorder and Postorder Traversal.md b/docs/solution/0101-0200/106 - Construct Binary Tree from Inorder and Postorder Traversal.md
deleted file mode 100644
index 83c1c28a..00000000
--- a/docs/solution/0101-0200/106 - Construct Binary Tree from Inorder and Postorder Traversal.md
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,92 +0,0 @@
-# 106. Construct Binary Tree from Inorder and Postorder Traversal [![share]](https://leetcode.com/problems/construct-binary-tree-from-inorder-and-postorder-traversal/)
-
-![][medium]
-
-## Problem Statement
-
-
Given two integer arrays inorder and postorder where inorder is the inorder traversal of a binary tree and postorder is the postorder traversal of the same tree, construct and return the binary tree.
inorder is guaranteed to be the inorder traversal of the tree.
-
postorder is guaranteed to be the postorder traversal of the tree.
-
-
-## Solution:
-
-::: code-group
-
-```go [Go]
-package main
-
-// Definition for a binary tree node.
-type TreeNode struct {
- Val int
- Left *TreeNode
- Right *TreeNode
-}
-
-func buildTree(inorder []int, postorder []int) *TreeNode {
- mapInOrder := make(map[int]int)
-
- for i, v := range inorder {
- mapInOrder[v] = i
- }
-
- var helper func(int, int) *TreeNode
- helper = func(left, right int) *TreeNode {
- if left > right {
- return nil
- }
-
- pop := postorder[len(postorder)-1]
- postorder = postorder[:len(postorder)-1]
-
- root := &TreeNode{Val: pop}
- mid := mapInOrder[pop]
- root.Right = helper(mid+1, right)
- root.Left = helper(left, mid-1)
-
- return root
- }
-
- return helper(0, len(inorder)-1)
-}
-
-```
-
-:::
-
-### [_..._](#)
-
-```
-
-```
-
-
-
-[share]: https://graph.org/file/3ea5234dda646b71c574a.png
-[easy]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Easy-bright.svg
-[medium]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Medium-yellow.svg
-[hard]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Hard-red.svg
diff --git a/docs/solution/0101-0200/108 - Convert Sorted Array to Binary Search Tree.md b/docs/solution/0101-0200/108 - Convert Sorted Array to Binary Search Tree.md
deleted file mode 100644
index af8b4b7f..00000000
--- a/docs/solution/0101-0200/108 - Convert Sorted Array to Binary Search Tree.md
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,85 +0,0 @@
-# 108. Convert Sorted Array to Binary Search Tree [![share]](https://leetcode.com/problems/convert-sorted-array-to-binary-search-tree/)
-
-![][easy]
-
-## Problem Statement
-
-
Given an integer array nums where the elements are sorted in ascending order, convert it to a height-balancedbinary search tree.
-
-
Example 1:
-
-
-```
-Input: nums = [-10,-3,0,5,9]
-Output: [0,-3,9,-10,null,5]
-Explanation: [0,-10,5,null,-3,null,9] is also accepted:
-
-```
-
-
Example 2:
-
-
-```
-Input: nums = [1,3]
-Output: [3,1]
-Explanation: [1,null,3] and [3,1] are both height-balanced BSTs.
-```
-
-
-
Constraints:
-
-
1 <= nums.length <= 104
-
-104 <= nums[i] <= 104
-
nums is sorted in a strictly increasing order.
-
-
-## Solution:
-
-::: code-group
-
-```go [Go]
-package main
-
-// Definition for a binary tree node.
-type TreeNode struct {
- Val int
- Left *TreeNode
- Right *TreeNode
-}
-
-func sortedArrayToBST(nums []int) *TreeNode {
- if len(nums) == 0 {
- return nil
- }
-
- return contructBST(nums, 0, len(nums)-1)
-}
-
-func contructBST(nums []int, left, right int) *TreeNode {
- if left > right {
- return nil
- }
-
- mid := (left + right) / 2
- node := &TreeNode{Val: nums[mid]}
- node.Left = contructBST(nums, left, mid-1)
- node.Right = contructBST(nums, mid+1, right)
- return node
-}
-
-```
-
-:::
-
-### [_..._](#)
-
-```
-
-```
-
-
-
-[share]: https://graph.org/file/3ea5234dda646b71c574a.png
-[easy]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Easy-bright.svg
-[medium]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Medium-yellow.svg
-[hard]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Hard-red.svg
diff --git a/docs/solution/0101-0200/109 - Convert Sorted List to Binary Search Tree.md b/docs/solution/0101-0200/109 - Convert Sorted List to Binary Search Tree.md
deleted file mode 100644
index a9f8a833..00000000
--- a/docs/solution/0101-0200/109 - Convert Sorted List to Binary Search Tree.md
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,97 +0,0 @@
-# 109. Convert Sorted List to Binary Search Tree [![share]](https://leetcode.com/problems/convert-sorted-list-to-binary-search-tree/)
-
-![][medium]
-
-## Problem Statement
-
-
Given the head of a singly linked list where elements are sorted in ascending order, convert it to a height-balancedbinary search tree.
-
-
Example 1:
-
-
-```
-Input: head = [-10,-3,0,5,9]
-Output: [0,-3,9,-10,null,5]
-Explanation: One possible answer is [0,-3,9,-10,null,5], which represents the shown height balanced BST.
-```
-
-
Example 2:
-
-```
-Input: head = []
-Output: []
-```
-
-
-
Constraints:
-
-
The number of nodes in head is in the range [0, 2 * 104].
-
-105 <= Node.val <= 105
-
-
-## Solution:
-
-::: code-group
-
-```go [Go]
-package main
-
-// Definition for singly-linked list.
-type ListNode struct {
- Val int
- Next *ListNode
-}
-
-// Definition for a binary tree node.
-type TreeNode struct {
- Val int
- Left *TreeNode
- Right *TreeNode
-}
-
-func sortedListToBST(head *ListNode) *TreeNode {
- if head == nil {
- return nil
- }
-
- if head.Next == nil {
- return &TreeNode{Val: head.Val}
- }
-
- slow, fast := head, head
- prev := slow
-
- for fast != nil && fast.Next != nil {
- prev = slow
- slow = slow.Next
- fast = fast.Next.Next
- }
-
- // slow points to the root of the current subtree
-
- // break the link between the left subtree and the root
- prev.Next = nil
-
- root := &TreeNode{Val: slow.Val}
- root.Left = sortedListToBST(head)
- root.Right = sortedListToBST(slow.Next)
-
- return root
-}
-
-```
-
-:::
-
-### [_..._](#)
-
-```
-
-```
-
-
-
-[share]: https://graph.org/file/3ea5234dda646b71c574a.png
-[easy]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Easy-bright.svg
-[medium]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Medium-yellow.svg
-[hard]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Hard-red.svg
diff --git a/docs/solution/0101-0200/110 - Balanced Binary Tree.md b/docs/solution/0101-0200/110 - Balanced Binary Tree.md
deleted file mode 100644
index 6ec4d7f2..00000000
--- a/docs/solution/0101-0200/110 - Balanced Binary Tree.md
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,77 +0,0 @@
-# 110. Balanced Binary Tree [![share]](https://leetcode.com/problems/balanced-binary-tree/)
-
-![][easy]
-
-## Problem Statement:
-
-Given a binary tree, determine if it is height-balanced.
-
-For this problem, a height-balanced binary tree is defined as:
-
-> a binary tree in which the left and right subtrees of every node differ in height by no more than 1.
-
-### Example 1:
-
-```
-Input: root = [3,9,20,null,null,15,7]
-Output: true
-```
-
-### Example 2:
-
-```
-Input: root = [1,2,2,3,3,null,null,4,4]
-Output: false
-```
-
-### Example 3:
-
-```
-Input: root = []
-Output: true
-```
-
-### Constraints:
-
-- The number of nodes in the tree is in the range [0, 5000].
-- -104 <= Node.val <= 104
-
-## Solution:
-
-::: code-group
-
-```java
-public class BalancedBinaryTree {
- public boolean isBalancedTree(TreeNode root) {
- return !(isBalTree(root) == -1);
- }
-
- private int isBalTree(TreeNode root) {
- if (root == null)
- return 0;
- int leftHeight = isBalTree(root.left);
- if (leftHeight == -1)
- return -1;
- int rightHeight = isBalTree(root.right);
- if (rightHeight == -1)
- return -1;
- if (Math.abs(leftHeight - rightHeight) > 1)
- return -1;
- else
- return Math.max(leftHeight, rightHeight) + 1;
- }
-}
-```
-
-:::
-
-### [_..._](#)
-
-```
-
-```
-
-
-
-[share]: https://img.icons8.com/external-anggara-blue-anggara-putra/20/000000/external-share-user-interface-basic-anggara-blue-anggara-putra-2.png
-[easy]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Easy-green.svg
diff --git a/docs/solution/0101-0200/111 - Minimum Depth of Binary Tree.md b/docs/solution/0101-0200/111 - Minimum Depth of Binary Tree.md
deleted file mode 100644
index e2ebd5bf..00000000
--- a/docs/solution/0101-0200/111 - Minimum Depth of Binary Tree.md
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,111 +0,0 @@
-# 111. Minimum Depth of Binary Tree [![share]](https://leetcode.com/problems/minimum-depth-of-binary-tree/)
-
-![][easy]
-
-## Problem Statement:
-
-Given a binary tree, find its minimum depth.
-
-The minimum depth is the number of nodes along the shortest path from the root node down to the nearest leaf node.
-
-**Note**: A leaf is a node with no children.
-
-### Example 1:
-
-
-
-```
-Input: root = [3,9,20,null,null,15,7]
-Output: 2
-```
-
-### Example 2:
-
-```
-Input: root = [2,null,3,null,4,null,5,null,6]
-Output: 5
-```
-
-### Constraints:
-
-- The number of nodes in the tree is in the range [0, 105].
-- -1000 <= Node.val <= 1000
-
-## Solution:
-
-::: code-group
-
-```rs [Rust]
-impl Solution {
- pub fn min_depth(root: Option>>) -> i32 {
- match root {
- Some(node) => {
- let left = Self::min_depth(node.borrow().left.clone());
- let right = Self::min_depth(node.borrow().right.clone());
-
- if left == 0 || right == 0 {
- left.max(right) + 1
- } else {
- left.min(right) + 1
- }
- }
-
- None => 0,
- }
- }
-}
-
-```
-
-```java [Java]
-import definitions.TreeNode;
-
-public class MinDepthOfBinaryTree {
- // Approach 1
- public static int minDepth(TreeNode root) {
- if (root == null)
- return 0;
- if (root.left == null && root.right == null)
- return 1;
- if (root.left == null)
- return minDepth(root.right) + 1;
- if (root.right == null)
- return minDepth(root.left) + 1;
- return Math.min(minDepth(root.left), minDepth(root.right)) + 1;
- }
-
- // Approach 2
- int min = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
-
- public int minDepth2(TreeNode root) {
- if (root == null)
- return 0;
- minDepth2(root, 0);
- return min;
- }
-
- public void minDepth2(TreeNode root, int level) {
- if (root == null)
- return;
- level++;
- if (root.left == null && root.right == null)
- min = Math.min(min, level);
- minDepth2(root.left, level);
- minDepth2(root.right, level);
- }
-}
-
-```
-
-:::
-
-### [_..._](#)
-
-```
-
-```
-
-
-
-[share]: https://img.icons8.com/external-anggara-blue-anggara-putra/20/000000/external-share-user-interface-basic-anggara-blue-anggara-putra-2.png
-[easy]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Easy-green.svg
diff --git a/docs/solution/0101-0200/112 - Path Sum.md b/docs/solution/0101-0200/112 - Path Sum.md
deleted file mode 100644
index 71e3bb8f..00000000
--- a/docs/solution/0101-0200/112 - Path Sum.md
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,94 +0,0 @@
-# 112. Path Sum [![share]](https://leetcode.com/problems/path-sum/)
-
-![][easy]
-
-## Problem Statement
-
-
Given the root of a binary tree and an integer targetSum, return true if the tree has a root-to-leaf path such that adding up all the values along the path equals targetSum.
-
A leaf is a node with no children.
-
-
Example 1:
-
-
-```
-Input: root = [5,4,8,11,null,13,4,7,2,null,null,null,1], targetSum = 22
-Output: true
-Explanation: The root-to-leaf path with the target sum is shown.
-```
-
-
Example 2:
-
-
-```
-Input: root = [1,2,3], targetSum = 5
-Output: false
-Explanation: There two root-to-leaf paths in the tree:
-(1 --> 2): The sum is 3.
-(1 --> 3): The sum is 4.
-There is no root-to-leaf path with sum = 5.
-```
-
-
Example 3:
-
-```
-Input: root = [], targetSum = 0
-Output: false
-Explanation: Since the tree is empty, there are no root-to-leaf paths.
-```
-
-
-
Constraints:
-
-
The number of nodes in the tree is in the range [0, 5000].
Follow up: Could you optimize your algorithm to use only O(rowIndex) extra space?
-
-## Solution:
-
-::: code-group
-
-```rs [Rust]
-impl Solution {
- pub fn get_row(row_index: i32) -> Vec {
- // create a vector of 1s with length row_index + 1
- let mut row = vec![1; (row_index + 1) as usize];
-
- // loop through the vector, starting at 1
- for i in 1..row_index {
- // loop through the vector, starting at i + 1 and going backwards
- for j in (1..=i).rev() {
- // add the value at the current index to the value at the previous index
- row[j as usize] += row[(j - 1) as usize];
- }
- }
-
- row
- }
-}
-
-```
-
-:::
-
-### [_..._](#)
-
-```
-
-```
-
-
-
-[share]: https://graph.org/file/3ea5234dda646b71c574a.png
-[easy]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Easy-bright.svg
-[medium]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Medium-yellow.svg
-[hard]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Hard-red.svg
diff --git a/docs/solution/0101-0200/121 - Best Time to Buy and Sell Stock.md b/docs/solution/0101-0200/121 - Best Time to Buy and Sell Stock.md
deleted file mode 100644
index bf6eb67f..00000000
--- a/docs/solution/0101-0200/121 - Best Time to Buy and Sell Stock.md
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,96 +0,0 @@
-# 121. Best Time to Buy and Sell Stock [![share]](https://leetcode.com/problems/best-time-to-buy-and-sell-stock/)
-
-![][easy]
-
-## Problem Statement
-
-
You are given an array prices where prices[i] is the price of a given stock on the ith day.
-
You want to maximize your profit by choosing a single day to buy one stock and choosing a different day in the future to sell that stock.
-
Return the maximum profit you can achieve from this transaction. If you cannot achieve any profit, return 0.
-
-
Example 1:
-
-```
-Input: prices = [7,1,5,3,6,4]
-Output: 5
-Explanation: Buy on day 2 (price = 1) and sell on day 5 (price = 6), profit = 6-1 = 5.
-Note that buying on day 2 and selling on day 1 is not allowed because you must buy before you sell.
-```
-
-
Example 2:
-
-```
-Input: prices = [7,6,4,3,1]
-Output: 0
-Explanation: In this case, no transactions are done and the max profit = 0.
-```
-
-
-
Constraints:
-
-
1 <= prices.length <= 105
-
0 <= prices[i] <= 104
-
-
-## Solution:
-
-::: code-group
-
-```rs [Rust]
-impl Solution {
- pub fn max_profit(prices: Vec) -> i32 {
- let (mut profit, mut min) = (0, prices[0]);
-
- // loop through the vector, starting at 1
- for i in 1..prices.len() {
- // if the current value is less than the minimum value, set the minimum value to the current value
- if prices[i] < min {
- min = prices[i];
- }
- // else if the current value minus the minimum value is greater than the current profit, set the profit to the current value minus the minimum value
- else if prices[i] - min > profit {
- profit = prices[i] - min;
- }
- }
-
- profit
- }
-}
-
-```
-
-```go [Go]
-package main
-
-func maxProfit(prices []int) int {
- profit, min := 0, prices[0]
-
- for _, price := range prices {
- // if the current price is lower than the min price, update the min price to the current price
- // else if the current price minus the min price is greater than the profit, update the profit to the current price minus the min price
- if price < min {
- min = price
- } else if price-min > profit {
- profit = price - min
- }
- }
-
- return profit
-}
-
-```
-
-:::
-
-### [_..._](#)
-
-```
-
-```
-
-
-
-[share]: https://graph.org/file/3ea5234dda646b71c574a.png
-[easy]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Easy-bright.svg
-[medium]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Medium-yellow.svg
-[hard]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Hard-red.svg
diff --git a/docs/solution/0101-0200/122 - Best Time to Buy and Sell Stock II.md b/docs/solution/0101-0200/122 - Best Time to Buy and Sell Stock II.md
deleted file mode 100644
index 4bfece2a..00000000
--- a/docs/solution/0101-0200/122 - Best Time to Buy and Sell Stock II.md
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,73 +0,0 @@
-# 122. Best Time to Buy and Sell Stock II [![][share]](https://leetcode.com/problems/best-time-to-buy-and-sell-stock-ii)
-
-![][medium]
-
-## Problem Statement:
-
-You are given an integer array `prices` where `prices[i]` is the price of a given stock on the ith day.
-
-On each day, you may decide to buy and/or sell the stock. You can only hold **at most one** share of the stock at any time. However, you can buy it then immediately sell it on the **same day**.
-
-Find and return the **maximum** profit you can achieve.
-
-### Example 1:
-
-```
-Input: prices = [7,1,5,3,6,4]
-Output: 7
-Explanation: Buy on day 2 (price = 1) and sell on day 3 (price = 5), profit = 5-1 = 4.
-Then buy on day 4 (price = 3) and sell on day 5 (price = 6), profit = 6-3 = 3.
-Total profit is 4 + 3 = 7.
-```
-
-### Example 2:
-
-```
-Input: prices = [1,2,3,4,5]
-Output: 4
-Explanation: Buy on day 1 (price = 1) and sell on day 5 (price = 5), profit = 5-1 = 4.
-Total profit is 4.
-```
-
-### Example 3:
-
-```
-Input: prices = [7,6,4,3,1]
-Output: 0
-Explanation: There is no way to make a positive profit, so we never buy the stock to achieve the maximum profit of 0.
-```
-
-### Constraints:
-
-- 1 <= prices.length <= 3 \* 104
-- 0 <= prices[i] <= 104
-
-## Solution:
-
-::: code-group
-
-```java
-public int maxProfit(int[] prices) {
- int n = prices.length,
- profit = 0;
- for (int i = 1; i < n; i++)
- if (prices[i] > prices[i - 1])
- profit += (prices[i] - prices[i - 1]);
- return profit;
-}
-```
-
-:::
-
-### [_..._](#)
-
-```
-
-```
-
-
-
-[share]: https://img.icons8.com/external-anggara-blue-anggara-putra/20/000000/external-share-user-interface-basic-anggara-blue-anggara-putra-2.png
-[easy]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Easy-bright.svg
-[medium]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Medium-yellow.svg
-[hard]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Hard-red.svg
diff --git a/docs/solution/0101-0200/125 - Valid Palindrome.md b/docs/solution/0101-0200/125 - Valid Palindrome.md
deleted file mode 100644
index 5f55fe53..00000000
--- a/docs/solution/0101-0200/125 - Valid Palindrome.md
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,92 +0,0 @@
-# 125. Valid Palindrome [![share]](https://leetcode.com/problems/valid-palindrome/)
-
-![][easy]
-
-## Problem Statement
-
-
A phrase is a palindrome if, after converting all uppercase letters into lowercase letters and removing all non-alphanumeric characters, it reads the same forward and backward. Alphanumeric characters include letters and numbers.
-
Given a string s, return true if it is a palindrome, or false otherwise.
-
-
Example 1:
-
-```
-Input: s = "A man, a plan, a canal: Panama"
-Output: true
-Explanation: "amanaplanacanalpanama" is a palindrome.
-```
-
-
Example 2:
-
-```
-Input: s = "race a car"
-Output: false
-Explanation: "raceacar" is not a palindrome.
-```
-
-
Example 3:
-
-```
-Input: s = " "
-Output: true
-Explanation: s is an empty string "" after removing non-alphanumeric characters.
-Since an empty string reads the same forward and backward, it is a palindrome.
-```
-
-
-
Constraints:
-
-
1 <= s.length <= 2 * 105
-
s consists only of printable ASCII characters.
-
-
-## Solution:
-
-::: code-group
-
-```rs [Rust]
-impl Solution {
- pub fn is_palindrome(s: String) -> bool {
- let chars: Vec = s
- .chars()
- .filter_map(|c| {
- if c.is_alphanumeric() {
- Some(c.to_ascii_lowercase())
- } else {
- None
- }
- })
- .collect();
-
- if chars.len() == 0 {
- return true;
- }
-
- let (mut i, mut j) = (0, chars.len() - 1);
- while i < j {
- if chars[i] != chars[j] {
- return false;
- }
- i += 1;
- j -= 1;
- }
-
- true
- }
-}
-
-```
-
-:::
-
-### [_..._](#)
-
-```
-
-```
-
-
-
-[share]: https://graph.org/file/3ea5234dda646b71c574a.png
-[easy]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Easy-bright.svg
-[medium]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Medium-yellow.svg
-[hard]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Hard-red.svg
diff --git a/docs/solution/0101-0200/129 - Sum Root to Leaf Numbers.md b/docs/solution/0101-0200/129 - Sum Root to Leaf Numbers.md
deleted file mode 100644
index 289fd902..00000000
--- a/docs/solution/0101-0200/129 - Sum Root to Leaf Numbers.md
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,94 +0,0 @@
-# 129. Sum Root to Leaf Numbers [![share]](https://leetcode.com/problems/sum-root-to-leaf-numbers/)
-
-![][medium]
-
-## Problem Statement
-
-
You are given the root of a binary tree containing digits from 0 to 9 only.
-
Each root-to-leaf path in the tree represents a number.
-
-
For example, the root-to-leaf path 1 -> 2 -> 3 represents the number 123.
-
-
Return the total sum of all root-to-leaf numbers. Test cases are generated so that the answer will fit in a 32-bit integer.
-
A leaf node is a node with no children.
-
-
Example 1:
-
-
-```
-Input: root = [1,2,3]
-Output: 25
-Explanation:
-The root-to-leaf path 1->2 represents the number 12.
-The root-to-leaf path 1->3 represents the number 13.
-Therefore, sum = 12 + 13 = 25.
-```
-
-
Example 2:
-
-
-```
-Input: root = [4,9,0,5,1]
-Output: 1026
-Explanation:
-The root-to-leaf path 4->9->5 represents the number 495.
-The root-to-leaf path 4->9->1 represents the number 491.
-The root-to-leaf path 4->0 represents the number 40.
-Therefore, sum = 495 + 491 + 40 = 1026.
-```
-
-
-
Constraints:
-
-
The number of nodes in the tree is in the range [1, 1000].
-
0 <= Node.val <= 9
-
The depth of the tree will not exceed 10.
-
-
-## Solution:
-
-::: code-group
-
-```go [Go]
-package main
-
-// Definition for a binary tree node.
-type TreeNode struct {
- Val int
- Left *TreeNode
- Right *TreeNode
-}
-
-func sumNumbers(root *TreeNode) int {
- return dfs(root, 0)
-}
-
-func dfs(root *TreeNode, num int) int {
- if root == nil {
- return 0
- }
-
- num = num*10 + root.Val
- if root.Left == nil && root.Right == nil {
- return num
- }
-
- return dfs(root.Left, num) + dfs(root.Right, num)
-}
-
-```
-
-:::
-
-### [_..._](#)
-
-```
-
-```
-
-
-
-[share]: https://graph.org/file/3ea5234dda646b71c574a.png
-[easy]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Easy-bright.svg
-[medium]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Medium-yellow.svg
-[hard]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Hard-red.svg
diff --git a/docs/solution/0101-0200/136 - Single Number.md b/docs/solution/0101-0200/136 - Single Number.md
deleted file mode 100644
index 73c5302b..00000000
--- a/docs/solution/0101-0200/136 - Single Number.md
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,74 +0,0 @@
-# 136. Single Number [![share]](https://leetcode.com/problems/single-number/)
-
-![][easy]
-
-## Problem Statement
-
-
Given a non-empty array of integers nums, every element appears twice except for one. Find that single one.
-
You must implement a solution with a linear runtime complexity and use only constant extra space.
Each element in the array appears twice except for one element which appears only once.
-
-
-## Solution:
-
-::: code-group
-
-```rs [Rust]
-impl Solution {
- pub fn single_number(nums: Vec) -> i32 {
- let mut res = 0;
- for num in nums {
- // a ^ a = 0
- // a ^ a ^ a = a
- // a ^ a ^ b = b
- // also position of a and b doesn't matter
- res ^= num;
- }
-
- res
- }
-}
-
-```
-
-:::
-
-### [_..._](#)
-
-```
-
-```
-
-
-
-[share]: https://graph.org/file/3ea5234dda646b71c574a.png
-[easy]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Easy-bright.svg
-[medium]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Medium-yellow.svg
-[hard]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Hard-red.svg
diff --git a/docs/solution/0101-0200/141 - Linked List Cycle.md b/docs/solution/0101-0200/141 - Linked List Cycle.md
deleted file mode 100644
index 8b0eb0c6..00000000
--- a/docs/solution/0101-0200/141 - Linked List Cycle.md
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,94 +0,0 @@
-# 141. Linked List Cycle [![share]](https://leetcode.com/problems/linked-list-cycle/)
-
-![][easy]
-
-## Problem Statement
-
-
Given head, the head of a linked list, determine if the linked list has a cycle in it.
-
There is a cycle in a linked list if there is some node in the list that can be reached again by continuously following the next pointer. Internally, pos is used to denote the index of the node that tail's next pointer is connected to. Note that pos is not passed as a parameter.
-
Return true if there is a cycle in the linked list. Otherwise, return false.
-
-
Example 1:
-
-
-```
-Input: head = [3,2,0,-4], pos = 1
-Output: true
-Explanation: There is a cycle in the linked list, where the tail connects to the 1st node (0-indexed).
-```
-
-
Example 2:
-
-
-```
-Input: head = [1,2], pos = 0
-Output: true
-Explanation: There is a cycle in the linked list, where the tail connects to the 0th node.
-```
-
-
Example 3:
-
-
-```
-Input: head = [1], pos = -1
-Output: false
-Explanation: There is no cycle in the linked list.
-```
-
-
-
Constraints:
-
-
The number of the nodes in the list is in the range [0, 104].
-
-105 <= Node.val <= 105
-
pos is -1 or a valid index in the linked-list.
-
-
-
Follow up: Can you solve it using O(1) (i.e. constant) memory?
-
-## Solution:
-
-::: code-group
-
-```go [Go]
-package main
-
-// Definition for singly-linked list.
-type ListNode struct {
- Val int
- Next *ListNode
-}
-
-func hasCycle(head *ListNode) bool {
- if head == nil {
- return false
- }
-
- slow, fast := head, head
-
- for fast != nil && fast.Next != nil {
- slow = slow.Next
- fast = fast.Next.Next
-
- if slow == fast {
- return true
- }
- }
- return false
-}
-
-```
-
-:::
-
-### [_..._](#)
-
-```
-
-```
-
-
-
-[share]: https://graph.org/file/3ea5234dda646b71c574a.png
-[easy]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Easy-bright.svg
-[medium]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Medium-yellow.svg
-[hard]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Hard-red.svg
diff --git a/docs/solution/0101-0200/142 - Linked List Cycle II.md b/docs/solution/0101-0200/142 - Linked List Cycle II.md
deleted file mode 100644
index 7a58977b..00000000
--- a/docs/solution/0101-0200/142 - Linked List Cycle II.md
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,97 +0,0 @@
-# 142. Linked List Cycle II [![share]](https://leetcode.com/problems/linked-list-cycle-ii/)
-
-![][medium]
-
-## Problem Statement
-
-
Given the head of a linked list, return the node where the cycle begins. If there is no cycle, return null.
-
There is a cycle in a linked list if there is some node in the list that can be reached again by continuously following the next pointer. Internally, pos is used to denote the index of the node that tail's next pointer is connected to (0-indexed). It is -1 if there is no cycle. Note thatposis not passed as a parameter.
-
Do not modify the linked list.
-
-
Example 1:
-
-
-```
-Input: head = [3,2,0,-4], pos = 1
-Output: tail connects to node index 1
-Explanation: There is a cycle in the linked list, where tail connects to the second node.
-```
-
-
Example 2:
-
-
-```
-Input: head = [1,2], pos = 0
-Output: tail connects to node index 0
-Explanation: There is a cycle in the linked list, where tail connects to the first node.
-```
-
-
Example 3:
-
-
-```
-Input: head = [1], pos = -1
-Output: no cycle
-Explanation: There is no cycle in the linked list.
-```
-
-
-
Constraints:
-
-
The number of the nodes in the list is in the range [0, 104].
-
-105 <= Node.val <= 105
-
pos is -1 or a valid index in the linked-list.
-
-
-
Follow up: Can you solve it using O(1) (i.e. constant) memory?
-
-## Solution:
-
-::: code-group
-
-```go [Go]
-package main
-
-// Definition for Singly-Linked List
-type ListNode struct {
- Val int
- Next *ListNode
-}
-
-func detectCycle(head *ListNode) *ListNode {
- slow, fast := head, head
-
- for fast != nil && fast.Next != nil {
- slow = slow.Next
- fast = fast.Next.Next
-
- if slow == fast {
- slow = head
- for slow != fast {
- slow = slow.Next
- fast = fast.Next
- }
-
- return slow
- }
- }
-
- return nil
-}
-
-```
-
-:::
-
-### [_..._](#)
-
-```
-
-```
-
-
-
-[share]: https://graph.org/file/3ea5234dda646b71c574a.png
-[easy]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Easy-bright.svg
-[medium]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Medium-yellow.svg
-[hard]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Hard-red.svg
diff --git a/docs/solution/0101-0200/144 - Binary Tree Preorder Traversal.md b/docs/solution/0101-0200/144 - Binary Tree Preorder Traversal.md
deleted file mode 100644
index 5d398e54..00000000
--- a/docs/solution/0101-0200/144 - Binary Tree Preorder Traversal.md
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,87 +0,0 @@
-# 144. Binary Tree Preorder Traversal [![share]](https://leetcode.com/problems/binary-tree-preorder-traversal/submissions)
-
-![][easy]
-
-## Problem Statement:
-
-Given the `root` of a binary tree, return the preorder traversal of its nodes' values.
-
-
-
-### Example 1:
-
-```
-Input: root = [1,null,2,3]
-Output: [1,2,3]
-```
-
-### Example 2:
-
-```
-Input: root = []
-Output: []
-```
-
-### Example 3:
-
-```
-Input: root = [1]
-Output: [1]
-```
-
-### Constraints:
-
-The number of nodes in the tree is in the range [0, 100].
--100 <= Node.val <= 100
-
-Follow up: Recursive solution is trivial, could you do it iteratively?
-
-## Solution:
-
-::: code-group
-
-```java
-List list = new ArrayList();
-
-// Iterative Approach
-public List preorderTraversal(TreeNode root) {
- if (root == null)
- return list;
- Stack stack = new Stack<>();
- stack.push(root);
- while (!stack.isEmpty()) {
- TreeNode current = stack.pop();
- list.add(current.val);
- if (current.right != null)
- stack.push(current.right);
- if (current.left != null)
- stack.push(current.left);
- }
- return list;
-}
-
-// Recursive Approach
-public List preorderTraversalRecursive(TreeNode root) {
- if (root != null) {
- list.add(root.val);
- preorderTraversalRecursive(root.left);
- preorderTraversalRecursive(root.right);
- }
- return list;
-}
-```
-
-:::
-
-### [_..._](#)
-
-```
-
-```
-
-
-
-[share]: https://img.icons8.com/external-anggara-blue-anggara-putra/20/000000/external-share-user-interface-basic-anggara-blue-anggara-putra-2.png
-[easy]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Easy-bright.svg
-[medium]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Medium-yellow.svg
-[hard]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Hard-red.svg
diff --git a/docs/solution/0101-0200/145 - Binary Tree Postorder Traversal.md b/docs/solution/0101-0200/145 - Binary Tree Postorder Traversal.md
deleted file mode 100644
index 10a5d177..00000000
--- a/docs/solution/0101-0200/145 - Binary Tree Postorder Traversal.md
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,83 +0,0 @@
-# 145. Binary Tree Postorder Traversal [![share]](https://leetcode.com/problems/binary-tree-postorder-traversal)
-
-![easy]
-
-## Problem Statement:
-
-Given the `root` of a binary tree, return the postorder traversal of its nodes' values.
-
-### Example 1:
-
-
-
-Input: root = [1,null,2,3]
-Output: [3,2,1]
-
-### Example 2:
-
-```
-Input: root = []
-Output: []
-```
-
-### Example 3:
-
-```
-Input: root = [1]
-Output: [1]
-```
-
-### Constraints:
-
-- The number of the nodes in the tree is in the range [0, 100].
-- -100 <= Node.val <= 100
-
-**Follow up:** Recursive solution is trivial, could you do it iteratively?
-
-## Solution:
-
-::: code-group
-
-```java
-private LinkedList list = new LinkedList<>();
-
-public List postorderTraversal(TreeNode root) {
- if (root == null)
- return list;
- Stack stack = new Stack<>();
- stack.push(root);
- while (!stack.isEmpty()) {
- TreeNode current = stack.pop();
- list.addFirst(current.val);
- if (current.left != null)
- stack.push(current.left);
- if (current.right != null)
- stack.push(current.right);
- }
- return list;
-}
-
-public List postorderTraversalRecursive(TreeNode root) {
- if (root == null)
- return list;
- postorderTraversalRecursive(root.left);
- postorderTraversalRecursive(root.right);
- list.add(root.val);
- return list;
- }
-```
-
-:::
-
-### [_..._](#)
-
-```
-
-```
-
-
-
-[share]: https://img.icons8.com/external-anggara-blue-anggara-putra/20/000000/external-share-user-interface-basic-anggara-blue-anggara-putra-2.png
-[easy]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Easy-bright.svg
-[medium]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Medium-yellow.svg
-[hard]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Hard-red.svg
diff --git a/docs/solution/0101-0200/160 - Intersection of Two Linked Lists.md b/docs/solution/0101-0200/160 - Intersection of Two Linked Lists.md
deleted file mode 100644
index 1e7ef7fc..00000000
--- a/docs/solution/0101-0200/160 - Intersection of Two Linked Lists.md
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,122 +0,0 @@
-# 160. Intersection of Two Linked Lists [![share]](https://leetcode.com/problems/intersection-of-two-linked-lists/)
-
-![][easy]
-
-## Problem Statement
-
-
Given the heads of two singly linked-lists headA and headB, return the node at which the two lists intersect. If the two linked lists have no intersection at all, return null.
-
For example, the following two linked lists begin to intersect at node c1:
-
-
The test cases are generated such that there are no cycles anywhere in the entire linked structure.
-
Note that the linked lists must retain their original structure after the function returns.
-
Custom Judge:
-
The inputs to the judge are given as follows (your program is not given these inputs):
-
-
intersectVal - The value of the node where the intersection occurs. This is 0 if there is no intersected node.
-
listA - The first linked list.
-
listB - The second linked list.
-
skipA - The number of nodes to skip ahead in listA (starting from the head) to get to the intersected node.
-
skipB - The number of nodes to skip ahead in listB (starting from the head) to get to the intersected node.
-
-
The judge will then create the linked structure based on these inputs and pass the two heads, headA and headB to your program. If you correctly return the intersected node, then your solution will be accepted.
-
-
Example 1:
-
-
-```
-Input: intersectVal = 8, listA = [4,1,8,4,5], listB = [5,6,1,8,4,5], skipA = 2, skipB = 3
-Output: Intersected at '8'
-Explanation: The intersected node's value is 8 (note that this must not be 0 if the two lists intersect).
-From the head of A, it reads as [4,1,8,4,5]. From the head of B, it reads as [5,6,1,8,4,5]. There are 2 nodes before the intersected node in A; There are 3 nodes before the intersected node in B.
-- Note that the intersected node's value is not 1 because the nodes with value 1 in A and B (2nd node in A and 3rd node in B) are different node references. In other words, they point to two different locations in memory, while the nodes with value 8 in A and B (3rd node in A and 4th node in B) point to the same location in memory.
-```
-
-
Example 2:
-
-
-```
-Input: intersectVal = 2, listA = [1,9,1,2,4], listB = [3,2,4], skipA = 3, skipB = 1
-Output: Intersected at '2'
-Explanation: The intersected node's value is 2 (note that this must not be 0 if the two lists intersect).
-From the head of A, it reads as [1,9,1,2,4]. From the head of B, it reads as [3,2,4]. There are 3 nodes before the intersected node in A; There are 1 node before the intersected node in B.
-```
-
-
Example 3:
-
-
-```
-Input: intersectVal = 0, listA = [2,6,4], listB = [1,5], skipA = 3, skipB = 2
-Output: No intersection
-Explanation: From the head of A, it reads as [2,6,4]. From the head of B, it reads as [1,5]. Since the two lists do not intersect, intersectVal must be 0, while skipA and skipB can be arbitrary values.
-Explanation: The two lists do not intersect, so return null.
-```
-
-
-
Constraints:
-
-
The number of nodes of listA is in the m.
-
The number of nodes of listB is in the n.
-
1 <= m, n <= 3 * 104
-
1 <= Node.val <= 105
-
0 <= skipA < m
-
0 <= skipB < n
-
intersectVal is 0 if listA and listB do not intersect.
-
intersectVal == listA[skipA] == listB[skipB] if listA and listB intersect.
-
-
-Follow up: Could you write a solution that runs in O(m + n) time and use only O(1) memory?
-
-## Solution:
-
-::: code-group
-
-```go [Go]
-package main
-
-// Definition for singly-linked list.
-type ListNode struct {
- Val int
- Next *ListNode
-}
-
-// https://leetcode.com/problems/intersection-of-two-linked-lists/solutions/49785/java-solution-without-knowing-the-difference-in-len/
-func getIntersectionNode(headA, headB *ListNode) *ListNode {
- if headA == nil || headB == nil {
- return nil
- }
-
- a, b := headA, headB
-
- for a != b {
- if a == nil {
- a = headB
- } else {
- a = a.Next
- }
-
- if b == nil {
- b = headA
- } else {
- b = b.Next
- }
- }
-
- return a
-}
-
-```
-
-:::
-
-### [_..._](#)
-
-```
-
-```
-
-
-
-[share]: https://graph.org/file/3ea5234dda646b71c574a.png
-[easy]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Easy-bright.svg
-[medium]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Medium-yellow.svg
-[hard]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Hard-red.svg
diff --git a/docs/solution/0101-0200/169 - Majority Element.md b/docs/solution/0101-0200/169 - Majority Element.md
deleted file mode 100644
index a6c249ba..00000000
--- a/docs/solution/0101-0200/169 - Majority Element.md
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,74 +0,0 @@
-# 169. Majority Element [![share]](https://leetcode.com/problems/majority-element/)
-
-![][easy]
-
-## Problem Statement
-
-
Given an array nums of size n, return the majority element.
-
The majority element is the element that appears more than ⌊n / 2⌋ times. You may assume that the majority element always exists in the array.
-Follow-up: Could you solve the problem in linear time and in O(1) space?
-
-## Solution:
-
-::: code-group
-
-```rs [Rust]
-impl Solution {
- pub fn majority_element(nums: Vec) -> i32 {
- let (mut element, mut count) = (nums[0], 0);
-
- for num in nums {
- if count == 0 {
- element = num;
- }
-
- if element == num {
- count += 1;
- } else {
- count -= 1;
- }
- }
-
- element
- }
-}
-
-```
-
-:::
-
-### [_..._](#)
-
-```
-
-```
-
-
-
-[share]: https://graph.org/file/3ea5234dda646b71c574a.png
-[easy]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Easy-bright.svg
-[medium]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Medium-yellow.svg
-[hard]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Hard-red.svg
diff --git a/docs/solution/0101-0200/172 - Factorial Trailing Zeroes.md b/docs/solution/0101-0200/172 - Factorial Trailing Zeroes.md
deleted file mode 100644
index 0663a171..00000000
--- a/docs/solution/0101-0200/172 - Factorial Trailing Zeroes.md
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,68 +0,0 @@
-# 172. Factorial Trailing Zeroes [![share]](https://leetcode.com/problems/factorial-trailing-zeroes)
-
-![][medium]
-
-## Problem Statement:
-
-Given an integer `n`, return the number of trailing zeroes in `n!`.
-
-Note that `n! = n * (n - 1) * (n - 2) * ... * 3 * 2 * 1`.
-
-### Example 1:
-
-```
-Input: n = 3
-Output: 0
-Explanation: 3! = 6, no trailing zero.
-```
-
-### Example 2:
-
-```
-Input: n = 5
-Output: 1
-Explanation: 5! = 120, one trailing zero.
-```
-
-### Example 3:
-
-```
-Input: n = 0
-Output: 0
-```
-
-### Constraints:
-
-- 0 <= n <= 104
-
-**Follow up:** Could you write a solution that works in logarithmic time complexity?
-
-## Solution:
-
-::: code-group
-
-```java
-public int trailingZeroes(int n) {
- int count = 0;
- while (n > 0) {
- n /= 5;
- count += n;
- }
- return count;
-}
-```
-
-:::
-
-### [_..._](#)
-
-```
-
-```
-
-
-
-[share]: https://img.icons8.com/external-anggara-blue-anggara-putra/20/000000/external-share-user-interface-basic-anggara-blue-anggara-putra-2.png
-[easy]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Easy-bright.svg
-[medium]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Medium-yellow.svg
-[hard]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Hard-red.svg
diff --git a/docs/solution/0101-0200/190 - Reverse Bits.md b/docs/solution/0101-0200/190 - Reverse Bits.md
deleted file mode 100644
index e4cff47e..00000000
--- a/docs/solution/0101-0200/190 - Reverse Bits.md
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,78 +0,0 @@
-# 190. Reverse Bits [![share]](https://leetcode.com/problems/reverse-bits/)
-
-![][easy]
-
-## Problem Statement
-
-
Reverse bits of a given 32 bits unsigned integer.
-
Note:
-
-
Note that in some languages, such as Java, there is no unsigned integer type. In this case, both input and output will be given as a signed integer type. They should not affect your implementation, as the integer's internal binary representation is the same, whether it is signed or unsigned.
-
In Java, the compiler represents the signed integers using 2's complement notation. Therefore, in Example 2 above, the input represents the signed integer -3 and the output represents the signed integer -1073741825.
-
-
-
Example 1:
-
-```
-Input: n = 00000010100101000001111010011100
-Output: 964176192 (00111001011110000010100101000000)
-Explanation: The input binary string 00000010100101000001111010011100 represents the unsigned integer 43261596, so return 964176192 which its binary representation is 00111001011110000010100101000000.
-```
-
-
Example 2:
-
-```
-Input: n = 11111111111111111111111111111101
-Output: 3221225471 (10111111111111111111111111111111)
-Explanation: The input binary string 11111111111111111111111111111101 represents the unsigned integer 4294967293, so return 3221225471 which its binary representation is 10111111111111111111111111111111.
-```
-
-
-
Constraints:
-
-
The input must be a binary string of length 32
-
-
-
Follow up: If this function is called many times, how would you optimize it?
-
-## Solution:
-
-::: code-group
-
-```rs [Rust]
-impl Solution {
- pub fn reverse_bits(x: u32) -> u32 {
- let (mut x, mut res) = (x, 0);
-
- // iterate 32 times, once for each bit
- for _ in 0..32 {
- // left-shift res by 1 bit to make room for the next bit
- res <<= 1;
- // adding the least significant bit of x to the result
- // using bitwise AND with 1
- res += x & 1;
- // right-shift x by 1 bit, discarding the least significant bit
- // that was just added to the result
- x >>= 1;
- }
-
- res
- }
-}
-
-```
-
-:::
-
-### [_..._](#)
-
-```
-
-```
-
-
-
-[share]: https://graph.org/file/3ea5234dda646b71c574a.png
-[easy]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Easy-bright.svg
-[medium]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Medium-yellow.svg
-[hard]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Hard-red.svg
diff --git a/docs/solution/0101-0200/191 - Number of 1 Bits.md b/docs/solution/0101-0200/191 - Number of 1 Bits.md
deleted file mode 100644
index 9caa1840..00000000
--- a/docs/solution/0101-0200/191 - Number of 1 Bits.md
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,74 +0,0 @@
-# 191. Number of 1 Bits [![share]](https://leetcode.com/problems/number-of-1-bits/)
-
-![][easy]
-
-## Problem Statement:
-
-Write a function that takes an unsigned integer and returns the number of '1' bits it has (also known as the `Hamming weight`).
-
-Note:
-
-- Note that in some languages, such as Java, there is no unsigned integer type. In this case, the input will be given as a signed integer type. It should not affect your implementation, as the integer's internal binary representation is the same, whether it is signed or unsigned.
-- In Java, the compiler represents the signed integers using `2's complement notation`. Therefore, in **Example 3**, the input represents the signed integer. `-3`.
-
-### Example 1:
-
-```
-Input: n = 00000000000000000000000000001011
-Output: 3
-Explanation: The input binary string 00000000000000000000000000001011 has a total of three '1' bits.
-```
-
-### Example 2:
-
-```
-Input: n = 00000000000000000000000010000000
-Output: 1
-Explanation: The input binary string 00000000000000000000000010000000 has a total of one '1' bit.
-```
-
-### Example 3:
-
-```
-Input: n = 11111111111111111111111111111101
-Output: 31
-Explanation: The input binary string 11111111111111111111111111111101 has a total of thirty one '1' bits.
-```
-
-### Constraints:
-
-- The input must be a **binary string** of length `32`.
-
-**Follow up:** If this function is called many times, how would you optimize it?
-
-## Solution:
-
-::: code-group
-
-```java
-public int hammingWeight(int n) {
- int count = 0,
- mask = 1;
- for (int i = 0; i < 32; i++) {
- if ((n & mask) != 0)
- count++;
- mask <<= 1;
- }
- return count;
-}
-```
-
-:::
-
-### [_..._](#)
-
-```
-
-```
-
-
-
-[share]: https://img.icons8.com/external-anggara-blue-anggara-putra/20/000000/external-share-user-interface-basic-anggara-blue-anggara-putra-2.png
-[easy]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Easy-bright.svg
-[medium]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Medium-yellow.svg
-[hard]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Hard-red.svg
diff --git a/docs/solution/0101-0200/193 - Valid Phone Numbers.md b/docs/solution/0101-0200/193 - Valid Phone Numbers.md
deleted file mode 100644
index d9f36815..00000000
--- a/docs/solution/0101-0200/193 - Valid Phone Numbers.md
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,53 +0,0 @@
-# 193. Valid Phone Numbers [![share]](https://leetcode.com/problems/valid-phone-numbers/)
-
-![][easy]
-
-## Problem Statement
-
-
Given a text file file.txt that contains a list of phone numbers (one per line), write a one-liner bash script to print all valid phone numbers.
-
-
You may assume that a valid phone number must appear in one of the following two formats: (xxx) xxx-xxxx or xxx-xxx-xxxx. (x means a digit)
-
-
You may also assume each line in the text file must not contain leading or trailing white spaces.
-
-
Example:
-
-
Assume that file.txt has the following content:
-
-
-987-123-4567
-123 456 7890
-(123) 456-7890
-
-
-
Your script should output the following valid phone numbers:
Your script should output the tenth line, which is:
-
-
-Line 10
-
-
-
Note:
-1. If the file contains less than 10 lines, what should you output?
-2. There's at least three different solutions. Try to explore all possibilities.
-
-## Solution:
-
-::: code-group
-
-```sh
-#!/usr/bin/env bash
-
-sed -n 10p file.txt
-```
-
-:::
-
-### [_..._](#)
-
-```
-
-```
-
-
-
-[share]: https://graph.org/file/3ea5234dda646b71c574a.png
-[easy]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Easy-bright.svg
-[medium]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Medium-yellow.svg
-[hard]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Hard-red.svg
diff --git a/docs/solution/0101-0200/199 - Binary Tree Right Side View.md b/docs/solution/0101-0200/199 - Binary Tree Right Side View.md
deleted file mode 100644
index 3514ba22..00000000
--- a/docs/solution/0101-0200/199 - Binary Tree Right Side View.md
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,75 +0,0 @@
-# 199. Binary Tree Right Side View [![share]](https://leetcode.com/problems/binary-tree-right-side-view/)
-
-![][medium]
-
-## Problem Statement:
-
-Given the `root` of a binary tree, imagine yourself standing on the **right side** of it, return the values of the nodes you can see ordered from top to bottom.
-
-### Example 1:
-
-
-
-```
-Input: root = [1,2,3,null,5,null,4]
-Output: [1,3,4]
-```
-
-### Example 2:
-
-```
-Input: root = [1,null,3]
-Output: [1,3]
-```
-
-### Example 3:
-
-```
-Input: root = []
-Output: []
-```
-
-### Constraints:
-
-- The number of nodes in the tree is in the range [0, 100].
-- -100 <= Node.val <= 100
-
-## Solution:
-
-::: code-group
-
-```java
-public class BinaryTreeRightSideView {
- int maxLevel = 0;
- List arr = new ArrayList();
-
- public List rightSideView(TreeNode root) {
- rightSideView(root, 1);
- return arr;
- }
-
- private void rightSideView(TreeNode root, int level) {
- if (root == null)
- return;
- if (maxLevel < level) {
- arr.add(root.val);
- maxLevel = level;
- }
- rightSideView(root.right, level + 1);
- rightSideView(root.left, level + 1);
- }
-}
-```
-
-:::
-
-### [_..._](#)
-
-```
-
-```
-
-
-
-[share]: https://img.icons8.com/external-anggara-blue-anggara-putra/20/000000/external-share-user-interface-basic-anggara-blue-anggara-putra-2.png
-[medium]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Medium-yellow.svg
diff --git a/docs/solution/0101-0200/200 - Number of Islands.md b/docs/solution/0101-0200/200 - Number of Islands.md
deleted file mode 100644
index 905d3a29..00000000
--- a/docs/solution/0101-0200/200 - Number of Islands.md
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,106 +0,0 @@
-# 200. Number of Islands [![share]](https://leetcode.com/problems/number-of-islands/)
-
-![][medium]
-
-## Problem Statement
-
-
Given an m x n 2D binary grid grid which represents a map of '1's (land) and '0's (water), return the number of islands.
-
An island is surrounded by water and is formed by connecting adjacent lands horizontally or vertically. You may assume all four edges of the grid are all surrounded by water.
-
-## Solution:
-
-::: code-group
-
-```rs [Rust]
-impl Solution {
- pub fn is_happy(n: i32) -> bool {
- let (mut slow, mut fast) = (n, n);
-
- loop {
- slow = Self::sum_of_squares(slow);
- fast = Self::sum_of_squares(Self::sum_of_squares(fast));
-
- if slow == 1 || fast == 1 {
- return true;
- }
-
- // Floyd's cycle detection
- if slow == fast {
- return false;
- }
- }
- }
-
- pub fn sum_of_squares(mut num: i32) -> i32 {
- let mut sum = 0;
-
- while num > 0 {
- let digit = num % 10;
- sum += digit * digit;
- num /= 10;
- }
-
- sum
- }
-}
-
-```
-
-:::
-
-### [_..._](#)
-
-```
-
-```
-
-
-
-[share]: https://graph.org/file/3ea5234dda646b71c574a.png
-[easy]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Easy-bright.svg
-[medium]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Medium-yellow.svg
-[hard]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Hard-red.svg
diff --git a/docs/solution/0201-0300/203 - Remove Linked List Elements.md b/docs/solution/0201-0300/203 - Remove Linked List Elements.md
deleted file mode 100644
index 6618088d..00000000
--- a/docs/solution/0201-0300/203 - Remove Linked List Elements.md
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,101 +0,0 @@
-# 203. Remove Linked List Elements [![share]](https://leetcode.com/problems/remove-linked-list-elements/)
-
-![][easy]
-
-## Problem Statement
-
-
Given the head of a linked list and an integer val, remove all the nodes of the linked list that has Node.val == val, and return the new head.
-
-
Example 1:
-
-
-```
-Input: head = [1,2,6,3,4,5,6], val = 6
-Output: [1,2,3,4,5]
-```
-
-
Example 2:
-
-```
-Input: head = [], val = 1
-Output: []
-```
-
-
Example 3:
-
-```
-Input: head = [7,7,7,7], val = 7
-Output: []
-```
-
-
-
Constraints:
-
-
The number of nodes in the list is in the range [0, 104].
-
1 <= Node.val <= 50
-
0 <= val <= 50
-
-
-## Solution:
-
-::: code-group
-
-```go [Go]
-package main
-
-// Definition for singly-linked list.
-type ListNode struct {
- Val int
- Next *ListNode
-}
-
-// Iterative
-func removeElements(head *ListNode, val int) *ListNode {
- if head == nil {
- return nil
- }
- for head != nil && head.Val == val {
- head = head.Next
- }
- if head == nil {
- return nil
- }
- for p := head; p.Next != nil; {
- if p.Next.Val == val {
- p.Next = p.Next.Next
- } else {
- p = p.Next
- }
- }
-
- return head
-}
-
-// Recursive
-func removeElementsRecursive(head *ListNode, val int) *ListNode {
- if head == nil {
- return nil
- }
- head.Next = removeElementsRecursive(head.Next, val)
- if head.Val == val {
- return head.Next
- }
- return head
-}
-
-```
-
-:::
-
-### [_..._](#)
-
-```
-
-```
-
-
-
-[share]: https://graph.org/file/3ea5234dda646b71c574a.png
-[easy]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Easy-bright.svg
-[medium]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Medium-yellow.svg
-[hard]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Hard-red.svg
diff --git a/docs/solution/0201-0300/205 - Isomorphic Strings.md b/docs/solution/0201-0300/205 - Isomorphic Strings.md
deleted file mode 100644
index 376d4ce5..00000000
--- a/docs/solution/0201-0300/205 - Isomorphic Strings.md
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,85 +0,0 @@
-# 205. Isomorphic Strings [![share]](https://leetcode.com/problems/isomorphic-strings/)
-
-![][easy]
-
-## Problem Statement
-
-
Given two strings s and t, determine if they are isomorphic.
-
Two strings s and t are isomorphic if the characters in s can be replaced to get t.
-
All occurrences of a character must be replaced with another character while preserving the order of characters. No two characters may map to the same character, but a character may map to itself.
-
-
Example 1:
-
-```
-Input: s = "egg", t = "add"
-Output: true
-```
-
-
Example 2:
-
-```
-Input: s = "foo", t = "bar"
-Output: false
-```
-
-
Example 3:
-
-```
-Input: s = "paper", t = "title"
-Output: true
-```
-
-
-
Constraints:
-
-
1 <= s.length <= 5 * 104
-
t.length == s.length
-
s and t consist of any valid ascii character.
-
-
-## Solution:
-
-::: code-group
-
-```go [Go]
-package main
-
-func isIsomorphic(s string, t string) bool {
- const max = 256
-
- var (
- sMap [max]int
- tMap [max]int
- )
-
- for i := 0; i < len(s); i++ {
- sIndex := s[i] - 'a'
- tIndex := t[i] - 'a'
-
- if sMap[sIndex] != tMap[tIndex] {
- return false
- }
-
- sMap[sIndex] = i + 1
- tMap[tIndex] = i + 1
- }
-
- return true
-}
-
-```
-
-:::
-
-### [_..._](#)
-
-```
-
-```
-
-
-
-[share]: https://graph.org/file/3ea5234dda646b71c574a.png
-[easy]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Easy-bright.svg
-[medium]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Medium-yellow.svg
-[hard]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Hard-red.svg
diff --git a/docs/solution/0201-0300/206 - Reverse Linked List.md b/docs/solution/0201-0300/206 - Reverse Linked List.md
deleted file mode 100644
index a1cae3b4..00000000
--- a/docs/solution/0201-0300/206 - Reverse Linked List.md
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,85 +0,0 @@
-# 206. Reverse Linked List [![][share]](https://leetcode.com/problems/reverse-linked-list)
-
-![][easy]
-
-## Problem Statement:
-
-Given the `head` of a singly linked list, reverse the list, and return the reversed list.
-
-### Example 1:
-
-
-
-```
-Input: head = [1,2,3,4,5]
-Output: [5,4,3,2,1]
-```
-
-### Example 2:
-
-
-
-```
-Input: head = [1,2]
-Output: [2,1]
-```
-
-### Example 3:
-
-```
-Input: head = []
-Output: []
-```
-
-### Constraints:
-
-- The number of nodes in the list is the range `[0, 5000]`.
-- `-5000 <= Node.val <= 5000`
-
-**Follow up:** A linked list can be reversed either iteratively or recursively. Could you implement both?
-
-## Solution:
-
-::: code-group
-
-```java
-public ListNode reverseList(ListNode head) {
- if (head == null || head.next == null)
- return head;
- ListNode newHead = reverseList(head.next);
- head.next.next = head;
- head.next = null;
- return newHead;
-}
-
-public ListNode reverseIterate(ListNode head) {
- if (head == null || head.next == null)
- return head;
- ListNode prevNode = head,
- currentNode = head.next;
- while (currentNode != null) {
- ListNode nextNode = currentNode.next;
- currentNode.next = prevNode;
- prevNode = currentNode;
- currentNode = nextNode;
- }
- head.next = null;
- head = prevNode;
- return prevNode;
-}
-```
-
-:::
-
-### [_..._](#)
-
-```
-
-```
-
-
-
-[share]: https://img.icons8.com/external-anggara-blue-anggara-putra/20/000000/external-share-user-interface-basic-anggara-blue-anggara-putra-2.png
-[easy]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Easy-bright.svg
-[medium]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Medium-yellow.svg
-[hard]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Hard-red.svg
diff --git a/docs/solution/0201-0300/211 - Design Add and Search Words Data Structure.md b/docs/solution/0201-0300/211 - Design Add and Search Words Data Structure.md
deleted file mode 100644
index c8d22ca7..00000000
--- a/docs/solution/0201-0300/211 - Design Add and Search Words Data Structure.md
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,124 +0,0 @@
-# 211. Design Add and Search Words Data Structure [![share]](https://leetcode.com/problems/design-add-and-search-words-data-structure/)
-
-![][medium]
-
-## Problem Statement
-
-
Design a data structure that supports adding new words and finding if a string matches any previously added string.
-
Implement the WordDictionary class:
-
-
WordDictionary() Initializes the object.
-
void addWord(word) Adds word to the data structure, it can be matched later.
-
bool search(word) Returns true if there is any string in the data structure that matches word or false otherwise. word may contain dots '.' where dots can be matched with any letter.
Given an integer array nums and an integer k, return trueif there are two distinct indicesi and j in the array such that nums[i] == nums[j] and abs(i - j) <= k.
-
-## Solution:
-
-::: code-group
-
-```go [Go]
-package main
-
-func containsNearbyDuplicate(nums []int, k int) bool {
- if len(nums) <= 1 {
- return false
- }
-
- set := make(map[int]int)
-
- // iterate over the array
- for i, v := range nums {
- // check if the value is in the set
- if _, ok := set[v]; ok {
- // if the value is in the set,
- // check if the difference between the current index and the index of the value in the set
- // is less than or equal to k
- if i-set[v] <= k {
- return true
- }
- }
- // add the value to the set
- set[v] = i
- }
-
- return false
-}
-
-```
-
-:::
-
-### [_..._](#)
-
-```
-
-```
-
-
-
-[share]: https://graph.org/file/3ea5234dda646b71c574a.png
-[easy]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Easy-bright.svg
-[medium]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Medium-yellow.svg
-[hard]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Hard-red.svg
diff --git a/docs/solution/0201-0300/222 - Count Complete Tree Nodes.md b/docs/solution/0201-0300/222 - Count Complete Tree Nodes.md
deleted file mode 100644
index 03c9675c..00000000
--- a/docs/solution/0201-0300/222 - Count Complete Tree Nodes.md
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,87 +0,0 @@
-# 222. Count Complete Tree Nodes [![share]](https://leetcode.com/problems/count-complete-tree-nodes/)
-
-![][medium]
-
-## Problem Statement:
-
-Given the `root` of a **complete** binary tree, return the number of the nodes in the tree.
-
-According to [Wikipedia][wikipedia], every level, except possibly the last, is completely filled in a complete binary tree, and all nodes in the last level are as far left as possible. It can have between `1` and 2h nodes inclusive at the last level `h`.
-
-Design an algorithm that runs in less than `O(n)` time complexity.
-
-### Example 1:
-
-```
-Input: root = [1,2,3,4,5,6]
-Output: 6
-```
-
-### Example 2:
-
-```
-Input: root = []
-Output: 0
-```
-
-### Example 3:
-
-```
-Input: root = [1]
-Output: 1
-```
-
-### Constraints:
-
-- The number of nodes in the tree is in the range [0, 5 * 104].
-- 0 <= Node.val <= 5 \* 104]
-- The tree is guaranteed to be **complete**.
-
-## Solution:
-
-::: code-group
-
-```java
-// Approach 1
-// Time Complexity -> O(n)
-public int countNodes(TreeNode root) {
- if (root == null)
- return 0;
- return countNodes(root.left) + countNodes(root.right) + 1;
-}
-```
-
-```java
-// Approach 2
-// Time Complexity -> O(logn * logn)
-public int countNodes2(TreeNode root) {
- int leftHeight = 0, rightHeight = 0;
- TreeNode currentNode = root;
- while (currentNode != null) {
- leftHeight++;
- currentNode = currentNode.left;
- }
- currentNode = root;
- while (currentNode != null) {
- rightHeight++;
- currentNode = currentNode.right;
- }
- if (leftHeight == rightHeight)
- return (int) Math.pow(2, leftHeight) - 1;
- return countNodes2(root.left) + countNodes2(root.right) + 1;
-}
-```
-
-:::
-
-### [_..._](#)
-
-```
-
-```
-
-
-
-[share]: https://img.icons8.com/external-anggara-blue-anggara-putra/20/000000/external-share-user-interface-basic-anggara-blue-anggara-putra-2.png
-[medium]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Medium-yellow.svg
-[wikipedia]: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Binary_tree#Types_of_binary_trees
diff --git a/docs/solution/0201-0300/225 - Implement Stack using Queues.md b/docs/solution/0201-0300/225 - Implement Stack using Queues.md
deleted file mode 100644
index 57b8a29c..00000000
--- a/docs/solution/0201-0300/225 - Implement Stack using Queues.md
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,107 +0,0 @@
-# 225. Implement Stack using Queues [![share]](https://leetcode.com/problems/implement-stack-using-queues/)
-
-![][easy]
-
-## Problem Statement
-
-
Implement a last-in-first-out (LIFO) stack using only two queues. The implemented stack should support all the functions of a normal stack (push, top, pop, and empty).
-
Implement the MyStack class:
-
-
void push(int x) Pushes element x to the top of the stack.
-
int pop() Removes the element on the top of the stack and returns it.
-
int top() Returns the element on the top of the stack.
-
boolean empty() Returns true if the stack is empty, false otherwise.
-
-
Notes:
-
-
You must use only standard operations of a queue, which means that only push to back, peek/pop from front, size and is empty operations are valid.
-
Depending on your language, the queue may not be supported natively. You may simulate a queue using a list or deque (double-ended queue) as long as you use only a queue's standard operations.
A range[a,b] is the set of all integers from a to b (inclusive).
-
Return the smallest sorted list of ranges that cover all the numbers in the array exactly. That is, each element of nums is covered by exactly one of the ranges, and there is no integer x such that x is in one of the ranges but not in nums.
-
-## Solution:
-
-::: code-group
-
-```go [Go]
-package main
-
-import (
- "fmt"
-)
-
-func summaryRanges(nums []int) []string {
- list := []string{}
- n := len(nums)
-
- for i := 0; i < n; i++ {
- start := nums[i]
- println(i)
- for i+1 < n && nums[i+1] == nums[i]+1 {
- i++
- }
- if start == nums[i] {
- list = append(list, fmt.Sprint(start))
- } else {
- list = append(list, fmt.Sprint(start, "->", nums[i]))
- }
- }
-
- return list
-}
-
-```
-
-```rs [Rust]
-impl Solution {
- pub fn summary_ranges(nums: Vec) -> Vec {
- let mut list = Vec::new();
- let n = nums.len();
- let mut i = 0;
-
- while i < n {
- let start = nums[i];
-
- while i + 1 < n && nums[i + 1] == nums[i] + 1 {
- i += 1;
- }
-
- if start == nums[i] {
- list.push(format!("{}", start));
- } else {
- list.push(format!("{}->{}", start, nums[i]));
- }
-
- i += 1;
- }
-
- list
- }
-}
-
-```
-
-:::
-
-### [_..._](#)
-
-```
-
-```
-
-
-
-[share]: https://graph.org/file/3ea5234dda646b71c574a.png
-[easy]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Easy-bright.svg
-[medium]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Medium-yellow.svg
-[hard]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Hard-red.svg
diff --git a/docs/solution/0201-0300/230 - Kth Smallest Element in a BST.md b/docs/solution/0201-0300/230 - Kth Smallest Element in a BST.md
deleted file mode 100644
index 3b8dd158..00000000
--- a/docs/solution/0201-0300/230 - Kth Smallest Element in a BST.md
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,72 +0,0 @@
-# 230. Kth Smallest Element in a BST [![share]](https://leetcode.com/problems/kth-smallest-element-in-a-bst/)
-
-![][medium]
-
-## Problem Statement:
-
-Given the `root` of a binary search tree, and an integer `k`, return the kth smallest value **(1-indexed)** of all the values of the nodes in the tree.
-
-### Example 1:
-
-
-
-```
-Input: root = [3,1,4,null,2], k = 1
-Output: 1
-```
-
-### Example 2:
-
-```
-Input: root = [5,3,6,2,4,null,null,1], k = 3
-Output: 3
-```
-
-### Constraints:
-
-- The number of nodes in the tree is `n`.
-- 1 <= k <= n <= 104]
-- 0 <= Node.val <= 104]
-
-**Follow up:** If the BST is modified often (i.e., we can do insert and delete operations) and you need to find the kth smallest frequently, how would you optimize?
-
-## Solution:
-
-::: code-group
-
-```java
-public class KthSmallestElement {
-
- public int kthSmallest(TreeNode root, int k) {
- int[] arr = new int[2];
- arr[0] = k;
- kthSmallest(root, arr);
- return arr[1];
- }
-
- private int[] kthSmallest(TreeNode root, int arr[]) {
- if (root != null) {
- kthSmallest(root.left, arr);
- if (--arr[0] == 0) {
- arr[1] = root.val;
- return arr;
- }
- kthSmallest(root.right, arr);
- }
- return arr;
- }
-}
-```
-
-:::
-
-### [_..._](#)
-
-```
-
-```
-
-
-
-[share]: https://img.icons8.com/external-anggara-blue-anggara-putra/20/000000/external-share-user-interface-basic-anggara-blue-anggara-putra-2.png
-[medium]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Medium-yellow.svg
diff --git a/docs/solution/0201-0300/231 - Power of Two.md b/docs/solution/0201-0300/231 - Power of Two.md
deleted file mode 100644
index 7e22ab13..00000000
--- a/docs/solution/0201-0300/231 - Power of Two.md
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,66 +0,0 @@
-# 231. Power of Two [![share]](https://leetcode.com/problems/power-of-two/)
-
-![][easy]
-
-## Problem Statement:
-
-Given an integer `n`, return `true` if it is a power of two. Otherwise, return `false`.
-
-An integer `n` is a power of two, if there exists an integer `x` such that n == 2x.
-
-### Example 1:
-
-```
-Input: n = 1
-Output: true
-Explanation: 20 = 1
-```
-
-### Example 2:
-
-```
-Input: n = 16
-Output: true
-Explanation: 24 = 16
-```
-
-### Example 3:
-
-```
-Input: n = 3
-Output: false
-```
-
-### Constraints:
-
-- -231 <= n <= 231 - 1
-
-**Follow up:** Could you solve it without loops/recursion?
-
-## Solution:
-
-::: code-group
-
-```java
-public boolean isPowerOfTwo(int n) {
- if (n == 0)
- return false;
- long x = (long) n;
- return (x & x - 1) == 0;
-}
-```
-
-:::
-
-### [_..._](#)
-
-```
-
-```
-
-
-
-[share]: https://img.icons8.com/external-anggara-blue-anggara-putra/20/000000/external-share-user-interface-basic-anggara-blue-anggara-putra-2.png
-[easy]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Easy-bright.svg
-[medium]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Medium-yellow.svg
-[hard]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Hard-red.svg
diff --git a/docs/solution/0201-0300/232 - Implement Queue using Stacks.md b/docs/solution/0201-0300/232 - Implement Queue using Stacks.md
deleted file mode 100644
index b8a86290..00000000
--- a/docs/solution/0201-0300/232 - Implement Queue using Stacks.md
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,107 +0,0 @@
-# 232. Implement Queue using Stacks [![share]](https://leetcode.com/problems/implement-queue-using-stacks/)
-
-![][easy]
-
-## Problem Statement
-
-
Implement a first in first out (FIFO) queue using only two stacks. The implemented queue should support all the functions of a normal queue (push, peek, pop, and empty).
-
Implement the MyQueue class:
-
-
void push(int x) Pushes element x to the back of the queue.
-
int pop() Removes the element from the front of the queue and returns it.
-
int peek() Returns the element at the front of the queue.
-
boolean empty() Returns true if the queue is empty, false otherwise.
-
-
Notes:
-
-
You must use only standard operations of a stack, which means only push to top, peek/pop from top, size, and is empty operations are valid.
-
Depending on your language, the stack may not be supported natively. You may simulate a stack using a list or deque (double-ended queue) as long as you use only a stack's standard operations.
-
-
-
Example 1:
-
-```
-Input
-["MyQueue", "push", "push", "peek", "pop", "empty"]
-[[], [1], [2], [], [], []]
-Output
-[null, null, null, 1, 1, false]
-
-Explanation
-MyQueue myQueue = new MyQueue();
-myQueue.push(1); // queue is: [1]
-myQueue.push(2); // queue is: [1, 2] (leftmost is front of the queue)
-myQueue.peek(); // return 1
-myQueue.pop(); // return 1, queue is [2]
-myQueue.empty(); // return false
-```
-
-
-
Constraints:
-
-
1 <= x <= 9
-
At most 100 calls will be made to push, pop, peek, and empty.
-
All the calls to pop and peek are valid.
-
-
-
Follow-up: Can you implement the queue such that each operation is amortizedO(1) time complexity? In other words, performing n operations will take overall O(n) time even if one of those operations may take longer.
-
-## Solution:
-
-::: code-group
-
-```go [Go]
-package main
-
-type MyQueue struct {
- stack []int
-}
-
-func Constructor() MyQueue {
- return MyQueue{}
-}
-
-// Push element x to the back of queue.
-func (this *MyQueue) Push(x int) {
- this.stack = append(this.stack, x)
-}
-
-// Removes and returns the element at the front of queue.
-func (this *MyQueue) Pop() int {
- if len(this.stack) == 0 {
- return 0
- }
- pop := this.stack[0]
- this.stack = this.stack[1:]
- return pop
-}
-
-// Get the front element.
-func (this *MyQueue) Peek() int {
- if len(this.stack) == 0 {
- return 0
- }
- return this.stack[0]
-}
-
-// Return whether the queue is empty.
-func (this *MyQueue) Empty() bool {
- return len(this.stack) == 0
-}
-
-```
-
-:::
-
-### [_..._](#)
-
-```
-
-```
-
-
-
-[share]: https://graph.org/file/3ea5234dda646b71c574a.png
-[easy]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Easy-bright.svg
-[medium]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Medium-yellow.svg
-[hard]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Hard-red.svg
diff --git a/docs/solution/0201-0300/234 - Palindrome Linked List.md b/docs/solution/0201-0300/234 - Palindrome Linked List.md
deleted file mode 100644
index c7881a57..00000000
--- a/docs/solution/0201-0300/234 - Palindrome Linked List.md
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,93 +0,0 @@
-# 234. Palindrome Linked List [![share]](https://leetcode.com/problems/palindrome-linked-list/)
-
-![][easy]
-
-## Problem Statement
-
-
Given the head of a singly linked list, return true if it is a palindrome or false otherwise.
The number of nodes in the list is in the range [1, 105].
-
0 <= Node.val <= 9
-
-
-Follow up: Could you do it in O(n) time and O(1) space?
-
-## Solution:
-
-::: code-group
-
-```go [Go]
-package main
-
-// Definition for singly-linked list.
-type ListNode struct {
- Val int
- Next *ListNode
-}
-
-func isPalindrome(head *ListNode) bool {
- if head == nil {
- return true
- }
- // find the middle node
- slow, fast := head, head
- for fast.Next != nil && fast.Next.Next != nil {
- slow = slow.Next
- fast = fast.Next.Next
- }
- // reverse the second half
- var prev *ListNode
- curr := slow.Next
- for curr != nil {
- next := curr.Next
- curr.Next = prev
- prev = curr
- curr = next
- }
- // compare the first half and the reversed second half
- for prev != nil {
- if head.Val != prev.Val {
- return false
- }
- head = head.Next
- prev = prev.Next
- }
-
- return true
-}
-
-```
-
-:::
-
-### [_..._](#)
-
-```
-
-```
-
-
-
-[share]: https://graph.org/file/3ea5234dda646b71c574a.png
-[easy]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Easy-bright.svg
-[medium]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Medium-yellow.svg
-[hard]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Hard-red.svg
diff --git a/docs/solution/0201-0300/236 - Lowest Common Ancestor of a Binary Tree.md b/docs/solution/0201-0300/236 - Lowest Common Ancestor of a Binary Tree.md
deleted file mode 100644
index ffccedd8..00000000
--- a/docs/solution/0201-0300/236 - Lowest Common Ancestor of a Binary Tree.md
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,91 +0,0 @@
-# 236. Lowest Common Ancestor of a Binary Tree [![share]](https://leetcode.com/problems/lowest-common-ancestor-of-a-binary-tree/)
-
-![][medium]
-
-## Problem Statement
-
-
Given a binary tree, find the lowest common ancestor (LCA) of two given nodes in the tree.
-
According to the definition of LCA on Wikipedia: “The lowest common ancestor is defined between two nodes p and q as the lowest node in T that has both p and q as descendants (where we allow a node to be a descendant of itself).”
-
-
Example 1:
-
-
-```
-Input: root = [3,5,1,6,2,0,8,null,null,7,4], p = 5, q = 1
-Output: 3
-Explanation: The LCA of nodes 5 and 1 is 3.
-```
-
-
Example 2:
-
-
-```
-Input: root = [3,5,1,6,2,0,8,null,null,7,4], p = 5, q = 4
-Output: 5
-Explanation: The LCA of nodes 5 and 4 is 5, since a node can be a descendant of itself according to the LCA definition.
-```
-
-
The number of nodes in the tree is in the range [1, 100].
-
-100 <= Node.val <= 100
-
-
-## Solution:
-
-::: code-group
-
-```go [Go]
-package main
-
-import "fmt"
-
-// Definition for a binary tree node.
-type TreeNode struct {
- Val int
- Left *TreeNode
- Right *TreeNode
-}
-
-func binaryTreePaths(root *TreeNode) []string {
- if root == nil {
- return nil
- }
-
- paths := make([]string, 0)
-
- // if root is leaf node
- if root.Left == nil && root.Right == nil {
- paths = append(paths, fmt.Sprint(root.Val))
- return paths
- }
-
- // traverse left subtree and append root value
- for _, path := range binaryTreePaths(root.Left) {
- paths = append(paths, fmt.Sprint(root.Val, "->", path))
- }
-
- // traverse right subtree and append root value
- for _, path := range binaryTreePaths(root.Right) {
- paths = append(paths, fmt.Sprint(root.Val, "->", path))
- }
-
- return paths
-}
-
-```
-
-:::
-
-### [_..._](#)
-
-```
-
-```
-
-
-
-[share]: https://graph.org/file/3ea5234dda646b71c574a.png
-[easy]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Easy-bright.svg
-[medium]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Medium-yellow.svg
-[hard]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Hard-red.svg
diff --git a/docs/solution/0201-0300/258 - Add Digits.md b/docs/solution/0201-0300/258 - Add Digits.md
deleted file mode 100644
index 32544835..00000000
--- a/docs/solution/0201-0300/258 - Add Digits.md
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,86 +0,0 @@
-# 258. Add Digits [![share]](https://leetcode.com/problems/add-digits/)
-
-![][easy]
-
-## Problem Statement
-
-
Given an integer num, repeatedly add all its digits until the result has only one digit, and return it.
-
-
Example 1:
-
-```
-Input: num = 38
-Output: 2
-Explanation: The process is
-38 --> 3 + 8 --> 11
-11 --> 1 + 1 --> 2
-Since 2 has only one digit, return it.
-```
-
-
Example 2:
-
-```
-Input: num = 0
-Output: 0
-```
-
-
-
Constraints:
-
-
0 <= num <= 231 - 1
-
-
-
Follow up: Could you do it without any loop/recursion in O(1) runtime?
-
-::: details _Click to open Hints_
-
-- A naive implementation of the above process is trivial. Could you come up with other methods?
-- What are all the possible results?
-- How do they occur, periodically or randomly?
-- You may find this Wikipedia article useful.
-
-:::
-
-## Solution:
-
-::: code-group
-
-```rs [Rust]
-impl Solution {
- pub fn add_digits(num: i32) -> i32 {
- let mut num = num;
-
- // loop while the number is greater than 9
- while num > 9 {
- let mut sum = 0;
- // loop while the number is greater than 0,
- // add the last digit to the sum,
- // and divide the number by 10
- while num > 0 {
- sum += num % 10;
- num /= 10;
- }
- // set the number to the sum
- num = sum;
- }
-
- num
- }
-}
-
-```
-
-:::
-
-### [_..._](#)
-
-```
-
-```
-
-
-
-[share]: https://graph.org/file/3ea5234dda646b71c574a.png
-[easy]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Easy-bright.svg
-[medium]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Medium-yellow.svg
-[hard]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Hard-red.svg
diff --git a/docs/solution/0201-0300/263 - Ugly Number.md b/docs/solution/0201-0300/263 - Ugly Number.md
deleted file mode 100644
index 795bcf85..00000000
--- a/docs/solution/0201-0300/263 - Ugly Number.md
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,80 +0,0 @@
-# 263. Ugly Number [![share]](https://leetcode.com/problems/ugly-number/)
-
-![][easy]
-
-## Problem Statement
-
-
An ugly number is a positive integer whose prime factors are limited to 2, 3, and 5.
-
Given an integer n, return trueifnis an ugly number.
-
-```
-Input: n = 1
-Output: true
-Explanation: 1 has no prime factors, therefore all of its prime factors are limited to 2, 3, and 5.
-```
-
-
Example 3:
-
-```
-Input: n = 14
-Output: false
-Explanation: 14 is not ugly since it includes the prime factor 7.
-```
-
-
-
Constraints:
-
-
-231 <= n <= 231 - 1
-
-
-## Solution:
-
-::: code-group
-
-```rs [Rust]
-impl Solution {
- pub fn is_ugly(n: i32) -> bool {
- if n < 1 {
- return false;
- }
-
- let divisors = [2, 3, 5];
- let mut n = n;
-
- for divisor in divisors {
- // Divide n by divisor as many times as possible
- while n % divisor == 0 {
- n /= divisor;
- }
- }
-
- n == 1
- }
-}
-
-```
-
-:::
-
-### [_..._](#)
-
-```
-
-```
-
-
-
-[share]: https://graph.org/file/3ea5234dda646b71c574a.png
-[easy]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Easy-bright.svg
-[medium]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Medium-yellow.svg
-[hard]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Hard-red.svg
diff --git a/docs/solution/0201-0300/268 - Missing Number.md b/docs/solution/0201-0300/268 - Missing Number.md
deleted file mode 100644
index 51cb853c..00000000
--- a/docs/solution/0201-0300/268 - Missing Number.md
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,77 +0,0 @@
-# 268. Missing Number [![share]](https://leetcode.com/problems/missing-number/)
-
-![][easy]
-
-## Problem Statement
-
-
Given an array nums containing n distinct numbers in the range [0, n], return the only number in the range that is missing from the array.
-
-
Example 1:
-
-```
-Input: nums = [3,0,1]
-Output: 2
-Explanation: n = 3 since there are 3 numbers, so all numbers are in the range [0,3]. 2 is the missing number in the range since it does not appear in nums.
-```
-
-
Example 2:
-
-```
-Input: nums = [0,1]
-Output: 2
-Explanation: n = 2 since there are 2 numbers, so all numbers are in the range [0,2]. 2 is the missing number in the range since it does not appear in nums.
-```
-
-
Example 3:
-
-```
-Input: nums = [9,6,4,2,3,5,7,0,1]
-Output: 8
-Explanation: n = 9 since there are 9 numbers, so all numbers are in the range [0,9]. 8 is the missing number in the range since it does not appear in nums.
-```
-
-
-
Constraints:
-
-
n == nums.length
-
1 <= n <= 104
-
0 <= nums[i] <= n
-
All the numbers of nums are unique.
-
-
-
Follow up: Could you implement a solution using only O(1) extra space complexity and O(n) runtime complexity?
-
-## Solution:
-
-::: code-group
-
-```rs [Rust]
-impl Solution {
- pub fn missing_number(nums: Vec) -> i32 {
- let len = nums.len();
- let mut sum = len * (len + 1) / 2;
-
- for num in nums {
- sum -= num as usize;
- }
-
- sum as i32
- }
-}
-
-```
-
-:::
-
-### [_..._](#)
-
-```
-
-```
-
-
-
-[share]: https://graph.org/file/3ea5234dda646b71c574a.png
-[easy]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Easy-bright.svg
-[medium]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Medium-yellow.svg
-[hard]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Hard-red.svg
diff --git a/docs/solution/0201-0300/278 - First Bad Version.md b/docs/solution/0201-0300/278 - First Bad Version.md
deleted file mode 100644
index 9c09fd4e..00000000
--- a/docs/solution/0201-0300/278 - First Bad Version.md
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,96 +0,0 @@
-# 278. First Bad Version [![share]](https://leetcode.com/problems/first-bad-version)
-
-![][easy]
-
-## Problem Statement:
-
-You are a product manager and currently leading a team to develop a new product. Unfortunately, the latest version of your product fails the quality check. Since each version is developed based on the previous version, all the versions after a bad version are also bad.
-
-Suppose you have n versions `[1, 2, ..., n]` and you want to find out the first bad one, which causes all the following ones to be bad.
-
-You are given an API `bool isBadVersion(version)` which returns whether `version` is bad. Implement a function to find the first bad version. You should minimize the number of calls to the API.
-
-### Example 1:
-
-```
-Input: n = 5, bad = 4
-Output: 4
-
-Explanation:
-call isBadVersion(3) -> false
-call isBadVersion(5) -> true
-call isBadVersion(4) -> true
-Then 4 is the first bad version.
-```
-
-### Example 2:
-
-```
-Input: n = 1, bad = 1
-Output: 1
-```
-
-### Constraints:
-
-- 1 <= bad <= n <= 231 - 1
-
-## Solution:
-
-::: code-group
-
-```java [Java]
-public class FirstBadVersion extends VersionControl {
- public int firstBadVersion(int n) {
- int low = 0, high = n;
- while (low < high) {
- int mid = low + (high - low) / 2;
- if (isBadVersion(mid))
- high = mid;
- else
- low = mid + 1;
- }
- return low;
- }
-}
-
-class VersionControl {
- boolean isBadVersion(int version) {
- return false;
- }
-}
-```
-
-```rs [Rust]
-impl Solution {
- pub fn first_bad_version(&self, n: i32) -> i32 {
- let (mut low, mut high) = (1, n);
-
- while low < high {
- let mid = low + (high - low) / 2;
- if self.isBadVersion(mid) {
- high = mid;
- } else {
- low = mid + 1;
- }
- }
-
- low
- }
-}
-
-```
-
-:::
-
-### [_..._](#)
-
-```
-
-```
-
-
-
-[share]: https://img.icons8.com/external-anggara-blue-anggara-putra/20/000000/external-share-user-interface-basic-anggara-blue-anggara-putra-2.png
-[easy]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Easy-bright.svg
-[medium]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Medium-yellow.svg
-[hard]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Hard-red.svg
diff --git a/docs/solution/0201-0300/279 - Perfect Squares.md b/docs/solution/0201-0300/279 - Perfect Squares.md
deleted file mode 100644
index 020a36a4..00000000
--- a/docs/solution/0201-0300/279 - Perfect Squares.md
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,74 +0,0 @@
-# 279. Perfect Squares [![share]](https://leetcode.com/problems/perfect-squares/)
-
-![][medium]
-
-## Problem Statement
-
-
Given an integer n, return the least number of perfect square numbers that sum ton.
-
A perfect square is an integer that is the square of an integer; in other words, it is the product of some integer with itself. For example, 1, 4, 9, and 16 are perfect squares while 3 and 11 are not.
s contains only lowercase English letters and spaces ' '.
-
sdoes not contain any leading or trailing spaces.
-
All the words in s are separated by a single space.
-
-
-## Solution:
-
-::: code-group
-
-```go [Go]
-package main
-
-import "strings"
-
-func wordPattern(pattern string, s string) bool {
- words := strings.Split(s, " ")
-
- if len(pattern) != len(words) {
- return false
- }
-
- map_ := make(map[byte]string)
-
- // loop through the pattern and process each character
- for i := 0; i < len(pattern); i++ {
- // if the word is already in the map, check if it matches the pattern
- if val, ok := map_[pattern[i]]; ok {
- if val != words[i] {
- return false
- }
- } else {
- // loop through the map to check if map contains the word
- for _, v := range map_ {
- // if the word is in the map, return false
- if v == words[i] {
- return false
- }
- }
-
- // if the word is not in the map, add it
- map_[pattern[i]] = words[i]
- }
- }
-
- return true
-}
-
-```
-
-:::
-
-### [_..._](#)
-
-```
-
-```
-
-
-
-[share]: https://graph.org/file/3ea5234dda646b71c574a.png
-[easy]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Easy-bright.svg
-[medium]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Medium-yellow.svg
-[hard]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Hard-red.svg
diff --git a/docs/solution/0201-0300/292 - Nim Game.md b/docs/solution/0201-0300/292 - Nim Game.md
deleted file mode 100644
index a928d5e0..00000000
--- a/docs/solution/0201-0300/292 - Nim Game.md
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,85 +0,0 @@
-# 292. Nim Game [![share]](https://leetcode.com/problems/nim-game/)
-
-![][easy]
-
-## Problem Statement
-
-
You are playing the following Nim Game with your friend:
-
-
Initially, there is a heap of stones on the table.
-
You and your friend will alternate taking turns, and you go first.
-
On each turn, the person whose turn it is will remove 1 to 3 stones from the heap.
-
The one who removes the last stone is the winner.
-
-
Given n, the number of stones in the heap, return true if you can win the game assuming both you and your friend play optimally, otherwise return false.
-
-
Example 1:
-
-```
-Input: n = 4
-Output: false
-Explanation: These are the possible outcomes:
-1. You remove 1 stone. Your friend removes 3 stones, including the last stone. Your friend wins.
-2. You remove 2 stones. Your friend removes 2 stones, including the last stone. Your friend wins.
-3. You remove 3 stones. Your friend removes the last stone. Your friend wins.
-In all outcomes, your friend wins.
-```
-
-
Example 2:
-
-```
-Input: n = 1
-Output: true
-```
-
-
Example 3:
-
-```
-Input: n = 2
-Output: true
-```
-
-
-
Constraints:
-
-
1 <= n <= 231 - 1
-
-
-::: details _Click to open Hints_
-
-- If there are 5 stones in the heap, could you figure out a way to remove the stones such that you will always be the winner?
-
-:::
-
-## Solution:
-
-::: code-group
-
-```rs [Rust]
-impl Solution {
- pub fn can_win_nim(n: i32) -> bool {
- // if n is divisible by 4, then the first player will always lose
- if n % 4 == 0 {
- return false;
- }
-
- true
- }
-}
-
-```
-
-:::
-
-### [_..._](#)
-
-```
-
-```
-
-
-
-[share]: https://graph.org/file/3ea5234dda646b71c574a.png
-[easy]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Easy-bright.svg
-[medium]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Medium-yellow.svg
-[hard]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Hard-red.svg
diff --git a/docs/solution/0201-0300/300 - Longest Increasing Subsequence.md b/docs/solution/0201-0300/300 - Longest Increasing Subsequence.md
deleted file mode 100644
index 22fdaae1..00000000
--- a/docs/solution/0201-0300/300 - Longest Increasing Subsequence.md
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,71 +0,0 @@
-# 300. Longest Increasing Subsequence [![share]](https://leetcode.com/problems/longest-increasing-subsequence/)
-
-![][medium]
-
-## Problem Statement:
-
-Given an integer array `nums`, return the length of the longest strictly increasing subsequence.
-
-### Example 1:
-
-```
-Input: nums = [10,9,2,5,3,7,101,18]
-Output: 4
-Explanation: The longest increasing subsequence is [2,3,7,101], therefore the length is 4.
-```
-
-### Example 2:
-
-```
-Input: nums = [0,1,0,3,2,3]
-Output: 4
-```
-
-### Example 3:
-
-```
-Input: nums = [7,7,7,7,7,7,7]
-Output: 1
-```
-
-### Constraints:
-
-- 1 <= nums.length <= 2500
-- -104 <= nums[i] <= 104
-
-**Follow up**: Can you come up with an algorithm that runs in O(n log(n)) time complexity?
-
-## Solution:
-
-::: code-group
-
-```java
-public int lengthOfLIS(int[] nums) {
- int[] lis = new int[nums.length];
- lis[0] = 1;
- for (int i = 1; i < lis.length; i++) {
- lis[i] = 1;
- for (int j = 0; j < i; j++) {
- if (nums[i] > nums[j])
- lis[i] = Math.max(lis[i], lis[j] + 1);
- }
- }
- int res = lis[0];
- for (int i : lis)
- res = Math.max(i, res);
- return res;
-}
-```
-
-:::
-
-### [_..._](#)
-
-```
-
-```
-
-
-
-[share]: https://img.icons8.com/external-anggara-blue-anggara-putra/20/000000/external-share-user-interface-basic-anggara-blue-anggara-putra-2.png
-[medium]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Medium-yellow.svg
diff --git a/docs/solution/0301-0400/322 - Coin Change.md b/docs/solution/0301-0400/322 - Coin Change.md
deleted file mode 100644
index df90d1ea..00000000
--- a/docs/solution/0301-0400/322 - Coin Change.md
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,74 +0,0 @@
-# 322. Coin Change [![share]](https://leetcode.com/problems/coin-change)
-
-![][medium]
-
-## Problem Statement:
-
-You are given an integer array `coins` representing coins of different denominations and an integer `amount` representing a total amount of money.
-
-Return the fewest number of coins that you need to make up that amount. If that amount of money cannot be made up by any combination of the coins, return `-1`.
-
-You may assume that you have an infinite number of each kind of coin.
-
-### Example 1:
-
-```
-Input: coins = [1,2,5], amount = 11
-Output: 3
-Explanation: 11 = 5 + 5 + 1
-```
-
-### Example 2:
-
-```
-Input: coins = [2], amount = 3
-Output: -1
-```
-
-### Example 3:
-
-```
-Input: coins = [1], amount = 0
-Output: 0
-```
-
-### Constraints:
-
-- 1 <= coins.length <= 12
-- 1 <= coins[i] <= 231 - 1
-- 0 <= amount <= 104>
-
-## Solution:
-
-::: code-group
-
-```java
-public int coinChange(int[] coins, int amount) {
- int max = amount + 1;
- int[] amtArr = new int[max];
- Arrays.fill(amtArr, max);
- amtArr[0] = 0;
- for (int i = 1; i <= amount; i++) {
- for (int j = 0; j < coins.length; j++) {
- if (coins[j] <= i)
- amtArr[i] = Math.min(amtArr[i], amtArr[i - coins[j]] + 1);
- }
- }
- return amtArr[amount] > amount ? -1 : amtArr[amount];
-}
-```
-
-:::
-
-### [_..._](#)
-
-```
-
-```
-
-
-
-[share]: https://img.icons8.com/external-anggara-blue-anggara-putra/20/000000/external-share-user-interface-basic-anggara-blue-anggara-putra-2.png
-[easy]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Easy-bright.svg
-[medium]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Medium-yellow.svg
-[hard]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Hard-red.svg
diff --git a/docs/solution/0301-0400/326 - Power Of Three.md b/docs/solution/0301-0400/326 - Power Of Three.md
deleted file mode 100644
index a809f459..00000000
--- a/docs/solution/0301-0400/326 - Power Of Three.md
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,77 +0,0 @@
-# 326. Power Of Three [![share]](https://leetcode.com/problems/power-of-three/)
-
-![][easy]
-
-## Problem Statement
-
-
Given an integer n, return true if it is a power of three. Otherwise, return false.
-
An integer n is a power of three, if there exists an integer x such that n == 3x.
-
-```
-Input: n = 0
-Output: false
-Explanation: There is no x where 3x = 0.
-```
-
-
Example 3:
-
-```
-Input: n = -1
-Output: false
-Explanation: There is no x where 3x = (-1).
-```
-
-
-
Constraints:
-
-
-231 <= n <= 231 - 1
-
-
-Follow up: Could you solve it without loops/recursion?
-
-## Solution:
-
-::: code-group
-
-```rs [Rust]
-impl Solution {
- pub fn is_power_of_three(n: i32) -> bool {
- if n <= 0 {
- return false;
- }
-
- let mut n = n;
- while n % 3 == 0 {
- n /= 3;
- }
-
- n == 1
- }
-}
-
-```
-
-:::
-
-### [_..._](#)
-
-```
-
-```
-
-
-
-[share]: https://graph.org/file/3ea5234dda646b71c574a.png
-[easy]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Easy-bright.svg
-[medium]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Medium-yellow.svg
-[hard]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Hard-red.svg
diff --git a/docs/solution/0301-0400/337 - House Robber III.md b/docs/solution/0301-0400/337 - House Robber III.md
deleted file mode 100644
index 155e5b44..00000000
--- a/docs/solution/0301-0400/337 - House Robber III.md
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,73 +0,0 @@
-# 337. House Robber III [![][share]](https://leetcode.com/problems/house-robber-iii)
-
-![][medium]
-
-## Problem Statement:
-
-The thief has found himself a new place for his thievery again. There is only one entrance to this area, called `root`.
-
-Besides the `root`, each house has one and only one parent house. After a tour, the smart thief realized that all houses in this place form a binary tree. It will automatically contact the police if **two directly-linked houses were broken into on the same night**.
-
-Given the `root` of the binary tree, return the maximum amount of money the thief can rob **without alerting the police**.
-
-### Example 1:
-
-
-
-```
-Input: root = [3,2,3,null,3,null,1]
-Output: 7
-Explanation: Maximum amount of money the thief can rob = 3 + 3 + 1 = 7.
-```
-
-### Example 2:
-
-
-
-```
-Input: root = [3,4,5,1,3,null,1]
-Output: 9
-Explanation: Maximum amount of money the thief can rob = 4 + 5 = 9.
-```
-
-### Constraints:
-
-- The number of nodes in the tree is in the range [1, 104].
-- 0 <= Node.val <= 104
-
-## Solution:
-
-::: code-group
-
-```java
-public int rob(TreeNode root) {
- int[] res = helper(root);
- return Math.max(res[0], res[1]);
-}
-
-private int[] helper(TreeNode root) {
- if (root == null)
- return new int[] { 0, 0 };
- int[] left = helper(root.left);
- int[] right = helper(root.right);
-
- int rob = root.val + left[1] + right[1];
- int notRob = Math.max(left[0], left[1]) + Math.max(right[0], right[1]);
- return new int[] { rob, notRob };
-}
-```
-
-:::
-
-### [_..._](#)
-
-```
-
-```
-
-
-
-[share]: https://img.icons8.com/external-anggara-blue-anggara-putra/20/000000/external-share-user-interface-basic-anggara-blue-anggara-putra-2.png
-[easy]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Easy-bright.svg
-[medium]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Medium-yellow.svg
-[hard]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Hard-red.svg
diff --git a/docs/solution/0301-0400/338 - Counting Bits.md b/docs/solution/0301-0400/338 - Counting Bits.md
deleted file mode 100644
index 0da40c78..00000000
--- a/docs/solution/0301-0400/338 - Counting Bits.md
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,89 +0,0 @@
-# 338. Counting Bits [![share]](https://leetcode.com/problems/counting-bits/)
-
-![][easy]
-
-## Problem Statement
-
-
Given an integer n, return an array ans of length n + 1 such that for each i(0 <= i <= n), ans[i] is the number of 1's in the binary representation of i.
It is very easy to come up with a solution with a runtime of O(n log n). Can you do it in linear time O(n) and possibly in a single pass?
-
Can you do it without using any built-in function (i.e., like __builtin_popcount in C++)?
-
-
-::: details _Click to open Hints_
-
-- You should make use of what you have produced already.
-- Divide the numbers in ranges like [2-3], [4-7], [8-15] and so on. And try to generate new range from previous.
-- Or does the odd/even status of the number help you in calculating the number of 1s?
-
-:::
-
-## Solution:
-
-::: code-group
-
-```rs [Rust]
-impl Solution {
- pub fn count_bits(n: i32) -> Vec {
- let mut res = vec![0; n as usize + 1];
-
- for i in 1..=n {
- let i = i as usize;
- // let i_and_i_minus_1 = i & (i - 1);
- // res[i] = res[i_and_i_minus_1] + 1;
- res[i] = res[i >> 1] + (i & 1) as i32;
- }
-
- res
- }
-}
-
-```
-
-:::
-
-### [_..._](#)
-
-```
-
-```
-
-
-
-[share]: https://graph.org/file/3ea5234dda646b71c574a.png
-[easy]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Easy-bright.svg
-[medium]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Medium-yellow.svg
-[hard]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Hard-red.svg
diff --git a/docs/solution/0301-0400/342 - Power of Four.md b/docs/solution/0301-0400/342 - Power of Four.md
deleted file mode 100644
index a498b9d7..00000000
--- a/docs/solution/0301-0400/342 - Power of Four.md
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,74 +0,0 @@
-# 342. Power of Four [![share]](https://leetcode.com/problems/power-of-four/)
-
-![][easy]
-
-## Problem Statement
-
-
Given an integer n, return true if it is a power of four. Otherwise, return false.
-
An integer n is a power of four, if there exists an integer x such that n == 4x.
-
-
Example 1:
-
-```
-Input: n = 16
-Output: true
-```
-
-
Example 2:
-
-```
-Input: n = 5
-Output: false
-```
-
-
Example 3:
-
-```
-Input: n = 1
-Output: true
-```
-
-
-
Constraints:
-
-
-231 <= n <= 231 - 1
-
-
-Follow up: Could you solve it without loops/recursion?
-
-## Solution:
-
-::: code-group
-
-```rs [Rust]
-impl Solution {
- pub fn is_power_of_four(n: i32) -> bool {
- if n <= 0 {
- return false;
- }
-
- let mut n = n;
- while n % 4 == 0 {
- n /= 4;
- }
-
- n == 1
- }
-}
-
-```
-
-:::
-
-### [_..._](#)
-
-```
-
-```
-
-
-
-[share]: https://graph.org/file/3ea5234dda646b71c574a.png
-[easy]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Easy-bright.svg
-[medium]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Medium-yellow.svg
-[hard]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Hard-red.svg
diff --git a/docs/solution/0301-0400/344 - Reverse String.md b/docs/solution/0301-0400/344 - Reverse String.md
deleted file mode 100644
index a2cc3e64..00000000
--- a/docs/solution/0301-0400/344 - Reverse String.md
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,60 +0,0 @@
-# 344. Reverse String [![share]](https://leetcode.com/problems/reverse-string)
-
-![][easy]
-
-## Problem Statement:
-
-Write a function that reverses a string. The input string is given as an array of characters s.
-
-You must do this by modifying the input array `in-place` with `O(1)` extra memory.
-
-### Example 1:
-
-```
-Input: s = ["h","e","l","l","o"]
-Output: ["o","l","l","e","h"]
-```
-
-### Example 2:
-
-```
-Input: s = ["H","a","n","n","a","h"]
-Output: ["h","a","n","n","a","H"]
-```
-
-### Constraints:
-
-- 1 <= s.length <= 105
-- s[i] is a printable ascii character.
-
-## Solution:
-
-::: code-group
-
-```java
-public void reverseString(char[] s) {
- for (int left = 0, right = s.length - 1; left < right; left++, right--)
- swap(s, left, right);
-}
-
-private void swap(char[] s, int a, int b) {
- char temp = s[a];
- s[a] = s[b];
- s[b] = temp;
-}
-```
-
-:::
-
-### [_..._](#)
-
-```
-
-```
-
-
-
-[share]: https://img.icons8.com/external-anggara-blue-anggara-putra/20/000000/external-share-user-interface-basic-anggara-blue-anggara-putra-2.png
-[easy]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Easy-bright.svg
-[medium]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Medium-yellow.svg
-[hard]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Hard-red.svg
diff --git a/docs/solution/0301-0400/345 - Reverse Vowels of a String.md b/docs/solution/0301-0400/345 - Reverse Vowels of a String.md
deleted file mode 100644
index 3fd8bc4a..00000000
--- a/docs/solution/0301-0400/345 - Reverse Vowels of a String.md
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,99 +0,0 @@
-# 345. Reverse Vowels of a String [![share]](https://leetcode.com/problems/reverse-vowels-of-a-string/)
-
-![][easy]
-
-## Problem Statement
-
-
Given a string s, reverse only all the vowels in the string and return it.
-
The vowels are 'a', 'e', 'i', 'o', and 'u', and they can appear in both lower and upper cases, more than once.
-
-## Solution:
-
-::: code-group
-
-```rs [Rust]
-impl Solution {
- pub fn reverse_vowels(s: String) -> String {
- let mut s = s.into_bytes();
- let (mut i, mut j) = (0, s.len() - 1);
-
- while i < j {
- if !Self::is_vowel(s[i] as char) {
- i += 1;
- continue;
- }
- if !Self::is_vowel(s[j] as char) {
- j -= 1;
- continue;
- }
- s.swap(i, j);
- i += 1;
- j -= 1;
- }
- String::from_utf8(s).unwrap()
-
- // let mut chars: Vec = s.chars().collect();
- // let (mut i, mut j) = (0, chars.len() - 1);
-
- // while i < j {
- // if !Self::is_vowel(chars[i]) {
- // i += 1;
- // continue;
- // }
- // if !Self::is_vowel(chars[j]) {
- // j -= 1;
- // continue;
- // }
- // chars.swap(i, j);
- // i += 1;
- // j -= 1;
- // }
-
- // chars.into_iter().collect()
- }
-
- fn is_vowel(ch: char) -> bool {
- match ch {
- 'a' | 'e' | 'i' | 'o' | 'u' | 'A' | 'E' | 'I' | 'O' | 'U' => true,
- _ => false,
- }
- }
-}
-
-```
-
-:::
-
-### [_..._](#)
-
-```
-
-```
-
-
-
-[share]: https://graph.org/file/3ea5234dda646b71c574a.png
-[easy]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Easy-bright.svg
-[medium]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Medium-yellow.svg
-[hard]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Hard-red.svg
diff --git a/docs/solution/0301-0400/349 - Intersection of Two Arrays.md b/docs/solution/0301-0400/349 - Intersection of Two Arrays.md
deleted file mode 100644
index 62c82428..00000000
--- a/docs/solution/0301-0400/349 - Intersection of Two Arrays.md
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,78 +0,0 @@
-# 349. Intersection of Two Arrays [![share]](https://leetcode.com/problems/intersection-of-two-arrays/)
-
-![][easy]
-
-## Problem Statement
-
-
Given two integer arrays nums1 and nums2, return an array of their intersection. Each element in the result must be unique and you may return the result in any order.
-
-```
-Input: nums1 = [4,9,5], nums2 = [9,4,9,8,4]
-Output: [9,4]
-Explanation: [4,9] is also accepted.
-```
-
-
-
Constraints:
-
-
1 <= nums1.length, nums2.length <= 1000
-
0 <= nums1[i], nums2[i] <= 1000
-
-
-## Solution:
-
-::: code-group
-
-```rs [Rust]
-impl Solution {
- pub fn intersection(nums1: Vec, nums2: Vec) -> Vec {
- let (mut nums1, mut nums2) = (nums1, nums2);
- let mut res = Vec::new();
- let (mut i, mut j) = (0, 0);
-
- nums1.sort();
- nums2.sort();
-
- while i <= nums1.len() - 1 && j <= nums2.len() - 1 {
- if nums1[i] == nums2[j] {
- if res.is_empty() || res[res.len() - 1] != nums1[i] {
- res.push(nums1[i]);
- }
- i += 1;
- j += 1;
- } else if nums1[i] < nums2[j] {
- i += 1;
- } else {
- j += 1;
- }
- }
-
- res
- }
-}
-
-```
-
-:::
-
-### [_..._](#)
-
-```
-
-```
-
-
-
-[share]: https://graph.org/file/3ea5234dda646b71c574a.png
-[easy]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Easy-bright.svg
-[medium]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Medium-yellow.svg
-[hard]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Hard-red.svg
diff --git a/docs/solution/0301-0400/350 - Intersection of Two Arrays II.md b/docs/solution/0301-0400/350 - Intersection of Two Arrays II.md
deleted file mode 100644
index 8641f330..00000000
--- a/docs/solution/0301-0400/350 - Intersection of Two Arrays II.md
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,83 +0,0 @@
-# 350. Intersection of Two Arrays II [![share]](https://leetcode.com/problems/intersection-of-two-arrays-ii/)
-
-![][easy]
-
-## Problem Statement
-
-
Given two integer arrays nums1 and nums2, return an array of their intersection. Each element in the result must appear as many times as it shows in both arrays and you may return the result in any order.
ransomNote and magazine consist of lowercase English letters.
-
-
-## Solution:
-
-::: code-group
-
-```rs [Rust]
-impl Solution {
- pub fn can_construct(ransom_note: String, magazine: String) -> bool {
- // Convert the magazine string to a vector of characters
- let mut magazine = magazine.chars().collect::>();
-
- // Iterate over the ransom note string
- for c in ransom_note.chars() {
- // If the magazine contains the character, remove it
- // Otherwise, return false
- // position() returns the index of the first element that matches the closure
- // else returns None
- if let Some(i) = magazine.iter().position(|&x| x == c) {
- magazine.remove(i);
- } else {
- return false;
- }
- }
-
- true
- }
-}
-
-```
-
-```go [Go]
-package main
-
-func canConstruct(ransomNote string, magazine string) bool {
- if len(ransomNote) > len(magazine) {
- return false
- }
- // make a map of the magazine
- mag := make(map[rune]int)
-
- // count the number of each character in the magazine
- for _, c := range magazine {
- mag[c]++
- }
-
- // check if the ransom note can be made from the magazine
- for _, c := range ransomNote {
- if mag[c] == 0 {
- return false
- }
- mag[c]--
- }
-
- // // make a vector of the magazine
- // magVec := make([]int, 26)
-
- // for _, c := range magazine {
- // magVec[c-'a']++
- // }
-
- // // check if ransomNote can be constructed from magazine
- // for _, c := range ransomNote {
- // if magVec[c-'a'] == 0 {
- // return false
- // }
- // magVec[c-'a']--
- // }
-
- return true
-}
-
-```
-
-:::
-
-### [_..._](#)
-
-```
-
-```
-
-
-
-[share]: https://graph.org/file/3ea5234dda646b71c574a.png
-[easy]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Easy-bright.svg
-[medium]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Medium-yellow.svg
-[hard]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Hard-red.svg
diff --git a/docs/solution/0301-0400/387 - First Unique Character in a String.md b/docs/solution/0301-0400/387 - First Unique Character in a String.md
deleted file mode 100644
index 502ffc7d..00000000
--- a/docs/solution/0301-0400/387 - First Unique Character in a String.md
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,79 +0,0 @@
-# 387. First Unique Character in a String [![share]](https://leetcode.com/problems/first-unique-character-in-a-string/)
-
-![][easy]
-
-## Problem Statement
-
-
Given a string s, find the first non-repeating character in it and return its index. If it does not exist, return -1.
-
-## Solution:
-
-::: code-group
-
-```rs [Rust]
-impl Solution {
- pub fn first_uniq_char(s: String) -> i32 {
- let mut map = std::collections::HashMap::new();
- for c in s.chars() {
- // increase the count of the character if exists
- // otherwise insert the character w/ default value 0
- // then increase the count by 1
- *map.entry(c).or_insert(0) += 1;
- }
-
- // iterate over the string and return the index of the first character
- // that has a count of 1
- for (i, c) in s.chars().enumerate() {
- if *map.get(&c).unwrap() == 1 {
- return i as i32;
- }
- }
-
- -1
- }
-}
-
-```
-
-:::
-
-### [_..._](#)
-
-```
-
-```
-
-
-
-[share]: https://graph.org/file/3ea5234dda646b71c574a.png
-[easy]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Easy-bright.svg
-[medium]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Medium-yellow.svg
-[hard]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Hard-red.svg
diff --git a/docs/solution/0301-0400/389 - Find the Difference.md b/docs/solution/0301-0400/389 - Find the Difference.md
deleted file mode 100644
index 4722583e..00000000
--- a/docs/solution/0301-0400/389 - Find the Difference.md
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,62 +0,0 @@
-# 389. Find the Difference [![share]](https://leetcode.com/problems/find-the-difference/)
-
-![][easy]
-
-## Problem Statement:
-
-You are given two strings `s` and `t`.
-
-String `t` is generated by random shuffling string `s` and then add one more letter at a random position.
-
-Return the letter that was added to `t`.
-
-### Example 1:
-
-```
-Input: s = "abcd", t = "abcde"
-Output: "e"
-Explanation: 'e' is the letter that was added.
-```
-
-### Example 2:
-
-```
-Input: s = "", t = "y"
-Output: "y"
-```
-
-### Constraints:
-
-- 0 <= s.length <= 1000
-- t.length == s.length + 1
-- s and t consist of lowercase English letters.
-
-## Solution:
-
-::: code-group
-
-```java
-public char findTheDifference(String s, String t) {
- char c = 0;
- for (int i = 0; i < s.length(); ++i)
- c ^= s.charAt(i);
- for (int i = 0; i < t.length(); ++i)
- c ^= t.charAt(i);
- return c;
-}
-```
-
-:::
-
-### [_..._](#)
-
-```
-
-```
-
-
-
-[share]: https://img.icons8.com/external-anggara-blue-anggara-putra/20/000000/external-share-user-interface-basic-anggara-blue-anggara-putra-2.png
-[easy]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Easy-bright.svg
-[medium]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Medium-yellow.svg
-[hard]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Hard-red.svg
diff --git a/docs/solution/0301-0400/392 - Is Subsequence.md b/docs/solution/0301-0400/392 - Is Subsequence.md
deleted file mode 100644
index b6cbf532..00000000
--- a/docs/solution/0301-0400/392 - Is Subsequence.md
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,69 +0,0 @@
-# 392. Is Subsequence [![share]](https://leetcode.com/problems/is-subsequence/)
-
-![][easy]
-
-## Problem Statement
-
-
Given two strings s and t, return true if s is a subsequence of t, or false otherwise.
-
A subsequence of a string is a new string that is formed from the original string by deleting some (can be none) of the characters without disturbing the relative positions of the remaining characters. (i.e., "ace" is a subsequence of "abcde" while "aec" is not).
-
-
Example 1:
-
-```
-Input: s = "abc", t = "ahbgdc"
-Output: true
-```
-
-
Example 2:
-
-```
-Input: s = "axc", t = "ahbgdc"
-Output: false
-```
-
-
-
Constraints:
-
-
0 <= s.length <= 100
-
0 <= t.length <= 104
-
s and t consist only of lowercase English letters.
-
-
-Follow up: Suppose there are lots of incoming s, say s1, s2, ..., sk where k >= 109, and you want to check one by one to see if t has its subsequence. In this scenario, how would you change your code?
-
-## Solution:
-
-::: code-group
-
-```rs [Rust]
-impl Solution {
- pub fn is_subsequence(s: String, t: String) -> bool {
- let (mut i, mut j) = (0, 0);
-
- while i < s.len() && j < t.len() {
- if s.as_bytes()[i] == t.as_bytes()[j] {
- i += 1;
- }
- j += 1;
- }
-
- i == s.len()
- }
-}
-
-```
-
-:::
-
-### [_..._](#)
-
-```
-
-```
-
-
-
-[share]: https://graph.org/file/3ea5234dda646b71c574a.png
-[easy]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Easy-bright.svg
-[medium]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Medium-yellow.svg
-[hard]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Hard-red.svg
diff --git a/docs/solution/0401-0500/401 - Binary Watch.md b/docs/solution/0401-0500/401 - Binary Watch.md
deleted file mode 100644
index 3d27ae98..00000000
--- a/docs/solution/0401-0500/401 - Binary Watch.md
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,90 +0,0 @@
-# 401. Binary Watch [![share]](https://leetcode.com/problems/binary-watch/)
-
-![][easy]
-
-## Problem Statement
-
-
A binary watch has 4 LEDs on the top to represent the hours (0-11), and 6 LEDs on the bottom to represent the minutes (0-59). Each LED represents a zero or one, with the least significant bit on the right.
-
-
For example, the below binary watch reads "4:51".
-
-
-
Given an integer turnedOn which represents the number of LEDs that are currently on (ignoring the PM), return all possible times the watch could represent. You may return the answer in any order.
-
The hour must not contain a leading zero.
-
-
For example, "01:00" is not valid. It should be "1:00".
-
-
The minute must be consist of two digits and may contain a leading zero.
-
-
For example, "10:2" is not valid. It should be "10:02".
-
-::: details _Click to open Hints_
-
-- Simplify by seeking for solutions that involve comparing bit counts.
-- Consider calculating all possible times for comparison purposes.
-
-:::
-
-## Solution:
-
-::: code-group
-
-```rs [Rust]
-impl Solution {
- pub fn read_binary_watch(turned_on: i32) -> Vec {
- let mut res = Vec::new();
-
- // 12 hours, 60 minutes
- // here we use 0_i32 to avoid the warning of type inference
- for i in 0_i32..12 {
- for j in 0_i32..60 {
- // if the sum of the number of 1s in the binary representation
- // of the hour and minute is equal to turned_on,
- // then the time is added to the res
- if i.count_ones() + j.count_ones() == turned_on as u32 {
- res.push(format!("{}:{:02}", i, j));
- }
- }
- }
-
- res
- }
-}
-
-```
-
-:::
-
-### [_..._](#)
-
-```
-
-```
-
-
-
-[share]: https://graph.org/file/3ea5234dda646b71c574a.png
-[easy]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Easy-bright.svg
-[medium]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Medium-yellow.svg
-[hard]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Hard-red.svg
diff --git a/docs/solution/0401-0500/404 - Sum of Left Leaves.md b/docs/solution/0401-0500/404 - Sum of Left Leaves.md
deleted file mode 100644
index f7a7abbd..00000000
--- a/docs/solution/0401-0500/404 - Sum of Left Leaves.md
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,107 +0,0 @@
-# 404. Sum of Left Leaves [![share]](https://leetcode.com/problems/sum-of-left-leaves/)
-
-![][easy]
-
-## Problem Statement
-
-
Given the root of a binary tree, return the sum of all left leaves.
-
A leaf is a node with no children. A left leaf is a leaf that is the left child of another node.
-
-
Example 1:
-
-
-```
-Input: root = [3,9,20,null,null,15,7]
-Output: 24
-Explanation: There are two left leaves in the binary tree, with values 9 and 15 respectively.
-```
-
-
Example 2:
-
-```
-Input: root = [1]
-Output: 0
-```
-
-
-
Constraints:
-
-
The number of nodes in the tree is in the range [1, 1000].
-
-1000 <= Node.val <= 1000
-
-
-## Solution:
-
-::: code-group
-
-```go [Go]
-package main
-
-// Definition for a binary tree node.
-type TreeNode struct {
- Val int
- Left *TreeNode
- Right *TreeNode
-}
-
-// Recursion
-func sumOfLeftLeaves(root *TreeNode) int {
- if root == nil {
- return 0
- }
-
- // if root.Left is a leaf node
- if root.Left != nil && root.Left.Left == nil && root.Left.Right == nil {
- return root.Left.Val + sumOfLeftLeaves(root.Right)
- }
-
- return sumOfLeftLeaves(root.Left) + sumOfLeftLeaves(root.Right)
-}
-
-// Iteration
-func sumOfLeftLeaves2(root *TreeNode) int {
- if root == nil {
- return 0
- }
-
- sum := 0
- stack := []*TreeNode{root}
-
- for len(stack) > 0 {
- // pop
- node := stack[len(stack)-1]
- stack = stack[:len(stack)-1]
-
- if node.Left != nil {
- // if node.Left is a leaf node
- if node.Left.Left == nil && node.Left.Right == nil {
- sum += node.Left.Val
- } else {
- stack = append(stack, node.Left)
- }
- }
-
- if node.Right != nil {
- stack = append(stack, node.Right)
- }
- }
-
- return sum
-}
-
-```
-
-:::
-
-### [_..._](#)
-
-```
-
-```
-
-
-
-[share]: https://graph.org/file/3ea5234dda646b71c574a.png
-[easy]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Easy-bright.svg
-[medium]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Medium-yellow.svg
-[hard]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Hard-red.svg
diff --git a/docs/solution/0401-0500/412 - Fizz Buzz.md b/docs/solution/0401-0500/412 - Fizz Buzz.md
deleted file mode 100644
index 3670bbb3..00000000
--- a/docs/solution/0401-0500/412 - Fizz Buzz.md
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,83 +0,0 @@
-# 412. Fizz Buzz [![share]](https://leetcode.com/problems/fizz-buzz/)
-
-![][easy]
-
-## Problem Statement
-
-
Given an integer n, return a string array answer (1-indexed) where:
-
-
answer[i] == "FizzBuzz" if i is divisible by 3 and 5.
-
answer[i] == "Fizz" if i is divisible by 3.
-
answer[i] == "Buzz" if i is divisible by 5.
-
answer[i] == i (as a string) if none of the above conditions are true.
-
-## Solution:
-
-::: code-group
-
-```rs [Rust]
-impl Solution {
- pub fn fizz_buzz(n: i32) -> Vec {
- let mut res = Vec::new();
-
- for i in 1..=n {
- // same as divisible by 3 and 5
- if i % 15 == 0 {
- res.push("FizzBuzz".to_string());
- } else if i % 3 == 0 {
- res.push("Fizz".to_string());
- } else if i % 5 == 0 {
- res.push("Buzz".to_string());
- } else {
- res.push(i.to_string());
- }
- }
-
- res
- }
-}
-
-```
-
-:::
-
-### [_..._](#)
-
-```
-
-```
-
-
-
-[share]: https://graph.org/file/3ea5234dda646b71c574a.png
-[easy]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Easy-bright.svg
-[medium]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Medium-yellow.svg
-[hard]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Hard-red.svg
diff --git a/docs/solution/0401-0500/414 - Third Maximum Number.md b/docs/solution/0401-0500/414 - Third Maximum Number.md
deleted file mode 100644
index 07845b20..00000000
--- a/docs/solution/0401-0500/414 - Third Maximum Number.md
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,87 +0,0 @@
-# 414. Third Maximum Number [![share]](https://leetcode.com/problems/third-maximum-number/)
-
-![][easy]
-
-## Problem Statement
-
-
Given an integer array nums, return the third distinct maximum number in this array. If the third maximum does not exist, return the maximum number.
-
-
Example 1:
-
-```
-Input: nums = [3,2,1]
-Output: 1
-Explanation:
-The first distinct maximum is 3.
-The second distinct maximum is 2.
-The third distinct maximum is 1.
-```
-
-
Example 2:
-
-```
-Input: nums = [1,2]
-Output: 2
-Explanation:
-The first distinct maximum is 2.
-The second distinct maximum is 1.
-The third distinct maximum does not exist, so the maximum (2) is returned instead.
-```
-
-
Example 3:
-
-```
-Input: nums = [2,2,3,1]
-Output: 1
-Explanation:
-The first distinct maximum is 3.
-The second distinct maximum is 2 (both 2's are counted together since they have the same value).
-The third distinct maximum is 1.
-```
-
-
-
Constraints:
-
-
1 <= nums.length <= 104
-
-231 <= nums[i] <= 231 - 1
-
-
-Follow up: Can you find an O(n) solution?
-
-## Solution:
-
-::: code-group
-
-```rs [Rust]
-impl Solution {
- pub fn third_max(nums: Vec) -> i32 {
- let mut sorted = nums.clone();
- // sort in descending order
- sorted.sort_by(|a, b| b.cmp(a));
- // remove duplicates
- sorted.dedup();
-
- if sorted.len() < 3 {
- return sorted[0];
- } else {
- return sorted[2];
- }
- }
-}
-
-```
-
-:::
-
-### [_..._](#)
-
-```
-
-```
-
-
-
-[share]: https://graph.org/file/3ea5234dda646b71c574a.png
-[easy]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Easy-bright.svg
-[medium]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Medium-yellow.svg
-[hard]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Hard-red.svg
diff --git a/docs/solution/0401-0500/434 - Number of Segments in a String.md b/docs/solution/0401-0500/434 - Number of Segments in a String.md
deleted file mode 100644
index 35a534cd..00000000
--- a/docs/solution/0401-0500/434 - Number of Segments in a String.md
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,70 +0,0 @@
-# 434. Number of Segments in a String [![share]](https://leetcode.com/problems/number-of-segments-in-a-string/)
-
-![][easy]
-
-## Problem Statement
-
-
Given a string s, return the number of segments in the string.
-
A segment is defined to be a contiguous sequence of non-space characters.
-
-
Example 1:
-
-```
-Input: s = "Hello, my name is John"
-Output: 5
-Explanation: The five segments are ["Hello,", "my", "name", "is", "John"]
-```
-
-
Example 2:
-
-```
-Input: s = "Hello"
-Output: 1
-```
-
-
-
Constraints:
-
-
0 <= s.length <= 300
-
s consists of lowercase and uppercase English letters, digits, or one of the following characters "!@#$%^&*()_+-=',.:".
-
The only space character in s is ' '.
-
-
-## Solution:
-
-::: code-group
-
-```rs [Rust]
-impl Solution {
- pub fn count_segments(s: String) -> i32 {
- let (mut count, mut is_space) = (0, true);
-
- for c in s.chars() {
- if c == ' ' {
- is_space = true;
- } else if is_space {
- is_space = false;
- count += 1;
- }
- }
-
- count
- }
-}
-
-```
-
-:::
-
-### [_..._](#)
-
-```
-
-```
-
-
-
-[share]: https://graph.org/file/3ea5234dda646b71c574a.png
-[easy]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Easy-bright.svg
-[medium]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Medium-yellow.svg
-[hard]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Hard-red.svg
diff --git a/docs/solution/0401-0500/438 - Find All Anagrams in a String.md b/docs/solution/0401-0500/438 - Find All Anagrams in a String.md
deleted file mode 100644
index a0cf97ea..00000000
--- a/docs/solution/0401-0500/438 - Find All Anagrams in a String.md
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,91 +0,0 @@
-# 438. Find All Anagrams in a String [![share]](https://leetcode.com/problems/find-all-anagrams-in-a-string/)
-
-![][medium]
-
-## Problem Statement
-
-
Given two strings s and p, return an array of all the start indices of p's anagrams in s. You may return the answer in any order.
-
An Anagram is a word or phrase formed by rearranging the letters of a different word or phrase, typically using all the original letters exactly once.
-
-
Example 1:
-
-```
-Input: s = "cbaebabacd", p = "abc"
-Output: [0,6]
-Explanation:
-The substring with start index = 0 is "cba", which is an anagram of "abc".
-The substring with start index = 6 is "bac", which is an anagram of "abc".
-```
-
-
Example 2:
-
-```
-Input: s = "abab", p = "ab"
-Output: [0,1,2]
-Explanation:
-The substring with start index = 0 is "ab", which is an anagram of "ab".
-The substring with start index = 1 is "ba", which is an anagram of "ab".
-The substring with start index = 2 is "ab", which is an anagram of "ab".
-```
-
-
-
Constraints:
-
-
1 <= s.length, p.length <= 3 * 104
-
s and p consist of lowercase English letters.
-
-
-## Solution:
-
-::: code-group
-
-```py [Python]
-class Solution:
- def findAnagrams(self, s: str, p: str) -> list[int]:
- s_len, p_len = len(s), len(p)
- if p_len > s_len:
- return []
- p_count, s_count = {}, {}
- # increment the count of each character in p and s,
- # for the first p_len characters in s
- # with get() we can set a default value if the key is not found
- for i in range(p_len):
- p_count[p[i]] = p_count.get(p[i], 0) + 1
- s_count[s[i]] = s_count.get(s[i], 0) + 1
-
- # if the counts are equal, we found an anagram
- res = [0] if p_count == s_count else []
- l = 0
- for r in range(p_len, s_len):
- # increment the count of the right character
- s_count[s[r]] = s_count.get(s[r], 0) + 1
- # decrement the count of the left character
- s_count[s[l]] -= 1
-
- # if the count of the left character is 0,
- # we can remove it from the dictionary
- if s_count[s[l]] == 0:
- del s_count[s[l]]
- # increment the left pointer
- l += 1
- # if the counts are equal, we found an anagram
- if p_count == s_count:
- res.append(l)
- return res
-
-```
-
-:::
-
-### [_..._](#)
-
-```
-
-```
-
-
-
-[share]: https://graph.org/file/3ea5234dda646b71c574a.png
-[easy]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Easy-bright.svg
-[medium]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Medium-yellow.svg
-[hard]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Hard-red.svg
diff --git a/docs/solution/0401-0500/441 - Arranging Coins.md b/docs/solution/0401-0500/441 - Arranging Coins.md
deleted file mode 100644
index 94ef0eb8..00000000
--- a/docs/solution/0401-0500/441 - Arranging Coins.md
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,67 +0,0 @@
-# 441. Arranging Coins [![share]](https://leetcode.com/problems/arranging-coins/)
-
-![][easy]
-
-## Problem Statement
-
-
You have n coins and you want to build a staircase with these coins. The staircase consists of k rows where the ith row has exactly i coins. The last row of the staircase may be incomplete.
-
Given the integer n, return the number of complete rows of the staircase you will build.
-
-
Example 1:
-
-
-```
-Input: n = 5
-Output: 2
-Explanation: Because the 3rd row is incomplete, we return 2.
-```
-
-
Example 2:
-
-
-```
-Input: n = 8
-Output: 3
-Explanation: Because the 4th row is incomplete, we return 3.
-```
-
-
-
Constraints:
-
-
1 <= n <= 231 - 1
-
-
-## Solution:
-
-::: code-group
-
-```rs [Rust]
-impl Solution {
- pub fn arrange_coins(n: i32) -> i32 {
- let (mut n, mut i) = (n, 1);
-
- while n >= i {
- n -= i;
- i += 1;
- }
-
- i - 1
- }
-}
-
-```
-
-:::
-
-### [_..._](#)
-
-```
-
-```
-
-
-
-[share]: https://graph.org/file/3ea5234dda646b71c574a.png
-[easy]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Easy-bright.svg
-[medium]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Medium-yellow.svg
-[hard]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Hard-red.svg
diff --git a/docs/solution/0401-0500/442 - Find All Duplicates in an Array.md b/docs/solution/0401-0500/442 - Find All Duplicates in an Array.md
deleted file mode 100644
index 9ed103a7..00000000
--- a/docs/solution/0401-0500/442 - Find All Duplicates in an Array.md
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,70 +0,0 @@
-# 442. Find All Duplicates in an Array [![share]](https://leetcode.com/problems/find-all-duplicates-in-an-array/)
-
-![][medium]
-
-## Problem Statement:
-
-Given an integer array `nums` of length `n` where all the integers of `nums` are in the range `[1, n]` and each integer appears **once** or **twice**, return an array of all the integers that appears **twice**.
-
-You must write an algorithm that runs in `O(n)` time and uses only constant extra space.
-
-### Example 1:
-
-```
-Input: nums = [4,3,2,7,8,2,3,1]
-Output: [2,3]
-```
-
-### Example 2:
-
-```
-Input: nums = [1,1,2]
-Output: [1]
-```
-
-### Example 3:
-
-```
-Input: nums = [1]
-Output: []
-```
-
-### Constraints:
-
-- n == nums.length
-- 1 <= n <= 105
-- 1 <= nums[i] <= n
-- Each element in nums appears **once** or **twice**.
-
-## Solution:
-
-::: code-group
-
-```java
-public List findDuplicates(int[] nums) {
- ArrayList list = new ArrayList<>();
- for (int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) {
- int n = Math.abs(nums[i]);
- if (nums[n - 1] < 0)
- list.add(n);
- else
- nums[n - 1] = -nums[n - 1];
- }
-return list;
-}
-```
-
-:::
-
-### [_..._](#)
-
-```
-
-```
-
-
-
-[share]: https://img.icons8.com/external-anggara-blue-anggara-putra/20/000000/external-share-user-interface-basic-anggara-blue-anggara-putra-2.png
-[easy]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Easy-bright.svg
-[medium]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Medium-yellow.svg
-[hard]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Hard-red.svg
diff --git a/docs/solution/0401-0500/443 - String Compression.md b/docs/solution/0401-0500/443 - String Compression.md
deleted file mode 100644
index 85f86685..00000000
--- a/docs/solution/0401-0500/443 - String Compression.md
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,110 +0,0 @@
-# 443. String Compression [![share]](https://leetcode.com/problems/string-compression/)
-
-![][medium]
-
-## Problem Statement
-
-
Given an array of characters chars, compress it using the following algorithm:
-
Begin with an empty string s. For each group of consecutive repeating characters in chars:
-
-
If the group's length is 1, append the character to s.
-
Otherwise, append the character followed by the group's length.
-
-
The compressed string sshould not be returned separately, but instead, be stored in the input character array chars. Note that group lengths that are 10 or longer will be split into multiple characters in chars.
-
After you are done modifying the input array, return the new length of the array.
-
You must write an algorithm that uses only constant extra space.
-
-
Example 1:
-
-```
-Input: chars = ["a","a","b","b","c","c","c"]
-Output: Return 6, and the first 6 characters of the input array should be: ["a","2","b","2","c","3"]
-Explanation: The groups are "aa", "bb", and "ccc". This compresses to "a2b2c3".
-```
-
-
Example 2:
-
-```
-Input: chars = ["a"]
-Output: Return 1, and the first character of the input array should be: ["a"]
-Explanation: The only group is "a", which remains uncompressed since it's a single character.
-```
-
-
Example 3:
-
-````
-Input: chars = ["a","b","b","b","b","b","b","b","b","b","b","b","b"]
-Output: Return 4, and the first 4 characters of the input array should be: ["a","b","1","2"].
-Explanation: The groups are "a" and "bbbbbbbbbbbb". This compresses to "ab12".```
-
-
-
Constraints:
-
-
1 <= chars.length <= 2000
-
chars[i] is a lowercase English letter, uppercase English letter, digit, or symbol.
-
-
-
-::: details _Click to open Hints_
-
-- How do you know if you are at the end of a consecutive group of characters?
-
-:::
-
-## Solution:
-
-::: code-group
-
-```rs [Rust]
-impl Solution {
- pub fn compress(chars: &mut Vec) -> i32 {
- let (mut i, n) = (0, chars.len());
- let mut new_len = 0;
-
- while i < n {
- let mut j = i;
-
- // increment j until we find a different character or reach the end
- while j < n && chars[j] == chars[i] {
- j += 1;
- }
-
- // place the character at the new position
- // e.g. if we have aabbccc, we place a at the start of the array
- chars[new_len] = chars[i];
- new_len += 1;
-
- // if the length of the group of characters is greater than 1
- // i.e. suppose if new_len is 12, we need to place 12 as characters [..., '1','2', ...]
- if j - i > 1 {
- for c in (j - i).to_string().chars() {
- chars[new_len] = c;
- new_len += 1;
- }
- }
-
- // place i at same position as j,
- // i.e. the start of the next group of characters
- i = j;
- }
-
- new_len as i32
- }
-}
-
-````
-
-:::
-
-### [_..._](#)
-
-```
-
-```
-
-
-
-[share]: https://graph.org/file/3ea5234dda646b71c574a.png
-[easy]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Easy-bright.svg
-[medium]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Medium-yellow.svg
-[hard]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Hard-red.svg
diff --git a/docs/solution/0401-0500/445 - Add Two Numbers II.md b/docs/solution/0401-0500/445 - Add Two Numbers II.md
deleted file mode 100644
index 12e8c760..00000000
--- a/docs/solution/0401-0500/445 - Add Two Numbers II.md
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,88 +0,0 @@
-# 445. Add Two Numbers II [![][share]](https://leetcode.com/problems/add-two-numbers-ii)
-
-![][medium]
-
-## Problem Statement:
-
-You are given two **non-empty** linked lists representing two non-negative integers. The most significant digit comes first and each of their nodes contains a single digit. Add the two numbers and return the sum as a linked list.
-
-You may assume the two numbers do not contain any leading zero, except the number 0 itself.
-
-### Example 1:
-
-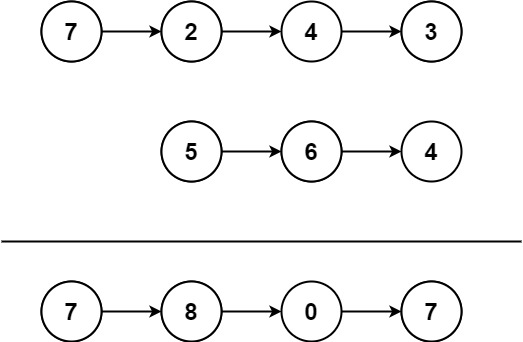
-
-```
-Input: l1 = [7,2,4,3], l2 = [5,6,4]
-Output: [7,8,0,7]
-```
-
-### Example 2:
-
-```
-Input: l1 = [2,4,3], l2 = [5,6,4]
-Output: [8,0,7]
-```
-
-### Example 3:
-
-```
-Input: l1 = [0], l2 = [0]
-Output: [0]
-```
-
-### Constraints:
-
-- The number of nodes in each linked list is in the range `[1, 100]`.
-- 0 <= Node.val <= 9
-- It is guaranteed that the list represents a number that does not have leading zeros.
-
-**Follow up:** Could you solve it without reversing the input lists?
-
-## Solution:
-
-::: code-group
-
-```java
-public static ListNode addTwoNumbers(ListNode l1, ListNode l2) {
- ListNode res = null;
- int carry = 0;
- Stack s1 = new Stack<>(),
- s2 = new Stack<>();
- while (l1 != null || l2 != null) {
- if (l1 != null) {
- s1.push(l1.val);
- l1 = l1.next;
- }
- if (l2 != null) {
- s2.push(l2.val);
- l2 = l2.next;
- }
- }
- while (!s1.isEmpty() || !s2.isEmpty() || carry != 0) {
- int n1 = s1.isEmpty() ? 0 : s1.pop(),
- n2 = s2.isEmpty() ? 0 : s2.pop();
- int temp = n1 + n2 + carry;
- ListNode newNode = new ListNode(temp % 10);
- newNode.next = res;
- res = newNode;
- carry = temp / 10;
- }
- return res;
-}
-```
-
-:::
-
-### [_..._](#)
-
-```
-
-```
-
-
-
-[share]: https://img.icons8.com/external-anggara-blue-anggara-putra/20/000000/external-share-user-interface-basic-anggara-blue-anggara-putra-2.png
-[easy]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Easy-bright.svg
-[medium]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Medium-yellow.svg
-[hard]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Hard-red.svg
diff --git a/docs/solution/0401-0500/448 - Find All Numbers Disappeared in an Array.md b/docs/solution/0401-0500/448 - Find All Numbers Disappeared in an Array.md
deleted file mode 100644
index 6e9a48bc..00000000
--- a/docs/solution/0401-0500/448 - Find All Numbers Disappeared in an Array.md
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,80 +0,0 @@
-# 448. Find All Numbers Disappeared in an Array [![share]](https://leetcode.com/problems/find-all-numbers-disappeared-in-an-array/)
-
-![][easy]
-
-## Problem Statement
-
-
Given an array nums of n integers where nums[i] is in the range [1, n], return an array of all the integers in the range[1, n]that do not appear innums.
Follow up: Could you do it without extra space and in O(n) runtime? You may assume the returned list does not count as extra space.
-
-::: details _Click to open Hints_
-
-- This is a really easy problem if you decide to use additional memory. For those trying to write an initial solution using additional memory, think counters!
-- However, the trick really is to not use any additional space than what is already available to use. Sometimes, multiple passes over the input array help find the solution. However, there's an interesting piece of information in this problem that makes it easy to re-use the input array itself for the solution.
-- The problem specifies that the numbers in the array will be in the range [1, n] where n is the number of elements in the array. Can we use this information and modify the array in-place somehow to find what we need?
-
-:::
-
-## Solution:
-
-::: code-group
-
-```rs [Rust]
-impl Solution {
- pub fn find_disappeared_numbers(nums: Vec) -> Vec {
- let mut res = Vec::new();
- let mut map = std::collections::HashMap::new();
-
- for i in 0..nums.len() {
- map.insert(nums[i], i);
- }
-
- for i in 1..=nums.len() {
- if !map.contains_key(&(i as i32)) {
- res.push(i as i32);
- }
- }
-
- res
- }
-}
-
-```
-
-:::
-
-### [_..._](#)
-
-```
-
-```
-
-
-
-[share]: https://graph.org/file/3ea5234dda646b71c574a.png
-[easy]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Easy-bright.svg
-[medium]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Medium-yellow.svg
-[hard]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Hard-red.svg
diff --git a/docs/solution/0401-0500/461 - Hamming Distance.md b/docs/solution/0401-0500/461 - Hamming Distance.md
deleted file mode 100644
index 3a5ba07a..00000000
--- a/docs/solution/0401-0500/461 - Hamming Distance.md
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,72 +0,0 @@
-# 461. Hamming Distance [![share]](https://leetcode.com/problems/hamming-distance/)
-
-![][easy]
-
-## Problem Statement
-
-
The Hamming distance between two integers is the number of positions at which the corresponding bits are different.
-
Given two integers x and y, return the Hamming distance between them.
-
-
Example 1:
-
-```
-Input: x = 1, y = 4
-Output: 2
-Explanation:
-1 (0 0 0 1)
-4 (0 1 0 0)
- ↑ ↑
-The above arrows point to positions where the corresponding bits are different.
-```
-
-
Example 2:
-
-```
-Input: x = 3, y = 1
-Output: 1
-```
-
-
-
Constraints:
-
-
0 <= x, y <= 231 - 1
-
-
-## Solution:
-
-::: code-group
-
-```rs [Rust]
-impl Solution {
- pub fn hamming_distance(x: i32, y: i32) -> i32 {
- let (mut x, mut y) = (x, y);
- let mut count = 0;
-
- while x != 0 || y != 0 {
- if x % 2 != y % 2 {
- count += 1;
- }
- x /= 2;
- y /= 2;
- }
-
- count
- }
-}
-
-```
-
-:::
-
-### [_..._](#)
-
-```
-
-```
-
-
-
-[share]: https://graph.org/file/3ea5234dda646b71c574a.png
-[easy]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Easy-bright.svg
-[medium]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Medium-yellow.svg
-[hard]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Hard-red.svg
diff --git a/docs/solution/0401-0500/463 - Island Perimeter.md b/docs/solution/0401-0500/463 - Island Perimeter.md
deleted file mode 100644
index e3c64674..00000000
--- a/docs/solution/0401-0500/463 - Island Perimeter.md
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,87 +0,0 @@
-# 463. Island Perimeter [![share]](https://leetcode.com/problems/island-perimeter/)
-
-![][easy]
-
-## Problem Statement
-
-
You are given row x colgrid representing a map where grid[i][j] = 1 represents land and grid[i][j] = 0 represents water.
-
Grid cells are connected horizontally/vertically (not diagonally). The grid is completely surrounded by water, and there is exactly one island (i.e., one or more connected land cells).
-
The island doesn't have "lakes", meaning the water inside isn't connected to the water around the island. One cell is a square with side length 1. The grid is rectangular, width and height don't exceed 100. Determine the perimeter of the island.
-
-
Example 1:
-
-
-```
-Input: grid = [[0,1,0,0],[1,1,1,0],[0,1,0,0],[1,1,0,0]]
-Output: 16
-Explanation: The perimeter is the 16 yellow stripes in the image above.
-```
-
-
The complement of an integer is the integer you get when you flip all the 0's to 1's and all the 1's to 0's in its binary representation.
-
-
For example, The integer 5 is "101" in binary and its complement is "010" which is the integer 2.
-
-
Given an integer num, return its complement.
-
-
Example 1:
-
-```
-Input: num = 5
-Output: 2
-Explanation: The binary representation of 5 is 101 (no leading zero bits), and its complement is 010. So you need to output 2.
-```
-
-
Example 2:
-
-```
-Input: num = 1
-Output: 0
-Explanation: The binary representation of 1 is 1 (no leading zero bits), and its complement is 0. So you need to output 0.
-```
-
-
You are given a license key represented as a string s that consists of only alphanumeric characters and dashes. The string is separated into n + 1 groups by n dashes. You are also given an integer k.
-
We want to reformat the string s such that each group contains exactly k characters, except for the first group, which could be shorter than k but still must contain at least one character. Furthermore, there must be a dash inserted between two groups, and you should convert all lowercase letters to uppercase.
-
Return the reformatted license key.
-
-
Example 1:
-
-```
-Input: s = "5F3Z-2e-9-w", k = 4
-Output: "5F3Z-2E9W"
-Explanation: The string s has been split into two parts, each part has 4 characters.
-Note that the two extra dashes are not needed and can be removed.
-```
-
-
Example 2:
-
-```
-Input: s = "2-5g-3-J", k = 2
-Output: "2-5G-3J"
-Explanation: The string s has been split into three parts, each part has 2 characters except the first part as it could be shorter as mentioned above.
-```
-
-
-
Constraints:
-
-
1 <= s.length <= 105
-
s consists of English letters, digits, and dashes '-'.
-
1 <= k <= 104
-
-
-## Solution:
-
-::: code-group
-
-```rs [Rust]
-impl Solution {
- pub fn license_key_formatting(s: String, k: i32) -> String {
- let mut s = s.replace("-", "");
- let mut i = s.len() as i32 - k;
-
- while i > 0 {
- s.insert(i as usize, '-');
- i -= k;
- }
-
- s.to_uppercase()
- }
-}
-
-```
-
-:::
-
-### [_..._](#)
-
-```
-
-```
-
-
-
-[share]: https://graph.org/file/3ea5234dda646b71c574a.png
-[easy]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Easy-bright.svg
-[medium]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Medium-yellow.svg
-[hard]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Hard-red.svg
diff --git a/docs/solution/0401-0500/485 - Max Consecutive Ones.md b/docs/solution/0401-0500/485 - Max Consecutive Ones.md
deleted file mode 100644
index 93ddb66d..00000000
--- a/docs/solution/0401-0500/485 - Max Consecutive Ones.md
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,82 +0,0 @@
-# 485. Max Consecutive Ones [![share]](https://leetcode.com/problems/max-consecutive-ones/)
-
-![][easy]
-
-## Problem Statement
-
-
Given a binary array nums, return the maximum number of consecutive 1's in the array.
-
-
Example 1:
-
-```
-Input: nums = [1,1,0,1,1,1]
-Output: 3
-Explanation: The first two digits or the last three digits are consecutive 1s. The maximum number of consecutive 1s is 3.
-```
-
-
-
-::: details _Click to open Hints_
-
-- You need to think about two things as far as any window is concerned. One is the starting point for the window. How do you detect that a new window of 1s has started? The next part is detecting the ending point for this window.
-
-How do you detect the ending point for an existing window? If you figure these two things out, you will be able to detect the windows of consecutive ones. All that remains afterward is to find the longest such window and return the size.
-
-:::
-
-## Solution:
-
-::: code-group
-
-```rs [Rust]
-impl Solution {
- pub fn find_max_consecutive_ones(nums: Vec) -> i32 {
- let (mut count, mut max) = (0, 0);
-
- for i in nums {
- if i == 1 {
- count += 1;
- } else {
- if count > max {
- max = count;
- }
- count = 0;
- }
- }
-
- if count > max {
- max = count;
- }
-
- max
- }
-}
-
-```
-
-:::
-
-### [_..._](#)
-
-```
-
-```
-
-
-
-[share]: https://graph.org/file/3ea5234dda646b71c574a.png
-[easy]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Easy-bright.svg
-[medium]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Medium-yellow.svg
-[hard]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Hard-red.svg
diff --git a/docs/solution/0401-0500/492 - Construct the Rectangle.md b/docs/solution/0401-0500/492 - Construct the Rectangle.md
deleted file mode 100644
index 6e9176b6..00000000
--- a/docs/solution/0401-0500/492 - Construct the Rectangle.md
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,85 +0,0 @@
-# 492. Construct the Rectangle [![share]](https://leetcode.com/problems/construct-the-rectangle/)
-
-![][easy]
-
-## Problem Statement
-
-
A web developer needs to know how to design a web page's size. So, given a specific rectangular web page’s area, your job by now is to design a rectangular web page, whose length L and width W satisfy the following requirements:
-
-
The area of the rectangular web page you designed must equal to the given target area.
-
The width W should not be larger than the length L, which means L >= W.
-
The difference between length L and width W should be as small as possible.
-
-
Return an array [L, W] where L and W are the length and width of the web page you designed in sequence.
-
-
Example 1:
-
-```
-Input: area = 4
-Output: [2,2]
-Explanation: The target area is 4, and all the possible ways to construct it are [1,4], [2,2], [4,1].
-But according to requirement 2, [1,4] is illegal; according to requirement 3, [4,1] is not optimal compared to [2,2]. So the length L is 2, and the width W is 2.
-```
-
-
-
-::: details _Click to open Hints_
-
-- The W is always less than or equal to the square root of the area, so we start searching at sqrt(area) till we find the result.
-
-:::
-
-## Solution:
-
-::: code-group
-
-```rs [Rust]
-impl Solution {
- pub fn construct_rectangle(area: i32) -> Vec {
- let mut w = (area as f64).sqrt() as i32;
-
- // until the remainder is 0, decrement w
- // this will find the largest w that is a factor of area
- while area % w != 0 {
- w -= 1;
- }
-
- // return the result
- vec![area / w, w]
- }
-}
-
-```
-
-:::
-
-### [_..._](#)
-
-```
-
-```
-
-
-
-[share]: https://graph.org/file/3ea5234dda646b71c574a.png
-[easy]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Easy-bright.svg
-[medium]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Medium-yellow.svg
-[hard]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Hard-red.svg
diff --git a/docs/solution/0401-0500/498 - Diagonal Traverse.md b/docs/solution/0401-0500/498 - Diagonal Traverse.md
deleted file mode 100644
index e77c61e9..00000000
--- a/docs/solution/0401-0500/498 - Diagonal Traverse.md
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,169 +0,0 @@
-# 498. Diagonal Traverse [![share]](https://leetcode.com/problems/diagonal-traverse/)
-
-![][medium]
-
-## Problem Statement
-
-
Given an m x n matrix mat, return an array of all the elements of the array in a diagonal order.
-
-## Solution:
-
-::: code-group
-
-```go [Go]
-package main
-
-type Direction int
-
-const (
- Up Direction = iota
- Down
-)
-
-func findDiagonalOrder(mat [][]int) []int {
- direction := Up
- row, col := 0, 0
- row_len, col_len := len(mat), len(mat[0])
- res := make([]int, row_len*col_len)
-
- for i := 0; i < row_len*col_len; i++ {
- res[i] = mat[row][col]
-
- if direction == Up {
- if row == 0 || col == col_len-1 {
- direction = Down
-
- if col == col_len-1 {
- row++
- } else {
- col++
- }
-
- } else {
- row--
- col++
- }
- } else {
- if col == 0 || row == row_len-1 {
- direction = Up
-
- if row == row_len-1 {
- col++
- } else {
- row++
- }
-
- } else {
- row++
- col--
- }
- }
- }
-
- return res
-}
-
-```
-
-```rs [Rust]
-enum Direction {
- Up,
- Down,
-}
-
-impl Solution {
- pub fn find_diagonal_order(mat: Vec>) -> Vec {
- let mut result = vec![];
- let mut direction = Direction::Up;
- let (mut row, mut col) = (0, 0);
- let (row_len, col_len) = (mat.len(), mat[0].len());
-
- while row < row_len && col < col_len {
- // push the current element to the result vector
- result.push(mat[row][col]);
-
- match direction {
- Direction::Up => {
- if row == 0 || col == col_len - 1 {
- // if we are at the top row or the rightmost column, change direction to "Down"
- direction = Direction::Down;
-
- if col == col_len - 1 {
- // if at the rightmost column, move to the next row
- row += 1;
- } else {
- // otherwise, move to the next column
- col += 1;
- }
- } else {
- // move diagonally upward
- row -= 1;
- col += 1;
- }
- }
- Direction::Down => {
- if col == 0 || row == row_len - 1 {
- // if we are at the leftmost column or the bottom row, change direction to "Up"
- direction = Direction::Up;
-
- if row == row_len - 1 {
- // if at the bottom row, move to the next column
- col += 1;
- } else {
- // otherwise, move to the next row
- row += 1;
- }
- } else {
- // move diagonally downward
- row += 1;
- col -= 1;
- }
- }
- }
- }
-
- result
- }
-}
-
-```
-
-:::
-
-### [_..._](#)
-
-```
-
-```
-
-
-
-[share]: https://graph.org/file/3ea5234dda646b71c574a.png
-[easy]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Easy-bright.svg
-[medium]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Medium-yellow.svg
-[hard]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Hard-red.svg
diff --git a/docs/solution/0501-0600/502 - IPO.md b/docs/solution/0501-0600/502 - IPO.md
deleted file mode 100644
index 7e3f1a24..00000000
--- a/docs/solution/0501-0600/502 - IPO.md
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,111 +0,0 @@
-# 502. IPO [![share]](https://leetcode.com/problems/ipo/)
-
-![][hard]
-
-## Problem Statement
-
-
Suppose LeetCode will start its IPO soon. In order to sell a good price of its shares to Venture Capital, LeetCode would like to work on some projects to increase its capital before the IPO. Since it has limited resources, it can only finish at most k distinct projects before the IPO. Help LeetCode design the best way to maximize its total capital after finishing at most k distinct projects.
-
You are given n projects where the ith project has a pure profit profits[i] and a minimum capital of capital[i] is needed to start it.
-
Initially, you have w capital. When you finish a project, you will obtain its pure profit and the profit will be added to your total capital.
-
Pick a list of at mostk distinct projects from given projects to maximize your final capital, and return the final maximized capital.
-
The answer is guaranteed to fit in a 32-bit signed integer.
-
-
Example 1:
-
-```
-Input: k = 2, w = 0, profits = [1,2,3], capital = [0,1,1]
-Output: 4
-Explanation: Since your initial capital is 0, you can only start the project indexed 0.
-After finishing it you will obtain profit 1 and your capital becomes 1.
-With capital 1, you can either start the project indexed 1 or the project indexed 2.
-Since you can choose at most 2 projects, you need to finish the project indexed 2 to get the maximum capital.
-Therefore, output the final maximized capital, which is 0 + 1 + 3 = 4.
-```
-
-
Example 2:
-
-```
-Input: k = 3, w = 0, profits = [1,2,3], capital = [0,1,2]
-Output: 6
-```
-
-
-
Constraints:
-
-
1 <= k <= 105
-
0 <= w <= 109
-
n == profits.length
-
n == capital.length
-
1 <= n <= 105
-
0 <= profits[i] <= 104
-
0 <= capital[i] <= 109
-
-
-## Solution:
-
-::: code-group
-
-```java [Java]
-import java.util.Arrays;
-import java.util.Collections;
-import java.util.PriorityQueue;
-
-class Pair implements Comparable {
- int capital;
- int profit;
-
- public Pair(int capital, int profit) {
- this.capital = capital;
- this.profit = profit;
- }
-
- @Override
- public int compareTo(Pair other) {
- return this.capital - other.capital;
- }
-}
-
-class Solution {
- public int findMaximizedCapital(int k, int w, int[] profits, int[] capital) {
- int n = profits.length;
- Pair[] pairs = new Pair[n];
-
- for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
- pairs[i] = new Pair(capital[i], profits[i]);
- }
-
- Arrays.sort(pairs);
- PriorityQueue pq = new PriorityQueue<>(Collections.reverseOrder());
- int i = 0;
-
- while (k > 0) {
- while (i < n && pairs[i].capital <= w) {
- pq.add(pairs[i].profit);
- i++;
- }
- if (pq.isEmpty()) {
- break;
- }
- w += pq.poll();
- k--;
- }
-
- return w;
- }
-}
-```
-
-:::
-
-### [_..._](#)
-
-```
-
-```
-
-
-
-[share]: https://graph.org/file/3ea5234dda646b71c574a.png
-[easy]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Easy-bright.svg
-[medium]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Medium-yellow.svg
-[hard]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Hard-red.svg
diff --git a/docs/solution/0501-0600/504 - Base 7.md b/docs/solution/0501-0600/504 - Base 7.md
deleted file mode 100644
index d5a41ceb..00000000
--- a/docs/solution/0501-0600/504 - Base 7.md
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,73 +0,0 @@
-# 504. Base 7 [![share]](https://leetcode.com/problems/base-7/)
-
-![][easy]
-
-## Problem Statement
-
-
Given an integer num, return a string of its base 7 representation.
-
-
Example 1:
-
-```
-Input: num = 100
-Output: "202"
-```
-
-
Example 2:
-
-```
-Input: num = -7
-Output: "-10"
-```
-
-
-
Constraints:
-
-
-107 <= num <= 107
-
-
-## Solution:
-
-::: code-group
-
-```rs [Rust]
-impl Solution {
- pub fn convert_to_base7(num: i32) -> String {
- if num == 0 {
- return "0".to_string();
- }
-
- let mut result = String::default();
- let is_negative = num < 0;
- let mut num = num.abs();
-
- while num > 0 {
- let rem = num % 7;
- result.push_str(&rem.to_string());
- num /= 7;
- }
-
- if is_negative {
- result.push('-');
- }
-
- result.chars().rev().collect()
- }
-}
-
-```
-
-:::
-
-### [_..._](#)
-
-```
-
-```
-
-
-
-[share]: https://graph.org/file/3ea5234dda646b71c574a.png
-[easy]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Easy-bright.svg
-[medium]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Medium-yellow.svg
-[hard]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Hard-red.svg
diff --git a/docs/solution/0501-0600/506 - Relative Ranks.md b/docs/solution/0501-0600/506 - Relative Ranks.md
deleted file mode 100644
index 38cc7157..00000000
--- a/docs/solution/0501-0600/506 - Relative Ranks.md
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,154 +0,0 @@
-# 506. Relative Ranks [![share]](https://leetcode.com/problems/relative-ranks)
-
-![][easy]
-
-## Problem Statement:
-
-You are given an integer array `score` of size `n`, where `score[i]` is the score of the ith athlete in a competition. All the scores are guaranteed to be **unique**.
-
-The athletes are **placed** based on their scores, where the `1st` place athlete has the highest score, the 2nd place athlete has the `2nd` highest score, and so on. The placement of each athlete determines their rank:
-
-- The 1st place athlete's rank is `"Gold Medal"`.
-- The 2nd place athlete's rank is `"Silver Medal"`.
-- The 3rd place athlete's rank is `"Bronze Medal"`.
-- For the 4th place to the nth place athlete, their rank is their placement number (i.e., the xth place athlete's rank is `"x"`).
-
-Return an array `answer` of size `n` where `answer[i]` is the **rank** of the ith athlete.
-
-### Example 1:
-
-```
-Input: score = [5,4,3,2,1]
-Output: ["Gold Medal","Silver Medal","Bronze Medal","4","5"]
-Explanation: The placements are [1st, 2nd, 3rd, 4th, 5th].
-```
-
-### Example 2:
-
-```
-Input: score = [10,3,8,9,4]
-Output: ["Gold Medal","5","Bronze Medal","Silver Medal","4"]
-Explanation: The placements are [1st, 5th, 3rd, 2nd, 4th].
-```
-
-### Constraints:
-
-- n == score.length
-- 1 <= n <= 104
-- 0 <= score[i] <= 106
-- All the values in `score` are **unique**.
-
-## Solution:
-
-::: code-group
-
-```go [Go]
-package main
-
-import (
- "fmt"
- "sort"
-)
-
-func findRelativeRanks(score []int) []string {
- sorted_score := append([]int(nil), score...)
- sort.Slice(sorted_score, func(i, j int) bool {
- return sorted_score[i] > sorted_score[j]
- })
-
- rank := make(map[int]string)
-
- for i, v := range sorted_score {
- switch i {
- case 0:
- rank[v] = "Gold Medal"
- case 1:
- rank[v] = "Silver Medal"
- case 2:
- rank[v] = "Bronze Medal"
- default:
- rank[v] = fmt.Sprintf("%d", i+1)
- }
- }
-
- result := make([]string, len(score))
- for i, v := range score {
- result[i] = rank[v]
- }
-
- return result
-}
-
-```
-
-```java [Java]
-import java.util.Arrays;
-import java.util.HashMap;
-import java.util.Map;
-
-public class RelativeRanks {
- public String[] findRelativeRanks(int[] score) {
- int[] temp = score.clone();
- Arrays.sort(temp);
- Map rankMap = new HashMap();
- String[] ranks = new String[score.length];
- for (int i = 0; i < score.length; i++) {
- if (i == score.length - 1)
- rankMap.put(temp[i], "Gold Medal");
- else if (i == score.length - 2)
- rankMap.put(temp[i], "Silver Medal");
- else if (i == score.length - 3)
- rankMap.put(temp[i], "Bronze Medal");
- else
- rankMap.put(temp[i], String.valueOf(score.length - i));
- }
- for (int i = 0; i < ranks.length; i++)
- ranks[i] = rankMap.get(score[i]);
- return ranks;
- }
-}
-
-```
-
-```rs [Rust]
-impl Solution {
- pub fn find_relative_ranks(score: Vec) -> Vec {
- let mut score_sorted = score.clone();
- score_sorted.sort_unstable_by(|a, b| b.cmp(a));
-
- let mut map = HashMap::new();
- for (i, s) in score_sorted.iter().enumerate() {
- map.insert(s, i + 1);
- }
-
- score
- .iter()
- .map(|s| {
- let rank = map.get(s).unwrap();
- match rank {
- 1 => "Gold Medal".to_string(),
- 2 => "Silver Medal".to_string(),
- 3 => "Bronze Medal".to_string(),
- _ => rank.to_string(),
- }
- })
- .collect()
- }
-}
-
-```
-
-:::
-
-### [_..._](#)
-
-```
-
-```
-
-
-
-[share]: https://img.icons8.com/external-anggara-blue-anggara-putra/20/000000/external-share-user-interface-basic-anggara-blue-anggara-putra-2.png
-[easy]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Easy-bright.svg
-[medium]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Medium-yellow.svg
-[hard]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Hard-red.svg
diff --git a/docs/solution/0501-0600/507 - Perfect Number.md b/docs/solution/0501-0600/507 - Perfect Number.md
deleted file mode 100644
index 0029183f..00000000
--- a/docs/solution/0501-0600/507 - Perfect Number.md
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,75 +0,0 @@
-# 507. Perfect Number [![share]](https://leetcode.com/problems/perfect-number/)
-
-![][easy]
-
-## Problem Statement
-
-
A perfect number is a positive integer that is equal to the sum of its positive divisors, excluding the number itself. A divisor of an integer x is an integer that can divide x evenly.
-
Given an integer n, return true if n is a perfect number, otherwise return false.
-
-
Example 1:
-
-```
-Input: num = 28
-Output: true
-Explanation: 28 = 1 + 2 + 4 + 7 + 14
-1, 2, 4, 7, and 14 are all divisors of 28.
-```
-
-
Example 2:
-
-```
-Input: num = 7
-Output: false
-```
-
-
-
Constraints:
-
-
1 <= num <= 108
-
-
-## Solution:
-
-::: code-group
-
-```rs [Rust]
-impl Solution {
- pub fn check_perfect_number(num: i32) -> bool {
- if num == 1 {
- return false;
- }
-
- let (mut sum, mut i) = (1, 2);
-
- while i * i <= num {
- // if i is a factor of num, add i and num / i to sum
- if num % i == 0 {
- sum += i;
- if i * i != num {
- sum += num / i;
- }
- }
- i += 1;
- }
-
- sum == num
- }
-}
-
-```
-
-:::
-
-### [_..._](#)
-
-```
-
-```
-
-
-
-[share]: https://graph.org/file/3ea5234dda646b71c574a.png
-[easy]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Easy-bright.svg
-[medium]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Medium-yellow.svg
-[hard]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Hard-red.svg
diff --git a/docs/solution/0501-0600/509 - Fibonacci Number.md b/docs/solution/0501-0600/509 - Fibonacci Number.md
deleted file mode 100644
index c10bc795..00000000
--- a/docs/solution/0501-0600/509 - Fibonacci Number.md
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,79 +0,0 @@
-# 509. Fibonacci Number [![share]](https://leetcode.com/problems/fibonacci-number/)
-
-![][easy]
-
-## Problem Statement:
-
-The **Fibonacci numbers**, commonly denoted `F(n)` form a sequence, called the **Fibonacci sequence**, such that each number is the sum of the two preceding ones, starting from `0` and `1`. That is,
-
-```
-F(0) = 0, F(1) = 1
-F(n) = F(n - 1) + F(n - 2), for n > 1.
-Given n, calculate F(n).
-```
-
-### Example 1:
-
-```
-Input: n = 2
-Output: 1
-Explanation: F(2) = F(1) + F(0) = 1 + 0 = 1.
-```
-
-### Example 2:
-
-```
-Input: n = 3
-Output: 2
-Explanation: F(3) = F(2) + F(1) = 1 + 1 = 2.
-```
-
-### Example 3:
-
-```
-Input: n = 4
-Output: 3
-Explanation: F(4) = F(3) + F(2) = 2 + 1 = 3.
-```
-
-### Constraints:
-
-- 0 <= n <= 30
-
-## Solution:
-
-::: code-group
-
-```java
-public int fib(int n) {
- if(n == 0 || n == 1)
- return n;
- int[] dp = new int[n + 1];
- dp[0] = 0;
- dp[1] = 1;
- for (int i = 2; i < n + 1; i++)
- dp[i] = dp[i - 1] + dp[i - 2];
- return dp[n];
-}
-
-public int fib2(int n) {
- if (n <= 1)
- return n;
- return fib(n - 1) + fib(n - 2);
-}
-```
-
-:::
-
-### [_..._](#)
-
-```
-
-```
-
-
-
-[share]: https://img.icons8.com/external-anggara-blue-anggara-putra/20/000000/external-share-user-interface-basic-anggara-blue-anggara-putra-2.png
-[easy]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Easy-bright.svg
-[medium]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Medium-yellow.svg
-[hard]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Hard-red.svg
diff --git a/docs/solution/0501-0600/516 - Longest Palindromic Subsequence.md b/docs/solution/0501-0600/516 - Longest Palindromic Subsequence.md
deleted file mode 100644
index 005de97c..00000000
--- a/docs/solution/0501-0600/516 - Longest Palindromic Subsequence.md
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,67 +0,0 @@
-# 516. Longest Palindromic Subsequence [![share]](https://leetcode.com/problems/longest-palindromic-subsequence/)
-
-![][medium]
-
-## Problem Statement:
-
-Given a string `s`, find the longest palindromic subsequence's length in `s`.
-
-A **subsequence** is a sequence that can be derived from another sequence by deleting some or no elements without changing the order of the remaining elements.
-
-### Example 1:
-
-```
-Input: s = "bbbab"
-Output: 4
-Explanation: One possible longest palindromic subsequence is "bbbb".
-```
-
-### Example 2:
-
-```
-Input: s = "cbbd"
-Output: 2
-Explanation: One possible longest palindromic subsequence is "bb".
-```
-
-### Constraints:
-
-- 1 <= s.length <= 1000
-- s consists only of lowercase English letters.
-
-## Solution:
-
-::: code-group
-
-```java
-public int longestPalindromeSubseq(String s) {
- String str1 = s,
- str2 = new StringBuilder(s).reverse().toString();
- int m = str1.length(),
- n = str2.length();
- int[][] dp = new int[m + 1][n + 1];
- for (int i = 0; i < m + 1; i++)
- for (int j = 0; j < n + 1; j++) {
- if (i == 0 || j == 0)
- dp[i][j] = 0;
- else if (str1.charAt(i - 1) == str2.charAt(j - 1))
- dp[i][j] = 1 + dp[i - 1][j - 1];
- else
- dp[i][j] = Math.max(dp[i - 1][j], dp[i][j - 1]);
- }
- return dp[m][n];
-}
-```
-
-:::
-
-### [_..._](#)
-
-```
-
-```
-
-
-
-[share]: https://img.icons8.com/external-anggara-blue-anggara-putra/20/000000/external-share-user-interface-basic-anggara-blue-anggara-putra-2.png
-[medium]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Medium-yellow.svg
diff --git a/docs/solution/0501-0600/518 - Coin Change 2.md b/docs/solution/0501-0600/518 - Coin Change 2.md
deleted file mode 100644
index ed6b91b0..00000000
--- a/docs/solution/0501-0600/518 - Coin Change 2.md
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,77 +0,0 @@
-# 518. Coin Change 2 [![share]](https://leetcode.com/problems/coin-change-2)
-
-![][medium]
-
-## Problem Statement:
-
-You are given an integer array `coins` representing coins of different denominations and an integer `amount` representing a total amount of money.
-
-Return the number of combinations that make up that amount. If that amount of money cannot be made up by any combination of the coins, return `0`.
-
-You may assume that you have an infinite number of each kind of coin.
-
-The answer is **guaranteed** to fit into a signed **32-bit** integer.
-
-### Example 1:
-
-```
-Input: amount = 5, coins = [1,2,5]
-Output: 4
-Explanation: there are four ways to make up the amount:
-5=5
-5=2+2+1
-5=2+1+1+1
-5=1+1+1+1+1
-```
-
-### Example 2:
-
-```
-Input: amount = 3, coins = [2]
-Output: 0
-Explanation: the amount of 3 cannot be made up just with coins of 2.
-```
-
-### Example 3:
-
-```
-Input: amount = 10, coins = [10]
-Output: 1
-```
-
-### Constraints:
-
-- 1 <= coins.length <= 300
-- 1 <= coins[i] <= 5000
-- All the values of coins are unique.
-- 0 <= amount <= 5000
-
-## Solution:
-
-::: code-group
-
-```java
-public int change(int amount, int[] coins) {
- int[] change = new int[amount + 1];
- change[0] = 1;
- for (int coin : coins)
- for (int i = coin; i < amount + 1; i++)
- change[i] += change[i - coin];
- return change[amount];
-}
-```
-
-:::
-
-### [_..._](#)
-
-```
-
-```
-
-
-
-[share]: https://img.icons8.com/external-anggara-blue-anggara-putra/20/000000/external-share-user-interface-basic-anggara-blue-anggara-putra-2.png
-[easy]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Easy-bright.svg
-[medium]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Medium-yellow.svg
-[hard]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Hard-red.svg
diff --git a/docs/solution/0501-0600/530 - Minimum Absolute Difference in BST.md b/docs/solution/0501-0600/530 - Minimum Absolute Difference in BST.md
deleted file mode 100644
index 8d1bb9a1..00000000
--- a/docs/solution/0501-0600/530 - Minimum Absolute Difference in BST.md
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,92 +0,0 @@
-# 530. Minimum Absolute Difference in BST [![share]](https://leetcode.com/problems/minimum-absolute-difference-in-bst/)
-
-![][easy]
-
-## Problem Statement
-
-
Given the root of a Binary Search Tree (BST), return the minimum absolute difference between the values of any two different nodes in the tree.
-
-## Solution:
-
-::: code-group
-
-```go [Go]
-package main
-
-func singleNonDuplicate(nums []int) int {
- res := 0
-
- for _, num := range nums {
- // a ^ a = 0
- // a ^ a ^ a = a
- // a ^ a ^ b = b
- // also position of a and b doesn't matter
- res ^= num
- }
-
- return res
-}
-
-```
-
-```rs [Rust]
-impl Solution {
- pub fn single_non_duplicate(nums: Vec) -> i32 {
- let mut res = 0;
-
- for num in nums {
- // a ^ a = 0
- // a ^ a ^ a = a
- // a ^ a ^ b = b
- // also position of a and b doesn't matter
- res ^= num;
- }
-
- res
- }
-}
-
-```
-
-:::
-
-### [_..._](#)
-
-```
-
-```
-
-
-
-[share]: https://graph.org/file/3ea5234dda646b71c574a.png
-[easy]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Easy-bright.svg
-[medium]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Medium-yellow.svg
-[hard]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Hard-red.svg
diff --git a/docs/solution/0501-0600/541 - Reverse String II.md b/docs/solution/0501-0600/541 - Reverse String II.md
deleted file mode 100644
index 67fb2652..00000000
--- a/docs/solution/0501-0600/541 - Reverse String II.md
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,63 +0,0 @@
-# 541. Reverse String II [![share]](https://leetcode.com/problems/reverse-string-ii/)
-
-![][easy]
-
-## Problem Statement:
-
-Given a string `s` and an integer `k`, reverse the first `k` characters for every 2k characters counting from the start of the string.
-
-If there are fewer than `k` characters left, reverse all of them. If there are less than `2k` but greater than or equal to `k` characters, then reverse the first `k` characters and leave the other as original.
-
-### Example 1:
-
-```
-Input: s = "abcdefg", k = 2
-Output: "bacdfeg"
-```
-
-### Example 2:
-
-```
-Input: s = "abcd", k = 2
-Output: "bacd"
-```
-
-### Constraints:
-
-- 1 <= s.length <= 104
-- s consists of only lowercase English letters.
-- 1 <= k <= 104
-
-## Solution:
-
-::: code-group
-
-```java
-public String reverseStr(String s, int k) {
- String res = "";
- int index = 0,
- flag = 0,
- len = s.length();
- while (index < len) {
- StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder(s.substring(index, (index + k > len) ? len : index + k));
- res += (flag++ % 2 == 0) ? sb.reverse() : sb;
- index += k;
- }
- return res;
-}
-```
-
-:::
-
-### [_..._](#)
-
-```
-
-```
-
-
-
-[share]: https://img.icons8.com/external-anggara-blue-anggara-putra/20/000000/external-share-user-interface-basic-anggara-blue-anggara-putra-2.png
-[easy]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Easy-bright.svg
-[medium]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Medium-yellow.svg
-[hard]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Hard-red.svg
diff --git a/docs/solution/0501-0600/543 - Diameter of Binary Tree.md b/docs/solution/0501-0600/543 - Diameter of Binary Tree.md
deleted file mode 100644
index ecdc8721..00000000
--- a/docs/solution/0501-0600/543 - Diameter of Binary Tree.md
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,90 +0,0 @@
-# 543. Diameter of Binary Tree [![share]](https://leetcode.com/problems/diameter-of-binary-tree/)
-
-![][easy]
-
-## Problem Statement:
-
-Given the `root` of a binary tree, return the length of the **diameter** of the tree.
-
-The diameter of a binary tree is the **length** of the longest path between any two nodes in a tree. This path may or may not pass through the `root`.
-
-The **length** of a path between two nodes is represented by the number of edges between them.
-
-### Example 1:
-
-```
-Input: root = [1,2,3,4,5]
-Output: 3
-```
-
-**Explanation:** 3 is the length of the path [4,2,1,3] or [5,2,1,3].
-
-### Example 2:
-
-```
-Input: root = [1,2]
-Output: 1
-```
-
-### Constraints:
-
-- The number of nodes in the tree is in the range [1, 104].
-- -100 <= Node.val <= 100
-
-## Solution:
-
-::: code-group
-
-```java
-public class DiameterOfBinaryTree {
- // Approach 1
- public static int diameterOfBinaryTree(TreeNode root) {
- if (root == null)
- return 0;
- int dia1 = diameterOfBinaryTree(root.left);
- int dia2 = diameterOfBinaryTree(root.right);
- int dia3 = MaximumDepthOfBinaryTree.maxDepth(root.left) + MaximumDepthOfBinaryTree.maxDepth(root.right) + 1;
- return Math.max(Math.max(dia1, dia2), dia3);
- }
-
- // Approach 2
- int diameter = 0;
-
- public int diameterOfBinaryTree2(TreeNode root) {
- getDiameter(root);
- return diameter - 1;
- }
-
- private int getDiameter(TreeNode root) {
- if (root == null)
- return 0;
- int leftHeight = getDiameter(root.left);
- int rightHeight = getDiameter(root.right);
- diameter = Math.max(diameter, leftHeight + rightHeight + 1);
- return Math.max(leftHeight, rightHeight) + 1;
- }
-}
-
-class MaximumDepthOfBinaryTree {
-
- public static int maxDepth(TreeNode root) {
- if (root == null)
- return 0;
- int depth = Math.max(maxDepth(root.left), maxDepth(root.right)) + 1;
- return depth;
- }
-}
-```
-
-:::
-
-### [_..._](#)
-
-```
-
-```
-
-
-
-[share]: https://img.icons8.com/external-anggara-blue-anggara-putra/20/000000/external-share-user-interface-basic-anggara-blue-anggara-putra-2.png
-[easy]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Easy-green.svg
diff --git a/docs/solution/0601-0700/605 - Can Place Flowers.md b/docs/solution/0601-0700/605 - Can Place Flowers.md
deleted file mode 100644
index 61a54720..00000000
--- a/docs/solution/0601-0700/605 - Can Place Flowers.md
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,112 +0,0 @@
-# 605. Can Place Flowers [![share]](https://leetcode.com/problems/can-place-flowers/)
-
-![][easy]
-
-## Problem Statement
-
-
You have a long flowerbed in which some of the plots are planted, and some are not. However, flowers cannot be planted in adjacent plots.
-
Given an integer array flowerbed containing 0's and 1's, where 0 means empty and 1 means not empty, and an integer n, return trueifnnew flowers can be planted in theflowerbedwithout violating the no-adjacent-flowers rule andfalseotherwise.
The number of the nodes in the tree will be in the range [1, 5000]
-
-200 <= Node.val <= 200
-
-
-## Solution:
-
-::: code-group
-
-```go [Go]
-package main
-
-import "strconv"
-
-// Definition for a binary tree node.
-type TreeNode struct {
- Val int
- Left *TreeNode
- Right *TreeNode
-}
-
-func findDuplicateSubtrees(root *TreeNode) []*TreeNode {
- // to store the hash value of subtrees
- hashMap := make(map[string]int)
- // to store the result
- res := make([]*TreeNode, 0)
- // traverse the tree
- traverse(root, hashMap, &res)
- return res
-}
-
-// traverse the tree
-func traverse(root *TreeNode, hashMap map[string]int, res *[]*TreeNode) string {
- // if the root is nil, return "#"
- if root == nil {
- return "#"
- }
- // traverse the left and right subtree
- left := traverse(root.Left, hashMap, res)
- right := traverse(root.Right, hashMap, res)
- // get the hash value of the subtree
- subTree := left + "," + right + "," + strconv.Itoa(root.Val)
- // if the hash value of the subtree is 1, it means that the subtree is duplicated
- if hashMap[subTree] == 1 {
- *res = append(*res, root)
- }
- // add the hash value of the subtree to the hashMap
- hashMap[subTree]++
- return subTree
-}
-
-```
-
-:::
-
-### [_..._](#)
-
-```
-
-```
-
-
-
-[share]: https://graph.org/file/3ea5234dda646b71c574a.png
-[easy]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Easy-bright.svg
-[medium]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Medium-yellow.svg
-[hard]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Hard-red.svg
diff --git a/docs/solution/0601-0700/653 - Two Sum IV - Input is a BST.md b/docs/solution/0601-0700/653 - Two Sum IV - Input is a BST.md
deleted file mode 100644
index 247fa077..00000000
--- a/docs/solution/0601-0700/653 - Two Sum IV - Input is a BST.md
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,70 +0,0 @@
-# 653. Two Sum IV - Input is a BST [![share]](https://leetcode.com/problems/two-sum-iv-input-is-a-bst/)
-
-![][easy]
-
-## Problem Statement:
-
-Given the `root` of a Binary Search Tree and a target number `k`, return `true` if there exist two elements in the BST such that their sum is equal to the given target.
-
-### Example 1:
-
-
-
-```
-Input: root = [5,3,6,2,4,null,7], k = 9
-Output: true
-```
-
-### Example 2:
-
-
-
-```
-Input: root = [5,3,6,2,4,null,7], k = 28
-Output: false
-```
-
-### Constraints:
-
-- The number of nodes in the tree is in the range [1, 104].
-- -104 <= Node.val <= 104
-- root is guaranteed to be a valid binary search tree.
-- -105 <= k <= 105
-
-## Solution:
-
-::: code-group
-
-```java
-public class TwoSumIV {
- public boolean findTarget(TreeNode root, int sum) {
- HashSet set = new HashSet<>();
- return findTarget(root, sum, set);
- }
-
- private boolean findTarget(TreeNode root, int sum, HashSet set) {
- if (root == null)
- return false;
- if (findTarget(root.left, sum, set) == true)
- return true;
- if (set.contains(sum - root.val))
- return true;
- else
- set.add(root.val);
- return findTarget(root.right, sum, set);
- }
-}
-```
-
-:::
-
-### [_..._](#)
-
-```
-
-```
-
-
-
-[share]: https://img.icons8.com/external-anggara-blue-anggara-putra/20/000000/external-share-user-interface-basic-anggara-blue-anggara-putra-2.png
-[easy]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Easy-green.svg
diff --git a/docs/solution/0601-0700/695 - Max Area of Island.md b/docs/solution/0601-0700/695 - Max Area of Island.md
deleted file mode 100644
index 7768900a..00000000
--- a/docs/solution/0601-0700/695 - Max Area of Island.md
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,87 +0,0 @@
-# 695. Max Area of Island [![share]](https://leetcode.com/problems/max-area-of-island/)
-
-![][medium]
-
-## Problem Statement
-
-
You are given an m x n binary matrix grid. An island is a group of 1's (representing land) connected 4-directionally (horizontal or vertical.) You may assume all four edges of the grid are surrounded by water.
-
The area of an island is the number of cells with a value 1 in the island.
-
Return the maximum area of an island in grid. If there is no island, return 0.
-
-
Example 1:
-
-
-```
-Input: grid = [[0,0,1,0,0,0,0,1,0,0,0,0,0],[0,0,0,0,0,0,0,1,1,1,0,0,0],[0,1,1,0,1,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0],[0,1,0,0,1,1,0,0,1,0,1,0,0],[0,1,0,0,1,1,0,0,1,1,1,0,0],[0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,1,0,0],[0,0,0,0,0,0,0,1,1,1,0,0,0],[0,0,0,0,0,0,0,1,1,0,0,0,0]]
-Output: 6
-Explanation: The answer is not 11, because the island must be connected 4-directionally.
-```
-
-
-
-## Solution:
-
-::: code-group
-
-```go [Go]
-package main
-
-import "math"
-
-// Definition for a binary tree node.
-type TreeNode struct {
- Val int
- Left *TreeNode
- Right *TreeNode
-}
-
-func minDiffInBST(root *TreeNode) int {
- var (
- minDiff = math.MaxInt
- prev = -1
- )
-
- var dfs func(*TreeNode)
- dfs = func(node *TreeNode) {
- if node == nil {
- return
- }
-
- dfs(node.Left)
-
- if prev != -1 {
- minDiff = int(math.Min(float64(minDiff), float64(node.Val-prev)))
- }
- prev = node.Val
-
- dfs(node.Right)
- }
-
- dfs(root)
-
- return minDiff
-}
-
-```
-
-:::
-
-### [_..._](#)
-
-```
-
-```
-
-
-
-[share]: https://graph.org/file/3ea5234dda646b71c574a.png
-[easy]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Easy-bright.svg
-[medium]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Medium-yellow.svg
-[hard]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Hard-red.svg
diff --git a/docs/solution/0801-0900/875 - Koko Eating Bananas.md b/docs/solution/0801-0900/875 - Koko Eating Bananas.md
deleted file mode 100644
index 0c9123cc..00000000
--- a/docs/solution/0801-0900/875 - Koko Eating Bananas.md
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,104 +0,0 @@
-# 875. Koko Eating Bananas [![share]](https://leetcode.com/problems/koko-eating-bananas/)
-
-![][medium]
-
-## Problem Statement
-
-
Koko loves to eat bananas. There are n piles of bananas, the ith pile has piles[i] bananas. The guards have gone and will come back in h hours.
-
Koko can decide her bananas-per-hour eating speed of k. Each hour, she chooses some pile of bananas and eats k bananas from that pile. If the pile has less than k bananas, she eats all of them instead and will not eat any more bananas during this hour.
-
Koko likes to eat slowly but still wants to finish eating all the bananas before the guards return.
-
Return the minimum integerksuch that she can eat all the bananas withinhhours.
-
-## Solution:
-
-::: code-group
-
-```rs [Rust]
-impl Solution {
- pub fn min_eating_speed(piles: Vec, h: i32) -> i32 {
- let mut min_spd = 1;
- let mut max_spd = piles.iter().max().unwrap().clone();
-
- while min_spd < max_spd {
- let speed = (min_spd + max_spd) / 2;
- let hours = piles
- .iter()
- .fold(0, |subtotal, &pile| subtotal + ((pile + speed - 1) / speed));
-
- if hours > h {
- min_spd = speed + 1;
- } else {
- max_spd = speed;
- }
- }
-
- min_spd
- }
-}
-
-```
-
-```py [Python]
-import math
-
-
-class Solution:
- def minEatingSpeed(self, p: list[int], h: int) -> int:
- left, right = 1, max(p)
-
- while left <= right:
- m = (left+right)//2
- # t = sum((i+m-1)//m for i in p)
- # t = sum(-(-i//m) for i in p)
- t = sum(math.ceil(i/m) for i in p)
- if t > h:
- left = m+1
- else:
- right = m-1
- return left
-
-```
-
-:::
-
-### [_..._](#)
-
-```
-
-```
-
-
-
-[share]: https://graph.org/file/3ea5234dda646b71c574a.png
-[easy]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Easy-bright.svg
-[medium]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Medium-yellow.svg
-[hard]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Hard-red.svg
diff --git a/docs/solution/0801-0900/876 - Middle of the Linked List.md b/docs/solution/0801-0900/876 - Middle of the Linked List.md
deleted file mode 100644
index 9c5a7663..00000000
--- a/docs/solution/0801-0900/876 - Middle of the Linked List.md
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,65 +0,0 @@
-# 876. Middle of the Linked List [![share]](https://leetcode.com/problems/middle-of-the-linked-list/)
-
-![][easy]
-
-## Problem Statement:
-
-Given the `head` of a singly linked list, return the middle node of the linked list.
-
-If there are two middle nodes, return **the second middle** node.
-
-### Example 1:
-
-
-
-```
-Input: head = [1,2,3,4,5]
-Output: [3,4,5]
-Explanation: The middle node of the list is node 3.
-```
-
-### Example 2:
-
-
-
-```
-Input: head = [1,2,3,4,5,6]
-Output: [4,5,6]
-Explanation: Since the list has two middle nodes with values 3 and 4, we return the second one.
-```
-
-### Constraints:
-
-- The number of nodes in the list is in the range `[1, 100]`.
-- 1 <= Node.val <= 100
-
-## Solution:
-
-::: code-group
-
-```java
-public ListNode middleNode(ListNode head) {
- ListNode slowPtr = head,
- fastPtr = head;
- while (fastPtr != null && fastPtr.next != null) {
- slowPtr = slowPtr.next;
- fastPtr = fastPtr.next.next;
- }
- return slowPtr;
-}
-```
-
-:::
-
-### [_..._](#)
-
-```
-
-```
-
-
-
-[share]: https://img.icons8.com/external-anggara-blue-anggara-putra/20/000000/external-share-user-interface-basic-anggara-blue-anggara-putra-2.png
-[easy]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Easy-bright.svg
-[medium]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Medium-yellow.svg
-[hard]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Hard-red.svg
diff --git a/docs/solution/0801-0900/888 - Fair Candy Swap.md b/docs/solution/0801-0900/888 - Fair Candy Swap.md
deleted file mode 100644
index a14af286..00000000
--- a/docs/solution/0801-0900/888 - Fair Candy Swap.md
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,90 +0,0 @@
-# 888. Fair Candy Swap [![share]](https://leetcode.com/problems/fair-candy-swap)
-
-![][easy]
-
-## Problem Statement:
-
-Alice and Bob have a different total number of candies. You are given two integer arrays `aliceSizes` and `bobSizes` where `aliceSizes[i]` is the number of candies of the ith box of candy that Alice has and bobSizes[j] is the number of candies of the jth box of candy that Bob has.
-
-Since they are friends, they would like to exchange one candy box each so that after the exchange, they both have the same total amount of candy. The total amount of candy a person has is the sum of the number of candies in each box they have.
-
-Return an integer array `answer` where `answer[0]` is the number of candies in the box that Alice must exchange, and `answer[1]` is the number of candies in the box that Bob must exchange. If there are multiple answers, you may **return any** one of them. It is guaranteed that at least one answer exists.
-
-### Example 1:
-
-```
-Input: aliceSizes = [1,1], bobSizes = [2,2]
-Output: [1,2]
-```
-
-### Example 2:
-
-```
-Input: aliceSizes = [1,2], bobSizes = [2,3]
-Output: [1,2]
-```
-
-### Example 3:
-
-```
-Input: aliceSizes = [2], bobSizes = [1,3]
-Output: [2,3]
-```
-
-### Constraints:
-
-- 1 <= aliceSizes.length, bobSizes.length <= 104
-- 1 <= aliceSizes[i], bobSizes[j] <= 105
-- Alice and Bob have a different total number of candies.
-- There will be at least one valid answer for the given input.
-
-## Solution:
-
-::: code-group
-
-```java
-public int[] fairCandySwap(int[] aliceSizes, int[] bobSizes) {
- int[] swap = new int[2];
- int aliceSum = 0,
- bobSum = 0,
- aliceIndex = 0,
- bobIndex = 0;
-
- for (int i : aliceSizes)
- aliceSum += i;
- for (int i : bobSizes)
- bobSum += i;
-
- Arrays.sort(aliceSizes);
- Arrays.sort(bobSizes);
-
- while (aliceIndex < aliceSizes.length && bobIndex < bobSizes.length) {
- int aliceTotal = aliceSum - aliceSizes[aliceIndex] + bobSizes[bobIndex],
- bobTotal = bobSum - bobSizes[bobIndex] + aliceSizes[aliceIndex];
- if (aliceTotal == bobTotal) {
- swap[0] = aliceSizes[aliceIndex];
- swap[1] = bobSizes[bobIndex];
- return swap;
- } else if (aliceTotal > bobTotal)
- aliceIndex++;
- else
- bobIndex++;
- }
- return swap;
-}
-```
-
-:::
-
-### [_..._](#)
-
-```
-
-```
-
-
-
-[share]: https://img.icons8.com/external-anggara-blue-anggara-putra/20/000000/external-share-user-interface-basic-anggara-blue-anggara-putra-2.png
-[easy]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Easy-bright.svg
-[medium]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Medium-yellow.svg
-[hard]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Hard-red.svg
diff --git a/docs/solution/0901-1000/912 - Sort an Array.md b/docs/solution/0901-1000/912 - Sort an Array.md
deleted file mode 100644
index 298e352d..00000000
--- a/docs/solution/0901-1000/912 - Sort an Array.md
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,142 +0,0 @@
-# 912. Sort an Array [![share]](https://leetcode.com/problems/sort-an-array/)
-
-![][medium]
-
-## Problem Statement
-
-
Given an array of integers nums, sort the array in ascending order and return it.
-
You must solve the problem without using any built-in functions in O(nlog(n)) time complexity and with the smallest space complexity possible.
-
-
Example 1:
-
-```
-Input: nums = [5,2,3,1]
-Output: [1,2,3,5]
-Explanation: After sorting the array, the positions of some numbers are not changed (for example, 2 and 3), while the positions of other numbers are changed (for example, 1 and 5).
-```
-
-
Example 2:
-
-```
-Input: nums = [5,1,1,2,0,0]
-Output: [0,0,1,1,2,5]
-Explanation: Note that the values of nums are not necessairly unique.
-```
-
-
-
Constraints:
-
-
1 <= nums.length <= 5 * 104
-
-5 * 104 <= nums[i] <= 5 * 104
-
-
-## Solution:
-
-::: code-group
-
-```go [Go]
-package main
-
-func sortArray(nums []int) []int {
- quickSort(nums, 0, len(nums)-1)
-
- return nums
-}
-
-func quickSort(nums []int, start, end int) {
- if start >= end {
- return
- }
-
- pivot := partition(nums, start, end)
- quickSort(nums, start, pivot-1)
- quickSort(nums, pivot+1, end)
-}
-
-func partition(arr []int, start int, end int) int {
- pivot := arr[end]
- i := start
-
- for j := start; j < end; j++ {
- if arr[j] < pivot {
- arr[i], arr[j] = arr[j], arr[i]
- i++
- }
- }
-
- arr[i], arr[end] = arr[end], arr[i]
-
- return i
-}
-
-```
-
-```rs [Rust]
-impl Solution {
- pub fn sort_array(nums: Vec) -> Vec {
- let len = nums.len() as i32;
- let mut nums = nums;
-
- Self::quick_sort(&mut nums, 0, len - 1);
-
- nums
- }
-
- fn quick_sort(nums: &mut Vec, start: i32, end: i32) {
- if start >= end {
- return;
- }
-
- let pivot = Self::partition(nums, start, end);
- Self::quick_sort(nums, start, pivot - 1);
- Self::quick_sort(nums, pivot + 1, end);
- }
-
- fn partition(nums: &mut Vec, start: i32, end: i32) -> i32 {
- let pivot_index = Self::choose_pivot(nums, start as usize, end as usize);
- let pivot = nums[pivot_index as usize];
- nums.swap(pivot_index as usize, end as usize);
-
- let mut i = start;
-
- for j in start..end {
- if nums[j as usize] < pivot {
- nums.swap(i as usize, j as usize);
- i += 1;
- }
- }
-
- nums.swap(i as usize, end as usize);
-
- i
- }
-
- // this is to optimize the pivot selection
- fn choose_pivot(nums: &mut Vec, start: usize, end: usize) -> usize {
- let mid = start + (end - start) / 2;
- if nums[start] <= nums[mid] && nums[mid] <= nums[end] {
- mid
- } else if nums[start] <= nums[end] && nums[end] <= nums[mid] {
- end
- } else {
- start
- }
- }
-}
-
-```
-
-:::
-
-### [_..._](#)
-
-```
-
-```
-
-
-
-[share]: https://graph.org/file/3ea5234dda646b71c574a.png
-[easy]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Easy-bright.svg
-[medium]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Medium-yellow.svg
-[hard]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Hard-red.svg
diff --git a/docs/solution/0901-1000/944 - Delete Columns to Make Sorted.md b/docs/solution/0901-1000/944 - Delete Columns to Make Sorted.md
deleted file mode 100644
index 70d78ccc..00000000
--- a/docs/solution/0901-1000/944 - Delete Columns to Make Sorted.md
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,113 +0,0 @@
-# 944. Delete Columns to Make Sorted [![share]](https://leetcode.com/problems/delete-columns-to-make-sorted/)
-
-![][easy]
-
-## Problem Statement
-
-
You are given an array of n strings strs, all of the same length.
-
-
The strings can be arranged such that there is one on each line, making a grid.
-
-
-
For example, strs = ["abc", "bce", "cae"] can be arranged as follows:
-
-
-
-abc
-bce
-cae
-
-
-
You want to delete the columns that are not sorted lexicographically. In the above example (0-indexed), columns 0 ('a', 'b', 'c') and 2 ('c', 'e', 'e') are sorted, while column 1 ('b', 'c', 'a') is not, so you would delete column 1.
-
-
Return the number of columns that you will delete.
-
-
-
Example 1:
-
-
-Input: strs = ["cba","daf","ghi"]
-Output: 1
-Explanation: The grid looks as follows:
- cba
- daf
- ghi
-Columns 0 and 2 are sorted, but column 1 is not, so you only need to delete 1 column.
-
-
-
Example 2:
-
-
-Input: strs = ["a","b"]
-Output: 0
-Explanation: The grid looks as follows:
- a
- b
-Column 0 is the only column and is sorted, so you will not delete any columns.
-
-
-
Example 3:
-
-
-Input: strs = ["zyx","wvu","tsr"]
-Output: 3
-Explanation: The grid looks as follows:
- zyx
- wvu
- tsr
-All 3 columns are not sorted, so you will delete all 3.
-
-
-
-
Constraints:
-
-
-
n == strs.length
-
1 <= n <= 100
-
1 <= strs[i].length <= 1000
-
strs[i] consists of lowercase English letters.
-
-
-## Solution:
-
-::: code-group
-
-```java
-class Solution {
- public int minDeletionSize(String[] strs) {
- if (strs == null || strs.length == 0)
- return 0;
-
- int count = 0;
-
- for (int i = 0; i < strs[0].length(); i++) {
- char ch = strs[0].charAt(i);
- for (int j = 0; j < strs.length; j++) {
- char curr = strs[j].charAt(i);
- if (curr < ch) {
- count++;
- break;
- }
- ch = curr;
- }
- }
-
- return count;
- }
-}
-```
-
-:::
-
-### [_..._](#)
-
-```
-
-```
-
-
-
-[share]: https://graph.org/file/3ea5234dda646b71c574a.png
-[easy]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Easy-bright.svg
-[medium]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Medium-yellow.svg
-[hard]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Hard-red.svg
diff --git a/docs/solution/0901-1000/958 - Check Completeness of a Binary Tree.md b/docs/solution/0901-1000/958 - Check Completeness of a Binary Tree.md
deleted file mode 100644
index a10d2b50..00000000
--- a/docs/solution/0901-1000/958 - Check Completeness of a Binary Tree.md
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,85 +0,0 @@
-# 958. Check Completeness of a Binary Tree [![share]](https://leetcode.com/problems/check-completeness-of-a-binary-tree/)
-
-![][medium]
-
-## Problem Statement
-
-
Given the root of a binary tree, determine if it is a complete binary tree.
-
In a complete binary tree, every level, except possibly the last, is completely filled, and all nodes in the last level are as far left as possible. It can have between 1 and 2h nodes inclusive at the last level h.
-
-
Example 1:
-
-
-```
-Input: root = [1,2,3,4,5,6]
-Output: true
-Explanation: Every level before the last is full (ie. levels with node-values {1} and {2, 3}), and all nodes in the last level ({4, 5, 6}) are as far left as possible.
-```
-
-
Example 2:
-
-
-```
-Input: root = [1,2,3,4,5,null,7]
-Output: false
-Explanation: The node with value 7 isn't as far left as possible.
-```
-
-
-
Constraints:
-
-
The number of nodes in the tree is in the range [1, 100].
-
1 <= Node.val <= 1000
-
-
-## Solution:
-
-::: code-group
-
-```go [Go]
-package main
-
-// Definition for a binary tree node.
-type TreeNode struct {
- Val int
- Left *TreeNode
- Right *TreeNode
-}
-
-func isCompleteTree(root *TreeNode) bool {
- if root == nil {
- return true
- }
-
- q := []*TreeNode{root}
-
- for q[0] != nil {
- q = append(q, q[0].Left, q[0].Right)
- q = q[1:]
- }
-
- for _, node := range q {
- if node != nil {
- return false
- }
- }
-
- return true
-}
-
-```
-
-:::
-
-### [_..._](#)
-
-```
-
-```
-
-
-
-[share]: https://graph.org/file/3ea5234dda646b71c574a.png
-[easy]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Easy-bright.svg
-[medium]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Medium-yellow.svg
-[hard]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Hard-red.svg
diff --git a/docs/solution/0901-1000/997 - Find the Town Judge.md b/docs/solution/0901-1000/997 - Find the Town Judge.md
deleted file mode 100644
index 3d2fba60..00000000
--- a/docs/solution/0901-1000/997 - Find the Town Judge.md
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,82 +0,0 @@
-# 997. Find the Town Judge [![share]](https://leetcode.com/problems/find-the-town-judge/)
-
-![][easy]
-
-## Problem Statement
-
-
In a town, there are n people labeled from 1 to n. There is a rumor that one of these people is secretly the town judge.
-
If the town judge exists, then:
-
-
The town judge trusts nobody.
-
Everybody (except for the town judge) trusts the town judge.
-
There is exactly one person that satisfies properties 1 and 2.
-
-
You are given an array trust where trust[i] = [ai, bi] representing that the person labeled ai trusts the person labeled bi.
-
Return the label of the town judge if the town judge exists and can be identified, or return -1 otherwise.
-
-## Solution:
-
-::: code-group
-
-```py [Python]
-class Solution:
- def findJudge(self, n: int, trust: list[list[int]]) -> int:
- count = [0] * (n + 1)
- for i, j in trust:
- count[i] -= 1
- count[j] += 1
-
- for i in range(1, n + 1):
- if count[i] == n - 1:
- return i
-
- return -1
-
-```
-
-:::
-
-### [_..._](#)
-
-```
-
-```
-
-
-
-[share]: https://graph.org/file/3ea5234dda646b71c574a.png
-[easy]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Easy-bright.svg
-[medium]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Medium-yellow.svg
-[hard]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Hard-red.svg
diff --git a/docs/solution/1001-1100/1011 - Capacity To Ship Packages Within D Days.md b/docs/solution/1001-1100/1011 - Capacity To Ship Packages Within D Days.md
deleted file mode 100644
index dc48e0f6..00000000
--- a/docs/solution/1001-1100/1011 - Capacity To Ship Packages Within D Days.md
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,126 +0,0 @@
-# 1011. Capacity To Ship Packages Within D Days [![share]](https://leetcode.com/problems/capacity-to-ship-packages-within-d-days/)
-
-![][medium]
-
-## Problem Statement
-
-
A conveyor belt has packages that must be shipped from one port to another within days days.
-
The ith package on the conveyor belt has a weight of weights[i]. Each day, we load the ship with packages on the conveyor belt (in the order given by weights). We may not load more weight than the maximum weight capacity of the ship.
-
Return the least weight capacity of the ship that will result in all the packages on the conveyor belt being shipped within days days.
-
-
Example 1:
-
-```
-
-Input: weights = [1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10], days = 5
-Output: 15
-Explanation: A ship capacity of 15 is the minimum to ship all the packages in 5 days like this:
-1st day: 1, 2, 3, 4, 5
-2nd day: 6, 7
-3rd day: 8
-4th day: 9
-5th day: 10
-
-Note that the cargo must be shipped in the order given, so using a ship of capacity 14 and splitting the packages into parts like (2, 3, 4, 5), (1, 6, 7), (8), (9), (10) is not allowed.
-```
-
-
Example 2:
-
-```
-
-Input: weights = [3,2,2,4,1,4], days = 3
-Output: 6
-Explanation: A ship capacity of 6 is the minimum to ship all the packages in 3 days like this:
-1st day: 3, 2
-2nd day: 2, 4
-3rd day: 1, 4
-```
-
-
-
-::: details _Click to open Hints_
-
-- Binary search on the answer. We need a function possible(capacity) which returns true if and only if we can do the task in D days.
-
-:::
-
-## Solution:
-
-::: code-group
-
-```rs [Rust]
-impl Solution {
- pub fn ship_within_days(weights: Vec, days: i32) -> i32 {
- let mut min_cap = 0; // it is the max of all weights
- let mut max_cap = 0; // sum of all weights
-
- for w in weights.iter() {
- // assign the max of all weights to min_cap
- min_cap = min_cap.max(*w);
- // add all the weights to right
- max_cap += w;
- }
-
- // binary search
- while min_cap < max_cap {
- let mid = (min_cap + max_cap) / 2;
- let mut days_used = 1;
- let mut cur_cap = 0;
-
- // for each weight, if the current capacity + weight is greater than mid,
- // then we need to use another day
- // otherwise, we can use the current day
- for w in weights.iter() {
- if cur_cap + w > mid {
- days_used += 1;
- cur_cap = 0;
- }
- cur_cap += w;
- }
-
- // if days_used is greater than days, then we need to increase the capacity
- if days_used > days {
- min_cap = mid + 1;
- } else {
- max_cap = mid;
- }
- }
-
- min_cap
- }
-}
-
-```
-
-:::
-
-### [_..._](#)
-
-```
-
-```
-
-
-
-[share]: https://graph.org/file/3ea5234dda646b71c574a.png
-[easy]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Easy-bright.svg
-[medium]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Medium-yellow.svg
-[hard]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Hard-red.svg
diff --git a/docs/solution/1001-1100/1029 - Two City Scheduling.md b/docs/solution/1001-1100/1029 - Two City Scheduling.md
deleted file mode 100644
index 093605d3..00000000
--- a/docs/solution/1001-1100/1029 - Two City Scheduling.md
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,89 +0,0 @@
-# 1029. Two City Scheduling [![share]](https://leetcode.com/problems/two-city-scheduling/)
-
-![][medium]
-
-## Problem Statement
-
-
A company is planning to interview 2n people. Given the array costs where costs[i] = [aCosti, bCosti], the cost of flying the ith person to city a is aCosti, and the cost of flying the ith person to city b is bCosti.
-
Return the minimum cost to fly every person to a city such that exactly n people arrive in each city.
-
-
Example 1:
-
-```
-Input: costs = [[10,20],[30,200],[400,50],[30,20]]
-Output: 110
-Explanation:
-The first person goes to city A for a cost of 10.
-The second person goes to city A for a cost of 30.
-The third person goes to city B for a cost of 50.
-The fourth person goes to city B for a cost of 20.
-
-The total minimum cost is 10 + 30 + 50 + 20 = 110 to have half the people interviewing in each city.
-```
-
-
-
-## Solution:
-
-::: code-group
-
-```rs [Rust]
-impl Solution {
- pub fn two_city_sched_cost(costs: Vec>) -> i32 {
- let mut costs = costs;
-
- let mut total = 0;
- let n = costs.len() / 2;
-
- // sort by a gain which company has
- // by sending a person to city A and not to city B
- costs.sort_by(|a, b| (a[0] - a[1]).cmp(&(b[0] - b[1])));
-
- // to optimize the company expenses,
- // send the first n persons to the city A
- // and the others to the city B
- for i in 0..n {
- total += costs[i][0] + costs[i + n][1]; // city A + city B
- }
-
- total
- }
-}
-
-```
-
-:::
-
-### [_..._](#)
-
-```
-
-```
-
-
-
-[share]: https://graph.org/file/3ea5234dda646b71c574a.png
-[easy]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Easy-bright.svg
-[medium]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Medium-yellow.svg
-[hard]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Hard-red.svg
diff --git a/docs/solution/1001-1100/1047 - Remove All Adjacent Duplicates In String.md b/docs/solution/1001-1100/1047 - Remove All Adjacent Duplicates In String.md
deleted file mode 100644
index 8c97d742..00000000
--- a/docs/solution/1001-1100/1047 - Remove All Adjacent Duplicates In String.md
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,76 +0,0 @@
-# 1047. Remove All Adjacent Duplicates In String [![share]](https://leetcode.com/problems/remove-all-adjacent-duplicates-in-string/)
-
-![][easy]
-
-## Problem Statement:
-
-You are given a string `s` consisting of lowercase English letters. A **duplicate removal** consists of choosing two **adjacent** and **equal** letters and removing them.
-
-We repeatedly make **duplicate removals** on `s` until we no longer can.
-
-Return the final string after all such duplicate removals have been made. It can be proven that the answer is **unique**.
-
-### Example 1:
-
-```
-Input: s = "abbaca"
-Output: "ca"
-```
-
-### Explanation:
-
-```
-For example, in "abbaca" we could remove "bb" since the letters are adjacent and equal, and this is the only possible move. The result of this move is that the string is "aaca", of which only "aa" is possible, so the final string is "ca".
-```
-
-### Example 2:
-
-```
-Input: s = "azxxzy"
-Output: "ay"
-```
-
-### Constraints:
-
-- 1 <= s.length <= 105
-- s consists of lowercase English letters.
-
-## Solution:
-
-::: code-group
-
-```java
-public class RemoveAllAdjacentDuplicatesInString {
- public static String removeDuplicates(String s) {
- Stack stk = new Stack<>();
- for (char ch : s.toCharArray()) {
- if (!stk.isEmpty() && ch == stk.peek())
- stk.pop();
- else
- stk.push(ch);
- }
- StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
- for (char ch : stk)
- sb.append(ch);
- return sb.toString();
- }
-
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- System.out.println(removeDuplicates("azxxzy"));
- System.out.println(removeDuplicates("abbaca"));
- }
-}
-```
-
-:::
-
-### [_..._](#)
-
-```
-
-```
-
-
-
-[share]: https://img.icons8.com/external-anggara-blue-anggara-putra/20/000000/external-share-user-interface-basic-anggara-blue-anggara-putra-2.png
-[medium]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Medium-yellow.svg
diff --git a/docs/solution/1001-1100/1092 - Shortest Common Supersequence.md b/docs/solution/1001-1100/1092 - Shortest Common Supersequence.md
deleted file mode 100644
index 3a6b3a0e..00000000
--- a/docs/solution/1001-1100/1092 - Shortest Common Supersequence.md
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,95 +0,0 @@
-# 1092. Shortest Common Supersequence [![share]](https://leetcode.com/problems/shortest-common-supersequence/)
-
-![][hard]
-
-## Problem Statement:
-
-Given two strings `str1` and `str2`, return the shortest string that has both `str1` and `str2` as subsequences. If there are multiple valid strings, return any of them.
-
-A string `s` is a subsequence of string `t` if deleting some number of characters from `t` (possibly `0`) results in the string `s`.
-
-### Example 1:
-
-```
-Input: str1 = "abac", str2 = "cab"
-Output: "cabac"
-Explanation:
-str1 = "abac" is a subsequence of "cabac" because we can delete the first "c".
-str2 = "cab" is a subsequence of "cabac" because we can delete the last "ac".
-The answer provided is the shortest such string that satisfies these properties.
-```
-
-### Example 2:
-
-```
-Input: str1 = "aaaaaaaa", str2 = "aaaaaaaa"
-Output: "aaaaaaaa"
-```
-
-### Constraints:
-
-- 1 <= str1.length, str2.length <= 1000
-- `str1` and `str2` consist of lowercase English letters.
-
-## Solution:
-
-::: code-group
-
-```java
-public String shortestCommonSupersequence(String str1, String str2) {
- int m = str1.length(),
- n = str2.length();
- int[][] dp = new int[m + 1][n + 1];
- for (int i = 0; i < m + 1; i++)
- for (int j = 0; j < n + 1; j++) {
- if (i == 0)
- dp[i][j] = j;
- else if (j == 0)
- dp[i][j] = i;
- else if (str1.charAt(i - 1) == str2.charAt(j - 1))
- dp[i][j] = 1 + dp[i - 1][j - 1];
- else
- dp[i][j] = 1 + Math.min(dp[i - 1][j], dp[i][j - 1]);
- }
- int i = m, j = n;
- StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
- while (i > 0 && j > 0) {
- if (str1.charAt(i - 1) == str2.charAt(j - 1)) {
- sb.append(str1.charAt(i - 1));
- i--;
- j--;
- } else if (dp[i - 1][j] < dp[i][j - 1]) {
- sb.append(str1.charAt(i - 1));
- i--;
- }
- else {
- sb.append(str2.charAt(j - 1));
- j--;
- }
- }
- while(i > 0) {
- sb.append(str1.charAt(i - 1));
- i--;
- }
- while(j > 0) {
- sb.append(str2.charAt(j - 1));
- j--;
- }
- return sb.reverse().toString();
-}
-```
-
-:::
-
-### [_..._](#)
-
-```
-
-```
-
-
-
-[share]: https://img.icons8.com/external-anggara-blue-anggara-putra/20/000000/external-share-user-interface-basic-anggara-blue-anggara-putra-2.png
-[easy]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Easy-bright.svg
-[medium]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Medium-yellow.svg
-[hard]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Hard-red.svg
diff --git a/docs/solution/1101-1200/1108 - Defanging an IP Address.md b/docs/solution/1101-1200/1108 - Defanging an IP Address.md
deleted file mode 100644
index ab68fe15..00000000
--- a/docs/solution/1101-1200/1108 - Defanging an IP Address.md
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,66 +0,0 @@
-# 1108. Defanging an IP Address [![share]](https://leetcode.com/problems/defanging-an-ip-address/)
-
-![][easy]
-
-## Problem Statement
-
-
Given a valid (IPv4) IP address, return a defanged version of that IP address.
-
A defanged IP address replaces every period "." with "[.]".
-
-## Solution:
-
-::: code-group
-
-```rs [Rust]
-impl Solution {
- pub fn defang_i_paddr(address: String) -> String {
- let mut result = String::default();
-
- for c in address.chars() {
- if c == '.' {
- result.push_str("[.]");
- } else {
- result.push(c);
- }
- }
-
- result
- }
-}
-
-```
-
-:::
-
-### [_..._](#)
-
-```
-
-```
-
-
-
-[share]: https://graph.org/file/3ea5234dda646b71c574a.png
-[easy]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Easy-bright.svg
-[medium]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Medium-yellow.svg
-[hard]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Hard-red.svg
diff --git a/docs/solution/1101-1200/1143 - Longest Common Subsequence.md b/docs/solution/1101-1200/1143 - Longest Common Subsequence.md
deleted file mode 100644
index 2235707c..00000000
--- a/docs/solution/1101-1200/1143 - Longest Common Subsequence.md
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,76 +0,0 @@
-# 1143. Longest Common Subsequence [![share]](https://leetcode.com/problems/longest-common-subsequence/)
-
-![][medium]
-
-## Problem Statement:
-
-Given two strings `text1` and `text2`, return the length of their longest **common subsequence**. If there is no **common subsequence**, return `0`.
-
-A **subsequence** of a string is a new string generated from the original string with some characters (can be none) deleted without changing the relative order of the remaining characters.
-
-- For example, `"ace"` is a subsequence of `"abcde"`.
- A **common subsequence** of two strings is a subsequence that is common to both strings.
-
-### Example 1:
-
-```
-Input: text1 = "abcde", text2 = "ace"
-Output: 3
-Explanation: The longest common subsequence is "ace" and its length is 3.
-```
-
-### Example 2:
-
-```
-Input: text1 = "abc", text2 = "abc"
-Output: 3
-Explanation: The longest common subsequence is "abc" and its length is 3.
-```
-
-### Example 3:
-
-```
-Input: text1 = "abc", text2 = "def"
-Output: 0
-Explanation: There is no such common subsequence, so the result is 0.
-```
-
-### Constraints:
-
-- 1 <= text1.length, text2.length <= 1000
-- `text1` and `text2` consist of only lowercase English characters.
-
-## Solution:
-
-::: code-group
-
-```java
-public int longestCommonSubsequence(String str1, String str2) {
- int m = str1.length(),
- n = str2.length();
- int[][] dp = new int[m + 1][n + 1];
- for (int i = 0; i < m + 1; i++)
- for (int j = 0; j < n + 1; j++) {
- if (i == 0 || j == 0)
- dp[i][j] = 0;
- else if (str1.charAt(i - 1) == str2.charAt(j - 1))
- dp[i][j] = 1 + dp[i - 1][j - 1];
- else
- dp[i][j] = Math.max(dp[i - 1][j], dp[i][j - 1]);
- }
- return dp[m][n];
-}
-```
-
-:::
-
-### [_..._](#)
-
-```
-
-```
-
-
-
-[share]: https://img.icons8.com/external-anggara-blue-anggara-putra/20/000000/external-share-user-interface-basic-anggara-blue-anggara-putra-2.png
-[medium]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Medium-yellow.svg
diff --git a/docs/solution/1201-1300/1232 - Check If It Is a Straight Line.md b/docs/solution/1201-1300/1232 - Check If It Is a Straight Line.md
deleted file mode 100644
index f75b9520..00000000
--- a/docs/solution/1201-1300/1232 - Check If It Is a Straight Line.md
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,75 +0,0 @@
-# 1232. Check If It Is a Straight Line [![share]](https://leetcode.com/problems/check-if-it-is-a-straight-line)
-
-![][easy]
-
-## Problem Statement:
-
-You are given an array `coordinates`, `coordinates[i] = [x, y]`, where [x, y] represents the coordinate of a point. Check if these points make a straight line in the XY plane.
-
-### Example 1:
-
-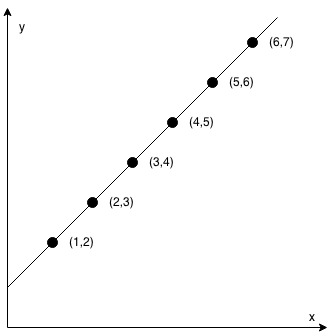
-
-```
-Input: coordinates = [[1,2],[2,3],[3,4],[4,5],[5,6],[6,7]]
-Output: true
-```
-
-### Example 2:
-
-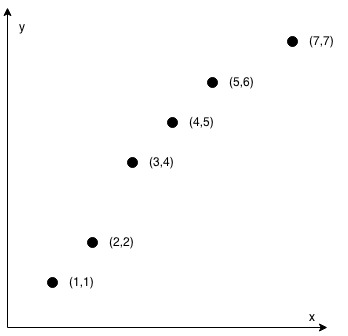
-
-```
-Input: coordinates = [[1,1],[2,2],[3,4],[4,5],[5,6],[7,7]]
-Output: false
-```
-
-### Constraints:
-
-- 2 <= coordinates.length <= 1000
-- coordinates[i].length == 2
-- -10^4 <= coordinates[i][0], coordinates[i][1] <= 10^4
-- coordinates contains no duplicate point.
-
-## Solution:
-
-::: code-group
-
-```java
- /*
- * slope = tan0 = (x - x1) / (y - y1)
- * for line being straight line,
- * slope b/w every two points must be equal, i.e.
- * (x - x1) / (y - y1) = (x1 - x0) / (y1 - y0)
- */
-
-public boolean checkStraightLine(int[][] coordinates) {
- if (coordinates.length == 2)
- return true;
- int x0 = coordinates[0][0], y0 = coordinates[0][1],
- x1 = coordinates[1][0], y1 = coordinates[1][1];
- int dx = x1 - x0,
- dy = y1 - y0;
- for (int[] coordinate : coordinates) {
- int x = coordinate[0], y = coordinate[1];
- if (dx * (y - y1) != dy * (x - x1))
- return false;
- }
- return true;
-}
-```
-
-:::
-
-### [_..._](#)
-
-```
-
-```
-
-
-
-[share]: https://img.icons8.com/external-anggara-blue-anggara-putra/20/000000/external-share-user-interface-basic-anggara-blue-anggara-putra-2.png
-[easy]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Easy-bright.svg
-[medium]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Medium-yellow.svg
-[hard]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Hard-red.svg
diff --git a/docs/solution/1301-1400/1345 - Jump Game IV.md b/docs/solution/1301-1400/1345 - Jump Game IV.md
deleted file mode 100644
index 6f3d46f8..00000000
--- a/docs/solution/1301-1400/1345 - Jump Game IV.md
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,122 +0,0 @@
-# 1345. Jump Game IV [![share]](https://leetcode.com/problems/jump-game-iv/)
-
-![][hard]
-
-## Problem Statement
-
-
Given an array of integers arr, you are initially positioned at the first index of the array.
-
In one step you can jump from index i to index:
-
-
i + 1 where: i + 1 < arr.length.
-
i - 1 where: i - 1 >= 0.
-
j where: arr[i] == arr[j] and i != j.
-
-
Return the minimum number of steps to reach the last index of the array.
-
Notice that you can not jump outside of the array at any time.
-
-
Example 1:
-
-```
-Input: arr = [100,-23,-23,404,100,23,23,23,3,404]
-Output: 3
-Explanation: You need three jumps from index 0 --> 4 --> 3 --> 9. Note that index 9 is the last index of the array.
-```
-
-
Example 2:
-
-```
-Input: arr = [7]
-Output: 0
-Explanation: Start index is the last index. You do not need to jump.
-```
-
-
Example 3:
-
-```
-Input: arr = [7,6,9,6,9,6,9,7]
-Output: 1
-Explanation: You can jump directly from index 0 to index 7 which is last index of the array.
-```
-
-
-
Constraints:
-
-
1 <= arr.length <= 5 * 104
-
-108 <= arr[i] <= 108
-
-
-::: details _Click to open Hints_
-
-- Build a graph of n nodes where nodes are the indices of the array and edges for node i are nodes i+1, i-1, j where arr[i] == arr[j].
-- Start bfs from node 0 and keep distance. The answer is the distance when you reach node n-1.
-
-:::
-
-## Solution:
-
-::: code-group
-
-```rs [Rust]
-use std::collections::{HashMap, VecDeque};
-
-impl Solution {
- pub fn min_jumps(arr: Vec) -> i32 {
- let mut map = HashMap::new();
-
- for (i, &v) in arr.iter().enumerate() {
- map.entry(v).or_insert(vec![]).push(i);
- }
-
- let mut q = VecDeque::new();
- q.push_back((0, 0_i32));
-
- let mut visited = vec![false; arr.len()];
- visited[0] = true;
-
- while let Some((i, mut step)) = q.pop_front() {
- if i == arr.len() - 1 {
- return step;
- }
-
- step += 1;
-
- if let Some(v) = map.remove(&arr[i]) {
- for j in v {
- if !visited[j] {
- visited[j] = true;
- q.push_back((j, step));
- }
- }
- }
-
- if i + 1 < arr.len() && !visited[i + 1] {
- visited[i + 1] = true;
- q.push_back((i + 1, step));
- }
-
- if i >= 1 && !visited[i - 1] {
- visited[i - 1] = true;
- q.push_back((i - 1, step));
- }
- }
-
- -1
- }
-}
-
-```
-
-:::
-
-### [_..._](#)
-
-```
-
-```
-
-
-
-[share]: https://graph.org/file/3ea5234dda646b71c574a.png
-[easy]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Easy-bright.svg
-[medium]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Medium-yellow.svg
-[hard]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Hard-red.svg
diff --git a/docs/solution/1401-1500/1431 - Kids With the Greatest Number of Candies.md b/docs/solution/1401-1500/1431 - Kids With the Greatest Number of Candies.md
deleted file mode 100644
index 2c19118f..00000000
--- a/docs/solution/1401-1500/1431 - Kids With the Greatest Number of Candies.md
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,153 +0,0 @@
-# 1431. Kids With the Greatest Number of Candies [![share]](https://leetcode.com/problems/kids-with-the-greatest-number-of-candies/)
-
-![][easy]
-
-## Problem Statement
-
-
There are n kids with candies. You are given an integer array candies, where each candies[i] represents the number of candies the ith kid has, and an integer extraCandies, denoting the number of extra candies that you have.
-
Return a boolean array result of length n, where result[i] is true if, after giving the ith kid all the extraCandies, they will have the greatest number of candies among all the kids, or false otherwise.
-
Note that multiple kids can have the greatest number of candies.
-
-
Example 1:
-
-```
-Input: candies = [2,3,5,1,3], extraCandies = 3
-Output: [true,true,true,false,true]
-Explanation: If you give all extraCandies to:
-- Kid 1, they will have 2 + 3 = 5 candies, which is the greatest among the kids.
-- Kid 2, they will have 3 + 3 = 6 candies, which is the greatest among the kids.
-- Kid 3, they will have 5 + 3 = 8 candies, which is the greatest among the kids.
-- Kid 4, they will have 1 + 3 = 4 candies, which is not the greatest among the kids.
-- Kid 5, they will have 3 + 3 = 6 candies, which is the greatest among the kids.
-```
-
-
Example 2:
-
-```
-Input: candies = [4,2,1,1,2], extraCandies = 1
-Output: [true,false,false,false,false]
-Explanation: There is only 1 extra candy.
-Kid 1 will always have the greatest number of candies, even if a different kid is given the extra candy.
-```
-
-
-
-::: details _Click to open Hints_
-
-- Use greedy approach. For each kid check if candies[i] + extraCandies ≥ maximum in Candies[i].
-
-:::
-
-## Solution:
-
-::: code-group
-
-```go [Go]
-package main
-
-func kidsWithCandies(candies []int, extraCandies int) []bool {
- max := 0
-
- for _, candy := range candies {
- if candy > max {
- max = candy
- }
- }
-
- result := make([]bool, len(candies))
-
- for i, candy := range candies {
- if candy+extraCandies >= max {
- result[i] = true
- }
- }
-
- return result
-}
-
-```
-
-```rs [Rust]
-impl Solution {
- pub fn kids_with_candies(candies: Vec, extra_candies: i32) -> Vec {
- let mut max = 0;
-
- for i in 0..candies.len() {
- if candies[i] > max {
- max = candies[i];
- }
- }
-
- let mut result = Vec::new();
-
- for i in 0..candies.len() {
- if candies[i] + extra_candies >= max {
- result.push(true);
- } else {
- result.push(false);
- }
- }
-
- result
- }
-}
-
-```
-
-```java [Java]
-import java.util.ArrayList;
-import java.util.List;
-
-class Solution {
- public List kidsWithCandies(int[] candies, int extraCandies) {
- int max = 0;
-
- for (int candy : candies) {
- if (candy > max) {
- max = candy;
- }
- }
-
- List res = new ArrayList<>();
-
- for (int i = 0; i < candies.length; i++) {
- if (candies[i] + extraCandies >= max) {
- res.add(true);
- } else {
- res.add(false);
- }
- }
-
- return res;
- }
-}
-```
-
-:::
-
-### [_..._](#)
-
-```
-
-```
-
-
-
-[share]: https://graph.org/file/3ea5234dda646b71c574a.png
-[easy]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Easy-bright.svg
-[medium]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Medium-yellow.svg
-[hard]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Hard-red.svg
diff --git a/docs/solution/1401-1500/1461 - Check If a String Contains All Binary Codes of Size K.md b/docs/solution/1401-1500/1461 - Check If a String Contains All Binary Codes of Size K.md
deleted file mode 100644
index 936b1a99..00000000
--- a/docs/solution/1401-1500/1461 - Check If a String Contains All Binary Codes of Size K.md
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,92 +0,0 @@
-# 1461. Check If a String Contains All Binary Codes of Size K [![share]](https://leetcode.com/problems/check-if-a-string-contains-all-binary-codes-of-size-k/)
-
-![][medium]
-
-## Problem Statement:
-
-Given a binary string `s` and an integer `k`, return `true` if every binary code of length `k` is a substring of `s`. Otherwise, return `false`.
-
-### Example 1:
-
-```
-Input: s = "00110110", k = 2
-Output: true
-```
-
-### Explanation:
-
-```
-The binary codes of length 2 are "00", "01", "10" and "11". They can be all found as substrings at indices 0, 1, 3 and 2 respectively.
-```
-
-### Example 2:
-
-```
-Input: s = "0110", k = 1
-Output: true
-```
-
-### Explanation:
-
-```
-The binary codes of length 1 are "0" and "1", it is clear that both exist as a substring.
-```
-
-### Example 3:
-
-```
-Input: s = "0110", k = 2
-Output: false
-```
-
-### Explanation:
-
-```
-The binary code "00" is of length 2 and does not exist in the array.
-```
-
-### Constraints:
-
-- 1 <= s.length <= 5 \* 105
-- s[i] is either '0' or '1'.
-- 1 <= k <= 20
-
-## Solution:
-
-::: code-group
-
-```java
-public class CheckIfaStringContainsAllBinaryCodesOfSizeK {
- public static boolean hasAllCodes(String s, int k) {
- int count = 1 << k; // this is same as 2^K
- Set res = new HashSet<>();
- for (int i = k; i <= s.length(); i++) {
- String temp = s.substring(i - k, i);
- if (!res.contains(temp)) {
- res.add(temp);
- count--;
- }
- if (count == 0)
- return true;
- }
- return false;
- }
-
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- System.out.println(hasAllCodes("00110", 2));
- }
-}
-```
-
-:::
-
-### [_..._](#)
-
-```
-
-```
-
-
-
-[share]: https://img.icons8.com/external-anggara-blue-anggara-putra/20/000000/external-share-user-interface-basic-anggara-blue-anggara-putra-2.png
-[medium]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Medium-yellow.svg
diff --git a/docs/solution/1401-1500/1470 - Shuffle the Array.md b/docs/solution/1401-1500/1470 - Shuffle the Array.md
deleted file mode 100644
index 04a72b8e..00000000
--- a/docs/solution/1401-1500/1470 - Shuffle the Array.md
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,84 +0,0 @@
-# 1470. Shuffle the Array [![share]](https://leetcode.com/problems/shuffle-the-array/)
-
-![][easy]
-
-## Problem Statement
-
-
Given the array nums consisting of 2n elements in the form [x1,x2,...,xn,y1,y2,...,yn].
-
Return the array in the form[x1,y1,x2,y2,...,xn,yn].
-
-
Example 1:
-
-```
-
-Input: nums = [2,5,1,3,4,7], n = 3
-Output: [2,3,5,4,1,7]
-Explanation: Since x1=2, x2=5, x3=1, y1=3, y2=4, y3=7 then the answer is [2,3,5,4,1,7].
-```
-
-
-
-::: details _Click to open Hints_
-
-- Use two pointers to create the new array of 2n elements. The first starting at the beginning and the other starting at (n+1)th position. Alternate between them and create the new array.
-
-:::
-
-## Solution:
-
-::: code-group
-
-```go [Go]
-package main
-
-func shuffle(nums []int, n int) []int {
- res := make([]int, n*2)
-
- for i := 0; i < n; i++ {
- // at even indices, put the slice of the array from 0 to n
- res[i*2] = nums[i]
- // at odd indices, put the slice of the array from n to the end
- res[i*2+1] = nums[n+i]
- }
-
- return res
-}
-
-```
-
-:::
-
-### [_..._](#)
-
-```
-
-```
-
-
-
-[share]: https://graph.org/file/3ea5234dda646b71c574a.png
-[easy]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Easy-bright.svg
-[medium]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Medium-yellow.svg
-[hard]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Hard-red.svg
diff --git a/docs/solution/1401-1500/1472 - Design Browser History.md b/docs/solution/1401-1500/1472 - Design Browser History.md
deleted file mode 100644
index 6fd78952..00000000
--- a/docs/solution/1401-1500/1472 - Design Browser History.md
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,127 +0,0 @@
-# 1472. Design Browser History [![share]](https://leetcode.com/problems/design-browser-history/)
-
-![][medium]
-
-## Problem Statement
-
-
You have a browser of one tab where you start on the homepage and you can visit another url, get back in the history number of steps or move forward in the history number of steps.
-
Implement the BrowserHistory class:
-
-
BrowserHistory(string homepage) Initializes the object with the homepage of the browser.
-
void visit(string url) Visits url from the current page. It clears up all the forward history.
-
string back(int steps) Move steps back in history. If you can only return x steps in the history and steps > x, you will return only x steps. Return the current url after moving back in history at moststeps.
-
string forward(int steps) Move steps forward in history. If you can only forward x steps in the history and steps > x, you will forward only x steps. Return the current url after forwarding in history at moststeps.
-
-
-
Example:
-
-```
-Input:
-["BrowserHistory","visit","visit","visit","back","back","forward","visit","forward","back","back"]
-[["leetcode.com"],["google.com"],["facebook.com"],["youtube.com"],[1],[1],[1],["linkedin.com"],[2],[2],[7]]
-Output:
-[null,null,null,null,"facebook.com","google.com","facebook.com",null,"linkedin.com","google.com","leetcode.com"]
-
-Explanation:
-BrowserHistory browserHistory = new BrowserHistory("leetcode.com");
-browserHistory.visit("google.com"); // You are in "leetcode.com". Visit "google.com"
-browserHistory.visit("facebook.com"); // You are in "google.com". Visit "facebook.com"
-browserHistory.visit("youtube.com"); // You are in "facebook.com". Visit "youtube.com"
-browserHistory.back(1); // You are in "youtube.com", move back to "facebook.com" return "facebook.com"
-browserHistory.back(1); // You are in "facebook.com", move back to "google.com" return "google.com"
-browserHistory.forward(1); // You are in "google.com", move forward to "facebook.com" return "facebook.com"
-browserHistory.visit("linkedin.com"); // You are in "facebook.com". Visit "linkedin.com"
-browserHistory.forward(2); // You are in "linkedin.com", you cannot move forward any steps.
-browserHistory.back(2); // You are in "linkedin.com", move back two steps to "facebook.com" then to "google.com". return "google.com"
-browserHistory.back(7); // You are in "google.com", you can move back only one step to "leetcode.com". return "leetcode.com"
-```
-
-
-
Constraints:
-
-
1 <= homepage.length <= 20
-
1 <= url.length <= 20
-
1 <= steps <= 100
-
homepage and url consist of '.' or lower case English letters.
-
At most 5000 calls will be made to visit, back, and forward.
-
-
-::: details _Click to open Hints_
-
-- Use two stacks: one for back history, and one for forward history. You can simulate the functions by popping an element from one stack and pushing it into the other.
-- Can you improve program runtime by using a different data structure?
-
-:::
-
-## Solution:
-
-::: code-group
-
-```go [Go]
-package main
-
-type BrowserHistory struct {
- histories []string
- currentPage int
-}
-
-func Constructor(homepage string) BrowserHistory {
- return BrowserHistory{
- histories: []string{homepage},
- currentPage: 0,
- }
-}
-
-func (this *BrowserHistory) Visit(url string) {
- if this.currentPage != len(this.histories)-1 {
- this.histories = append(this.histories[:this.currentPage+1], []string{}...)
- }
-
- this.histories = append(this.histories, url)
- this.currentPage++
-}
-
-func (this *BrowserHistory) Back(steps int) string {
- for i := this.currentPage; 0 <= i; i-- {
- if steps == 0 || this.currentPage == 0 {
- break
- }
-
- this.currentPage--
- steps--
- }
-
- return this.histories[this.currentPage]
-}
-
-func (this *BrowserHistory) Forward(steps int) string {
- lenHistories := len(this.histories)
-
- for i := this.currentPage; i < lenHistories; i++ {
- if steps == 0 || this.currentPage == lenHistories-1 {
- break
- }
-
- this.currentPage++
- steps--
- }
-
- return this.histories[this.currentPage]
-}
-
-```
-
-:::
-
-### [_..._](#)
-
-```
-
-```
-
-
-
-[share]: https://graph.org/file/3ea5234dda646b71c574a.png
-[easy]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Easy-bright.svg
-[medium]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Medium-yellow.svg
-[hard]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Hard-red.svg
diff --git a/docs/solution/1401-1500/1480 - Running Sum of 1d Array.md b/docs/solution/1401-1500/1480 - Running Sum of 1d Array.md
deleted file mode 100644
index 62e2b9e0..00000000
--- a/docs/solution/1401-1500/1480 - Running Sum of 1d Array.md
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,83 +0,0 @@
-# 1480. Running Sum of 1d Array [![share]](https://leetcode.com/problems/running-sum-of-1d-array/)
-
-![][easy]
-
-## Problem Statement:
-
-Given an array `nums`. We define a running sum of an array as `runningSum[i] = sum(nums[0]…nums[i])`.
-
-Return the running sum of `nums`.
-
-### Example 1:
-
-```
-Input: nums = [1,2,3,4]
-Output: [1,3,6,10]
-```
-
-### Explanation:
-
-```
-Running sum is obtained as follows: [1, 1+2, 1+2+3, 1+2+3+4].
-```
-
-### Example 2:
-
-```
-Input: nums = [1,1,1,1,1]
-Output: [1,2,3,4,5]
-```
-
-### Explanation:
-
-```
-Running sum is obtained as follows: [1, 1+1, 1+1+1, 1+1+1+1, 1+1+1+1+1].
-```
-
-### Example 3:
-
-```
-Input: nums = [3,1,2,10,1]
-Output: [3,4,6,16,17]
-```
-
-### Constraints:
-
-- 1 <= nums.length <= 1000
-- -106 <= nums[i] <= 106
-
-## Solution:
-
-::: code-group
-
-```java
-public class RunningSumOfOneDimensionalArray {
- public static int[] runningSum(int[] nums) {
- int sum = 0;
- for (int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) {
- sum += nums[i];
- nums[i] = sum;
- }
- return nums;
- }
-
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- int[] nums = { 1, 1, 1, 1, 1 };
- for (int i : runningSum(nums))
- System.out.print(i + " ");
- }
-}
-```
-
-:::
-
-### [_..._](#)
-
-```
-
-```
-
-
-
-[share]: https://img.icons8.com/external-anggara-blue-anggara-putra/20/000000/external-share-user-interface-basic-anggara-blue-anggara-putra-2.png
-[medium]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Medium-yellow.svg
diff --git a/docs/solution/1401-1500/1491 - Average Salary Excluding the Minimum and Maximum Salary.md b/docs/solution/1401-1500/1491 - Average Salary Excluding the Minimum and Maximum Salary.md
deleted file mode 100644
index 6d4019b4..00000000
--- a/docs/solution/1401-1500/1491 - Average Salary Excluding the Minimum and Maximum Salary.md
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,63 +0,0 @@
-# 1491. Average Salary Excluding the Minimum and Maximum Salary [![share]](https://leetcode.com/problems/average-salary-excluding-the-minimum-and-maximum-salary)
-
-![easy]
-
-## Problem Statement:
-
-You are given an array of **unique** integers `salary` where` salary[i]` is the salary of the ith employee.
-
-Return the average salary of employees excluding the minimum and maximum salary. Answers within 10-5 of the actual answer will be accepted.
-
-### Example 1:
-
-```
-Input: salary = [4000,3000,1000,2000]
-Output: 2500.00000
-Explanation: Minimum salary and maximum salary are 1000 and 4000 respectively.
-Average salary excluding minimum and maximum salary is (2000+3000) / 2 = 2500
-```
-
-### Example 2:
-
-```
-Input: salary = [1000,2000,3000]
-Output: 2000.00000
-Explanation: Minimum salary and maximum salary are 1000 and 3000 respectively.
-Average salary excluding minimum and maximum salary is (2000) / 1 = 2000
-```
-
-### Constraints:
-
-- 3 <= salary.length <= 100
-- 1000 <= salary[i] <= 106
-- All the integers of salary are **unique**.
-
-## Solution:
-
-::: code-group
-
-```java
-public double average(int[] salary) {
- Arrays.sort(salary);
- int len = salary.length;
- double res = 0;
- for (int i = 1; i < len - 1; i++)
- res += salary[i];
- return res / (len - 2);
-}
-```
-
-:::
-
-### [_..._](#)
-
-```
-
-```
-
-
-
-[share]: https://img.icons8.com/external-anggara-blue-anggara-putra/20/000000/external-share-user-interface-basic-anggara-blue-anggara-putra-2.png
-[easy]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Easy-bright.svg
-[medium]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Medium-yellow.svg
-[hard]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Hard-red.svg
diff --git a/docs/solution/1401-1500/1498 - Number of Subsequences That Satisfy the Given Sum Condition.md b/docs/solution/1401-1500/1498 - Number of Subsequences That Satisfy the Given Sum Condition.md
deleted file mode 100644
index 727df3ec..00000000
--- a/docs/solution/1401-1500/1498 - Number of Subsequences That Satisfy the Given Sum Condition.md
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,87 +0,0 @@
-# 1498. Number of Subsequences That Satisfy the Given Sum Condition [![share]](https://leetcode.com/problems/number-of-subsequences-that-satisfy-the-given-sum-condition)
-
-![][medium]
-
-## Problem Statement:
-
-You are given an array of integers `nums` and an integer `target`.
-
-Return the number of **non-empty** subsequences of `nums` such that the sum of the minimum and maximum element on it is less or equal to `target`. Since the answer may be too large, return it modulo 109 + 7.
-
-### Example 1:
-
-```
-Input: nums = [3,5,6,7], target = 9
-Output: 4
-Explanation: There are 4 subsequences that satisfy the condition.
-[3] -> Min value + max value <= target (3 + 3 <= 9)
-[3,5] -> (3 + 5 <= 9)
-[3,5,6] -> (3 + 6 <= 9)
-[3,6] -> (3 + 6 <= 9)
-```
-
-### Example 2:
-
-```
-Input: nums = [3,3,6,8], target = 10
-Output: 6
-Explanation: There are 6 subsequences that satisfy the condition. (nums can have repeated numbers).
-[3] , [3] , [3,3], [3,6] , [3,6] , [3,3,6]
-```
-
-### Example 3:
-
-```
-Input: nums = [2,3,3,4,6,7], target = 12
-Output: 61
-Explanation: There are 63 non-empty subsequences, two of them do not satisfy the condition ([6,7], [7]).
-Number of valid subsequences (63 - 2 = 61).
-```
-
-### Constraints:
-
-- 1 <= nums.length <= 105
-- 1 <= nums[i] <= 106
-- 1 <= target <= 106
-
-## Solution:
-
-::: code-group
-
-```java
-public int numSubseq(int[] nums, int target) {
- Arrays.sort(nums);
- int count = 0,
- len = nums.length,
- left = 0,
- right = len - 1;
- int[] pow2 = new int[len];
- pow2[0] = 1;
- for (int i = 1; i < len; i++)
- pow2[i] = pow2[i - 1] * 2 % 1000000007;
- while (left <= right) {
- if (nums[left] + nums[right] > target)
- right--;
- else {
- count += pow2[right - left++];
- count %= 1000000007;
- }
- }
- return count;
-}
-```
-
-:::
-
-### [_..._](#)
-
-```
-
-```
-
-
-
-[share]: https://img.icons8.com/external-anggara-blue-anggara-putra/20/000000/external-share-user-interface-basic-anggara-blue-anggara-putra-2.png
-[easy]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Easy-bright.svg
-[medium]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Medium-yellow.svg
-[hard]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Hard-red.svg
diff --git a/docs/solution/1501-1600/1512 - Number of Good Pairs.md b/docs/solution/1501-1600/1512 - Number of Good Pairs.md
deleted file mode 100644
index 1e7b720f..00000000
--- a/docs/solution/1501-1600/1512 - Number of Good Pairs.md
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,81 +0,0 @@
-# 1512. Number of Good Pairs [![share]](https://leetcode.com/problems/number-of-good-pairs/)
-
-![][easy]
-
-## Problem Statement
-
-
Given an array of integers nums, return the number of good pairs.
-
A pair (i, j) is called good if nums[i] == nums[j] and i < j.
-
-
Example 1:
-
-```
-Input: nums = [1,2,3,1,1,3]
-Output: 4
-Explanation: There are 4 good pairs (0,3), (0,4), (3,4), (2,5) 0-indexed.
-```
-
-
Example 2:
-
-```
-Input: nums = [1,1,1,1]
-Output: 6
-Explanation: Each pair in the array are good.
-```
-
-
Example 3:
-
-```
-Input: nums = [1,2,3]
-Output: 0
-```
-
-
-
Constraints:
-
-
1 <= nums.length <= 100
-
1 <= nums[i] <= 100
-
-
-::: details _Click to open Hints_
-
-- Count how many times each number appears. If a number appears n times, then n \* (n – 1) // 2 good pairs can be made with this number.
-
-:::
-
-## Solution:
-
-::: code-group
-
-```rs [Rust]
-impl Solution {
- pub fn num_identical_pairs(nums: Vec) -> i32 {
- let mut count = 0;
- let mut map = std::collections::HashMap::new();
-
- for num in nums {
- let entry = map.entry(num).or_insert(0);
- count += *entry;
- *entry += 1;
- }
-
- count
- }
-}
-
-```
-
-:::
-
-### [_..._](#)
-
-```
-
-```
-
-
-
-[share]: https://graph.org/file/3ea5234dda646b71c574a.png
-[easy]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Easy-bright.svg
-[medium]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Medium-yellow.svg
-[hard]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Hard-red.svg
diff --git a/docs/solution/1501-1600/1523 - Count Odd Numbers in an Interval Range.md b/docs/solution/1501-1600/1523 - Count Odd Numbers in an Interval Range.md
deleted file mode 100644
index e2bb4633..00000000
--- a/docs/solution/1501-1600/1523 - Count Odd Numbers in an Interval Range.md
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,74 +0,0 @@
-# 1523. Count Odd Numbers in an Interval Range [![share]](https://leetcode.com/problems/count-odd-numbers-in-an-interval-range/)
-
-![][easy]
-
-## Problem Statement
-
-
Given two non-negative integers low and high. Return the count of odd numbers between low and high (inclusive).
-
-
Example 1:
-
-````
-
-Input: low = 3, high = 7
-Output: 3
-Explanation: The odd numbers between 3 and 7 are [3,5,7].```
-
-
Example 2:
-
-````
-
-Input: low = 8, high = 10
-Output: 1
-Explanation: The odd numbers between 8 and 10 are [9].```
-
-
-
Constraints:
-
-
0 <= low <= high <= 10^9
-
-
-::: details _Click to open Hints_
-
-- If the range (high - low + 1) is even, the number of even and odd numbers in this range will be the same.
-- If the range (high - low + 1) is odd, the solution will depend on the parity of high and low.
-
-:::
-
-## Solution:
-
-::: code-group
-
-```rs [Rust]
-impl Solution {
- pub fn count_odds(low: i32, high: i32) -> i32 {
- // ((high + 1) / 2) - (low / 2)
- ((high + 1) >> 1) - (low >> 1) // same as above
- }
-}
-
-```
-
-```go [Go]
-package main
-
-func countOdds(low int, high int) int {
- return ((high + 1) / 2) - (low / 2)
-}
-
-```
-
-:::
-
-### [_..._](#)
-
-```
-
-```
-
-
-
-[share]: https://graph.org/file/3ea5234dda646b71c574a.png
-[easy]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Easy-bright.svg
-[medium]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Medium-yellow.svg
-[hard]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Hard-red.svg
diff --git a/docs/solution/1501-1600/1537 - Get the Maximum Score.md b/docs/solution/1501-1600/1537 - Get the Maximum Score.md
deleted file mode 100644
index fcb5da7e..00000000
--- a/docs/solution/1501-1600/1537 - Get the Maximum Score.md
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,119 +0,0 @@
-# 1537. Get the Maximum Score [![share]](https://leetcode.com/problems/get-the-maximum-score/)
-
-![][hard]
-
-## Problem Statement:
-
-You are given two **sorted** arrays of distinct integers `nums1` and `nums2`.
-
-A **valid path** is defined as follows:
-
-- Choose array `nums1` or `nums2` to traverse (from index-0).
-- Traverse the current array from left to right.
-- If you are reading any value that is present in `nums1` and `nums2` you are allowed to change your path to the other array. (Only one repeated value is considered in the valid path).
-
-The **score** is defined as the sum of uniques values in a valid path.
-
-Return the maximum score you can obtain of all possible **valid paths**. Since the answer may be too large, return it modulo 109 + 7.
-
-### Example 1:
-
-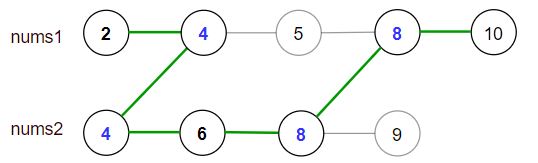
-
-```
-Input: nums1 = [2,4,5,8,10], nums2 = [4,6,8,9]
-Output: 30
-Explanation: Valid paths:
-[2,4,5,8,10], [2,4,5,8,9], [2,4,6,8,9], [2,4,6,8,10], (starting from nums1)
-[4,6,8,9], [4,5,8,10], [4,5,8,9], [4,6,8,10] (starting from nums2)
-The maximum is obtained with the path in green [2,4,6,8,10].
-```
-
-### Example 2:
-
-```
-Input: nums1 = [1,3,5,7,9], nums2 = [3,5,100]
-Output: 109
-Explanation: Maximum sum is obtained with the path [1,3,5,100].
-```
-
-### Example 3:
-
-```
-Input: nums1 = [1,2,3,4,5], nums2 = [6,7,8,9,10]
-Output: 40
-Explanation: There are no common elements between nums1 and nums2.
-Maximum sum is obtained with the path [6,7,8,9,10].
-```
-
-### Constraints:
-
-- 1 <= nums1.length, nums2.length <= 105
-- 1 <= nums1[i], nums2[i] <= 107
-- nums1 **and** nums2 are strictly increasing.
-
-## Solution:
-
-::: code-group
-
-```java
-public class GetTheMaxScore {
-
- /* Two Pointer Approach */
- public int maxSum(int[] nums1, int[] nums2) {
- // initializing two pointer vars
- int i = 0, j = 0;
- int len1 = nums1.length, len2 = nums2.length;
-
- // taking the vars of long type to avoid integer overflow or runtime error
- long upperSum = 0, lowerSum = 0;
-
- // traverse till one of the arrays length
- while (i < len1 && j < len2) {
-
- // adding the element to the upperSum until element of first array is >=
- // the element of second array & then increamenting the pointer var by 1
- if (nums1[i] < nums2[j])
- upperSum += nums1[i++];
-
- // adding the element to the lowerSum until element of second array is >=
- // the element of first array & then increamenting the pointer var by 1
- else if (nums1[i] > nums2[j])
- lowerSum += nums2[j++];
-
- // when the element of both arrays are equal,
- // assign the value of max of upperSum & lowerSum and adding the element itself
- else {
- upperSum = lowerSum = Math.max(upperSum, lowerSum) + nums1[i];
- // increasing both pointer by 1, as the value at both the pointers is same,
- // avoiding the repetition of element in the sum
- i++;
- j++;
- }
- }
-
- // adding the remaining element from first array
- while (i < len1)
- upperSum += nums1[i++];
-
- // adding the remaining element from second array
- while (j < len2)
- lowerSum += nums2[j++];
-
- return (int) (Math.max(upperSum, lowerSum) % 1000000007);
- }
-}
-```
-
-:::
-
-### [_..._](#)
-
-```
-
-```
-
-
-
-[share]: https://img.icons8.com/external-anggara-blue-anggara-putra/20/000000/external-share-user-interface-basic-anggara-blue-anggara-putra-2.png
-[hard]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Hard-red.svg
diff --git a/docs/solution/1501-1600/1539 - Kth Missing Positive Number.md b/docs/solution/1501-1600/1539 - Kth Missing Positive Number.md
deleted file mode 100644
index e19749e1..00000000
--- a/docs/solution/1501-1600/1539 - Kth Missing Positive Number.md
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,82 +0,0 @@
-# 1539. Kth Missing Positive Number [![share]](https://leetcode.com/problems/kth-missing-positive-number/)
-
-![][easy]
-
-## Problem Statement
-
-
Given an array arr of positive integers sorted in a strictly increasing order, and an integer k.
-
Return thekthpositive integer that is missing from this array.
-
-
Example 1:
-
-```
-Input: arr = [2,3,4,7,11], k = 5
-Output: 9
-Explanation: The missing positive integers are [1,5,6,8,9,10,12,13,...]. The 5th missing positive integer is 9.
-```
-
-
Example 2:
-
-```
-Input: arr = [1,2,3,4], k = 2
-Output: 6
-Explanation: The missing positive integers are [5,6,7,...]. The 2nd missing positive integer is 6.
-```
-
-
-
Constraints:
-
-
1 <= arr.length <= 1000
-
1 <= arr[i] <= 1000
-
1 <= k <= 1000
-
arr[i] < arr[j] for 1 <= i < j <= arr.length
-
-
-
Follow up:
-
Could you solve this problem in less than O(n) complexity?
-
-::: details _Click to open Hints_
-
-- Keep track of how many positive numbers are missing as you scan the array.
-
-:::
-
-## Solution:
-
-::: code-group
-
-```rs [Rust]
-impl Solution {
- pub fn find_kth_positive(arr: Vec, k: i32) -> i32 {
- let (mut l, mut r) = (0, arr.len());
-
- while l < r {
- let mid = l + (r - l) / 2;
-
- if arr[mid] - mid as i32 - 1 >= k {
- r = mid;
- } else {
- l = mid + 1;
- }
- }
-
- l as i32 + k
- }
-}
-
-```
-
-:::
-
-### [_..._](#)
-
-```
-
-```
-
-
-
-[share]: https://graph.org/file/3ea5234dda646b71c574a.png
-[easy]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Easy-bright.svg
-[medium]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Medium-yellow.svg
-[hard]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Hard-red.svg
diff --git a/docs/solution/1601-1700/1672 - Richest Customer Wealth.md b/docs/solution/1601-1700/1672 - Richest Customer Wealth.md
deleted file mode 100644
index be927bee..00000000
--- a/docs/solution/1601-1700/1672 - Richest Customer Wealth.md
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,95 +0,0 @@
-# 1672. Richest Customer Wealth [![share]](https://leetcode.com/problems/richest-customer-wealth/)
-
-![][easy]
-
-## Problem Statement
-
-
You are given an m x n integer grid accounts where accounts[i][j] is the amount of money the ith customer has in the jth bank. Return the wealth that the richest customer has.
-
A customer's wealth is the amount of money they have in all their bank accounts. The richest customer is the customer that has the maximum wealth.
-
-
Example 1:
-
-```
-Input: accounts = [[1,2,3],[3,2,1]]
-Output: 6
-Explanation:
-1st customer has wealth = 1 + 2 + 3 = 6
-2nd customer has wealth = 3 + 2 + 1 = 6
-Both customers are considered the richest with a wealth of 6 each, so return 6.
-```
-
-
Example 2:
-
-````
-Input: accounts = [[1,5],[7,3],[3,5]]
-Output: 10
-Explanation:
-1st customer has wealth = 6
-2nd customer has wealth = 10
-3rd customer has wealth = 8
-The 2nd customer is the richest with a wealth of 10.```
-
-
-
-
-::: details _Click to open Hints_
-
-- Calculate the wealth of each customer
-- Find the maximum element in array.
-
-:::
-
-## Solution:
-
-::: code-group
-
-```rs [Rust]
-impl Solution {
- pub fn maximum_wealth(accounts: Vec>) -> i32 {
- let mut max = 0;
-
- for account in accounts {
- let mut sum = 0;
- for money in account {
- sum += money;
- }
- if sum > max {
- max = sum;
- }
- }
- max
- }
-}
-
-````
-
-:::
-
-### [_..._](#)
-
-```
-
-```
-
-
-
-[share]: https://graph.org/file/3ea5234dda646b71c574a.png
-[easy]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Easy-bright.svg
-[medium]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Medium-yellow.svg
-[hard]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Hard-red.svg
diff --git a/docs/solution/1601-1700/1689 - Partitioning Into Minimum Number Of Deci-Binary Numbers.md b/docs/solution/1601-1700/1689 - Partitioning Into Minimum Number Of Deci-Binary Numbers.md
deleted file mode 100644
index 972531c4..00000000
--- a/docs/solution/1601-1700/1689 - Partitioning Into Minimum Number Of Deci-Binary Numbers.md
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,79 +0,0 @@
-# 1689. Partitioning Into Minimum Number Of Deci-Binary Numbers [![share]](https://leetcode.com/problems/partitioning-into-minimum-number-of-deci-binary-numbers/)
-
-![][medium]
-
-## Problem Statement
-
-
A decimal number is called deci-binary if each of its digits is either 0 or 1 without any leading zeros. For example, 101 and 1100 are deci-binary, while 112 and 3001 are not.
-
Given a string n that represents a positive decimal integer, return the minimum number of positive deci-binary numbers needed so that they sum up to n.
n does not contain any leading zeros and represents a positive integer.
-
-
-::: details _Click to open Hints_
-
-- Think about if the input was only one digit. Then you need to add up as many ones as the value of this digit.
-- If the input has multiple digits, then you can solve for each digit independently, and merge the answers to form numbers that add up to that input.
-- Thus the answer is equal to the max digit.
-
-:::
-
-## Solution:
-
-::: code-group
-
-```rs [Rust]
-impl Solution {
- pub fn min_partitions(n: String) -> i32 {
- // this will be slightly faster as it doesn't need to convert the char to a digit
- // as the max() function will return the max char value (in ASCII) which is the same as the max digit value
-
- // n.chars().max().unwrap().to_digit(10).unwrap() as i32
-
- n.chars().map(|c| c.to_digit(10).unwrap()).max().unwrap() as i32
- }
-}
-
-```
-
-:::
-
-### [_..._](#)
-
-```
-
-```
-
-
-
-[share]: https://graph.org/file/3ea5234dda646b71c574a.png
-[easy]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Easy-bright.svg
-[medium]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Medium-yellow.svg
-[hard]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Hard-red.svg
diff --git a/docs/solution/1901-2000/1920 - Build Array from Permutation.md b/docs/solution/1901-2000/1920 - Build Array from Permutation.md
deleted file mode 100644
index f7efd2ee..00000000
--- a/docs/solution/1901-2000/1920 - Build Array from Permutation.md
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,81 +0,0 @@
-# 1920. Build Array from Permutation [![share]](https://leetcode.com/problems/build-array-from-permutation/)
-
-![][easy]
-
-## Problem Statement
-
-
Given a zero-based permutationnums (0-indexed), build an array ans of the same length where ans[i] = nums[nums[i]] for each 0 <= i < nums.length and return it.
-
A zero-based permutationnums is an array of distinct integers from 0 to nums.length - 1 (inclusive).
-
-
Example 1:
-
-```
-Input: nums = [0,2,1,5,3,4]
-Output: [0,1,2,4,5,3]
-Explanation: The array ans is built as follows:
-ans = [nums[nums[0]], nums[nums[1]], nums[nums[2]], nums[nums[3]], nums[nums[4]], nums[nums[5]]]
- = [nums[0], nums[2], nums[1], nums[5], nums[3], nums[4]]
- = [0,1,2,4,5,3]
-```
-
-
Example 2:
-
-```
-Input: nums = [5,0,1,2,3,4]
-Output: [4,5,0,1,2,3]
-Explanation: The array ans is built as follows:
-ans = [nums[nums[0]], nums[nums[1]], nums[nums[2]], nums[nums[3]], nums[nums[4]], nums[nums[5]]]
- = [nums[5], nums[0], nums[1], nums[2], nums[3], nums[4]]
- = [4,5,0,1,2,3]
-```
-
-
-
Constraints:
-
-
1 <= nums.length <= 1000
-
0 <= nums[i] < nums.length
-
The elements in nums are distinct.
-
-
-
Follow-up: Can you solve it without using an extra space (i.e., O(1) memory)?
-
-::: details _Click to open Hints_
-
-- Just apply what's said in the statement.
-- Notice that you can't apply it on the same array directly since some elements will change after application
-
-:::
-
-## Solution:
-
-::: code-group
-
-```rs [Rust]
-impl Solution {
- pub fn build_array(nums: Vec) -> Vec {
- let mut result = Vec::new();
-
- for i in 0..nums.len() {
- result.push(nums[nums[i] as usize]);
- }
-
- result
- }
-}
-
-```
-
-:::
-
-### [_..._](#)
-
-```
-
-```
-
-
-
-[share]: https://graph.org/file/3ea5234dda646b71c574a.png
-[easy]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Easy-bright.svg
-[medium]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Medium-yellow.svg
-[hard]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Hard-red.svg
diff --git a/docs/solution/1901-2000/1929 - Concatenation of Array.md b/docs/solution/1901-2000/1929 - Concatenation of Array.md
deleted file mode 100644
index 9768458d..00000000
--- a/docs/solution/1901-2000/1929 - Concatenation of Array.md
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,78 +0,0 @@
-# 1929. Concatenation of Array [![share]](https://leetcode.com/problems/concatenation-of-array/)
-
-![][easy]
-
-## Problem Statement
-
-
Given an integer array nums of length n, you want to create an array ans of length 2n where ans[i] == nums[i] and ans[i + n] == nums[i] for 0 <= i < n (0-indexed).
-
Specifically, ans is the concatenation of two nums arrays.
-
Return the array ans.
-
-
Example 1:
-
-````
-Input: nums = [1,2,1]
-Output: [1,2,1,1,2,1]
-Explanation: The array ans is formed as follows:
-- ans = [nums[0],nums[1],nums[2],nums[0],nums[1],nums[2]]
-- ans = [1,2,1,1,2,1]```
-
-
Example 2:
-
-````
-
-Input: nums = [1,3,2,1]
-Output: [1,3,2,1,1,3,2,1]
-Explanation: The array ans is formed as follows:
-
-- ans = [nums[0],nums[1],nums[2],nums[3],nums[0],nums[1],nums[2],nums[3]]
-- ans = [1,3,2,1,1,3,2,1]
-
-````
-
-
-
Constraints:
-
-
n == nums.length
-
1 <= n <= 1000
-
1 <= nums[i] <= 1000
-
-
-
-::: details _Click to open Hints_
-
-- Build an array of size 2 * n and assign num[i] to ans[i] and ans[i + n]
-
-:::
-
-## Solution:
-
-::: code-group
-
-```rs [Rust]
-impl Solution {
- pub fn get_concatenation(nums: Vec) -> Vec {
- let mut result = nums.clone();
-
- result.extend(nums);
-
- result
- }
-}
-
-````
-
-:::
-
-### [_..._](#)
-
-```
-
-```
-
-
-
-[share]: https://graph.org/file/3ea5234dda646b71c574a.png
-[easy]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Easy-bright.svg
-[medium]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Medium-yellow.svg
-[hard]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Hard-red.svg
diff --git a/docs/solution/1901-2000/1957 - Delete Characters to Make Fancy String.md b/docs/solution/1901-2000/1957 - Delete Characters to Make Fancy String.md
deleted file mode 100644
index cb7c915e..00000000
--- a/docs/solution/1901-2000/1957 - Delete Characters to Make Fancy String.md
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,94 +0,0 @@
-# 1957. Delete Characters to Make Fancy String [![share]](https://leetcode.com/problems/delete-characters-to-make-fancy-string/)
-
-![][easy]
-
-## Problem Statement
-
-
A fancy string is a string where no threeconsecutive characters are equal.
-
-
Given a string s, delete the minimum possible number of characters from s to make it fancy.
-
-
Return the final string after the deletion. It can be shown that the answer will always be unique.
-
-
-
Example 1:
-
-
-Input: s = "leeetcode"
-Output: "leetcode"
-Explanation:
-Remove an 'e' from the first group of 'e's to create "leetcode".
-No three consecutive characters are equal, so return "leetcode".
-
-
-
Example 2:
-
-
-Input: s = "aaabaaaa"
-Output: "aabaa"
-Explanation:
-Remove an 'a' from the first group of 'a's to create "aabaaaa".
-Remove two 'a's from the second group of 'a's to create "aabaa".
-No three consecutive characters are equal, so return "aabaa".
-
-
-
Example 3:
-
-
-Input: s = "aab"
-Output: "aab"
-Explanation: No three consecutive characters are equal, so return "aab".
-
-
-
-
Constraints:
-
-
-
1 <= s.length <= 105
-
s consists only of lowercase English letters.
-
-
-::: details _Click to open Hints_
-
-- What's the optimal way to delete characters if three or more consecutive characters are equal?
-- If three or more consecutive characters are equal, keep two of them and delete the rest.
-
-:::
-
-## Solution:
-
-::: code-group
-
-```java
-class Solution {
- public String makeFancyString(String s) {
- int n = s.length();
-
- if (n == 1 || n == 2)
- return s;
-
- StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder(s.substring(0, 2));
-
- for (int i = 2; i < n; i++)
- if (s.charAt(i) != s.charAt(i - 1) || s.charAt(i) != s.charAt(i - 2))
- sb.append(s.charAt(i));
-
- return sb.toString();
- }
-}
-```
-
-:::
-
-### [_..._](#)
-
-```
-
-```
-
-
-
-[share]: https://graph.org/file/3ea5234dda646b71c574a.png
-[easy]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Easy-bright.svg
-[medium]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Medium-yellow.svg
-[hard]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Hard-red.svg
diff --git a/docs/solution/2101-2200/2011 - Final Value of Variable After Performing Operations.md b/docs/solution/2101-2200/2011 - Final Value of Variable After Performing Operations.md
deleted file mode 100644
index 1487c30b..00000000
--- a/docs/solution/2101-2200/2011 - Final Value of Variable After Performing Operations.md
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,106 +0,0 @@
-# 2011. Final Value of Variable After Performing Operations [![share]](https://leetcode.com/problems/final-value-of-variable-after-performing-operations/)
-
-![][easy]
-
-## Problem Statement
-
-
There is a programming language with only four operations and one variable X:
-
-
++X and X++increments the value of the variable X by 1.
-
--X and X--decrements the value of the variable X by 1.
-
-
Initially, the value of X is 0.
-
Given an array of strings operations containing a list of operations, return the final value of Xafter performing all the operations.
-
-
Example 1:
-
-```
-Input: operations = ["--X","X++","X++"]
-Output: 1
-Explanation: The operations are performed as follows:
-Initially, X = 0.
---X: X is decremented by 1, X = 0 - 1 = -1.
-X++: X is incremented by 1, X = -1 + 1 = 0.
-X++: X is incremented by 1, X = 0 + 1 = 1.
-```
-
-
Example 2:
-
-```
-Input: operations = ["++X","++X","X++"]
-Output: 3
-Explanation: The operations are performed as follows:
-Initially, X = 0.
-++X: X is incremented by 1, X = 0 + 1 = 1.
-++X: X is incremented by 1, X = 1 + 1 = 2.
-X++: X is incremented by 1, X = 2 + 1 = 3.
-```
-
-
Example 3:
-
-```
-Input: operations = ["X++","++X","--X","X--"]
-Output: 0
-Explanation: The operations are performed as follows:
-Initially, X = 0.
-X++: X is incremented by 1, X = 0 + 1 = 1.
-++X: X is incremented by 1, X = 1 + 1 = 2.
---X: X is decremented by 1, X = 2 - 1 = 1.
-X--: X is decremented by 1, X = 1 - 1 = 0.
-```
-
-
-
Constraints:
-
-
1 <= operations.length <= 100
-
operations[i] will be either "++X", "X++", "--X", or "X--".
-
-
-::: details _Click to open Hints_
-
-- There are only two operations to keep track of.
-- Use a variable to store the value after each operation.
-
-:::
-
-## Solution:
-
-::: code-group
-
-```rs [Rust]
-impl Solution {
- pub fn final_value_after_operations(operations: Vec) -> i32 {
- let mut x = 0;
-
- for op in operations {
- if op == "--X" || op == "X--" {
- x -= 1;
- } else {
- x += 1;
- }
- }
-
- x
-
- // operations
- // .iter()
- // .fold(0, |acc, op| acc + (44 - op.as_bytes()[1] as i32))
- }
-}
-
-```
-
-:::
-
-### [_..._](#)
-
-```
-
-```
-
-
-
-[share]: https://graph.org/file/3ea5234dda646b71c574a.png
-[easy]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Easy-bright.svg
-[medium]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Medium-yellow.svg
-[hard]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Hard-red.svg
diff --git a/docs/solution/2101-2200/2114 - Maximum Number of Words Found in Sentences.md b/docs/solution/2101-2200/2114 - Maximum Number of Words Found in Sentences.md
deleted file mode 100644
index 97358b8b..00000000
--- a/docs/solution/2101-2200/2114 - Maximum Number of Words Found in Sentences.md
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,83 +0,0 @@
-# 2114. Maximum Number of Words Found in Sentences [![share]](https://leetcode.com/problems/maximum-number-of-words-found-in-sentences/)
-
-![][easy]
-
-## Problem Statement
-
-
A sentence is a list of words that are separated by a single space with no leading or trailing spaces.
-
You are given an array of strings sentences, where each sentences[i] represents a single sentence.
-
Return the maximum number of words that appear in a single sentence.
-
-
Example 1:
-
-```
-Input: sentences = ["alice and bob love leetcode", "i think so too", "this is great thanks very much"]
-Output: 6
-Explanation:
-- The first sentence, "alice and bob love leetcode", has 5 words in total.
-- The second sentence, "i think so too", has 4 words in total.
-- The third sentence, "this is great thanks very much", has 6 words in total.
-Thus, the maximum number of words in a single sentence comes from the third sentence, which has 6 words.
-```
-
-
Example 2:
-
-```
-Input: sentences = ["please wait", "continue to fight", "continue to win"]
-Output: 3
-Explanation: It is possible that multiple sentences contain the same number of words.
-In this example, the second and third sentences (underlined) have the same number of words.
-```
-
-
-
Constraints:
-
-
1 <= sentences.length <= 100
-
1 <= sentences[i].length <= 100
-
sentences[i] consists only of lowercase English letters and ' ' only.
-
sentences[i] does not have leading or trailing spaces.
-
All the words in sentences[i] are separated by a single space.
-
-
-::: details _Click to open Hints_
-
-- Process each sentence separately and count the number of words by looking for the number of space characters in the sentence and adding it by 1.
-
-:::
-
-## Solution:
-
-::: code-group
-
-```rs [Rust]
-impl Solution {
- pub fn most_words_found(sentences: Vec) -> i32 {
- let mut max_words = 0;
-
- for sentence in sentences {
- let words = sentence.split_whitespace().count();
- if words > max_words {
- max_words = words;
- }
- }
-
- max_words as i32
- }
-}
-
-```
-
-:::
-
-### [_..._](#)
-
-```
-
-```
-
-
-
-[share]: https://graph.org/file/3ea5234dda646b71c574a.png
-[easy]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Easy-bright.svg
-[medium]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Medium-yellow.svg
-[hard]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Hard-red.svg
diff --git a/docs/solution/2101-2200/2160 - Minimum Sum of Four Digit Number After Splitting Digits.md b/docs/solution/2101-2200/2160 - Minimum Sum of Four Digit Number After Splitting Digits.md
deleted file mode 100644
index 2a4c1602..00000000
--- a/docs/solution/2101-2200/2160 - Minimum Sum of Four Digit Number After Splitting Digits.md
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,82 +0,0 @@
-# 2160. Minimum Sum of Four Digit Number After Splitting Digits [![share]](https://leetcode.com/problems/minimum-sum-of-four-digit-number-after-splitting-digits/)
-
-![][easy]
-
-## Problem Statement
-
-
You are given a positive integer num consisting of exactly four digits. Split num into two new integers new1 and new2 by using the digits found in num. Leading zeros are allowed in new1 and new2, and all the digits found in num must be used.
-
-
For example, given num = 2932, you have the following digits: two 2's, one 9 and one 3. Some of the possible pairs [new1, new2] are [22, 93], [23, 92], [223, 9] and [2, 329].
-
-
Return the minimum possible sum of new1 and new2.
-
-
Example 1:
-
-```
-Input: num = 2932
-Output: 52
-Explanation: Some possible pairs [new1, new2] are [29, 23], [223, 9], etc.
-The minimum sum can be obtained by the pair [29, 23]: 29 + 23 = 52.
-```
-
-
Example 2:
-
-```
-Input: num = 4009
-Output: 13
-Explanation: Some possible pairs [new1, new2] are [0, 49], [490, 0], etc.
-The minimum sum can be obtained by the pair [4, 9]: 4 + 9 = 13.
-```
-
-
-
Constraints:
-
-
1000 <= num <= 9999
-
-
-::: details _Click to open Hints_
-
-- Notice that the most optimal way to obtain the minimum possible sum using 4 digits is by summing up two 2-digit numbers.
-- We can use the two smallest digits out of the four as the digits found in the tens place respectively.
-- Similarly, we use the final 2 larger digits as the digits found in the ones place.
-
-:::
-
-## Solution:
-
-::: code-group
-
-```rs [Rust]
-impl Solution {
- pub fn minimum_sum(num: i32) -> i32 {
- let mut number: Vec = num
- .to_string()
- .chars()
- .map(|x| x.to_digit(10).unwrap())
- .collect();
-
- number.sort();
-
- let a: i32 = format!("{}{}", number[0], number[2]).parse().unwrap();
- let b: i32 = format!("{}{}", number[1], number[2]).parse().unwrap();
-
- a + b
- }
-}
-
-```
-
-:::
-
-### [_..._](#)
-
-```
-
-```
-
-
-
-[share]: https://graph.org/file/3ea5234dda646b71c574a.png
-[easy]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Easy-bright.svg
-[medium]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Medium-yellow.svg
-[hard]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Hard-red.svg
diff --git a/docs/solution/2101-2200/2176 - Count Equal and Divisible Pairs in an Array.md b/docs/solution/2101-2200/2176 - Count Equal and Divisible Pairs in an Array.md
deleted file mode 100644
index ed99c7d4..00000000
--- a/docs/solution/2101-2200/2176 - Count Equal and Divisible Pairs in an Array.md
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,80 +0,0 @@
-# 2176. Count Equal and Divisible Pairs in an Array [![share]](https://leetcode.com/problems/count-equal-and-divisible-pairs-in-an-array/)
-
-![][easy]
-
-## Problem Statement
-
-Given a 0-indexed integer array nums of length n and an integer k, return the number of pairs(i, j)where0 <= i < j < n, such thatnums[i] == nums[j]and(i \* j)is divisible byk.
-
-
-
Example 1:
-
-```
-Input: nums = [3,1,2,2,2,1,3], k = 2
-Output: 4
-Explanation:
-There are 4 pairs that meet all the requirements:
-- nums[0] == nums[6], and 0 * 6 == 0, which is divisible by 2.
-- nums[2] == nums[3], and 2 * 3 == 6, which is divisible by 2.
-- nums[2] == nums[4], and 2 * 4 == 8, which is divisible by 2.
-- nums[3] == nums[4], and 3 * 4 == 12, which is divisible by 2.
-```
-
-
Example 2:
-
-```
-Input: nums = [1,2,3,4], k = 1
-Output: 0
-Explanation: Since no value in nums is repeated, there are no pairs (i,j) that meet all the requirements.
-```
-
-
-
Constraints:
-
-
1 <= nums.length <= 100
-
1 <= nums[i], k <= 100
-
-
-::: details _Click to open Hints_
-
-- For every possible pair of indices (i, j) where i < j, check if it satisfies the given conditions.
-
-:::
-
-## Solution:
-
-::: code-group
-
-```rs [Rust]
-impl Solution {
- pub fn count_pairs(nums: Vec, k: i32) -> i32 {
- let mut ans = 0;
-
- for i in 0..nums.len() {
- for j in i + 1..nums.len() {
- if nums[i] == nums[j] && (i * j) % k as usize == 0 {
- ans += 1;
- }
- }
- }
-
- ans
- }
-}
-
-```
-
-:::
-
-### [_..._](#)
-
-```
-
-```
-
-
-
-[share]: https://graph.org/file/3ea5234dda646b71c574a.png
-[easy]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Easy-bright.svg
-[medium]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Medium-yellow.svg
-[hard]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Hard-red.svg
diff --git a/docs/solution/2101-2200/2187 - Minimum Time to Complete Trips.md b/docs/solution/2101-2200/2187 - Minimum Time to Complete Trips.md
deleted file mode 100644
index 32f4af71..00000000
--- a/docs/solution/2101-2200/2187 - Minimum Time to Complete Trips.md
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,97 +0,0 @@
-# 2187. Minimum Time to Complete Trips [![share]](https://leetcode.com/problems/minimum-time-to-complete-trips/)
-
-![][medium]
-
-## Problem Statement
-
-
You are given an array time where time[i] denotes the time taken by the ith bus to complete one trip.
-
Each bus can make multiple trips successively; that is, the next trip can start immediately after completing the current trip. Also, each bus operates independently; that is, the trips of one bus do not influence the trips of any other bus.
-
You are also given an integer totalTrips, which denotes the number of trips all buses should make in total. Return the minimum time required for all buses to complete at leasttotalTrips trips.
-
-
Example 1:
-
-```
-Input: time = [1,2,3], totalTrips = 5
-Output: 3
-Explanation:
-- At time t = 1, the number of trips completed by each bus are [1,0,0].
- The total number of trips completed is 1 + 0 + 0 = 1.
-- At time t = 2, the number of trips completed by each bus are [2,1,0].
- The total number of trips completed is 2 + 1 + 0 = 3.
-- At time t = 3, the number of trips completed by each bus are [3,1,1].
- The total number of trips completed is 3 + 1 + 1 = 5.
-So the minimum time needed for all buses to complete at least 5 trips is 3.
-```
-
-
Example 2:
-
-```
-Input: time = [2], totalTrips = 1
-Output: 2
-Explanation:
-There is only one bus, and it will complete its first trip at t = 2.
-So the minimum time needed to complete 1 trip is 2.
-```
-
-
-
Constraints:
-
-
1 <= time.length <= 105
-
1 <= time[i], totalTrips <= 107
-
-
-::: details _Click to open Hints_
-
-- For a given amount of time, how can we count the total number of trips completed by all buses within that time?
-- Consider using binary search.
-
-:::
-
-## Solution:
-
-::: code-group
-
-```rs [Rust]
-impl Solution {
- pub fn minimum_time(time: Vec, total_trips: i32) -> i64 {
- let mut time = time;
- time.sort();
-
- let mut left = 0_i64;
- let mut right = 100_000_000_000_000;
- let mut ans = right;
-
- while left < right {
- let mid = (left + right) / 2;
- let mut trips = 0;
- for i in 0..time.len() {
- trips += mid / time[i] as i64;
- }
- if trips >= total_trips as i64 {
- ans = ans.min(mid);
- right = mid;
- } else {
- left = mid + 1;
- }
- }
-
- ans
- }
-}
-
-```
-
-:::
-
-### [_..._](#)
-
-```
-
-```
-
-
-
-[share]: https://graph.org/file/3ea5234dda646b71c574a.png
-[easy]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Easy-bright.svg
-[medium]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Medium-yellow.svg
-[hard]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Hard-red.svg
diff --git a/docs/solution/2101-2200/2413 - Smallest Even Multiple.md b/docs/solution/2101-2200/2413 - Smallest Even Multiple.md
deleted file mode 100644
index 919de98f..00000000
--- a/docs/solution/2101-2200/2413 - Smallest Even Multiple.md
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,69 +0,0 @@
-# 2413. Smallest Even Multiple [![share]](https://leetcode.com/problems/smallest-even-multiple/)
-
-![][easy]
-
-## Problem Statement
-
-Given a positive integer n, return the smallest positive integer that is a multiple of both2 and n.
-
-
-
Example 1:
-
-```
-Input: n = 5
-Output: 10
-Explanation: The smallest multiple of both 5 and 2 is 10.
-```
-
-
Example 2:
-
-```
-Input: n = 6
-Output: 6
-Explanation: The smallest multiple of both 6 and 2 is 6. Note that a number is a multiple of itself.
-```
-
-
-
Constraints:
-
-
1 <= n <= 150
-
-
-::: details _Click to open Hints_
-
-- A guaranteed way to find a multiple of 2 and n is to multiply them together. When is this the answer, and when is there a smaller answer?
-- There is a smaller answer when n is even.
-
-:::
-
-## Solution:
-
-::: code-group
-
-```rs [Rust]
-impl Solution {
- pub fn smallest_even_multiple(n: i32) -> i32 {
- if n % 2 == 0 {
- return n;
- } else {
- return n * 2;
- }
- }
-}
-
-```
-
-:::
-
-### [_..._](#)
-
-```
-
-```
-
-
-
-[share]: https://graph.org/file/3ea5234dda646b71c574a.png
-[easy]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Easy-bright.svg
-[medium]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Medium-yellow.svg
-[hard]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Hard-red.svg
diff --git a/docs/solution/2201-2300/2235 - Add Two Integers.md b/docs/solution/2201-2300/2235 - Add Two Integers.md
deleted file mode 100644
index 498badc5..00000000
--- a/docs/solution/2201-2300/2235 - Add Two Integers.md
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,58 +0,0 @@
-# 2235. Add Two Integers [![share]](https://leetcode.com/problems/add-two-integers/)
-
-![][easy]
-
-## Problem Statement
-
-Given two integers num1 and num2, return the sum of the two integers.
-
-
-
Example 1:
-
-```
-Input: num1 = 12, num2 = 5
-Output: 17
-Explanation: num1 is 12, num2 is 5, and their sum is 12 + 5 = 17, so 17 is returned.
-```
-
-
-
-## Solution:
-
-::: code-group
-
-```rs [Rust]
-impl Solution {
- pub fn sum(num1: i32, num2: i32) -> i32 {
- num1 + num2
- }
-}
-
-```
-
-:::
-
-### [_..._](#)
-
-```
-
-```
-
-
-
-[share]: https://graph.org/file/3ea5234dda646b71c574a.png
-[easy]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Easy-bright.svg
-[medium]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Medium-yellow.svg
-[hard]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Hard-red.svg
diff --git a/docs/solution/2201-2300/2236 - Root Equals Sum of Children.md b/docs/solution/2201-2300/2236 - Root Equals Sum of Children.md
deleted file mode 100644
index cbad8645..00000000
--- a/docs/solution/2201-2300/2236 - Root Equals Sum of Children.md
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,71 +0,0 @@
-# 2236. Root Equals Sum of Children [![share]](https://leetcode.com/problems/root-equals-sum-of-children/)
-
-![][easy]
-
-## Problem Statement:
-
-You are given the root of a **binary tree** that consists of exactly `3` nodes: the root, its left child, and its right child.
-
-Return `true` if the value of the root is equal to the **sum** of the values of its two children, or `false` otherwise.
-
-### Example 1:
-
-
-
-```
-Input: root = [10,4,6]
-Output: true
-```
-
-### Explanation:
-
-```
-The values of the root, its left child, and its right child are 10, 4, and 6, respectively.
-10 is equal to 4 + 6, so we return true.
-```
-
-### Example 2:
-
-
-
-```
-Input: root = [5,3,1]
-Output: false
-```
-
-### Explanation:
-
-```
-The values of the root, its left child, and its right child are 5, 3, and 1, respectively.
-5 is not equal to 3 + 1, so we return false.
-```
-
-### Constraints:
-
-- The tree consists only of the root, its left child, and its right child.
-- -100 <= Node.val <= 100
-
-## Solution:
-
-::: code-group
-
-```java
-public class RootEqualsSumOfChildren {
- public boolean checkTree(TreeNode root) {
- return root.val == root.left.val + root.right.val;
- }
-}
-```
-
-:::
-
-### [_..._](#)
-
-```
-
-```
-
-
-
-[share]: https://img.icons8.com/external-anggara-blue-anggara-putra/20/000000/external-share-user-interface-basic-anggara-blue-anggara-putra-2.png
-[easy]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Easy-green.svg
diff --git a/docs/solution/2301-2400/2348 - Number of Zero-Filled Subarrays.md b/docs/solution/2301-2400/2348 - Number of Zero-Filled Subarrays.md
deleted file mode 100644
index 59467594..00000000
--- a/docs/solution/2301-2400/2348 - Number of Zero-Filled Subarrays.md
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,98 +0,0 @@
-# 2348. Number of Zero-Filled Subarrays [![share]](https://leetcode.com/problems/number-of-zero-filled-subarrays/)
-
-![][medium]
-
-## Problem Statement
-
-
Given an integer array nums, return the number of subarrays filled with 0.
-
A subarray is a contiguous non-empty sequence of elements within an array.
-
-
Example 1:
-
-````
-Input: nums = [1,3,0,0,2,0,0,4]
-Output: 6
-Explanation:
-There are 4 occurrences of [0] as a subarray.
-There are 2 occurrences of [0,0] as a subarray.
-There is no occurrence of a subarray with a size more than 2 filled with 0. Therefore, we return 6.```
-
-
Example 2:
-
-````
-
-Input: nums = [0,0,0,2,0,0]
-Output: 9
-Explanation:
-There are 5 occurrences of [0] as a subarray.
-There are 3 occurrences of [0,0] as a subarray.
-There is 1 occurrence of [0,0,0] as a subarray.
-There is no occurrence of a subarray with a size more than 3 filled with 0. Therefore, we return 9.
-
-```
-
-
Example 3:
-
-```
-
-Input: nums = [2,10,2019]
-Output: 0
-Explanation: There is no subarray filled with 0. Therefore, we return 0.
-
-````
-
-
-
Constraints:
-
-
1 <= nums.length <= 105
-
-109 <= nums[i] <= 109
-
-
-
-::: details _Click to open Hints_
-
-- For each zero, you can calculate the number of zero-filled subarrays that end on that index, which is the number of consecutive zeros behind the current element + 1.
-- Maintain the number of consecutive zeros behind the current element, count the number of zero-filled subarrays that end on each index, sum it up to get the answer.
-
-:::
-
-## Solution:
-
-::: code-group
-
-```rs [Rust]
-impl Solution {
- pub fn zero_filled_subarray(nums: Vec) -> i64 {
- let mut nums = nums;
- nums.push(1);
-
- let (mut res, mut count) = (0, 0);
- for num in nums {
- if num == 0 {
- count += 1;
- } else {
- res += count * (count + 1) / 2;
- count = 0;
- }
- }
-
- res
- }
-}
-
-````
-
-:::
-
-### [_..._](#)
-
-```
-
-```
-
-
-
-[share]: https://graph.org/file/3ea5234dda646b71c574a.png
-[easy]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Easy-bright.svg
-[medium]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Medium-yellow.svg
-[hard]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Hard-red.svg
diff --git a/docs/solution/2301-2400/2396 - Strictly Palindromic Number.md b/docs/solution/2301-2400/2396 - Strictly Palindromic Number.md
deleted file mode 100644
index b0e86444..00000000
--- a/docs/solution/2301-2400/2396 - Strictly Palindromic Number.md
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,79 +0,0 @@
-# 2396. Strictly Palindromic Number [![share]](https://leetcode.com/problems/strictly-palindromic-number/)
-
-![][medium]
-
-## Problem Statement
-
-
An integer n is strictly palindromic if, for every base b between 2 and n - 2 (inclusive), the string representation of the integer n in base b is palindromic.
-
Given an integer n, return trueif n is strictly palindromic and false otherwise.
-
A string is palindromic if it reads the same forward and backward.
-
-
Example 1:
-
-```
-Input: n = 9
-Output: false
-Explanation: In base 2: 9 = 1001 (base 2), which is palindromic.
-In base 3: 9 = 100 (base 3), which is not palindromic.
-Therefore, 9 is not strictly palindromic so we return false.
-Note that in bases 4, 5, 6, and 7, n = 9 is also not palindromic.
-```
-
-
Example 2:
-
-```
-Input: n = 4
-Output: false
-Explanation: We only consider base 2: 4 = 100 (base 2), which is not palindromic.
-Therefore, we return false.
-
-```
-
-
-
Constraints:
-
-
4 <= n <= 105
-
-
-::: details _Click to open Hints_
-
-- Consider the representation of the given number in the base n - 2.
-- The number n in base (n - 2) is always 12, which is not palindromic.
-
-:::
-
-## Solution:
-
-::: code-group
-
-```rs [Rust]
-impl Solution {
- pub fn is_strictly_palindromic(n: i32) -> bool {
- let mut n = n;
- let mut rev = 0;
-
- while n > 0 {
- rev = rev * 10 + n % 10;
- n /= 10;
- }
-
- rev == n
- }
-}
-
-```
-
-:::
-
-### [_..._](#)
-
-```
-
-```
-
-
-
-[share]: https://graph.org/file/3ea5234dda646b71c574a.png
-[easy]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Easy-bright.svg
-[medium]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Medium-yellow.svg
-[hard]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Hard-red.svg
diff --git a/docs/solution/2401-2500/2427 - Number of Common Factors.md b/docs/solution/2401-2500/2427 - Number of Common Factors.md
deleted file mode 100644
index b7c520ac..00000000
--- a/docs/solution/2401-2500/2427 - Number of Common Factors.md
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,73 +0,0 @@
-# 2427. Number of Common Factors [![share]](https://leetcode.com/problems/number-of-common-factors/)
-
-![][easy]
-
-## Problem Statement
-
-
Given two positive integers a and b, return the number of common factors of a and b.
-
An integer x is a common factor of a and b if x divides both a and b.
-
-
Example 1:
-
-```
-Input: a = 12, b = 6
-Output: 4
-Explanation: The common factors of 12 and 6 are 1, 2, 3, 6.
-```
-
-
Example 2:
-
-```
-Input: a = 25, b = 30
-Output: 2
-Explanation: The common factors of 25 and 30 are 1, 5.
-```
-
-
-
Constraints:
-
-
1 <= a, b <= 1000
-
-
-::: details _Click to open Hints_
-
-- For each integer in range [1,1000], check if it’s divisible by both A and B.
-
-:::
-
-## Solution:
-
-::: code-group
-
-```rs [Rust]
-impl Solution {
- pub fn common_factors(a: i32, b: i32) -> i32 {
- let mut count = 0;
- let limit = i32::min(a, b);
-
- for i in 1..=limit {
- if a % i == 0 && b % i == 0 {
- count += 1;
- }
- }
-
- count
- }
-}
-
-```
-
-:::
-
-### [_..._](#)
-
-```
-
-```
-
-
-
-[share]: https://graph.org/file/3ea5234dda646b71c574a.png
-[easy]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Easy-bright.svg
-[medium]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Medium-yellow.svg
-[hard]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Hard-red.svg
diff --git a/docs/solution/2401-2500/2444 - Count Subarrays With Fixed Bounds.md b/docs/solution/2401-2500/2444 - Count Subarrays With Fixed Bounds.md
deleted file mode 100644
index a0ba658d..00000000
--- a/docs/solution/2401-2500/2444 - Count Subarrays With Fixed Bounds.md
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,101 +0,0 @@
-# 2444. Count Subarrays With Fixed Bounds [![share]](https://leetcode.com/problems/count-subarrays-with-fixed-bounds/)
-
-![][hard]
-
-## Problem Statement
-
-
You are given an integer array nums and two integers minK and maxK.
-
A fixed-bound subarray of nums is a subarray that satisfies the following conditions:
-
-
The minimum value in the subarray is equal to minK.
-
The maximum value in the subarray is equal to maxK.
-
-
Return the number of fixed-bound subarrays.
-
A subarray is a contiguous part of an array.
-
-
Example 1:
-
-```
-Input: nums = [1,3,5,2,7,5], minK = 1, maxK = 5
-Output: 2
-Explanation: The fixed-bound subarrays are [1,3,5] and [1,3,5,2].
-```
-
-
Example 2:
-
-```
-Input: nums = [1,1,1,1], minK = 1, maxK = 1
-Output: 10
-Explanation: Every subarray of nums is a fixed-bound subarray. There are 10 possible subarrays.
-```
-
-
-
Constraints:
-
-
2 <= nums.length <= 105
-
1 <= nums[i], minK, maxK <= 106
-
-
-::: details _Click to open Hints_
-
-- Can you solve the problem if all the numbers in the array were between minK and maxK inclusive?
-- Think of the inclusion-exclusion principle.
-- Divide the array into multiple subarrays such that each number in each subarray is between minK and maxK inclusive, solve the previous problem for each subarray, and sum all the answers.
-
-:::
-
-## Solution:
-
-::: code-group
-
-```rs [Rust]
-impl Solution {
- pub fn count_subarrays(nums: Vec, min_k: i32, max_k: i32) -> i64 {
- let (mut bad, mut min, mut max) = (-1, -1, -1);
- // bad is the index of the first number that is not in the range [min_k, max_k]
- let mut res = 0;
-
- for (i, &num) in nums.iter().enumerate() {
- let i = i as i64;
-
- // set i to bad index if it is not in the range [min_k, max_k]
- if !(min_k <= num && num <= max_k) {
- bad = i;
- }
-
- // set i to min index if num is equal to min_k
- if min_k == num {
- min = i;
- }
- // set i to max index if num is equal to max_k
- if max_k == num {
- max = i;
- }
-
- // it is the last starting point for the subarray
- let start = min.min(max);
- if start > bad {
- res += start - bad; // add the number of subarrays b/w [bad + 1, start]
- }
- }
-
- res
- }
-}
-
-```
-
-:::
-
-### [_..._](#)
-
-```
-
-```
-
-
-
-[share]: https://graph.org/file/3ea5234dda646b71c574a.png
-[easy]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Easy-bright.svg
-[medium]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Medium-yellow.svg
-[hard]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Hard-red.svg
diff --git a/docs/solution/2401-2500/2469 - Convert the Temperature.md b/docs/solution/2401-2500/2469 - Convert the Temperature.md
deleted file mode 100644
index 17514b11..00000000
--- a/docs/solution/2401-2500/2469 - Convert the Temperature.md
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,74 +0,0 @@
-# 2469. Convert the Temperature [![share]](https://leetcode.com/problems/convert-the-temperature/)
-
-![][easy]
-
-## Problem Statement
-
-
You are given a non-negative floating point number rounded to two decimal places celsius, that denotes the temperature in Celsius.
-
You should convert Celsius into Kelvin and Fahrenheit and return it as an array ans = [kelvin, fahrenheit].
-
Return the array ans. Answers within 10-5 of the actual answer will be accepted.
-
Note that:
-
-
Kelvin = Celsius + 273.15
-
Fahrenheit = Celsius * 1.80 + 32.00
-
-
-
Example 1:
-
-```
-Input: celsius = 36.50
-Output: [309.65000,97.70000]
-Explanation: Temperature at 36.50 Celsius converted in Kelvin is 309.65 and converted in Fahrenheit is 97.70.
-```
-
-
Example 2:
-
-```
-Input: celsius = 122.11
-Output: [395.26000,251.79800]
-Explanation: Temperature at 122.11 Celsius converted in Kelvin is 395.26 and converted in Fahrenheit is 251.798.
-```
-
-
-
Constraints:
-
-
0 <= celsius <= 1000
-
-
-::: details _Click to open Hints_
-
-- Implement formulas that are given in the statement.
-
-:::
-
-## Solution:
-
-::: code-group
-
-```rs [Rust]
-impl Solution {
- pub fn convert_temperature(celsius: f64) -> Vec {
- let fahrenheit = celsius * 1.8 + 32.0;
-
- let kelvin = celsius + 273.15;
-
- vec![fahrenheit, kelvin]
- }
-}
-
-```
-
-:::
-
-### [_..._](#)
-
-```
-
-```
-
-
-
-[share]: https://graph.org/file/3ea5234dda646b71c574a.png
-[easy]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Easy-bright.svg
-[medium]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Medium-yellow.svg
-[hard]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Hard-red.svg
diff --git a/docs/solution/2401-2500/2574 - Left and Right Sum Differences.md b/docs/solution/2401-2500/2574 - Left and Right Sum Differences.md
deleted file mode 100644
index 97705f4c..00000000
--- a/docs/solution/2401-2500/2574 - Left and Right Sum Differences.md
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,88 +0,0 @@
-# 2574. Left and Right Sum Differences [![share]](https://leetcode.com/problems/left-and-right-sum-differences/)
-
-![][easy]
-
-## Problem Statement
-
-
Given a 0-indexed integer array nums, find a 0-indexed integer array answer where:
-
-
answer.length == nums.length.
-
answer[i] = |leftSum[i] - rightSum[i]|.
-
-
Where:
-
-
leftSum[i] is the sum of elements to the left of the index i in the array nums. If there is no such element, leftSum[i] = 0.
-
rightSum[i] is the sum of elements to the right of the index i in the array nums. If there is no such element, rightSum[i] = 0.
-
-
Return the arrayanswer.
-
-
Example 1:
-
-```
-Input: nums = [10,4,8,3]
-Output: [15,1,11,22]
-Explanation: The array leftSum is [0,10,14,22] and the array rightSum is [15,11,3,0].
-The array answer is [|0 - 15|,|10 - 11|,|14 - 3|,|22 - 0|] = [15,1,11,22].
-```
-
-
Example 2:
-
-```
-Input: nums = [1]
-Output: [0]
-Explanation: The array leftSum is [0] and the array rightSum is [0].
-The array answer is [|0 - 0|] = [0].
-```
-
-
-
Constraints:
-
-
1 <= nums.length <= 1000
-
1 <= nums[i] <= 105
-
-
-::: details _Click to open Hints_
-
-- For each index i, maintain two variables leftSum and rightSum.
-- Iterate on the range j: [0 … i - 1] and add nums[j] to the leftSum and similarly iterate on the range j: [i + 1 … nums.length - 1] and add nums[j] to the rightSum.
-
-:::
-
-## Solution:
-
-::: code-group
-
-```rs [Rust]
-impl Solution {
- pub fn left_rigth_difference(nums: Vec) -> Vec {
- let mut result = vec![];
-
- let sum = nums.iter().sum::();
- let mut left_sum = 0;
-
- for i in 0..nums.len() {
- let right_sum = sum - left_sum - nums[i];
- result.push((left_sum - right_sum).abs());
- left_sum += nums[i];
- }
-
- result
- }
-}
-
-```
-
-:::
-
-### [_..._](#)
-
-```
-
-```
-
-
-
-[share]: https://graph.org/file/3ea5234dda646b71c574a.png
-[easy]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Easy-bright.svg
-[medium]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Medium-yellow.svg
-[hard]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Hard-red.svg
diff --git a/docs/solution/2501-2600/2551 - Put Marbles in Bags.md b/docs/solution/2501-2600/2551 - Put Marbles in Bags.md
deleted file mode 100644
index 4e6eb9f7..00000000
--- a/docs/solution/2501-2600/2551 - Put Marbles in Bags.md
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,88 +0,0 @@
-# 2551. Put Marbles in Bags [![share]](https://leetcode.com/problems/put-marbles-in-bags/)
-
-![][hard]
-
-## Problem Statement
-
-
You have k bags. You are given a 0-indexed integer array weights where weights[i] is the weight of the ith marble. You are also given the integer k.
-
Divide the marbles into the k bags according to the following rules:
-
-
No bag is empty.
-
If the ith marble and jth marble are in a bag, then all marbles with an index between the ith and jth indices should also be in that same bag.
-
If a bag consists of all the marbles with an index from i to j inclusively, then the cost of the bag is weights[i] + weights[j].
-
-
The score after distributing the marbles is the sum of the costs of all the k bags.
-
Return the difference between the maximum and minimum scores among marble distributions.
-
-
Example 1:
-
-```
-Input: weights = [1,3,5,1], k = 2
-Output: 4
-Explanation:
-The distribution [1],[3,5,1] results in the minimal score of (1+1) + (3+1) = 6.
-The distribution [1,3],[5,1], results in the maximal score of (1+3) + (5+1) = 10.
-Thus, we return their difference 10 - 6 = 4.
-```
-
-
Example 2:
-
-```
-Input: weights = [1, 3], k = 2
-Output: 0
-Explanation: The only distribution possible is [1],[3].
-Since both the maximal and minimal score are the same, we return 0.
-```
-
-
-
Constraints:
-
-
1 <= k <= weights.length <= 105
-
1 <= weights[i] <= 109
-
-
-::: details _Click to open Hints_
-
-- Each bag will contain a sub-array.
-- Only the endpoints of the sub-array matter.
-- Try to use a priority queue.
-
-:::
-
-## Solution:
-
-::: code-group
-
-```rs [Rust]
-impl Solution {
- pub fn put_marbles(weights: Vec, k: i32) -> i64 {
- let n = weights.len();
- // pair weights of adjacent bags
- let mut pair_weights: Vec<_> = (0..n - 1).map(|i| weights[i] + weights[i + 1]).collect();
-
- // sort the pair weights
- pair_weights.sort();
-
- // sum the difference between the largest and smallest pair weights
- (0..(k - 1) as usize).fold(0_i64, |ans, i| {
- ans + (pair_weights[n - 2 - i] - pair_weights[i]) as i64
- })
- }
-}
-
-```
-
-:::
-
-### [_..._](#)
-
-```
-
-```
-
-
-
-[share]: https://graph.org/file/3ea5234dda646b71c574a.png
-[easy]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Easy-bright.svg
-[medium]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Medium-yellow.svg
-[hard]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Hard-red.svg
diff --git a/docs/public/favicon.ico b/favicon.ico
similarity index 100%
rename from docs/public/favicon.ico
rename to favicon.ico
diff --git a/hashmap.json b/hashmap.json
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..17f13b12
--- /dev/null
+++ b/hashmap.json
@@ -0,0 +1 @@
+{"serialwise.md":"cba008fe","topicwise.md":"cd380769","solution_0001-0100_001 - two sum.md":"9e2ed953","solution_0001-0100_002 - add two numbers.md":"bf9d46ea","solution_0001-0100_004 - median of two sorted arrays.md":"2001f2e0","solution_0001-0100_007 - reverse integer.md":"c5e5d46f","solution_0001-0100_013 - roman to integer.md":"1346a5a7","solution_0001-0100_014 - longest common prefix.md":"7401d23f","solution_0001-0100_020 - valid parentheses.md":"616b717c","solution_0001-0100_021 - merge two sorted lists.md":"b809ff60","solution_0001-0100_022 - generate parentheses.md":"ca0d2d49","solution_0001-0100_024 - swap nodes in pairs.md":"db61724e","solution_0001-0100_026 - remove duplicates from sorted array.md":"47a74ae0","solution_0001-0100_027 - remove element.md":"9692244b","solution_0001-0100_028 - find the index of the first occurrence in a string.md":"94646e7c","solution_0001-0100_035 - search insert position.md":"a30de18c","solution_0001-0100_037 - sudoku solver.md":"a467e446","solution_0001-0100_041 - first missing positive.md":"3bfd8d7b","solution_0001-0100_042 - trapping rain water.md":"d9f1c14d","solution_0001-0100_048 - rotate image.md":"9d96a01b","solution_0001-0100_051 - n-queens.md":"36f60070","solution_0001-0100_053 - maximum subarray.md":"edde9bbd","solution_0001-0100_055 - jump game.md":"dc2f1b6e","solution_0001-0100_061 - rotate list .md":"27b79047","solution_0001-0100_067 - add binary.md":"19cdcaa1","solution_0001-0100_069 - sqrt(x).md":"ceb92e95","solution_0001-0100_070 - climbing stairs.md":"c08915ef","solution_0001-0100_072 - edit distance.md":"f074a098","solution_0001-0100_075 - sort colors.md":"ccfc4cbd","solution_0001-0100_078 - subsets.md":"159b7a87","solution_0001-0100_083 - remove duplicates from sorted list.md":"bc9d7b08","solution_0001-0100_088 - merge sorted array.md":"a68d9d11","solution_0001-0100_094 - binary tree inorder traversal.md":"e8803ad6","solution_0001-0100_098 - validate binary search tree.md":"be478d08","solution_0001-0100_100 - same tree.md":"38f2f9a7","solution_0101-0200_101 - symmetric tree.md":"c2f61c5c","solution_0101-0200_103 - binary tree zigzag level order traversal.md":"919e5381","solution_0101-0200_104 - maximum depth of binary tree.md":"3f09bfed","solution_0101-0200_106 - construct binary tree from inorder and postorder traversal.md":"106c3d58","solution_0101-0200_108 - convert sorted array to binary search tree.md":"da20b39a","solution_0101-0200_109 - convert sorted list to binary search tree.md":"c39d8c6b","solution_0101-0200_110 - balanced binary tree.md":"ecffe2ce","solution_0101-0200_111 - minimum depth of binary tree.md":"2d59e11c","solution_1401-1500_1480 - running sum of 1d array.md":"67f66fb0","solution_1401-1500_1491 - average salary excluding the minimum and maximum salary.md":"80cb080a","solution_1401-1500_1498 - number of subsequences that satisfy the given sum condition.md":"318f6205","solution_1501-1600_1512 - number of good pairs.md":"f54c2eec","solution_1501-1600_1523. count odd numbers in an interval range.md":"4cc92523","solution_1501-1600_1537 - get the maximum score.md":"73e65486","solution_1501-1600_1539 - kth missing positive number.md":"ee787093","solution_1601-1700_1672 - richest customer wealth.md":"0aef5bd3","solution_1601-1700_1689 - partitioning into minimum number of deci-binary numbers.md":"289724ac","solution_1901-2000_1920 - build array from permutation.md":"d4764baf","solution_1901-2000_1929 - concatenation of array.md":"f1106b2b","solution_1901-2000_1957 - delete characters to make fancy string.md":"c16dbb86","solution_2101-2200_2114 - maximum number of words found in sentences.md":"9727b95e","solution_2101-2200_2160 - minimum sum of four digit number after splitting digits.md":"8944b3ee","solution_2101-2200_2176 - count equal and divisible pairs in an array.md":"43e7bbc1","solution_2101-2200_2413 - smallest even multiple.md":"45b7de05","solution_2201-2300_2236 - root equals sum of children.md":"2e414e5e","solution_2301-2400_2348 - number of zero-filled subarrays.md":"a6743e9b","solution_2301-2400_2396 - strictly palindromic number.md":"b6902872","solution_2401-2500_2427 - number of common factors.md":"7e6bc604","solution_2401-2500_2444 - count subarrays with fixed bounds.md":"f7164976","solution_2401-2500_2469 - convert the temperature.md":"539adef9","solution_2401-2500_2574 - left and right sum differences.md":"98c97f87","solution_2501-2600_2551 - put marbles in bags.md":"50c1a855","solution_0001-0100_009 - palindrome number.md":"93ab32fc","solution_0001-0100_058 - length of last word.md":"af3582e3","solution_0001-0100_074 - search a 2d matrix.md":"a7bd4ebb","solution_2101-2200_2011 - final value of variable after performing operations.md":"7ad7e527","solution_2101-2200_2187 - minimum time to complete trips.md":"5a37b03e","solution_0401-0500_441 - arranging coins.md":"312e9d1b","solution_0101-0200_118 - pascals triangle.md":"feaa05af","solution_0101-0200_119 - pascals triangle ii.md":"c0152e68","solution_0101-0200_121 - best time to buy and sell stock.md":"0356a772","solution_0101-0200_125 - valid palindrome.md":"e80bb385","solution_0101-0200_136 - single number.md":"3349dbec","solution_0101-0200_141 - linked list cycle.md":"1872d26d","solution_0101-0200_142 - linked list cycle ii.md":"8c585262","solution_0101-0200_144 - binary tree preorder traversal.md":"a71cb20b","solution_0101-0200_145 - binary tree postorder traversal.md":"291be10d","solution_0101-0200_160 - intersection of two linked lists.md":"a8640b62","solution_0101-0200_169 - majority element.md":"015189a4","solution_0101-0200_172 - factorial trailing zeroes.md":"1462e553","solution_0101-0200_190 - reverse bits.md":"8531cca3","solution_0301-0400_387 - first unique character in a string.md":"8181902a","solution_0101-0200_193 - valid phone numbers.md":"c98e421d","solution_0101-0200_195 - tenth line.md":"e150afd0","solution_0101-0200_199 - binary tree right side view.md":"82de7b92","solution_0101-0200_200 - number of islands.md":"e951265d","solution_0201-0300_202 - happy number.md":"b9b908eb","solution_0201-0300_203 - remove linked list elements.md":"a2c7afdc","solution_0201-0300_205 - isomorphic strings.md":"2ba3422c","solution_0201-0300_206 - reverse linked list.md":"ab4ec40f","solution_0201-0300_211 - design add and search words data structure.md":"c4db6b8f","solution_0201-0300_217 - contains duplicate.md":"b212f1d3","solution_0201-0300_219 - contains duplicate ii.md":"398125d0","solution_0201-0300_222 - count complete tree nodes.md":"6017f601","solution_0201-0300_225 - implement stack using queues.md":"02261001","solution_0201-0300_226 - invert binary tree.md":"c4fc3284","solution_0201-0300_228 - summary ranges.md":"d08299a4","solution_0201-0300_230 - kth smallest element in a bst.md":"e2a247db","solution_0201-0300_231 - power of two.md":"30383506","solution_0201-0300_232 - implement queue using stacks.md":"06884d6c","solution_0201-0300_236 - lowest common ancestor of a binary tree.md":"ba62af67","solution_0201-0300_242 - valid anagram.md":"1cd985ae","solution_0201-0300_257 - binary tree paths.md":"61b6511a","solution_0201-0300_258 - add digits.md":"24d40eb3","solution_0201-0300_263 - ugly number.md":"428eec53","solution_0201-0300_268 - missing number.md":"bcd71582","solution_0201-0300_278 - first bad version.md":"0ff223ca","solution_0201-0300_279 - perfect squares.md":"ca4aeddd","solution_0201-0300_283 - move zeroes.md":"0f076f12","solution_0201-0300_290 - word pattern.md":"be428cac","solution_0201-0300_292 - nim game.md":"006de971","solution_0201-0300_300 - longest increasing subsequence.md":"703c8451","solution_0301-0400_322 - coin change.md":"6d01d772","solution_0301-0400_326 - power of three.md":"b7dde1c6","solution_0301-0400_337 - house robber iii.md":"d865bde5","solution_0301-0400_338 - counting bits.md":"56c698f2","solution_0301-0400_342 - power of four.md":"2f5bf262","solution_0301-0400_345 - reverse vowels of a string.md":"b4c01eaf","solution_0301-0400_349 - intersection of two arrays.md":"9ea1c865","solution_0301-0400_350 - intersection of two arrays ii.md":"1ee76df3","solution_0301-0400_367 - valid perfect square.md":"b3c76a65","solution_0301-0400_369 - plus one linked list.md":"4a3f5d04","solution_0301-0400_374 - guess number higher or lower.md":"e3e786f3","solution_0301-0400_382 - linked list random node.md":"4fcba4d4","solution_0301-0400_383 - ransom note.md":"5edeca1f","solution_0101-0200_122 - best time to buy and sell stock ii.md":"4ca5a16f","solution_0101-0200_129 - sum root to leaf numbers.md":"d631d681","solution_0301-0400_389 - find the difference.md":"c48692f5","solution_0101-0200_191 - number of 1 bits.md":"b5946bbe","solution_0401-0500_401 - binary watch.md":"ae7474be","solution_0201-0300_234 - palindrome linked list.md":"cb51ca4c","solution_0401-0500_404 - sum of left leaves.md":"5332ffa3","solution_0401-0500_414 - third maximum number.md":"04251e05","solution_0401-0500_438 - find all anagrams in a string.md":"5b3e782c","solution_0401-0500_443 - string compression.md":"fb53fd46","solution_0401-0500_445 - add two numbers ii.md":"f824629e","solution_0401-0500_448 - find all numbers disappeared in an array.md":"84c610eb","solution_0401-0500_461 - hamming distance.md":"2603ff11","solution_0401-0500_463 - island perimeter.md":"13bee12f","solution_0401-0500_476 - number complement.md":"71b7487d","solution_0401-0500_482 - license key formatting.md":"e6ac4c2e","solution_0401-0500_485 - max consecutive ones.md":"7b21de3a","solution_0401-0500_492 - construct the rectangle.md":"8f462143","solution_0401-0500_498 - diagonal traverse.md":"7eba0edb","solution_0501-0600_502 - ipo.md":"4354a877","solution_0501-0600_504 - base 7.md":"9103810c","solution_0501-0600_506 - relative ranks.md":"f3d9e740","solution_0501-0600_507 - perfect number.md":"9ad0760b","solution_0501-0600_509 - fibonacci number.md":"2d1e2e4f","solution_0501-0600_516 - longest palindromic subsequence.md":"9a713bf8","solution_0501-0600_518 - coin change 2.md":"43e4471e","solution_0501-0600_530 - minimum absolute difference in bst.md":"fec8d767","solution_0501-0600_540 - single element in a sorted array.md":"5c58c806","solution_0501-0600_543 - diameter of binary tree.md":"f7974f63","solution_0601-0700_605 - can place flowers.md":"8c88c122","solution_0601-0700_652 - find duplicate subtrees.md":"3c293139","solution_0601-0700_653 - two sum iv - input is a bst.md":"f2c07c17","solution_0601-0700_695 - max area of island.md":"04d7865e","solution_0701-0800_704 - binary search.md":"6403df35","solution_0701-0800_739 - daily temperatures.md":"9a4ce852","solution_0701-0800_771 - jewels and stones.md":"ec1795d8","solution_0701-0800_783 - minimum distance between bst nodes.md":"81c07254","solution_0801-0900_875 - koko eating bananas.md":"21b969d9","solution_0801-0900_876 - middle of the linked list.md":"937594a8","solution_0801-0900_888 - fair candy swap.md":"53ce1729","solution_0901-1000_912 - sort an array.md":"c7062b3f","solution_0501-0600_541 - reverse string ii.md":"436195ea","solution_0901-1000_944 - delete columns to make sorted.md":"793056e7","solution_0901-1000_997 - find the town judge.md":"694eeaa4","solution_0401-0500_442 - find all duplicates in an array.md":"f14f98a8","solution_2201-2300_2235 - add two integers.md":"21a42abe","solution_0101-0200_112 - path sum.md":"798d4a4f","solution_1001-1100_1011 - capacity to ship packages within d days.md":"504fac7a","solution_1001-1100_1029 - two city scheduling.md":"c22c31a1","solution_1001-1100_1047 - remove all adjacent duplicates in string.md":"31288eef","solution_1001-1100_1092 - shortest common supersequence.md":"edf11803","solution_1101-1200_1108 - defanging an ip address.md":"947c6073","solution_1101-1200_1143 - longest common subsequence.md":"301e9543","solution_1201-1300_1232 - check if it is a straight line.md":"e1add48e","solution_1301-1400_1345 - jump game iv.md":"99cd0bd2","solution_1401-1500_1461 - check if a string contains all binary codes of size k.md":"fa1d7f44","solution_1401-1500_1470 - shuffle the array.md":"498e516b","solution_1401-1500_1472 - design browser history.md":"fd8d7d2f","solution_1401-1500_1431 - kids with the greatest number of candies.md":"6ccb0bd0","solution_0301-0400_344 - reverse string.md":"c33e162e","index.md":"7b37d749","solution_0001-0100_066 - plus one.md":"4a367264","solution_0301-0400_392 - is subsequence.md":"e5387d7d","solution_0401-0500_434 - number of segments in a string.md":"8dcdd995","solution_0901-1000_958 - check completeness of a binary tree.md":"f4c7668c","solution_0401-0500_412 - fizz buzz.md":"7494f36e"}
diff --git a/index.html b/index.html
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..ee8c3474
--- /dev/null
+++ b/index.html
@@ -0,0 +1,27 @@
+
+
+
+
+
+ rajput-hemant | Leetcode
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
You are given two non-empty linked lists representing two non-negative integers. The digits are stored in reverse order, and each of their nodes contains a single digit. Add the two numbers and return the sum as a linked list.
You may assume the two numbers do not contain any leading zero, except the number 0 itself.
+
+
+
+
+
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/solution/0001-0100/004 - Median of Two Sorted Arrays.html b/solution/0001-0100/004 - Median of Two Sorted Arrays.html
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..7bd1be51
--- /dev/null
+++ b/solution/0001-0100/004 - Median of Two Sorted Arrays.html
@@ -0,0 +1,56 @@
+
+
+
+
+
+ 4. Median of Two Sorted Arrays | 🏆 Leetcode
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
Given a signed 32-bit integer x, return x with its digits reversed. If reversing x causes the value to go outside the signed 32-bit integer range [-231, 231 - 1], then return 0.
Assume the environment does not allow you to store 64-bit integers (signed or unsigned).
Input: x = -121
+Output: false
+Explanation: From left to right, it reads -121. From right to left, it becomes 121-. Therefore it is not a palindrome.
+
+
+
+
+
+
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/solution/0001-0100/013 - Roman to Integer.html b/solution/0001-0100/013 - Roman to Integer.html
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..66be6b22
--- /dev/null
+++ b/solution/0001-0100/013 - Roman to Integer.html
@@ -0,0 +1,65 @@
+
+
+
+
+
+ 13. Roman to Integer | 🏆 Leetcode
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
Roman numerals are represented by seven different symbols: I, V, X, L, C, D and M.
Symbol Value
+I 1
+V 5
+X 10
+L 50
+C 100
+D 500
+M 1000
+
For example, 2 is written as II in Roman numeral, just two ones added together. 12 is written as XII, which is simply X + II. The number 27 is written as XXVII, which is XX + V + II.
Roman numerals are usually written largest to smallest from left to right. However, the numeral for four is not IIII. Instead, the number four is written as IV. Because the one is before the five we subtract it making four. The same principle applies to the number nine, which is written as IX. There are six instances where subtraction is used:
I can be placed before V (5) and X (10) to make 4 and 9.
X can be placed before L (50) and C (100) to make 40 and 90.
C can be placed before D (500) and M (1000) to make 400 and 900. Given a roman numeral, convert it to an integer.
- 1 <= s.length <= 15
+- s contains only the characters `('I', 'V', 'X', 'L', 'C', 'D', 'M')`.
+- It is guaranteed that s is a valid roman numeral in the range [`1, 3999]`.
+
Given a linked list, swap every two adjacent nodes and return its head. You must solve the problem without modifying the values in the list's nodes (i.e., only nodes themselves may be changed.)
Given an integer array nums sorted in non-decreasing order, remove the duplicates in-place such that each unique element appears only once. The relative order of the elements should be kept the same.
Since it is impossible to change the length of the array in some languages, you must instead have the result be placed in the first part of the array nums. More formally, if there are k elements after removing the duplicates, then the first k elements of nums should hold the final result. It does not matter what you leave beyond the first k elements.
Return k after placing the final result in the first k slots of nums.
Do not allocate extra space for another array. You must do this by modifying the input array in-place with O(1) extra memory.
The judge will test your solution with the following code:
+
+int[] nums = [...]; // Input array
+int[] expectedNums = [...]; // The expected answer with correct length
+
+int k = removeDuplicates(nums); // Calls your implementation
+
+assert k == expectedNums.length;
+for (int i = 0; i < k; i++) {
+ assert nums[i] == expectedNums[i];
+}
+
If all assertions pass, then your solution will be accepted.
Input: nums = [1,1,2]
+Output: 2, nums = [1,2,_]
+Explanation: Your function should return k = 2, with the first two elements of nums being 1 and 2 respectively.
+It does not matter what you leave beyond the returned k (hence they are underscores).
+
Input: nums = [0,0,1,1,1,2,2,3,3,4]
+Output: 5, nums = [0,1,2,3,4,_,_,_,_,_]
+Explanation: Your function should return k = 5, with the first five elements of nums being 0, 1, 2, 3, and 4 respectively.
+It does not matter what you leave beyond the returned k (hence they are underscores).
+
Given an integer array nums and an integer val, remove all occurrences of val in nums in-place. The relative order of the elements may be changed.
Since it is impossible to change the length of the array in some languages, you must instead have the result be placed in the first part of the array nums. More formally, if there are k elements after removing the duplicates, then the first k elements of nums should hold the final result. It does not matter what you leave beyond the first k elements.
Return k after placing the final result in the first k slots of nums.
Do not allocate extra space for another array. You must do this by modifying the input array in-place with O(1) extra memory.
The judge will test your solution with the following code:
+
+int[] nums = [...]; // Input array
+int val = ...; // Value to remove
+int[] expectedNums = [...]; // The expected answer with correct length.
+// It is sorted with no values equaling val.
+
+int k = removeElement(nums, val); // Calls your implementation
+
+assert k == expectedNums.length;
+sort(nums, 0, k); // Sort the first k elements of nums
+for (int i = 0; i < actualLength; i++) {
+assert nums[i] == expectedNums[i];
+}
+
If all assertions pass, then your solution will be accepted.
Input: nums = [3,2,2,3], val = 3
+Output: 2, nums = [2,2,_,_]
+Explanation: Your function should return k = 2, with the first two elements of nums being 2.
+It does not matter what you leave beyond the returned k (hence they are underscores).
+
Input: nums = [0,1,2,2,3,0,4,2], val = 2
+Output: 5, nums = [0,1,4,0,3,_,_,_]
+Explanation: Your function should return k = 5, with the first five elements of nums containing 0, 0, 1, 3, and 4.
+Note that the five elements can be returned in any order.
+It does not matter what you leave beyond the returned k (hence they are underscores).
+
+
+
+
+
+
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/solution/0001-0100/028 - Find the Index of the First Occurrence in a String.html b/solution/0001-0100/028 - Find the Index of the First Occurrence in a String.html
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..f182d3e1
--- /dev/null
+++ b/solution/0001-0100/028 - Find the Index of the First Occurrence in a String.html
@@ -0,0 +1,54 @@
+
+
+
+
+
+ 28. Find the Index of the First Occurrence in a String | 🏆 Leetcode
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
Given two strings needle and haystack, return the index of the first occurrence of needle in haystack, or -1 if needle is not part of haystack.
Example 1:
Input: haystack = "sadbutsad", needle = "sad"
+Output: 0
+Explanation: "sad" occurs at index 0 and 6.
+The first occurrence is at index 0, so we return 0.
+
Example 2:
Input: haystack = "leetcode", needle = "leeto"
+Output: -1
+Explanation: "leeto" did not occur in "leetcode", so we return -1.
+
Constraints:
1 <= haystack.length, needle.length <= 104
haystack and needle consist of only lowercase English characters.
implSolution{
+pubfnstr_str(haystack:String, needle:String)->i32{
+let(m, n)=(haystack.len(), needle.len());
+
+if m < n {
+return-1;
+}
+
+ // iterate over the haystack from 0 to m - n
+ // because the needle can't be longer than the haystack
+for i in0..=m - n {
+if haystack[i..i + n]== needle {
+return i asi32;
+}
+}
+
+-1
+}
+}
+
+
Given a sorted array of distinct integers and a target value, return the index if the target is found. If not, return the index where it would be if it were inserted in order.
You must write an algorithm with O(log n) runtime complexity.
Example 1:
Input: nums = [1,3,5,6], target = 5
+Output: 2
+
Example 2:
Input: nums = [1,3,5,6], target = 2
+Output: 1
+
Example 3:
Input: nums = [1,3,5,6], target = 7
+Output: 4
+
Constraints:
1 <= nums.length <= 104
-104 <= nums[i] <= 104
nums contains distinct values sorted in ascending order.
/*
+A sudoku solution must satisfy all of the following rules:
+-> Each of the digits 1-9 must occur exactly once in each row.
+-> Each of the digits 1-9 must occur exactly once in each column.
+-> Each of the digits 1-9 must occur exactly once in each of the 9 3x3 sub-boxes of the grid.
+The "." character indicates empty cells.
+*/
+
+publicclassSudokuSolver2{
+publicvoidsolveSudoku(char[][]board){
+helper(board,0,0);
+}
+
+// a utility function to solve the board
+booleanhelper(char[][]board,introw,intcol){
+// base case -> recursion stops at the 10th row
+if(row == board.length)
+returntrue;
+int newRow =0, newCol =0;
+// when its the last col of the board, goto next row & first col
+if(col == board.length -1){
+ newRow = row +1;
+ newCol =0;
+}
+// else, keep increasing the col by one & the row remains the same
+else{
+ newRow = row;
+ newCol = col +1;
+}
+// if the cell isn't empty, i.e. there is a number present in that cell
+if(board[row][col]!='.'){
+// do a recursive call, if the fn returns true, i.e. the board is solved,
+// we'll also return true
+if(helper(board, newRow, newCol))
+returntrue;
+}
+// if cell is empty
+else{
+for(int i =1; i <=9; i++){
+// if it's safe to place 'i' at that cell
+if(isValidPlacement(board, row, col, i)){
+ board[row][col]=(char)(i +'0');
+// after placing the number, do a recursive call,
+// if the fn returns true, we'll also return true
+if(helper(board, newRow, newCol))
+returntrue;
+// if the recursive call returns false, i.e. it wasn't safe to place 'i',
+// we'll empty the cell & and will try for the next value of 'i' (backtracking)
+else
+ board[row][col]='.';
+}
+}
+}
+// return false if it isn't posssible to place a number in the cell
+returnfalse;
+}
+
+// a utility fn to check for valid placement of a number in cell of Sudoku Board
+booleanisValidPlacement(char[][]board,introw,intcol,intnumber){
+// to check if 'number' is present in the row or the col
+for(int i =0; i < board.length; i++){
+// return false if 'number' is present in the col
+if(board[i][col]==(char)(number +'0'))
+returnfalse;
+// return false if 'number' is present in the row
+if(board[row][i]==(char)(number +'0'))
+returnfalse;
+}
+// to check if the 'number' is present in the 3X3 grid
+// There are two ways to get the initial row and column of 3X3 grid
+// 1
+int startingRow =(row /3)*3;
+int startingCol =(col /3)*3;
+// 2
+// int startingRow = (row % 3) - row;
+// int startingCol = (col % 3) - col;
+for(int i = startingRow; i < startingRow +3; i++)
+for(int j = startingCol; j < startingCol +3; j++)
+// return false if 'number' is present in the 3X3 grid or matrix
+if(board[i][j]==(char)(number +'0'))
+returnfalse;
+// return true if 'number' isn't present in row, col & grid
+returntrue;
+}
+}
+
packagemain
+
+funcfirstMissingPositive(nums []int)int{
+ i :=0
+
+for i <len(nums){
+if nums[i]>0&& nums[i]<=len(nums)&& nums[nums[i]-1]!= nums[i]{
+ nums[nums[i]-1], nums[i]= nums[i], nums[nums[i]-1]
+}else{
+ i++
+}
+}
+
+for i, num :=range nums {
+if num != i+1{
+return i +1
+}
+}
+
+returnlen(nums)+1
+}
+
+
rs
implSolution{
+pubfnfirst_missing_positive(nums:Vec<i32>)->i32{
+let(mut nums,mut i)=(nums,0);
+
+while i < nums.len(){
+let num = nums[i];
+
+ // if the number is in the range [1, nums.len()] and not in the right position
+ // swap it with the number at the right position
+if num >0&& num <= nums.len()asi32&& num != nums[num asusize-1]{
+ nums.swap(i, num asusize-1);
+}else{
+ i +=1;
+}
+}
+
+ // find the first missing positive number
+for(i, num)in nums.iter().enumerate(){
+if num !=&(i asi32+1){
+return i asi32+1;
+}
+}
+
+ nums.len()asi32+1
+}
+}
+
+
Given n non-negative integers representing an elevation map where the width of each bar is 1, compute how much water it can trap after raining.
Example 1:
Input: height = [0,1,0,2,1,0,1,3,2,1,2,1]
+Output: 6
+Explanation: The above elevation map (black section) is represented by array [0,1,0,2,1,0,1,3,2,1,2,1]. In this case, 6 units of rain water (blue section) are being trapped.
+
implSolution{
+pubfntrap(height:Vec<i32>)->i32{
+let(mut left,mut right)=(0, height.len()-1);
+let(mut left_max,mut right_max)=(0,0);
+letmut ans =0;
+
+ // iterate from both sides to the middle
+while left < right {
+ // if left is lower than right, then the water level depends on left
+ // else the water level depends on right
+if height[left]< height[right]{
+ // if left height is higher than left_max, then update left_max
+ // else add the difference between left_max and left height to ans
+if height[left]>= left_max {
+ left_max = height[left];
+}else{
+ ans += left_max - height[left];
+}
+ left +=1;
+}else{
+ // if right height is higher than right_max, then update right_max
+ // else add the difference between right_max and right height to ans
+if height[right]>= right_max {
+ right_max = height[right];
+}else{
+ ans += right_max - height[right];
+}
+ right -=1;
+}
+}
+
+ ans
+}
+}
+
+
You are given an n x n 2D matrix representing an image, rotate the image by 90 degrees (clockwise).
You have to rotate the image in-place, which means you have to modify the input 2D matrix directly. DO NOT allocate another 2D matrix and do the rotation.
The n-queens puzzle is the problem of placing n queens on an n x n chessboard such that no two queens attack each other.
Given an integer n, return all distinct solutions to the n-queens puzzle. You may return the answer in any order.
Each solution contains a distinct board configuration of the n-queens' placement, where 'Q' and '.' both indicate a queen and an empty space, respectively.
publicclassNQueens2{
+
+publicstaticList<List<String>>nQueens(intn){
+// List of Lists of boards
+List<List<String>> allBoards =newArrayList<>();
+char[][] board =newchar[n][n];
+helper(board, allBoards,0);
+return allBoards;
+}
+
+staticvoidhelper(char[][]board,List<List<String>>allBoards,intcol){
+// save board to allBoards after placing Queens on all possible cols
+if(col == board.length){
+saveBoard(board, allBoards);
+return;
+}
+for(int row =0; row < board.length; row++){
+// if it's safe, place queen at row
+if(isSafe(row, col, board)){
+ board[row][col]='Q';
+helper(board, allBoards, col +1);
+// backtracking
+ board[row][col]='.';
+}
+}
+}
+
+// Fn to check if it's safe to place Queen
+staticbooleanisSafe(introw,intcol,char[][]board){
+int len = board.length;
+// traverse in all cols to check if a queen is already present or not
+for(int i =0; i < len; i++){
+if(board[row][i]=='Q')
+returnfalse;
+}
+// traverse in all rows to check if a queen is already present or not
+for(int i =0; i < len; i++){
+if(board[i][col]=='Q')
+returnfalse;
+}
+// traverse through upper left diagonal to check if queen is present
+int r = row;
+for(int c = col; c >=0&& r >=0; r--, c--){
+if(board[r][c]=='Q')
+returnfalse;
+}
+// traverse through upper right diagonal to check if queen is present
+ r = row;
+for(int c = col; c < len && r >=0; r--, c++){
+if(board[r][c]=='Q')
+returnfalse;
+}
+// traverse through lower left diagonal to check if queen is present
+ r = row;
+for(int c = col; c >=0&& r < len; r++, c--){
+if(board[r][c]=='Q')
+returnfalse;
+}
+// traverse through lower right diagonal to check if queen is present
+ r = row;
+for(int c = col; c < len && r < len; r++, c++){
+if(board[r][c]=='Q')
+returnfalse;
+}
+returntrue;
+}
+
+// Fn to save a board to List of Boards
+staticvoidsaveBoard(char[][]board,List<List<String>>allBoards){
+int len = board.length;
+String row ="";
+List<String> newBoard =newArrayList<>();
+for(int i =0; i < len; i++){
+ row ="";
+for(int j =0; j < len; j++){
+if(board[i][j]=='Q')
+ row +='Q';
+else
+ row +='.';
+}
+// this adds the row to the newBoards -> "Q..." or "..Q."
+ newBoard.add(row);
+}
+// this add the board to the list of boards -> [[..Q., Q..., ...Q, .Q..],...]
+ allBoards.add(newBoard);
+}
+}
+
You are given an integer array nums. You are initially positioned at the array's first index, and each element in the array represents your maximum jump length at that position.
Return true if you can reach the last index, or false otherwise.
Input: nums = [3,2,1,0,4]
+Output: false
+Explanation: You will always arrive at index 3 no matter what. Its maximum jump length is 0, which makes it impossible to reach the last index.
+
publicbooleancanJump(int[] nums){
+int n = nums.length,
+ max =0;
+if(n ==1)
+returntrue;
+for(int i =0; i < n -1&& max >= i; i++){
+if(max < i + nums[i])
+ max = i + nums[i];
+if(max >= n -1)
+returntrue;
+}
+returnfalse;
+}
+
+
+
+
+
+
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/solution/0001-0100/058 - Length of Last Word.html b/solution/0001-0100/058 - Length of Last Word.html
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..510c7282
--- /dev/null
+++ b/solution/0001-0100/058 - Length of Last Word.html
@@ -0,0 +1,46 @@
+
+
+
+
+
+ 58. Length of Last Word | 🏆 Leetcode
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
You are given a large integer represented as an integer array digits, where each digits[i] is the ith digit of the integer. The digits are ordered from most significant to least significant in left-to-right order. The large integer does not contain any leading 0's.
Increment the large integer by one and return the resulting array of digits.
Example 1:
Input: digits = [1,2,3]
+Output: [1,2,4]
+Explanation: The array represents the integer 123.
+Incrementing by one gives 123 + 1 = 124.
+Thus, the result should be [1,2,4].
+
Example 2:
Input: digits = [4,3,2,1]
+Output: [4,3,2,2]
+Explanation: The array represents the integer 4321.
+Incrementing by one gives 4321 + 1 = 4322.
+Thus, the result should be [4,3,2,2].
+
Example 3:
Input: digits = [9]
+Output: [1,0]
+Explanation: The array represents the integer 9.
+Incrementing by one gives 9 + 1 = 10.
+Thus, the result should be [1,0].
+
packagemain
+
+funcmySqrt(x int)int{
+ start :=0
+ end := x
+
+for start < end {
+// this is to floor the mid value
+// mid of 8 will be 4 , (8+1)/2 = 4.5
+// mid of 9 will be 5 , (9+1)/2 = 5
+ mid := start +(end-start+1)/2
+if mid*mid > x {
+ end = mid -1
+}else{
+ start = mid
+}
+}
+
+return end
+}
+
+
Given an array nums with n objects colored red, white, or blue, sort them in-place so that objects of the same color are adjacent, with the colors in the order red, white, and blue.
We will use the integers 0, 1, and 2 to represent the color red, white, and blue, respectively.
You must solve this problem without using the library's sort function.
packagemain
+
+funcsubsets(nums []int)[][]int{
+ res :=make([][]int,0)
+ curr_subset :=make([]int,0)
+
+var backtrack func(i int)
+
+ backtrack =func(i int){
+println(i)
+if i >=len(nums){
+ curr_dup :=make([]int,len(curr_subset))
+copy(curr_dup, curr_subset)
+ res =append(res, curr_dup)
+return
+}
+
+// include the current element
+ curr_subset =append(curr_subset, nums[i])
+backtrack(i +1)
+
+// exclude the current element
+ curr_subset = curr_subset[:len(curr_subset)-1]// pop the last element
+backtrack(i +1)
+}
+
+backtrack(0)
+
+return res
+}
+
+
py
classSolution:
+defsubsets(self,nums: list[int])-> list[list[int]]:
+ res, curr =[],[]
+
+defbacktrack(i:int)->None:
+if i >=len(nums):
+print(curr.copy())
+ res.append(curr.copy())
+return
+
+# include the current element
+ curr.append(nums[i])
+backtrack(i +1)
+
+# exclude the current element
+ curr.pop()
+backtrack(i +1)
+
+backtrack(0)
+
+return res
+
+
You are given two integer arrays nums1 and nums2, sorted in non-decreasing order, and two integers m and n, representing the number of elements in nums1 and nums2 respectively.
Mergenums1 and nums2 into a single array sorted in non-decreasing order.
The final sorted array should not be returned by the function, but instead be stored inside the array nums1. To accommodate this, nums1 has a length of m + n, where the first m elements denote the elements that should be merged, and the last n elements are set to 0 and should be ignored. nums2 has a length of n.
Example 1:
Input: nums1 = [1,2,3,0,0,0], m = 3, nums2 = [2,5,6], n = 3
+Output: [1,2,2,3,5,6]
+Explanation: The arrays we are merging are [1,2,3] and [2,5,6].
+The result of the merge is [1,2,2,3,5,6] with the underlined elements coming from nums1.
+
Example 2:
Input: nums1 = [1], m = 1, nums2 = [], n = 0
+Output: [1]
+Explanation: The arrays we are merging are [1] and [].
+The result of the merge is [1].
+
Example 3:
Input: nums1 = [0], m = 0, nums2 = [1], n = 1
+Output: [1]
+Explanation: The arrays we are merging are [] and [1].
+The result of the merge is [1].
+Note that because m = 0, there are no elements in nums1. The 0 is only there to ensure the merge result can fit in nums1.
+
Constraints:
nums1.length == m + n
nums2.length == n
0 <= m, n <= 200
1 <= m + n <= 200
-109 <= nums1[i], nums2[j] <= 109
Follow up: Can you come up with an algorithm that runs in O(m + n) time?
Click to open Hints
You can easily solve this problem if you simply think about two elements at a time rather than two arrays. We know that each of the individual arrays is sorted. What we don't know is how they will intertwine. Can we take a local decision and arrive at an optimal solution?
If you simply consider one element each at a time from the two arrays and make a decision and proceed accordingly, you will arrive at the optimal solution.
Given the root of a binary tree, return the zigzag level order traversal of its nodes' values. (i.e., from left to right, then right to left for the next level and alternate between).
+
+
+
+
+
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/solution/0101-0200/106 - Construct Binary Tree from Inorder and Postorder Traversal.html b/solution/0101-0200/106 - Construct Binary Tree from Inorder and Postorder Traversal.html
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..55268448
--- /dev/null
+++ b/solution/0101-0200/106 - Construct Binary Tree from Inorder and Postorder Traversal.html
@@ -0,0 +1,67 @@
+
+
+
+
+
+ 106. Construct Binary Tree from Inorder and Postorder Traversal | 🏆 Leetcode
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
Given two integer arrays inorder and postorder where inorder is the inorder traversal of a binary tree and postorder is the postorder traversal of the same tree, construct and return the binary tree.
Given the head of a singly linked list where elements are sorted in ascending order, convert it to a height-balancedbinary search tree.
Example 1:
Input: head = [-10,-3,0,5,9]
+Output: [0,-3,9,-10,null,5]
+Explanation: One possible answer is [0,-3,9,-10,null,5], which represents the shown height balanced BST.
+
Example 2:
Input: head = []
+Output: []
+
Constraints:
The number of nodes in head is in the range [0, 2 * 104].
packagemain
+
+// Definition for singly-linked list.
+typeListNodestruct{
+ Val int
+ Next *ListNode
+}
+
+// Definition for a binary tree node.
+typeTreeNodestruct{
+ Val int
+ Left *TreeNode
+ Right *TreeNode
+}
+
+funcsortedListToBST(head *ListNode)*TreeNode {
+if head ==nil{
+returnnil
+}
+
+if head.Next ==nil{
+return&TreeNode{Val: head.Val}
+}
+
+ slow, fast := head, head
+ prev := slow
+
+for fast !=nil&& fast.Next !=nil{
+ prev = slow
+ slow = slow.Next
+ fast = fast.Next.Next
+}
+
+// slow points to the root of the current subtree
+
+// break the link between the left subtree and the root
+ prev.Next =nil
+
+ root :=&TreeNode{Val: slow.Val}
+ root.Left =sortedListToBST(head)
+ root.Right =sortedListToBST(slow.Next)
+
+return root
+}
+
+
Given the root of a binary tree and an integer targetSum, return true if the tree has a root-to-leaf path such that adding up all the values along the path equals targetSum.
A leaf is a node with no children.
Example 1:
Input: root = [5,4,8,11,null,13,4,7,2,null,null,null,1], targetSum = 22
+Output: true
+Explanation: The root-to-leaf path with the target sum is shown.
+
Example 2:
Input: root = [1,2,3], targetSum = 5
+Output: false
+Explanation: There two root-to-leaf paths in the tree:
+(1 --> 2): The sum is 3.
+(1 --> 3): The sum is 4.
+There is no root-to-leaf path with sum = 5.
+
Example 3:
Input: root = [], targetSum = 0
+Output: false
+Explanation: Since the tree is empty, there are no root-to-leaf paths.
+
Constraints:
The number of nodes in the tree is in the range [0, 5000].
implSolution{
+pubfnget_row(row_index:i32)->Vec<i32>{
+ // create a vector of 1s with length row_index + 1
+letmut row =vec![1;(row_index +1)asusize];
+
+ // loop through the vector, starting at 1
+for i in1..row_index {
+ // loop through the vector, starting at i + 1 and going backwards
+for j in(1..=i).rev(){
+ // add the value at the current index to the value at the previous index
+ row[j asusize]+= row[(j -1)asusize];
+}
+}
+
+ row
+}
+}
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/solution/0101-0200/121 - Best Time to Buy and Sell Stock.html b/solution/0101-0200/121 - Best Time to Buy and Sell Stock.html
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..c984e698
--- /dev/null
+++ b/solution/0101-0200/121 - Best Time to Buy and Sell Stock.html
@@ -0,0 +1,72 @@
+
+
+
+
+
+ 121. Best Time to Buy and Sell Stock | 🏆 Leetcode
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
You are given an array prices where prices[i] is the price of a given stock on the ith day.
You want to maximize your profit by choosing a single day to buy one stock and choosing a different day in the future to sell that stock.
Return the maximum profit you can achieve from this transaction. If you cannot achieve any profit, return 0.
Example 1:
Input: prices = [7,1,5,3,6,4]
+Output: 5
+Explanation: Buy on day 2 (price = 1) and sell on day 5 (price = 6), profit = 6-1 = 5.
+Note that buying on day 2 and selling on day 1 is not allowed because you must buy before you sell.
+
Example 2:
Input: prices = [7,6,4,3,1]
+Output: 0
+Explanation: In this case, no transactions are done and the max profit = 0.
+
implSolution{
+pubfnmax_profit(prices:Vec<i32>)->i32{
+let(mut profit,mut min)=(0, prices[0]);
+
+ // loop through the vector, starting at 1
+for i in1..prices.len(){
+ // if the current value is less than the minimum value, set the minimum value to the current value
+if prices[i]< min {
+ min = prices[i];
+}
+ // else if the current value minus the minimum value is greater than the current profit, set the profit to the current value minus the minimum value
+elseif prices[i]- min > profit {
+ profit = prices[i]- min;
+}
+}
+
+ profit
+}
+}
+
+
go
packagemain
+
+funcmaxProfit(prices []int)int{
+ profit, min :=0, prices[0]
+
+for _, price :=range prices {
+// if the current price is lower than the min price, update the min price to the current price
+// else if the current price minus the min price is greater than the profit, update the profit to the current price minus the min price
+if price < min {
+ min = price
+}elseif price-min > profit {
+ profit = price - min
+}
+}
+
+return profit
+}
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/solution/0101-0200/122 - Best Time to Buy and Sell Stock II.html b/solution/0101-0200/122 - Best Time to Buy and Sell Stock II.html
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..87de12af
--- /dev/null
+++ b/solution/0101-0200/122 - Best Time to Buy and Sell Stock II.html
@@ -0,0 +1,47 @@
+
+
+
+
+
+ 122. Best Time to Buy and Sell Stock II | 🏆 Leetcode
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
You are given an integer array prices where prices[i] is the price of a given stock on the ith day.
On each day, you may decide to buy and/or sell the stock. You can only hold at most one share of the stock at any time. However, you can buy it then immediately sell it on the same day.
Find and return the maximum profit you can achieve.
Input: prices = [7,6,4,3,1]
+Output: 0
+Explanation: There is no way to make a positive profit, so we never buy the stock to achieve the maximum profit of 0.
+
A phrase is a palindrome if, after converting all uppercase letters into lowercase letters and removing all non-alphanumeric characters, it reads the same forward and backward. Alphanumeric characters include letters and numbers.
Given a string s, return true if it is a palindrome, or false otherwise.
Example 1:
Input: s = "A man, a plan, a canal: Panama"
+Output: true
+Explanation: "amanaplanacanalpanama" is a palindrome.
+
Example 2:
Input: s = "race a car"
+Output: false
+Explanation: "raceacar" is not a palindrome.
+
Example 3:
Input: s = " "
+Output: true
+Explanation: s is an empty string "" after removing non-alphanumeric characters.
+Since an empty string reads the same forward and backward, it is a palindrome.
+
implSolution{
+pubfnsingle_number(nums:Vec<i32>)->i32{
+letmut res =0;
+for num in nums {
+ // a ^ a = 0
+ // a ^ a ^ a = a
+ // a ^ a ^ b = b
+ // also position of a and b doesn't matter
+ res ^= num;
+}
+
+ res
+}
+}
+
+
Given head, the head of a linked list, determine if the linked list has a cycle in it.
There is a cycle in a linked list if there is some node in the list that can be reached again by continuously following the next pointer. Internally, pos is used to denote the index of the node that tail's next pointer is connected to. Note that pos is not passed as a parameter.
Return true if there is a cycle in the linked list. Otherwise, return false.
Example 1:
Input: head = [3,2,0,-4], pos = 1
+Output: true
+Explanation: There is a cycle in the linked list, where the tail connects to the 1st node (0-indexed).
+
Example 2:
Input: head = [1,2], pos = 0
+Output: true
+Explanation: There is a cycle in the linked list, where the tail connects to the 0th node.
+
Example 3:
Input: head = [1], pos = -1
+Output: false
+Explanation: There is no cycle in the linked list.
+
Constraints:
The number of the nodes in the list is in the range [0, 104].
-105 <= Node.val <= 105
pos is -1 or a valid index in the linked-list.
Follow up: Can you solve it using O(1) (i.e. constant) memory?
Given the head of a linked list, return the node where the cycle begins. If there is no cycle, return null.
There is a cycle in a linked list if there is some node in the list that can be reached again by continuously following the next pointer. Internally, pos is used to denote the index of the node that tail's next pointer is connected to (0-indexed). It is -1 if there is no cycle. Note thatposis not passed as a parameter.
Do not modify the linked list.
Example 1:
Input: head = [3,2,0,-4], pos = 1
+Output: tail connects to node index 1
+Explanation: There is a cycle in the linked list, where tail connects to the second node.
+
Example 2:
Input: head = [1,2], pos = 0
+Output: tail connects to node index 0
+Explanation: There is a cycle in the linked list, where tail connects to the first node.
+
Example 3:
Input: head = [1], pos = -1
+Output: no cycle
+Explanation: There is no cycle in the linked list.
+
Constraints:
The number of the nodes in the list is in the range [0, 104].
-105 <= Node.val <= 105
pos is -1 or a valid index in the linked-list.
Follow up: Can you solve it using O(1) (i.e. constant) memory?
Given the heads of two singly linked-lists headA and headB, return the node at which the two lists intersect. If the two linked lists have no intersection at all, return null.
For example, the following two linked lists begin to intersect at node c1:
The test cases are generated such that there are no cycles anywhere in the entire linked structure.
Note that the linked lists must retain their original structure after the function returns.
Custom Judge:
The inputs to the judge are given as follows (your program is not given these inputs):
intersectVal - The value of the node where the intersection occurs. This is 0 if there is no intersected node.
listA - The first linked list.
listB - The second linked list.
skipA - The number of nodes to skip ahead in listA (starting from the head) to get to the intersected node.
skipB - The number of nodes to skip ahead in listB (starting from the head) to get to the intersected node.
The judge will then create the linked structure based on these inputs and pass the two heads, headA and headB to your program. If you correctly return the intersected node, then your solution will be accepted.
Example 1:
Input: intersectVal = 8, listA = [4,1,8,4,5], listB = [5,6,1,8,4,5], skipA = 2, skipB = 3
+Output: Intersected at '8'
+Explanation: The intersected node's value is 8 (note that this must not be 0 if the two lists intersect).
+From the head of A, it reads as [4,1,8,4,5]. From the head of B, it reads as [5,6,1,8,4,5]. There are 2 nodes before the intersected node in A; There are 3 nodes before the intersected node in B.
+- Note that the intersected node's value is not 1 because the nodes with value 1 in A and B (2nd node in A and 3rd node in B) are different node references. In other words, they point to two different locations in memory, while the nodes with value 8 in A and B (3rd node in A and 4th node in B) point to the same location in memory.
+
Example 2:
Input: intersectVal = 2, listA = [1,9,1,2,4], listB = [3,2,4], skipA = 3, skipB = 1
+Output: Intersected at '2'
+Explanation: The intersected node's value is 2 (note that this must not be 0 if the two lists intersect).
+From the head of A, it reads as [1,9,1,2,4]. From the head of B, it reads as [3,2,4]. There are 3 nodes before the intersected node in A; There are 1 node before the intersected node in B.
+
Example 3:
Input: intersectVal = 0, listA = [2,6,4], listB = [1,5], skipA = 3, skipB = 2
+Output: No intersection
+Explanation: From the head of A, it reads as [2,6,4]. From the head of B, it reads as [1,5]. Since the two lists do not intersect, intersectVal must be 0, while skipA and skipB can be arbitrary values.
+Explanation: The two lists do not intersect, so return null.
+
Constraints:
The number of nodes of listA is in the m.
The number of nodes of listB is in the n.
1 <= m, n <= 3 * 104
1 <= Node.val <= 105
0 <= skipA < m
0 <= skipB < n
intersectVal is 0 if listA and listB do not intersect.
intersectVal == listA[skipA] == listB[skipB] if listA and listB intersect.
Follow up: Could you write a solution that runs in O(m + n) time and use only O(1) memory?
Note that in some languages, such as Java, there is no unsigned integer type. In this case, both input and output will be given as a signed integer type. They should not affect your implementation, as the integer's internal binary representation is the same, whether it is signed or unsigned.
In Java, the compiler represents the signed integers using 2's complement notation. Therefore, in Example 2 above, the input represents the signed integer -3 and the output represents the signed integer -1073741825.
Example 1:
Input: n = 00000010100101000001111010011100
+Output: 964176192 (00111001011110000010100101000000)
+Explanation: The input binary string 00000010100101000001111010011100 represents the unsigned integer 43261596, so return 964176192 which its binary representation is 00111001011110000010100101000000.
+
Example 2:
Input: n = 11111111111111111111111111111101
+Output: 3221225471 (10111111111111111111111111111111)
+Explanation: The input binary string 11111111111111111111111111111101 represents the unsigned integer 4294967293, so return 3221225471 which its binary representation is 10111111111111111111111111111111.
+
Constraints:
The input must be a binary string of length 32
Follow up: If this function is called many times, how would you optimize it?
implSolution{
+pubfnreverse_bits(x:u32)->u32{
+let(mut x,mut res)=(x,0);
+
+ // iterate 32 times, once for each bit
+for _ in0..32{
+ // left-shift res by 1 bit to make room for the next bit
+ res <<=1;
+ // adding the least significant bit of x to the result
+ // using bitwise AND with 1
+ res += x &1;
+ // right-shift x by 1 bit, discarding the least significant bit
+ // that was just added to the result
+ x >>=1;
+}
+
+ res
+}
+}
+
+
Write a function that takes an unsigned integer and returns the number of '1' bits it has (also known as the Hamming weight).
Note:
Note that in some languages, such as Java, there is no unsigned integer type. In this case, the input will be given as a signed integer type. It should not affect your implementation, as the integer's internal binary representation is the same, whether it is signed or unsigned.
In Java, the compiler represents the signed integers using 2's complement notation. Therefore, in Example 3, the input represents the signed integer. -3.
Input: n = 00000000000000000000000000001011
+Output: 3
+Explanation: The input binary string 00000000000000000000000000001011 has a total of three '1' bits.
+
Input: n = 00000000000000000000000010000000
+Output: 1
+Explanation: The input binary string 00000000000000000000000010000000 has a total of one '1' bit.
+
Input: n = 11111111111111111111111111111101
+Output: 31
+Explanation: The input binary string 11111111111111111111111111111101 has a total of thirty one '1' bits.
+
Your script should output the tenth line, which is:
Line 10
+
Note: 1. If the file contains less than 10 lines, what should you output? 2. There's at least three different solutions. Try to explore all possibilities.
+
+
+
+
+
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/solution/0101-0200/199 - Binary Tree Right Side View.html b/solution/0101-0200/199 - Binary Tree Right Side View.html
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..43780fc2
--- /dev/null
+++ b/solution/0101-0200/199 - Binary Tree Right Side View.html
@@ -0,0 +1,53 @@
+
+
+
+
+
+ 199. Binary Tree Right Side View | 🏆 Leetcode
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
Given the root of a binary tree, imagine yourself standing on the right side of it, return the values of the nodes you can see ordered from top to bottom.
+
+
+
+
+
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/solution/0101-0200/200 - Number of Islands.html b/solution/0101-0200/200 - Number of Islands.html
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..bf26aac5
--- /dev/null
+++ b/solution/0101-0200/200 - Number of Islands.html
@@ -0,0 +1,84 @@
+
+
+
+
+
+ 200. Number of Islands | 🏆 Leetcode
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
Given an m x n 2D binary grid grid which represents a map of '1's (land) and '0's (water), return the number of islands.
An island is surrounded by water and is formed by connecting adjacent lands horizontally or vertically. You may assume all four edges of the grid are all surrounded by water.
packagemain
+
+funcnumIslands(grid [][]byte)int{
+ result :=0
+
+for i :=0; i <len(grid); i++{
+for j :=0; j <len(grid[i]); j++{
+if grid[i][j]=='1'{
+dfs(grid, i, j)
+ result++
+}
+}
+}
+
+return result
+}
+
+funcdfs(grid [][]byte, row, col int){
+// return if it is out of bound horizontally
+if row <0|| row >=len(grid){
+return
+}
+
+// return if it is out of bound vertically
+if col <0|| col >=len(grid[row]){
+return
+}
+
+// return if it is not an island
+if grid[row][col]=='0'{
+return
+}
+
+// mark the current cell as visited
+ grid[row][col]='0'
+
+dfs(grid, row-1, col)
+dfs(grid, row+1, col)
+
+dfs(grid, row, col-1)
+dfs(grid, row, col+1)
+}
+
+
Given two strings s and t, determine if they are isomorphic.
Two strings s and t are isomorphic if the characters in s can be replaced to get t.
All occurrences of a character must be replaced with another character while preserving the order of characters. No two characters may map to the same character, but a character may map to itself.
+
+
+
+
+
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/solution/0201-0300/211 - Design Add and Search Words Data Structure.html b/solution/0201-0300/211 - Design Add and Search Words Data Structure.html
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..01c6f913
--- /dev/null
+++ b/solution/0201-0300/211 - Design Add and Search Words Data Structure.html
@@ -0,0 +1,95 @@
+
+
+
+
+
+ 211. Design Add and Search Words Data Structure | 🏆 Leetcode
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
Design a data structure that supports adding new words and finding if a string matches any previously added string.
Implement the WordDictionary class:
WordDictionary() Initializes the object.
void addWord(word) Adds word to the data structure, it can be matched later.
bool search(word) Returns true if there is any string in the data structure that matches word or false otherwise. word may contain dots '.' where dots can be matched with any letter.
Given an integer array nums and an integer k, return trueif there are two distinct indicesi and j in the array such that nums[i] == nums[j] and abs(i - j) <= k.
Example 1:
Input: nums = [1,2,3,1], k = 3
+Output: true
+
Example 2:
Input: nums = [1,0,1,1], k = 1
+Output: true
+
Example 3:
Input: nums = [1,2,3,1,2,3], k = 2
+Output: false
+
packagemain
+
+funccontainsNearbyDuplicate(nums []int, k int)bool{
+iflen(nums)<=1{
+returnfalse
+}
+
+ set :=make(map[int]int)
+
+// iterate over the array
+for i, v :=range nums {
+// check if the value is in the set
+if _, ok := set[v]; ok {
+// if the value is in the set,
+// check if the difference between the current index and the index of the value in the set
+// is less than or equal to k
+if i-set[v]<= k {
+returntrue
+}
+}
+// add the value to the set
+ set[v]= i
+}
+
+returnfalse
+}
+
+
Given the root of a complete binary tree, return the number of the nodes in the tree.
According to Wikipedia, every level, except possibly the last, is completely filled in a complete binary tree, and all nodes in the last level are as far left as possible. It can have between 1 and 2h nodes inclusive at the last level h.
Design an algorithm that runs in less than O(n) time complexity.
Implement a last-in-first-out (LIFO) stack using only two queues. The implemented stack should support all the functions of a normal stack (push, top, pop, and empty).
Implement the MyStack class:
void push(int x) Pushes element x to the top of the stack.
int pop() Removes the element on the top of the stack and returns it.
int top() Returns the element on the top of the stack.
boolean empty() Returns true if the stack is empty, false otherwise.
Notes:
You must use only standard operations of a queue, which means that only push to back, peek/pop from front, size and is empty operations are valid.
Depending on your language, the queue may not be supported natively. You may simulate a queue using a list or deque (double-ended queue) as long as you use only a queue's standard operations.
A range[a,b] is the set of all integers from a to b (inclusive).
Return the smallest sorted list of ranges that cover all the numbers in the array exactly. That is, each element of nums is covered by exactly one of the ranges, and there is no integer x such that x is in one of the ranges but not in nums.
+
+
+
+
+
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/solution/0201-0300/230 - Kth Smallest Element in a BST.html b/solution/0201-0300/230 - Kth Smallest Element in a BST.html
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..4e5cfa4e
--- /dev/null
+++ b/solution/0201-0300/230 - Kth Smallest Element in a BST.html
@@ -0,0 +1,52 @@
+
+
+
+
+
+ 230. Kth Smallest Element in a BST | 🏆 Leetcode
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
Follow up: If the BST is modified often (i.e., we can do insert and delete operations) and you need to find the kth smallest frequently, how would you optimize?
+
+
+
+
+
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/solution/0201-0300/231 - Power of Two.html b/solution/0201-0300/231 - Power of Two.html
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..3b80c464
--- /dev/null
+++ b/solution/0201-0300/231 - Power of Two.html
@@ -0,0 +1,41 @@
+
+
+
+
+
+ 231. Power of Two | 🏆 Leetcode
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
Implement a first in first out (FIFO) queue using only two stacks. The implemented queue should support all the functions of a normal queue (push, peek, pop, and empty).
Implement the MyQueue class:
void push(int x) Pushes element x to the back of the queue.
int pop() Removes the element from the front of the queue and returns it.
int peek() Returns the element at the front of the queue.
boolean empty() Returns true if the queue is empty, false otherwise.
Notes:
You must use only standard operations of a stack, which means only push to top, peek/pop from top, size, and is empty operations are valid.
Depending on your language, the stack may not be supported natively. You may simulate a stack using a list or deque (double-ended queue) as long as you use only a stack's standard operations.
Example 1:
Input
+["MyQueue", "push", "push", "peek", "pop", "empty"]
+[[], [1], [2], [], [], []]
+Output
+[null, null, null, 1, 1, false]
+
+Explanation
+MyQueue myQueue = new MyQueue();
+myQueue.push(1); // queue is: [1]
+myQueue.push(2); // queue is: [1, 2] (leftmost is front of the queue)
+myQueue.peek(); // return 1
+myQueue.pop(); // return 1, queue is [2]
+myQueue.empty(); // return false
+
Constraints:
1 <= x <= 9
At most 100 calls will be made to push, pop, peek, and empty.
All the calls to pop and peek are valid.
Follow-up: Can you implement the queue such that each operation is amortizedO(1) time complexity? In other words, performing n operations will take overall O(n) time even if one of those operations may take longer.
packagemain
+
+typeMyQueuestruct{
+ stack []int
+}
+
+funcConstructor() MyQueue {
+return MyQueue{}
+}
+
+// Push element x to the back of queue.
+func(this *MyQueue)Push(x int){
+ this.stack =append(this.stack, x)
+}
+
+// Removes and returns the element at the front of queue.
+func(this *MyQueue)Pop()int{
+iflen(this.stack)==0{
+return0
+}
+ pop := this.stack[0]
+ this.stack = this.stack[1:]
+return pop
+}
+
+// Get the front element.
+func(this *MyQueue)Peek()int{
+iflen(this.stack)==0{
+return0
+}
+return this.stack[0]
+}
+
+// Return whether the queue is empty.
+func(this *MyQueue)Empty()bool{
+returnlen(this.stack)==0
+}
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/solution/0201-0300/236 - Lowest Common Ancestor of a Binary Tree.html b/solution/0201-0300/236 - Lowest Common Ancestor of a Binary Tree.html
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..1d1a2c28
--- /dev/null
+++ b/solution/0201-0300/236 - Lowest Common Ancestor of a Binary Tree.html
@@ -0,0 +1,61 @@
+
+
+
+
+
+ 236. Lowest Common Ancestor of a Binary Tree | 🏆 Leetcode
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
Given a binary tree, find the lowest common ancestor (LCA) of two given nodes in the tree.
According to the definition of LCA on Wikipedia: “The lowest common ancestor is defined between two nodes p and q as the lowest node in T that has both p and q as descendants (where we allow a node to be a descendant of itself).”
Example 1:
Input: root = [3,5,1,6,2,0,8,null,null,7,4], p = 5, q = 1
+Output: 3
+Explanation: The LCA of nodes 5 and 1 is 3.
+
Example 2:
Input: root = [3,5,1,6,2,0,8,null,null,7,4], p = 5, q = 4
+Output: 5
+Explanation: The LCA of nodes 5 and 4 is 5, since a node can be a descendant of itself according to the LCA definition.
+
Example 3:
Input: root = [1,2], p = 1, q = 2
+Output: 1
+
Constraints:
The number of nodes in the tree is in the range [2, 105].
packagemain
+
+// Definition for a binary tree node.
+typeTreeNodestruct{
+ Val int
+ Left *TreeNode
+ Right *TreeNode
+}
+
+funclowestCommonAncestor(root, p, q *TreeNode)*TreeNode {
+if root ==nil|| root == p || root == q {
+return root
+}
+
+ left :=lowestCommonAncestor(root.Left, p, q)
+ right :=lowestCommonAncestor(root.Right, p, q)
+
+if left ==nil{
+return right
+}elseif right ==nil{
+return left
+}else{
+return root
+}
+}
+
+
implSolution{
+pubfnadd_digits(num:i32)->i32{
+letmut num = num;
+
+ // loop while the number is greater than 9
+while num >9{
+letmut sum =0;
+ // loop while the number is greater than 0,
+ // add the last digit to the sum,
+ // and divide the number by 10
+while num >0{
+ sum += num %10;
+ num /=10;
+}
+ // set the number to the sum
+ num = sum;
+}
+
+ num
+}
+}
+
+
implSolution{
+pubfnis_ugly(n:i32)->bool{
+if n <1{
+returnfalse;
+}
+
+let divisors =[2,3,5];
+letmut n = n;
+
+for divisor in divisors {
+ // Divide n by divisor as many times as possible
+while n % divisor ==0{
+ n /= divisor;
+}
+}
+
+ n ==1
+}
+}
+
+
Given an array nums containing n distinct numbers in the range [0, n], return the only number in the range that is missing from the array.
Example 1:
Input: nums = [3,0,1]
+Output: 2
+Explanation: n = 3 since there are 3 numbers, so all numbers are in the range [0,3]. 2 is the missing number in the range since it does not appear in nums.
+
Example 2:
Input: nums = [0,1]
+Output: 2
+Explanation: n = 2 since there are 2 numbers, so all numbers are in the range [0,2]. 2 is the missing number in the range since it does not appear in nums.
+
Example 3:
Input: nums = [9,6,4,2,3,5,7,0,1]
+Output: 8
+Explanation: n = 9 since there are 9 numbers, so all numbers are in the range [0,9]. 8 is the missing number in the range since it does not appear in nums.
+
Constraints:
n == nums.length
1 <= n <= 104
0 <= nums[i] <= n
All the numbers of nums are unique.
Follow up: Could you implement a solution using only O(1) extra space complexity and O(n) runtime complexity?
implSolution{
+pubfnmissing_number(nums:Vec<i32>)->i32{
+let len = nums.len();
+letmut sum = len *(len +1)/2;
+
+for num in nums {
+ sum -= num asusize;
+}
+
+ sum asi32
+}
+}
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/solution/0201-0300/278 - First Bad Version.html b/solution/0201-0300/278 - First Bad Version.html
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..97d7d15b
--- /dev/null
+++ b/solution/0201-0300/278 - First Bad Version.html
@@ -0,0 +1,73 @@
+
+
+
+
+
+ 278. First Bad Version | 🏆 Leetcode
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
You are a product manager and currently leading a team to develop a new product. Unfortunately, the latest version of your product fails the quality check. Since each version is developed based on the previous version, all the versions after a bad version are also bad.
Suppose you have n versions [1, 2, ..., n] and you want to find out the first bad one, which causes all the following ones to be bad.
You are given an API bool isBadVersion(version) which returns whether version is bad. Implement a function to find the first bad version. You should minimize the number of calls to the API.
Given an integer n, return the least number of perfect square numbers that sum ton.
A perfect square is an integer that is the square of an integer; in other words, it is the product of some integer with itself. For example, 1, 4, 9, and 16 are perfect squares while 3 and 11 are not.
use std::cmp::min;
+
+implSolution{
+pubfnnum_squares(n:i32)->i32{
+ // make a dp array of size n + 1 and filled with 0
+letmut dp =vec![n; n asusize+1];
+
+ // set the first element to 0
+ dp[0]=0;
+
+ // iterate from 1 to n
+for i in1..=n asusize{
+ // iterate from 1 to sqrt(i)
+for j in1..=(i asf64).sqrt()asusize{
+ // set dp[i] to the minimum of dp[i] and dp[i - j * j] + 1
+ dp[i]=min(dp[i], dp[i - j * j]+1);
+}
+}
+
+ dp[n asusize]
+}
+}
+
packagemain
+
+import"strings"
+
+funcwordPattern(pattern string, s string)bool{
+ words := strings.Split(s,"")
+
+iflen(pattern)!=len(words){
+returnfalse
+}
+
+ map_ :=make(map[byte]string)
+
+// loop through the pattern and process each character
+for i :=0; i <len(pattern); i++{
+// if the word is already in the map, check if it matches the pattern
+if val, ok := map_[pattern[i]]; ok {
+if val != words[i]{
+returnfalse
+}
+}else{
+// loop through the map to check if map contains the word
+for _, v :=range map_ {
+// if the word is in the map, return false
+if v == words[i]{
+returnfalse
+}
+}
+
+// if the word is not in the map, add it
+ map_[pattern[i]]= words[i]
+}
+}
+
+returntrue
+}
+
+
You are playing the following Nim Game with your friend:
Initially, there is a heap of stones on the table.
You and your friend will alternate taking turns, and you go first.
On each turn, the person whose turn it is will remove 1 to 3 stones from the heap.
The one who removes the last stone is the winner.
Given n, the number of stones in the heap, return true if you can win the game assuming both you and your friend play optimally, otherwise return false.
Example 1:
Input: n = 4
+Output: false
+Explanation: These are the possible outcomes:
+1. You remove 1 stone. Your friend removes 3 stones, including the last stone. Your friend wins.
+2. You remove 2 stones. Your friend removes 2 stones, including the last stone. Your friend wins.
+3. You remove 3 stones. Your friend removes the last stone. Your friend wins.
+In all outcomes, your friend wins.
+
Example 2:
Input: n = 1
+Output: true
+
Example 3:
Input: n = 2
+Output: true
+
Constraints:
1 <= n <= 231 - 1
Click to open Hints
If there are 5 stones in the heap, could you figure out a way to remove the stones such that you will always be the winner?
implSolution{
+pubfncan_win_nim(n:i32)->bool{
+ // if n is divisible by 4, then the first player will always lose
+if n %4==0{
+returnfalse;
+}
+
+true
+}
+}
+
+
You are given an integer array coins representing coins of different denominations and an integer amount representing a total amount of money.
Return the fewest number of coins that you need to make up that amount. If that amount of money cannot be made up by any combination of the coins, return -1.
You may assume that you have an infinite number of each kind of coin.
+
+
+
+
+
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/solution/0301-0400/326 - Power Of Three.html b/solution/0301-0400/326 - Power Of Three.html
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..0b5b2136
--- /dev/null
+++ b/solution/0301-0400/326 - Power Of Three.html
@@ -0,0 +1,51 @@
+
+
+
+
+
+ 326. Power Of Three | 🏆 Leetcode
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
The thief has found himself a new place for his thievery again. There is only one entrance to this area, called root.
Besides the root, each house has one and only one parent house. After a tour, the smart thief realized that all houses in this place form a binary tree. It will automatically contact the police if two directly-linked houses were broken into on the same night.
Given the root of the binary tree, return the maximum amount of money the thief can rob without alerting the police.
Given an integer n, return an array ans of length n + 1 such that for each i(0 <= i <= n), ans[i] is the number of 1's in the binary representation of i.
+
+
+
+
+
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/solution/0301-0400/342 - Power of Four.html b/solution/0301-0400/342 - Power of Four.html
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..bb482830
--- /dev/null
+++ b/solution/0301-0400/342 - Power of Four.html
@@ -0,0 +1,48 @@
+
+
+
+
+
+ 342. Power of Four | 🏆 Leetcode
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
Given two integer arrays nums1 and nums2, return an array of their intersection. Each element in the result must be unique and you may return the result in any order.
Given two integer arrays nums1 and nums2, return an array of their intersection. Each element in the result must appear as many times as it shows in both arrays and you may return the result in any order.
+
+
+
+
+
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/solution/0301-0400/369 - Plus One Linked List.html b/solution/0301-0400/369 - Plus One Linked List.html
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..a56a9558
--- /dev/null
+++ b/solution/0301-0400/369 - Plus One Linked List.html
@@ -0,0 +1,58 @@
+
+
+
+
+
+ 369 Plus One Linked List | 🏆 Leetcode
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
implSolution{
+pubfncan_construct(ransom_note:String, magazine:String)->bool{
+ // Convert the magazine string to a vector of characters
+letmut magazine = magazine.chars().collect::<Vec<char>>();
+
+ // Iterate over the ransom note string
+for c in ransom_note.chars(){
+ // If the magazine contains the character, remove it
+ // Otherwise, return false
+ // position() returns the index of the first element that matches the closure
+ // else returns None
+ifletSome(i)= magazine.iter().position(|&x| x == c){
+ magazine.remove(i);
+}else{
+returnfalse;
+}
+}
+
+true
+}
+}
+
+
go
packagemain
+
+funccanConstruct(ransomNote string, magazine string)bool{
+iflen(ransomNote)>len(magazine){
+returnfalse
+}
+// make a map of the magazine
+ mag :=make(map[rune]int)
+
+// count the number of each character in the magazine
+for _, c :=range magazine {
+ mag[c]++
+}
+
+// check if the ransom note can be made from the magazine
+for _, c :=range ransomNote {
+if mag[c]==0{
+returnfalse
+}
+ mag[c]--
+}
+
+// // make a vector of the magazine
+// magVec := make([]int, 26)
+
+// for _, c := range magazine {
+// magVec[c-'a']++
+// }
+
+// // check if ransomNote can be constructed from magazine
+// for _, c := range ransomNote {
+// if magVec[c-'a'] == 0 {
+// return false
+// }
+// magVec[c-'a']--
+// }
+
+returntrue
+}
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/solution/0301-0400/387 - First Unique Character in a String.html b/solution/0301-0400/387 - First Unique Character in a String.html
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..a155d20b
--- /dev/null
+++ b/solution/0301-0400/387 - First Unique Character in a String.html
@@ -0,0 +1,55 @@
+
+
+
+
+
+ 387. First Unique Character in a String | 🏆 Leetcode
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
implSolution{
+pubfnfirst_uniq_char(s:String)->i32{
+letmut map =std::collections::HashMap::new();
+for c in s.chars(){
+ // increase the count of the character if exists
+ // otherwise insert the character w/ default value 0
+ // then increase the count by 1
+*map.entry(c).or_insert(0)+=1;
+}
+
+ // iterate over the string and return the index of the first character
+ // that has a count of 1
+for(i, c)in s.chars().enumerate(){
+if*map.get(&c).unwrap()==1{
+return i asi32;
+}
+}
+
+-1
+}
+}
+
+
publiccharfindTheDifference(String s,String t){
+char c =0;
+for(int i =0; i < s.length();++i)
+ c ^= s.charAt(i);
+for(int i =0; i < t.length();++i)
+ c ^= t.charAt(i);
+return c;
+}
+
Given two strings s and t, return true if s is a subsequence of t, or false otherwise.
A subsequence of a string is a new string that is formed from the original string by deleting some (can be none) of the characters without disturbing the relative positions of the remaining characters. (i.e., "ace" is a subsequence of "abcde" while "aec" is not).
Example 1:
Input: s = "abc", t = "ahbgdc"
+Output: true
+
Example 2:
Input: s = "axc", t = "ahbgdc"
+Output: false
+
Constraints:
0 <= s.length <= 100
0 <= t.length <= 104
s and t consist only of lowercase English letters.
Follow up: Suppose there are lots of incoming s, say s1, s2, ..., sk where k >= 109, and you want to check one by one to see if t has its subsequence. In this scenario, how would you change your code?
A binary watch has 4 LEDs on the top to represent the hours (0-11), and 6 LEDs on the bottom to represent the minutes (0-59). Each LED represents a zero or one, with the least significant bit on the right.
For example, the below binary watch reads "4:51".
Given an integer turnedOn which represents the number of LEDs that are currently on (ignoring the PM), return all possible times the watch could represent. You may return the answer in any order.
The hour must not contain a leading zero.
For example, "01:00" is not valid. It should be "1:00".
The minute must be consist of two digits and may contain a leading zero.
For example, "10:2" is not valid. It should be "10:02".
implSolution{
+pubfnread_binary_watch(turned_on:i32)->Vec<String>{
+letmut res =Vec::new();
+
+ // 12 hours, 60 minutes
+ // here we use 0_i32 to avoid the warning of type inference
+for i in0_i32..12{
+for j in0_i32..60{
+ // if the sum of the number of 1s in the binary representation
+ // of the hour and minute is equal to turned_on,
+ // then the time is added to the res
+if i.count_ones()+ j.count_ones()== turned_on asu32{
+ res.push(format!("{}:{:02}", i, j));
+}
+}
+}
+
+ res
+}
+}
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/solution/0401-0500/404 - Sum of Left Leaves.html b/solution/0401-0500/404 - Sum of Left Leaves.html
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..c75cd1cc
--- /dev/null
+++ b/solution/0401-0500/404 - Sum of Left Leaves.html
@@ -0,0 +1,86 @@
+
+
+
+
+
+ 404. Sum of Left Leaves | 🏆 Leetcode
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
implSolution{
+pubfnfizz_buzz(n:i32)->Vec<String>{
+letmut res =Vec::new();
+
+for i in1..=n {
+ // same as divisible by 3 and 5
+if i %15==0{
+ res.push("FizzBuzz".to_string());
+}elseif i %3==0{
+ res.push("Fizz".to_string());
+}elseif i %5==0{
+ res.push("Buzz".to_string());
+}else{
+ res.push(i.to_string());
+}
+}
+
+ res
+}
+}
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/solution/0401-0500/414 - Third Maximum Number.html b/solution/0401-0500/414 - Third Maximum Number.html
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..53491146
--- /dev/null
+++ b/solution/0401-0500/414 - Third Maximum Number.html
@@ -0,0 +1,61 @@
+
+
+
+
+
+ 414. Third Maximum Number | 🏆 Leetcode
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
Given an integer array nums, return the third distinct maximum number in this array. If the third maximum does not exist, return the maximum number.
Example 1:
Input: nums = [3,2,1]
+Output: 1
+Explanation:
+The first distinct maximum is 3.
+The second distinct maximum is 2.
+The third distinct maximum is 1.
+
Example 2:
Input: nums = [1,2]
+Output: 2
+Explanation:
+The first distinct maximum is 2.
+The second distinct maximum is 1.
+The third distinct maximum does not exist, so the maximum (2) is returned instead.
+
Example 3:
Input: nums = [2,2,3,1]
+Output: 1
+Explanation:
+The first distinct maximum is 3.
+The second distinct maximum is 2 (both 2's are counted together since they have the same value).
+The third distinct maximum is 1.
+
+
+
+
+
+
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/solution/0401-0500/434 - Number of Segments in a String.html b/solution/0401-0500/434 - Number of Segments in a String.html
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..2f047682
--- /dev/null
+++ b/solution/0401-0500/434 - Number of Segments in a String.html
@@ -0,0 +1,49 @@
+
+
+
+
+
+ 434. Number of Segments in a String | 🏆 Leetcode
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/solution/0401-0500/438 - Find All Anagrams in a String.html b/solution/0401-0500/438 - Find All Anagrams in a String.html
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..9df263ca
--- /dev/null
+++ b/solution/0401-0500/438 - Find All Anagrams in a String.html
@@ -0,0 +1,71 @@
+
+
+
+
+
+ 438. Find All Anagrams in a String | 🏆 Leetcode
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
Given two strings s and p, return an array of all the start indices of p's anagrams in s. You may return the answer in any order.
An Anagram is a word or phrase formed by rearranging the letters of a different word or phrase, typically using all the original letters exactly once.
Example 1:
Input: s = "cbaebabacd", p = "abc"
+Output: [0,6]
+Explanation:
+The substring with start index = 0 is "cba", which is an anagram of "abc".
+The substring with start index = 6 is "bac", which is an anagram of "abc".
+
Example 2:
Input: s = "abab", p = "ab"
+Output: [0,1,2]
+Explanation:
+The substring with start index = 0 is "ab", which is an anagram of "ab".
+The substring with start index = 1 is "ba", which is an anagram of "ab".
+The substring with start index = 2 is "ab", which is an anagram of "ab".
+
classSolution:
+deffindAnagrams(self,s:str,p:str)-> list[int]:
+ s_len, p_len =len(s),len(p)
+if p_len > s_len:
+return[]
+ p_count, s_count ={},{}
+# increment the count of each character in p and s,
+# for the first p_len characters in s
+# with get() we can set a default value if the key is not found
+for i inrange(p_len):
+ p_count[p[i]]= p_count.get(p[i],0)+1
+ s_count[s[i]]= s_count.get(s[i],0)+1
+
+# if the counts are equal, we found an anagram
+ res =[0]if p_count == s_count else[]
+ l =0
+for r inrange(p_len, s_len):
+# increment the count of the right character
+ s_count[s[r]]= s_count.get(s[r],0)+1
+# decrement the count of the left character
+ s_count[s[l]]-=1
+
+# if the count of the left character is 0,
+# we can remove it from the dictionary
+if s_count[s[l]]==0:
+del s_count[s[l]]
+# increment the left pointer
+ l +=1
+# if the counts are equal, we found an anagram
+if p_count == s_count:
+ res.append(l)
+return res
+
+
You have n coins and you want to build a staircase with these coins. The staircase consists of k rows where the ith row has exactly i coins. The last row of the staircase may be incomplete.
Given the integer n, return the number of complete rows of the staircase you will build.
Example 1:
Input: n = 5
+Output: 2
+Explanation: Because the 3rd row is incomplete, we return 2.
+
Example 2:
Input: n = 8
+Output: 3
+Explanation: Because the 4th row is incomplete, we return 3.
+
+
+
+
+
+
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/solution/0401-0500/442 - Find All Duplicates in an Array.html b/solution/0401-0500/442 - Find All Duplicates in an Array.html
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..353ec4d0
--- /dev/null
+++ b/solution/0401-0500/442 - Find All Duplicates in an Array.html
@@ -0,0 +1,44 @@
+
+
+
+
+
+ 442. Find All Duplicates in an Array | 🏆 Leetcode
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
Given an integer array nums of length n where all the integers of nums are in the range [1, n] and each integer appears once or twice, return an array of all the integers that appears twice.
You must write an algorithm that runs in O(n) time and uses only constant extra space.
Given an array of characters chars, compress it using the following algorithm:
Begin with an empty string s. For each group of consecutive repeating characters in chars:
If the group's length is 1, append the character to s.
Otherwise, append the character followed by the group's length.
The compressed string sshould not be returned separately, but instead, be stored in the input character array chars. Note that group lengths that are 10 or longer will be split into multiple characters in chars.
After you are done modifying the input array, return the new length of the array.
You must write an algorithm that uses only constant extra space.
Example 1:
Input: chars = ["a","a","b","b","c","c","c"]
+Output: Return 6, and the first 6 characters of the input array should be: ["a","2","b","2","c","3"]
+Explanation: The groups are "aa", "bb", and "ccc". This compresses to "a2b2c3".
+
Example 2:
Input: chars = ["a"]
+Output: Return 1, and the first character of the input array should be: ["a"]
+Explanation: The only group is "a", which remains uncompressed since it's a single character.
+
Example 3:
Input: chars = ["a","b","b","b","b","b","b","b","b","b","b","b","b"]
+Output: Return 4, and the first 4 characters of the input array should be: ["a","b","1","2"].
+Explanation: The groups are "a" and "bbbbbbbbbbbb". This compresses to "ab12".```
+
+<p> </p>
+<p><strong>Constraints:</strong></p>
+<ul>
+<li><code>1 <= chars.length <= 2000</code></li>
+<li><code>chars[i]</code> is a lowercase English letter, uppercase English letter, digit, or symbol.</li>
+</ul>
+
+
+::: details _Click to open Hints_
+
+- How do you know if you are at the end of a consecutive group of characters?
+
+:::
+
+## Solution:
+
+::: code-group
+
+```rs [Rust]
+impl Solution {
+ pub fn compress(chars: &mut Vec<char>) -> i32 {
+ let (mut i, n) = (0, chars.len());
+ let mut new_len = 0;
+
+ while i < n {
+ let mut j = i;
+
+ // increment j until we find a different character or reach the end
+ while j < n && chars[j] == chars[i] {
+ j += 1;
+ }
+
+ // place the character at the new position
+ // e.g. if we have aabbccc, we place a at the start of the array
+ chars[new_len] = chars[i];
+ new_len += 1;
+
+ // if the length of the group of characters is greater than 1
+ // i.e. suppose if new_len is 12, we need to place 12 as characters [..., '1','2', ...]
+ if j - i > 1 {
+ for c in (j - i).to_string().chars() {
+ chars[new_len] = c;
+ new_len += 1;
+ }
+ }
+
+ // place i at same position as j,
+ // i.e. the start of the next group of characters
+ i = j;
+ }
+
+ new_len as i32
+ }
+}
+
+
You are given two non-empty linked lists representing two non-negative integers. The most significant digit comes first and each of their nodes contains a single digit. Add the two numbers and return the sum as a linked list.
You may assume the two numbers do not contain any leading zero, except the number 0 itself.
+
+
+
+
+
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/solution/0401-0500/448 - Find All Numbers Disappeared in an Array.html b/solution/0401-0500/448 - Find All Numbers Disappeared in an Array.html
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..cfbf532b
--- /dev/null
+++ b/solution/0401-0500/448 - Find All Numbers Disappeared in an Array.html
@@ -0,0 +1,50 @@
+
+
+
+
+
+ 448. Find All Numbers Disappeared in an Array | 🏆 Leetcode
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
Given an array nums of n integers where nums[i] is in the range [1, n], return an array of all the integers in the range[1, n]that do not appear innums.
Example 1:
Input: nums = [4,3,2,7,8,2,3,1]
+Output: [5,6]
+
Example 2:
Input: nums = [1,1]
+Output: [2]
+
Constraints:
n == nums.length
1 <= n <= 105
1 <= nums[i] <= n
Follow up: Could you do it without extra space and in O(n) runtime? You may assume the returned list does not count as extra space.
Click to open Hints
This is a really easy problem if you decide to use additional memory. For those trying to write an initial solution using additional memory, think counters!
However, the trick really is to not use any additional space than what is already available to use. Sometimes, multiple passes over the input array help find the solution. However, there's an interesting piece of information in this problem that makes it easy to re-use the input array itself for the solution.
The problem specifies that the numbers in the array will be in the range [1, n] where n is the number of elements in the array. Can we use this information and modify the array in-place somehow to find what we need?
You are given row x colgrid representing a map where grid[i][j] = 1 represents land and grid[i][j] = 0 represents water.
Grid cells are connected horizontally/vertically (not diagonally). The grid is completely surrounded by water, and there is exactly one island (i.e., one or more connected land cells).
The island doesn't have "lakes", meaning the water inside isn't connected to the water around the island. One cell is a square with side length 1. The grid is rectangular, width and height don't exceed 100. Determine the perimeter of the island.
Example 1:
Input: grid = [[0,1,0,0],[1,1,1,0],[0,1,0,0],[1,1,0,0]]
+Output: 16
+Explanation: The perimeter is the 16 yellow stripes in the image above.
+
The complement of an integer is the integer you get when you flip all the 0's to 1's and all the 1's to 0's in its binary representation.
For example, The integer 5 is "101" in binary and its complement is "010" which is the integer 2.
Given an integer num, return its complement.
Example 1:
Input: num = 5
+Output: 2
+Explanation: The binary representation of 5 is 101 (no leading zero bits), and its complement is 010. So you need to output 2.
+
Example 2:
Input: num = 1
+Output: 0
+Explanation: The binary representation of 1 is 1 (no leading zero bits), and its complement is 0. So you need to output 0.
+
You are given a license key represented as a string s that consists of only alphanumeric characters and dashes. The string is separated into n + 1 groups by n dashes. You are also given an integer k.
We want to reformat the string s such that each group contains exactly k characters, except for the first group, which could be shorter than k but still must contain at least one character. Furthermore, there must be a dash inserted between two groups, and you should convert all lowercase letters to uppercase.
Return the reformatted license key.
Example 1:
Input: s = "5F3Z-2e-9-w", k = 4
+Output: "5F3Z-2E9W"
+Explanation: The string s has been split into two parts, each part has 4 characters.
+Note that the two extra dashes are not needed and can be removed.
+
Example 2:
Input: s = "2-5g-3-J", k = 2
+Output: "2-5G-3J"
+Explanation: The string s has been split into three parts, each part has 2 characters except the first part as it could be shorter as mentioned above.
+
Constraints:
1 <= s.length <= 105
s consists of English letters, digits, and dashes '-'.
Given a binary array nums, return the maximum number of consecutive 1's in the array.
Example 1:
Input: nums = [1,1,0,1,1,1]
+Output: 3
+Explanation: The first two digits or the last three digits are consecutive 1s. The maximum number of consecutive 1s is 3.
+
Example 2:
Input: nums = [1,0,1,1,0,1]
+Output: 2
+
Constraints:
1 <= nums.length <= 105
nums[i] is either 0 or 1.
Click to open Hints
You need to think about two things as far as any window is concerned. One is the starting point for the window. How do you detect that a new window of 1s has started? The next part is detecting the ending point for this window.
How do you detect the ending point for an existing window? If you figure these two things out, you will be able to detect the windows of consecutive ones. All that remains afterward is to find the longest such window and return the size.
A web developer needs to know how to design a web page's size. So, given a specific rectangular web page’s area, your job by now is to design a rectangular web page, whose length L and width W satisfy the following requirements:
The area of the rectangular web page you designed must equal to the given target area.
The width W should not be larger than the length L, which means L >= W.
The difference between length L and width W should be as small as possible.
Return an array [L, W] where L and W are the length and width of the web page you designed in sequence.
Example 1:
Input: area = 4
+Output: [2,2]
+Explanation: The target area is 4, and all the possible ways to construct it are [1,4], [2,2], [4,1].
+But according to requirement 2, [1,4] is illegal; according to requirement 3, [4,1] is not optimal compared to [2,2]. So the length L is 2, and the width W is 2.
+
Example 2:
Input: area = 37
+Output: [37,1]
+
Example 3:
Input: area = 122122
+Output: [427,286]
+
Constraints:
1 <= area <= 107
Click to open Hints
The W is always less than or equal to the square root of the area, so we start searching at sqrt(area) till we find the result.
implSolution{
+pubfnconstruct_rectangle(area:i32)->Vec<i32>{
+letmut w =(area asf64).sqrt()asi32;
+
+ // until the remainder is 0, decrement w
+ // this will find the largest w that is a factor of area
+while area % w !=0{
+ w -=1;
+}
+
+ // return the result
+vec![area / w, w]
+}
+}
+
+
packagemain
+
+typeDirectionint
+
+const(
+ Up Direction =iota
+ Down
+)
+
+funcfindDiagonalOrder(mat [][]int)[]int{
+ direction := Up
+ row, col :=0,0
+ row_len, col_len :=len(mat),len(mat[0])
+ res :=make([]int, row_len*col_len)
+
+for i :=0; i < row_len*col_len; i++{
+ res[i]= mat[row][col]
+
+if direction == Up {
+if row ==0|| col == col_len-1{
+ direction = Down
+
+if col == col_len-1{
+ row++
+}else{
+ col++
+}
+
+}else{
+ row--
+ col++
+}
+}else{
+if col ==0|| row == row_len-1{
+ direction = Up
+
+if row == row_len-1{
+ col++
+}else{
+ row++
+}
+
+}else{
+ row++
+ col--
+}
+}
+}
+
+return res
+}
+
+
rs
enumDirection{
+Up,
+Down,
+}
+
+implSolution{
+pubfnfind_diagonal_order(mat:Vec<Vec<i32>>)->Vec<i32>{
+letmut result =vec![];
+letmut direction =Direction::Up;
+let(mut row,mut col)=(0,0);
+let(row_len, col_len)=(mat.len(), mat[0].len());
+
+while row < row_len && col < col_len {
+ // push the current element to the result vector
+ result.push(mat[row][col]);
+
+match direction {
+Direction::Up=>{
+if row ==0|| col == col_len -1{
+ // if we are at the top row or the rightmost column, change direction to "Down"
+ direction =Direction::Down;
+
+if col == col_len -1{
+ // if at the rightmost column, move to the next row
+ row +=1;
+}else{
+ // otherwise, move to the next column
+ col +=1;
+}
+}else{
+ // move diagonally upward
+ row -=1;
+ col +=1;
+}
+}
+Direction::Down=>{
+if col ==0|| row == row_len -1{
+ // if we are at the leftmost column or the bottom row, change direction to "Up"
+ direction =Direction::Up;
+
+if row == row_len -1{
+ // if at the bottom row, move to the next column
+ col +=1;
+}else{
+ // otherwise, move to the next row
+ row +=1;
+}
+}else{
+ // move diagonally downward
+ row +=1;
+ col -=1;
+}
+}
+}
+}
+
+ result
+}
+}
+
+
Suppose LeetCode will start its IPO soon. In order to sell a good price of its shares to Venture Capital, LeetCode would like to work on some projects to increase its capital before the IPO. Since it has limited resources, it can only finish at most k distinct projects before the IPO. Help LeetCode design the best way to maximize its total capital after finishing at most k distinct projects.
You are given n projects where the ith project has a pure profit profits[i] and a minimum capital of capital[i] is needed to start it.
Initially, you have w capital. When you finish a project, you will obtain its pure profit and the profit will be added to your total capital.
Pick a list of at mostk distinct projects from given projects to maximize your final capital, and return the final maximized capital.
The answer is guaranteed to fit in a 32-bit signed integer.
Example 1:
Input: k = 2, w = 0, profits = [1,2,3], capital = [0,1,1]
+Output: 4
+Explanation: Since your initial capital is 0, you can only start the project indexed 0.
+After finishing it you will obtain profit 1 and your capital becomes 1.
+With capital 1, you can either start the project indexed 1 or the project indexed 2.
+Since you can choose at most 2 projects, you need to finish the project indexed 2 to get the maximum capital.
+Therefore, output the final maximized capital, which is 0 + 1 + 3 = 4.
+
Example 2:
Input: k = 3, w = 0, profits = [1,2,3], capital = [0,1,2]
+Output: 6
+
You are given an integer array score of size n, where score[i] is the score of the ith athlete in a competition. All the scores are guaranteed to be unique.
The athletes are placed based on their scores, where the 1st place athlete has the highest score, the 2nd place athlete has the 2nd highest score, and so on. The placement of each athlete determines their rank:
The 1st place athlete's rank is "Gold Medal".
The 2nd place athlete's rank is "Silver Medal".
The 3rd place athlete's rank is "Bronze Medal".
For the 4th place to the nth place athlete, their rank is their placement number (i.e., the xth place athlete's rank is "x").
Return an array answer of size n where answer[i] is the rank of the ith athlete.
A perfect number is a positive integer that is equal to the sum of its positive divisors, excluding the number itself. A divisor of an integer x is an integer that can divide x evenly.
Given an integer n, return true if n is a perfect number, otherwise return false.
Example 1:
Input: num = 28
+Output: true
+Explanation: 28 = 1 + 2 + 4 + 7 + 14
+1, 2, 4, 7, and 14 are all divisors of 28.
+
implSolution{
+pubfncheck_perfect_number(num:i32)->bool{
+if num ==1{
+returnfalse;
+}
+
+let(mut sum,mut i)=(1,2);
+
+while i * i <= num {
+ // if i is a factor of num, add i and num / i to sum
+if num % i ==0{
+ sum += i;
+if i * i != num {
+ sum += num / i;
+}
+}
+ i +=1;
+}
+
+ sum == num
+}
+}
+
+
The Fibonacci numbers, commonly denoted F(n) form a sequence, called the Fibonacci sequence, such that each number is the sum of the two preceding ones, starting from 0 and 1. That is,
F(0) = 0, F(1) = 1
+F(n) = F(n - 1) + F(n - 2), for n > 1.
+Given n, calculate F(n).
+
Given a string s, find the longest palindromic subsequence's length in s.
A subsequence is a sequence that can be derived from another sequence by deleting some or no elements without changing the order of the remaining elements.
+
+
+
+
+
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/solution/0501-0600/540 - Single Element in a Sorted Array.html b/solution/0501-0600/540 - Single Element in a Sorted Array.html
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..0b0cd6da
--- /dev/null
+++ b/solution/0501-0600/540 - Single Element in a Sorted Array.html
@@ -0,0 +1,63 @@
+
+
+
+
+
+ 540. Single Element in a Sorted Array | 🏆 Leetcode
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
packagemain
+
+funcsingleNonDuplicate(nums []int)int{
+ res :=0
+
+for _, num :=range nums {
+// a ^ a = 0
+// a ^ a ^ a = a
+// a ^ a ^ b = b
+// also position of a and b doesn't matter
+ res ^= num
+}
+
+return res
+}
+
+
rs
implSolution{
+pubfnsingle_non_duplicate(nums:Vec<i32>)->i32{
+letmut res =0;
+
+for num in nums {
+ // a ^ a = 0
+ // a ^ a ^ a = a
+ // a ^ a ^ b = b
+ // also position of a and b doesn't matter
+ res ^= num;
+}
+
+ res
+}
+}
+
+
Given a string s and an integer k, reverse the first k characters for every 2k characters counting from the start of the string.
If there are fewer than k characters left, reverse all of them. If there are less than 2k but greater than or equal to k characters, then reverse the first k characters and leave the other as original.
publicStringreverseStr(String s,int k){
+String res ="";
+int index =0,
+ flag =0,
+ len = s.length();
+while(index < len){
+StringBuilder sb =newStringBuilder(s.substring(index,(index + k > len)? len : index + k));
+ res +=(flag++%2==0)? sb.reverse(): sb;
+ index += k;
+}
+return res;
+}
+
+
+
+
+
+
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/solution/0601-0700/605 - Can Place Flowers.html b/solution/0601-0700/605 - Can Place Flowers.html
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..9e6c2707
--- /dev/null
+++ b/solution/0601-0700/605 - Can Place Flowers.html
@@ -0,0 +1,84 @@
+
+
+
+
+
+ 605. Can Place Flowers | 🏆 Leetcode
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
You have a long flowerbed in which some of the plots are planted, and some are not. However, flowers cannot be planted in adjacent plots.
Given an integer array flowerbed containing 0's and 1's, where 0 means empty and 1 means not empty, and an integer n, return trueifnnew flowers can be planted in theflowerbedwithout violating the no-adjacent-flowers rule andfalseotherwise.
Example 1:
Input: flowerbed = [1,0,0,0,1], n = 1
+Output: true
+
Example 2:
Input: flowerbed = [1,0,0,0,1], n = 2
+Output: false
+
packagemain
+
+import"strconv"
+
+// Definition for a binary tree node.
+typeTreeNodestruct{
+ Val int
+ Left *TreeNode
+ Right *TreeNode
+}
+
+funcfindDuplicateSubtrees(root *TreeNode)[]*TreeNode {
+// to store the hash value of subtrees
+ hashMap :=make(map[string]int)
+// to store the result
+ res :=make([]*TreeNode,0)
+// traverse the tree
+traverse(root, hashMap,&res)
+return res
+}
+
+// traverse the tree
+functraverse(root *TreeNode, hashMap map[string]int, res *[]*TreeNode)string{
+// if the root is nil, return "#"
+if root ==nil{
+return"#"
+}
+// traverse the left and right subtree
+ left :=traverse(root.Left, hashMap, res)
+ right :=traverse(root.Right, hashMap, res)
+// get the hash value of the subtree
+ subTree := left +","+ right +","+ strconv.Itoa(root.Val)
+// if the hash value of the subtree is 1, it means that the subtree is duplicated
+if hashMap[subTree]==1{
+*res =append(*res, root)
+}
+// add the hash value of the subtree to the hashMap
+ hashMap[subTree]++
+return subTree
+}
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/solution/0601-0700/653 - Two Sum IV - Input is a BST.html b/solution/0601-0700/653 - Two Sum IV - Input is a BST.html
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..bb6b8128
--- /dev/null
+++ b/solution/0601-0700/653 - Two Sum IV - Input is a BST.html
@@ -0,0 +1,49 @@
+
+
+
+
+
+ 653. Two Sum IV - Input is a BST | 🏆 Leetcode
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
Given the root of a Binary Search Tree and a target number k, return true if there exist two elements in the BST such that their sum is equal to the given target.
+
+
+
+
+
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/solution/0601-0700/695 - Max Area of Island.html b/solution/0601-0700/695 - Max Area of Island.html
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..e1ade39b
--- /dev/null
+++ b/solution/0601-0700/695 - Max Area of Island.html
@@ -0,0 +1,63 @@
+
+
+
+
+
+ 695. Max Area of Island | 🏆 Leetcode
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
You are given an m x n binary matrix grid. An island is a group of 1's (representing land) connected 4-directionally (horizontal or vertical.) You may assume all four edges of the grid are surrounded by water.
The area of an island is the number of cells with a value 1 in the island.
Return the maximum area of an island in grid. If there is no island, return 0.
Example 1:
Input: grid = [[0,0,1,0,0,0,0,1,0,0,0,0,0],[0,0,0,0,0,0,0,1,1,1,0,0,0],[0,1,1,0,1,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0],[0,1,0,0,1,1,0,0,1,0,1,0,0],[0,1,0,0,1,1,0,0,1,1,1,0,0],[0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,1,0,0],[0,0,0,0,0,0,0,1,1,1,0,0,0],[0,0,0,0,0,0,0,1,1,0,0,0,0]]
+Output: 6
+Explanation: The answer is not 11, because the island must be connected 4-directionally.
+
Given an array of integers nums which is sorted in ascending order, and an integer target, write a function to search target in nums. If target exists, then return its index. Otherwise, return -1.
You must write an algorithm with O(log n) runtime complexity.
Given an array of integers temperatures represents the daily temperatures, return an array answer such that answer[i] is the number of days you have to wait after the ith day to get a warmer temperature. If there is no future day for which this is possible, keep answer[i] == 0 instead.
You're given strings jewels representing the types of stones that are jewels, and stones representing the stones you have. Each character in stones is a type of stone you have. You want to know how many of the stones you have are also jewels.
Letters are case sensitive, so "a" is considered a different type of stone from "A".
Koko loves to eat bananas. There are n piles of bananas, the ith pile has piles[i] bananas. The guards have gone and will come back in h hours.
Koko can decide her bananas-per-hour eating speed of k. Each hour, she chooses some pile of bananas and eats k bananas from that pile. If the pile has less than k bananas, she eats all of them instead and will not eat any more bananas during this hour.
Koko likes to eat slowly but still wants to finish eating all the bananas before the guards return.
Return the minimum integerksuch that she can eat all the bananas withinhhours.
Example 1:
Input: piles = [3,6,7,11], h = 8
+Output: 4
+
Example 2:
Input: piles = [30,11,23,4,20], h = 5
+Output: 30
+
Example 3:
Input: piles = [30,11,23,4,20], h = 6
+Output: 23
+
import math
+
+
+classSolution:
+defminEatingSpeed(self,p: list[int],h:int)->int:
+ left, right =1,max(p)
+
+while left <= right:
+ m =(left+right)//2
+# t = sum((i+m-1)//m for i in p)
+# t = sum(-(-i//m) for i in p)
+ t =sum(math.ceil(i/m)for i in p)
+if t > h:
+ left = m+1
+else:
+ right = m-1
+return left
+
+
Alice and Bob have a different total number of candies. You are given two integer arrays aliceSizes and bobSizes where aliceSizes[i] is the number of candies of the ith box of candy that Alice has and bobSizes[j] is the number of candies of the jth box of candy that Bob has.
Since they are friends, they would like to exchange one candy box each so that after the exchange, they both have the same total amount of candy. The total amount of candy a person has is the sum of the number of candies in each box they have.
Return an integer array answer where answer[0] is the number of candies in the box that Alice must exchange, and answer[1] is the number of candies in the box that Bob must exchange. If there are multiple answers, you may return any one of them. It is guaranteed that at least one answer exists.
Given an array of integers nums, sort the array in ascending order and return it.
You must solve the problem without using any built-in functions in O(nlog(n)) time complexity and with the smallest space complexity possible.
Example 1:
Input: nums = [5,2,3,1]
+Output: [1,2,3,5]
+Explanation: After sorting the array, the positions of some numbers are not changed (for example, 2 and 3), while the positions of other numbers are changed (for example, 1 and 5).
+
Example 2:
Input: nums = [5,1,1,2,0,0]
+Output: [0,0,1,1,2,5]
+Explanation: Note that the values of nums are not necessairly unique.
+
You are given an array of n strings strs, all of the same length.
The strings can be arranged such that there is one on each line, making a grid.
For example, strs = ["abc", "bce", "cae"] can be arranged as follows:
abc
+bce
+cae
+
You want to delete the columns that are not sorted lexicographically. In the above example (0-indexed), columns 0 ('a', 'b', 'c') and 2 ('c', 'e', 'e') are sorted, while column 1 ('b', 'c', 'a') is not, so you would delete column 1.
Return the number of columns that you will delete.
Example 1:
Input: strs = ["cba","daf","ghi"]
+Output: 1
+Explanation: The grid looks as follows:
+ cba
+ daf
+ ghi
+Columns 0 and 2 are sorted, but column 1 is not, so you only need to delete 1 column.
+
Example 2:
Input: strs = ["a","b"]
+Output: 0
+Explanation: The grid looks as follows:
+ a
+ b
+Column 0 is the only column and is sorted, so you will not delete any columns.
+
Example 3:
Input: strs = ["zyx","wvu","tsr"]
+Output: 3
+Explanation: The grid looks as follows:
+ zyx
+ wvu
+ tsr
+All 3 columns are not sorted, so you will delete all 3.
+
Given the root of a binary tree, determine if it is a complete binary tree.
In a complete binary tree, every level, except possibly the last, is completely filled, and all nodes in the last level are as far left as possible. It can have between 1 and 2h nodes inclusive at the last level h.
Example 1:
Input: root = [1,2,3,4,5,6]
+Output: true
+Explanation: Every level before the last is full (ie. levels with node-values {1} and {2, 3}), and all nodes in the last level ({4, 5, 6}) are as far left as possible.
+
Example 2:
Input: root = [1,2,3,4,5,null,7]
+Output: false
+Explanation: The node with value 7 isn't as far left as possible.
+
Constraints:
The number of nodes in the tree is in the range [1, 100].
+
+
+
+
+
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/solution/1001-1100/1011 - Capacity To Ship Packages Within D Days.html b/solution/1001-1100/1011 - Capacity To Ship Packages Within D Days.html
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..da5b947c
--- /dev/null
+++ b/solution/1001-1100/1011 - Capacity To Ship Packages Within D Days.html
@@ -0,0 +1,94 @@
+
+
+
+
+
+ 1011. Capacity To Ship Packages Within D Days | 🏆 Leetcode
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
A conveyor belt has packages that must be shipped from one port to another within days days.
The ith package on the conveyor belt has a weight of weights[i]. Each day, we load the ship with packages on the conveyor belt (in the order given by weights). We may not load more weight than the maximum weight capacity of the ship.
Return the least weight capacity of the ship that will result in all the packages on the conveyor belt being shipped within days days.
Example 1:
+Input: weights = [1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10], days = 5
+Output: 15
+Explanation: A ship capacity of 15 is the minimum to ship all the packages in 5 days like this:
+1st day: 1, 2, 3, 4, 5
+2nd day: 6, 7
+3rd day: 8
+4th day: 9
+5th day: 10
+
+Note that the cargo must be shipped in the order given, so using a ship of capacity 14 and splitting the packages into parts like (2, 3, 4, 5), (1, 6, 7), (8), (9), (10) is not allowed.
+
Example 2:
+Input: weights = [3,2,2,4,1,4], days = 3
+Output: 6
+Explanation: A ship capacity of 6 is the minimum to ship all the packages in 3 days like this:
+1st day: 3, 2
+2nd day: 2, 4
+3rd day: 1, 4
+
implSolution{
+pubfnship_within_days(weights:Vec<i32>, days:i32)->i32{
+letmut min_cap =0; // it is the max of all weights
+letmut max_cap =0; // sum of all weights
+
+for w in weights.iter(){
+ // assign the max of all weights to min_cap
+ min_cap = min_cap.max(*w);
+ // add all the weights to right
+ max_cap += w;
+}
+
+ // binary search
+while min_cap < max_cap {
+let mid =(min_cap + max_cap)/2;
+letmut days_used =1;
+letmut cur_cap =0;
+
+ // for each weight, if the current capacity + weight is greater than mid,
+ // then we need to use another day
+ // otherwise, we can use the current day
+for w in weights.iter(){
+if cur_cap + w > mid {
+ days_used +=1;
+ cur_cap =0;
+}
+ cur_cap += w;
+}
+
+ // if days_used is greater than days, then we need to increase the capacity
+if days_used > days {
+ min_cap = mid +1;
+}else{
+ max_cap = mid;
+}
+}
+
+ min_cap
+}
+}
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/solution/1001-1100/1029 - Two City Scheduling.html b/solution/1001-1100/1029 - Two City Scheduling.html
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..e23106f0
--- /dev/null
+++ b/solution/1001-1100/1029 - Two City Scheduling.html
@@ -0,0 +1,62 @@
+
+
+
+
+
+ 1029. Two City Scheduling | 🏆 Leetcode
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
A company is planning to interview 2n people. Given the array costs where costs[i] = [aCosti, bCosti], the cost of flying the ith person to city a is aCosti, and the cost of flying the ith person to city b is bCosti.
Return the minimum cost to fly every person to a city such that exactly n people arrive in each city.
Example 1:
Input: costs = [[10,20],[30,200],[400,50],[30,20]]
+Output: 110
+Explanation:
+The first person goes to city A for a cost of 10.
+The second person goes to city A for a cost of 30.
+The third person goes to city B for a cost of 50.
+The fourth person goes to city B for a cost of 20.
+
+The total minimum cost is 10 + 30 + 50 + 20 = 110 to have half the people interviewing in each city.
+
implSolution{
+pubfntwo_city_sched_cost(costs:Vec<Vec<i32>>)->i32{
+letmut costs = costs;
+
+letmut total =0;
+let n = costs.len()/2;
+
+ // sort by a gain which company has
+ // by sending a person to city A and not to city B
+ costs.sort_by(|a, b|(a[0]- a[1]).cmp(&(b[0]- b[1])));
+
+ // to optimize the company expenses,
+ // send the first n persons to the city A
+ // and the others to the city B
+for i in0..n {
+ total += costs[i][0]+ costs[i + n][1]; // city A + city B
+}
+
+ total
+}
+}
+
+
You are given a string s consisting of lowercase English letters. A duplicate removal consists of choosing two adjacent and equal letters and removing them.
We repeatedly make duplicate removals on s until we no longer can.
Return the final string after all such duplicate removals have been made. It can be proven that the answer is unique.
For example, in "abbaca" we could remove "bb" since the letters are adjacent and equal, and this is the only possible move. The result of this move is that the string is "aaca", of which only "aa" is possible, so the final string is "ca".
+
Given two strings str1 and str2, return the shortest string that has both str1 and str2 as subsequences. If there are multiple valid strings, return any of them.
A string s is a subsequence of string t if deleting some number of characters from t (possibly 0) results in the string s.
Input: str1 = "abac", str2 = "cab"
+Output: "cabac"
+Explanation:
+str1 = "abac" is a subsequence of "cabac" because we can delete the first "c".
+str2 = "cab" is a subsequence of "cabac" because we can delete the last "ac".
+The answer provided is the shortest such string that satisfies these properties.
+
Given two strings text1 and text2, return the length of their longest common subsequence. If there is no common subsequence, return 0.
A subsequence of a string is a new string generated from the original string with some characters (can be none) deleted without changing the relative order of the remaining characters.
For example, "ace" is a subsequence of "abcde". A common subsequence of two strings is a subsequence that is common to both strings.
+
+
+
+
+
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/solution/1201-1300/1232 - Check If It Is a Straight Line.html b/solution/1201-1300/1232 - Check If It Is a Straight Line.html
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..cbd57caa
--- /dev/null
+++ b/solution/1201-1300/1232 - Check If It Is a Straight Line.html
@@ -0,0 +1,52 @@
+
+
+
+
+
+ 1232. Check If It Is a Straight Line | 🏆 Leetcode
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
You are given an array coordinates, coordinates[i] = [x, y], where [x, y] represents the coordinate of a point. Check if these points make a straight line in the XY plane.
Given an array of integers arr, you are initially positioned at the first index of the array.
In one step you can jump from index i to index:
i + 1 where: i + 1 < arr.length.
i - 1 where: i - 1 >= 0.
j where: arr[i] == arr[j] and i != j.
Return the minimum number of steps to reach the last index of the array.
Notice that you can not jump outside of the array at any time.
Example 1:
Input: arr = [100,-23,-23,404,100,23,23,23,3,404]
+Output: 3
+Explanation: You need three jumps from index 0 --> 4 --> 3 --> 9. Note that index 9 is the last index of the array.
+
Example 2:
Input: arr = [7]
+Output: 0
+Explanation: Start index is the last index. You do not need to jump.
+
Example 3:
Input: arr = [7,6,9,6,9,6,9,7]
+Output: 1
+Explanation: You can jump directly from index 0 to index 7 which is last index of the array.
+
Constraints:
1 <= arr.length <= 5 * 104
-108 <= arr[i] <= 108
Click to open Hints
Build a graph of n nodes where nodes are the indices of the array and edges for node i are nodes i+1, i-1, j where arr[i] == arr[j].
Start bfs from node 0 and keep distance. The answer is the distance when you reach node n-1.
+
+
+
+
+
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/solution/1401-1500/1431 - Kids With the Greatest Number of Candies.html b/solution/1401-1500/1431 - Kids With the Greatest Number of Candies.html
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..51f0eab2
--- /dev/null
+++ b/solution/1401-1500/1431 - Kids With the Greatest Number of Candies.html
@@ -0,0 +1,113 @@
+
+
+
+
+
+ 1431. Kids With the Greatest Number of Candies | 🏆 Leetcode
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
There are n kids with candies. You are given an integer array candies, where each candies[i] represents the number of candies the ith kid has, and an integer extraCandies, denoting the number of extra candies that you have.
Return a boolean array result of length n, where result[i] is true if, after giving the ith kid all the extraCandies, they will have the greatest number of candies among all the kids, or false otherwise.
Note that multiple kids can have the greatest number of candies.
Example 1:
Input: candies = [2,3,5,1,3], extraCandies = 3
+Output: [true,true,true,false,true]
+Explanation: If you give all extraCandies to:
+- Kid 1, they will have 2 + 3 = 5 candies, which is the greatest among the kids.
+- Kid 2, they will have 3 + 3 = 6 candies, which is the greatest among the kids.
+- Kid 3, they will have 5 + 3 = 8 candies, which is the greatest among the kids.
+- Kid 4, they will have 1 + 3 = 4 candies, which is not the greatest among the kids.
+- Kid 5, they will have 3 + 3 = 6 candies, which is the greatest among the kids.
+
Example 2:
Input: candies = [4,2,1,1,2], extraCandies = 1
+Output: [true,false,false,false,false]
+Explanation: There is only 1 extra candy.
+Kid 1 will always have the greatest number of candies, even if a different kid is given the extra candy.
+
+
+
+
+
+
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/solution/1401-1500/1461 - Check If a String Contains All Binary Codes of Size K.html b/solution/1401-1500/1461 - Check If a String Contains All Binary Codes of Size K.html
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..921102eb
--- /dev/null
+++ b/solution/1401-1500/1461 - Check If a String Contains All Binary Codes of Size K.html
@@ -0,0 +1,56 @@
+
+
+
+
+
+ 1461. Check If a String Contains All Binary Codes of Size K | 🏆 Leetcode
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
Given the array nums consisting of 2n elements in the form [x1,x2,...,xn,y1,y2,...,yn].
Return the array in the form[x1,y1,x2,y2,...,xn,yn].
Example 1:
+Input: nums = [2,5,1,3,4,7], n = 3
+Output: [2,3,5,4,1,7]
+Explanation: Since x1=2, x2=5, x3=1, y1=3, y2=4, y3=7 then the answer is [2,3,5,4,1,7].
+
Example 2:
+Input: nums = [1,2,3,4,4,3,2,1], n = 4
+Output: [1,4,2,3,3,2,4,1]
+
Example 3:
+Input: nums = [1,1,2,2], n = 2
+Output: [1,2,1,2]
+
Constraints:
1 <= n <= 500
nums.length == 2n
1 <= nums[i] <= 10^3
Click to open Hints
Use two pointers to create the new array of 2n elements. The first starting at the beginning and the other starting at (n+1)th position. Alternate between them and create the new array.
packagemain
+
+funcshuffle(nums []int, n int)[]int{
+ res :=make([]int, n*2)
+
+for i :=0; i < n; i++{
+// at even indices, put the slice of the array from 0 to n
+ res[i*2]= nums[i]
+// at odd indices, put the slice of the array from n to the end
+ res[i*2+1]= nums[n+i]
+}
+
+return res
+}
+
+
You have a browser of one tab where you start on the homepage and you can visit another url, get back in the history number of steps or move forward in the history number of steps.
Implement the BrowserHistory class:
BrowserHistory(string homepage) Initializes the object with the homepage of the browser.
void visit(string url) Visits url from the current page. It clears up all the forward history.
string back(int steps) Move steps back in history. If you can only return x steps in the history and steps > x, you will return only x steps. Return the current url after moving back in history at moststeps.
string forward(int steps) Move steps forward in history. If you can only forward x steps in the history and steps > x, you will forward only x steps. Return the current url after forwarding in history at moststeps.
Example:
Input:
+["BrowserHistory","visit","visit","visit","back","back","forward","visit","forward","back","back"]
+[["leetcode.com"],["google.com"],["facebook.com"],["youtube.com"],[1],[1],[1],["linkedin.com"],[2],[2],[7]]
+Output:
+[null,null,null,null,"facebook.com","google.com","facebook.com",null,"linkedin.com","google.com","leetcode.com"]
+
+Explanation:
+BrowserHistory browserHistory = new BrowserHistory("leetcode.com");
+browserHistory.visit("google.com"); // You are in "leetcode.com". Visit "google.com"
+browserHistory.visit("facebook.com"); // You are in "google.com". Visit "facebook.com"
+browserHistory.visit("youtube.com"); // You are in "facebook.com". Visit "youtube.com"
+browserHistory.back(1); // You are in "youtube.com", move back to "facebook.com" return "facebook.com"
+browserHistory.back(1); // You are in "facebook.com", move back to "google.com" return "google.com"
+browserHistory.forward(1); // You are in "google.com", move forward to "facebook.com" return "facebook.com"
+browserHistory.visit("linkedin.com"); // You are in "facebook.com". Visit "linkedin.com"
+browserHistory.forward(2); // You are in "linkedin.com", you cannot move forward any steps.
+browserHistory.back(2); // You are in "linkedin.com", move back two steps to "facebook.com" then to "google.com". return "google.com"
+browserHistory.back(7); // You are in "google.com", you can move back only one step to "leetcode.com". return "leetcode.com"
+
Constraints:
1 <= homepage.length <= 20
1 <= url.length <= 20
1 <= steps <= 100
homepage and url consist of '.' or lower case English letters.
At most 5000 calls will be made to visit, back, and forward.
Click to open Hints
Use two stacks: one for back history, and one for forward history. You can simulate the functions by popping an element from one stack and pushing it into the other.
Can you improve program runtime by using a different data structure?
+
+
+
+
+
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/solution/1401-1500/1491 - Average Salary Excluding the Minimum and Maximum Salary.html b/solution/1401-1500/1491 - Average Salary Excluding the Minimum and Maximum Salary.html
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..da5262a4
--- /dev/null
+++ b/solution/1401-1500/1491 - Average Salary Excluding the Minimum and Maximum Salary.html
@@ -0,0 +1,43 @@
+
+
+
+
+
+ 1491. Average Salary Excluding the Minimum and Maximum Salary | 🏆 Leetcode
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
Input: salary = [4000,3000,1000,2000]
+Output: 2500.00000
+Explanation: Minimum salary and maximum salary are 1000 and 4000 respectively.
+Average salary excluding minimum and maximum salary is (2000+3000) / 2 = 2500
+
Input: salary = [1000,2000,3000]
+Output: 2000.00000
+Explanation: Minimum salary and maximum salary are 1000 and 3000 respectively.
+Average salary excluding minimum and maximum salary is (2000) / 1 = 2000
+
publicdoubleaverage(int[] salary){
+ Arrays.sort(salary);
+int len = salary.length;
+double res =0;
+for(int i =1; i < len -1; i++)
+ res += salary[i];
+return res /(len -2);
+}
+
+
+
+
+
+
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/solution/1401-1500/1498 - Number of Subsequences That Satisfy the Given Sum Condition.html b/solution/1401-1500/1498 - Number of Subsequences That Satisfy the Given Sum Condition.html
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..aeebbc53
--- /dev/null
+++ b/solution/1401-1500/1498 - Number of Subsequences That Satisfy the Given Sum Condition.html
@@ -0,0 +1,62 @@
+
+
+
+
+
+ 1498. Number of Subsequences That Satisfy the Given Sum Condition | 🏆 Leetcode
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
You are given an array of integers nums and an integer target.
Return the number of non-empty subsequences of nums such that the sum of the minimum and maximum element on it is less or equal to target. Since the answer may be too large, return it modulo 109 + 7.
Input: nums = [2,3,3,4,6,7], target = 12
+Output: 61
+Explanation: There are 63 non-empty subsequences, two of them do not satisfy the condition ([6,7], [7]).
+Number of valid subsequences (63 - 2 = 61).
+
+
+
+
+
+
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/solution/1501-1600/1512 - Number of Good Pairs.html b/solution/1501-1600/1512 - Number of Good Pairs.html
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..714fc9a4
--- /dev/null
+++ b/solution/1501-1600/1512 - Number of Good Pairs.html
@@ -0,0 +1,50 @@
+
+
+
+
+
+ 1512. Number of Good Pairs | 🏆 Leetcode
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
Given two non-negative integers low and . Return the count of odd numbers between low and (inclusive).
Example 1:
+Input: low = 3, high = 7
+Output: 3
+Explanation: The odd numbers between 3 and 7 are [3,5,7].```
+
+<p><strong class="example">Example 2:</strong></p>
+
+
Input: low = 8, high = 10 Output: 1 Explanation: The odd numbers between 8 and 10 are [9].```
Constraints:
0 <= low <= high <= 10^9
Click to open Hints
If the range (high - low + 1) is even, the number of even and odd numbers in this range will be the same.
If the range (high - low + 1) is odd, the solution will depend on the parity of high and low.
+
+
+
+
+
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/solution/1501-1600/1537 - Get the Maximum Score.html b/solution/1501-1600/1537 - Get the Maximum Score.html
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..b355ff07
--- /dev/null
+++ b/solution/1501-1600/1537 - Get the Maximum Score.html
@@ -0,0 +1,86 @@
+
+
+
+
+
+ 1537. Get the Maximum Score | 🏆 Leetcode
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
You are given two sorted arrays of distinct integers nums1 and nums2.
A valid path is defined as follows:
Choose array nums1 or nums2 to traverse (from index-0).
Traverse the current array from left to right.
If you are reading any value that is present in nums1 and nums2 you are allowed to change your path to the other array. (Only one repeated value is considered in the valid path).
The score is defined as the sum of uniques values in a valid path.
Return the maximum score you can obtain of all possible valid paths. Since the answer may be too large, return it modulo 109 + 7.
Input: nums1 = [2,4,5,8,10], nums2 = [4,6,8,9]
+Output: 30
+Explanation: Valid paths:
+[2,4,5,8,10], [2,4,5,8,9], [2,4,6,8,9], [2,4,6,8,10], (starting from nums1)
+[4,6,8,9], [4,5,8,10], [4,5,8,9], [4,6,8,10] (starting from nums2)
+The maximum is obtained with the path in green [2,4,6,8,10].
+
Input: nums1 = [1,2,3,4,5], nums2 = [6,7,8,9,10]
+Output: 40
+Explanation: There are no common elements between nums1 and nums2.
+Maximum sum is obtained with the path [6,7,8,9,10].
+
publicclassGetTheMaxScore{
+
+/* Two Pointer Approach */
+publicintmaxSum(int[]nums1,int[]nums2){
+// initializing two pointer vars
+int i =0, j =0;
+int len1 = nums1.length, len2 = nums2.length;
+
+// taking the vars of long type to avoid integer overflow or runtime error
+long upperSum =0, lowerSum =0;
+
+// traverse till one of the arrays length
+while(i < len1 && j < len2){
+
+// adding the element to the upperSum until element of first array is >=
+// the element of second array & then increamenting the pointer var by 1
+if(nums1[i]< nums2[j])
+ upperSum += nums1[i++];
+
+// adding the element to the lowerSum until element of second array is >=
+// the element of first array & then increamenting the pointer var by 1
+elseif(nums1[i]> nums2[j])
+ lowerSum += nums2[j++];
+
+// when the element of both arrays are equal,
+// assign the value of max of upperSum & lowerSum and adding the element itself
+else{
+ upperSum = lowerSum = Math.max(upperSum, lowerSum)+ nums1[i];
+// increasing both pointer by 1, as the value at both the pointers is same,
+// avoiding the repetition of element in the sum
+ i++;
+ j++;
+}
+}
+
+// adding the remaining element from first array
+while(i < len1)
+ upperSum += nums1[i++];
+
+// adding the remaining element from second array
+while(j < len2)
+ lowerSum += nums2[j++];
+
+return(int)(Math.max(upperSum, lowerSum)%1000000007);
+}
+}
+
Given an array arr of positive integers sorted in a strictly increasing order, and an integer k.
Return thekthpositive integer that is missing from this array.
Example 1:
Input: arr = [2,3,4,7,11], k = 5
+Output: 9
+Explanation: The missing positive integers are [1,5,6,8,9,10,12,13,...]. The 5th missing positive integer is 9.
+
Example 2:
Input: arr = [1,2,3,4], k = 2
+Output: 6
+Explanation: The missing positive integers are [5,6,7,...]. The 2nd missing positive integer is 6.
+
Constraints:
1 <= arr.length <= 1000
1 <= arr[i] <= 1000
1 <= k <= 1000
arr[i] < arr[j] for 1 <= i < j <= arr.length
Follow up:
Could you solve this problem in less than O(n) complexity?
Click to open Hints
Keep track of how many positive numbers are missing as you scan the array.
You are given an m x n integer grid accounts where accounts[i][j] is the amount of money the ith customer has in the jth bank. Return the wealth that the richest customer has.
A customer's wealth is the amount of money they have in all their bank accounts. The richest customer is the customer that has the maximum wealth.
Example 1:
Input: accounts = [[1,2,3],[3,2,1]]
+Output: 6
+Explanation:
+1st customer has wealth = 1 + 2 + 3 = 6
+2nd customer has wealth = 3 + 2 + 1 = 6
+Both customers are considered the richest with a wealth of 6 each, so return 6.
+
Example 2:
Input: accounts = [[1,5],[7,3],[3,5]]
+Output: 10
+Explanation:
+1st customer has wealth = 6
+2nd customer has wealth = 10
+3rd customer has wealth = 8
+The 2nd customer is the richest with a wealth of 10.```
+
+<p><strong class="example">Example 3:</strong></p>
+
+
+<p> </p>
+<p><strong>Constraints:</strong></p>
+<ul>
+<li><code>m == accounts.length</code></li>
+<li><code>n == accounts[i].length</code></li>
+<li><code>1 <= m, n <= 50</code></li>
+<li><code>1 <= accounts[i][j] <= 100</code></li>
+</ul>
+
+
+::: details _Click to open Hints_
+
+- Calculate the wealth of each customer
+- Find the maximum element in array.
+
+:::
+
+## Solution:
+
+::: code-group
+
+```rs [Rust]
+impl Solution {
+ pub fn maximum_wealth(accounts: Vec<Vec<i32>>) -> i32 {
+ let mut max = 0;
+
+ for account in accounts {
+ let mut sum = 0;
+ for money in account {
+ sum += money;
+ }
+ if sum > max {
+ max = sum;
+ }
+ }
+ max
+ }
+}
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/solution/1601-1700/1689 - Partitioning Into Minimum Number Of Deci-Binary Numbers.html b/solution/1601-1700/1689 - Partitioning Into Minimum Number Of Deci-Binary Numbers.html
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..9bd36ed9
--- /dev/null
+++ b/solution/1601-1700/1689 - Partitioning Into Minimum Number Of Deci-Binary Numbers.html
@@ -0,0 +1,45 @@
+
+
+
+
+
+ 1689. Partitioning Into Minimum Number Of Deci-Binary Numbers | 🏆 Leetcode
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
A decimal number is called deci-binary if each of its digits is either 0 or 1 without any leading zeros. For example, 101 and 1100 are deci-binary, while 112 and 3001 are not.
Given a string n that represents a positive decimal integer, return the minimum number of positive deci-binary numbers needed so that they sum up to n.
implSolution{
+pubfnmin_partitions(n:String)->i32{
+ // this will be slightly faster as it doesn't need to convert the char to a digit
+ // as the max() function will return the max char value (in ASCII) which is the same as the max digit value
+
+ // n.chars().max().unwrap().to_digit(10).unwrap() as i32
+
+ n.chars().map(|c| c.to_digit(10).unwrap()).max().unwrap()asi32
+}
+}
+
+
Given a zero-based permutationnums (0-indexed), build an array ans of the same length where ans[i] = nums[nums[i]] for each 0 <= i < nums.length and return it.
A zero-based permutationnums is an array of distinct integers from 0 to nums.length - 1 (inclusive).
Example 1:
Input: nums = [0,2,1,5,3,4]
+Output: [0,1,2,4,5,3]
+Explanation: The array ans is built as follows:
+ans = [nums[nums[0]], nums[nums[1]], nums[nums[2]], nums[nums[3]], nums[nums[4]], nums[nums[5]]]
+ = [nums[0], nums[2], nums[1], nums[5], nums[3], nums[4]]
+ = [0,1,2,4,5,3]
+
Example 2:
Input: nums = [5,0,1,2,3,4]
+Output: [4,5,0,1,2,3]
+Explanation: The array ans is built as follows:
+ans = [nums[nums[0]], nums[nums[1]], nums[nums[2]], nums[nums[3]], nums[nums[4]], nums[nums[5]]]
+ = [nums[5], nums[0], nums[1], nums[2], nums[3], nums[4]]
+ = [4,5,0,1,2,3]
+
Constraints:
1 <= nums.length <= 1000
0 <= nums[i] < nums.length
The elements in nums are distinct.
Follow-up: Can you solve it without using an extra space (i.e., O(1) memory)?
Click to open Hints
Just apply what's said in the statement.
Notice that you can't apply it on the same array directly since some elements will change after application
Given an integer array nums of length n, you want to create an array ans of length 2n where ans[i] == nums[i] and ans[i + n] == nums[i] for 0 <= i < n (0-indexed).
Specifically, ans is the concatenation of two nums arrays.
Return the array ans.
Example 1:
Input: nums = [1,2,1]
+Output: [1,2,1,1,2,1]
+Explanation: The array ans is formed as follows:
+- ans = [nums[0],nums[1],nums[2],nums[0],nums[1],nums[2]]
+- ans = [1,2,1,1,2,1]```
+
+<p><strong class="example">Example 2:</strong></p>
+
+
Input: nums = [1,3,2,1] Output: [1,3,2,1,1,3,2,1] Explanation: The array ans is formed as follows:
ans = [nums[0],nums[1],nums[2],nums[3],nums[0],nums[1],nums[2],nums[3]]
ans = [1,3,2,1,1,3,2,1]
+<p> </p>
+<p><strong>Constraints:</strong></p>
+<ul>
+<li><code>n == nums.length</code></li>
+<li><code>1 <= n <= 1000</code></li>
+<li><code>1 <= nums[i] <= 1000</code></li>
+</ul>
+
+
+::: details _Click to open Hints_
+
+- Build an array of size 2 * n and assign num[i] to ans[i] and ans[i + n]
+
+:::
+
+## Solution:
+
+::: code-group
+
+```rs [Rust]
+impl Solution {
+ pub fn get_concatenation(nums: Vec<i32>) -> Vec<i32> {
+ let mut result = nums.clone();
+
+ result.extend(nums);
+
+ result
+ }
+}
+
+
A fancy string is a string where no threeconsecutive characters are equal.
Given a string s, delete the minimum possible number of characters from s to make it fancy.
Return the final string after the deletion. It can be shown that the answer will always be unique.
Example 1:
Input: s = "leeetcode"
+Output: "leetcode"
+Explanation:
+Remove an 'e' from the first group of 'e's to create "leetcode".
+No three consecutive characters are equal, so return "leetcode".
+
Example 2:
Input: s = "aaabaaaa"
+Output: "aabaa"
+Explanation:
+Remove an 'a' from the first group of 'a's to create "aabaaaa".
+Remove two 'a's from the second group of 'a's to create "aabaa".
+No three consecutive characters are equal, so return "aabaa".
+
Example 3:
Input: s = "aab"
+Output: "aab"
+Explanation: No three consecutive characters are equal, so return "aab".
+
Constraints:
1 <= s.length <= 105
s consists only of lowercase English letters.
Click to open Hints
What's the optimal way to delete characters if three or more consecutive characters are equal?
If three or more consecutive characters are equal, keep two of them and delete the rest.
+
+
+
+
+
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/solution/2101-2200/2011 - Final Value of Variable After Performing Operations.html b/solution/2101-2200/2011 - Final Value of Variable After Performing Operations.html
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..8dc2c30e
--- /dev/null
+++ b/solution/2101-2200/2011 - Final Value of Variable After Performing Operations.html
@@ -0,0 +1,69 @@
+
+
+
+
+
+ 2011. Final Value of Variable After Performing Operations | 🏆 Leetcode
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
There is a programming language with only four operations and one variable X:
++X and X++increments the value of the variable X by 1.
--X and X--decrements the value of the variable X by 1.
Initially, the value of X is 0.
Given an array of strings operations containing a list of operations, return the final value of Xafter performing all the operations.
Example 1:
Input: operations = ["--X","X++","X++"]
+Output: 1
+Explanation: The operations are performed as follows:
+Initially, X = 0.
+--X: X is decremented by 1, X = 0 - 1 = -1.
+X++: X is incremented by 1, X = -1 + 1 = 0.
+X++: X is incremented by 1, X = 0 + 1 = 1.
+
Example 2:
Input: operations = ["++X","++X","X++"]
+Output: 3
+Explanation: The operations are performed as follows:
+Initially, X = 0.
+++X: X is incremented by 1, X = 0 + 1 = 1.
+++X: X is incremented by 1, X = 1 + 1 = 2.
+X++: X is incremented by 1, X = 2 + 1 = 3.
+
Example 3:
Input: operations = ["X++","++X","--X","X--"]
+Output: 0
+Explanation: The operations are performed as follows:
+Initially, X = 0.
+X++: X is incremented by 1, X = 0 + 1 = 1.
+++X: X is incremented by 1, X = 1 + 1 = 2.
+--X: X is decremented by 1, X = 2 - 1 = 1.
+X--: X is decremented by 1, X = 1 - 1 = 0.
+
Constraints:
1 <= operations.length <= 100
operations[i] will be either "++X", "X++", "--X", or "X--".
Click to open Hints
There are only two operations to keep track of.
Use a variable to store the value after each operation.
+
+
+
+
+
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/solution/2101-2200/2114 - Maximum Number of Words Found in Sentences.html b/solution/2101-2200/2114 - Maximum Number of Words Found in Sentences.html
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..960df561
--- /dev/null
+++ b/solution/2101-2200/2114 - Maximum Number of Words Found in Sentences.html
@@ -0,0 +1,53 @@
+
+
+
+
+
+ 2114. Maximum Number of Words Found in Sentences | 🏆 Leetcode
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
A sentence is a list of words that are separated by a single space with no leading or trailing spaces.
You are given an array of strings sentences, where each sentences[i] represents a single sentence.
Return the maximum number of words that appear in a single sentence.
Example 1:
Input: sentences = ["alice and bob love leetcode", "i think so too", "this is great thanks very much"]
+Output: 6
+Explanation:
+- The first sentence, "alice and bob love leetcode", has 5 words in total.
+- The second sentence, "i think so too", has 4 words in total.
+- The third sentence, "this is great thanks very much", has 6 words in total.
+Thus, the maximum number of words in a single sentence comes from the third sentence, which has 6 words.
+
Example 2:
Input: sentences = ["please wait", "continue to fight", "continue to win"]
+Output: 3
+Explanation: It is possible that multiple sentences contain the same number of words.
+In this example, the second and third sentences (underlined) have the same number of words.
+
Constraints:
1 <= sentences.length <= 100
1 <= sentences[i].length <= 100
sentences[i] consists only of lowercase English letters and ' ' only.
sentences[i] does not have leading or trailing spaces.
All the words in sentences[i] are separated by a single space.
Click to open Hints
Process each sentence separately and count the number of words by looking for the number of space characters in the sentence and adding it by 1.
+
+
+
+
+
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/solution/2101-2200/2160 - Minimum Sum of Four Digit Number After Splitting Digits.html b/solution/2101-2200/2160 - Minimum Sum of Four Digit Number After Splitting Digits.html
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..07e6de74
--- /dev/null
+++ b/solution/2101-2200/2160 - Minimum Sum of Four Digit Number After Splitting Digits.html
@@ -0,0 +1,52 @@
+
+
+
+
+
+ 2160. Minimum Sum of Four Digit Number After Splitting Digits | 🏆 Leetcode
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
You are given a positive integer num consisting of exactly four digits. Split num into two new integers new1 and new2 by using the digits found in num. Leading zeros are allowed in new1 and new2, and all the digits found in num must be used.
For example, given num = 2932, you have the following digits: two 2's, one 9 and one 3. Some of the possible pairs [new1, new2] are [22, 93], [23, 92], [223, 9] and [2, 329].
Return the minimum possible sum of new1 and new2.
Example 1:
Input: num = 2932
+Output: 52
+Explanation: Some possible pairs [new1, new2] are [29, 23], [223, 9], etc.
+The minimum sum can be obtained by the pair [29, 23]: 29 + 23 = 52.
+
Example 2:
Input: num = 4009
+Output: 13
+Explanation: Some possible pairs [new1, new2] are [0, 49], [490, 0], etc.
+The minimum sum can be obtained by the pair [4, 9]: 4 + 9 = 13.
+
Constraints:
1000 <= num <= 9999
Click to open Hints
Notice that the most optimal way to obtain the minimum possible sum using 4 digits is by summing up two 2-digit numbers.
We can use the two smallest digits out of the four as the digits found in the tens place respectively.
Similarly, we use the final 2 larger digits as the digits found in the ones place.
+
+
+
+
+
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/solution/2101-2200/2176 - Count Equal and Divisible Pairs in an Array.html b/solution/2101-2200/2176 - Count Equal and Divisible Pairs in an Array.html
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..18a566cb
--- /dev/null
+++ b/solution/2101-2200/2176 - Count Equal and Divisible Pairs in an Array.html
@@ -0,0 +1,54 @@
+
+
+
+
+
+ 2176. Count Equal and Divisible Pairs in an Array | 🏆 Leetcode
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
Given a 0-indexed integer array nums of length n and an integer k, return the number of pairs(i, j)where0 <= i < j < n, such thatnums[i] == nums[j]and(i * j)is divisible byk.
Example 1:
Input: nums = [3,1,2,2,2,1,3], k = 2
+Output: 4
+Explanation:
+There are 4 pairs that meet all the requirements:
+- nums[0] == nums[6], and 0 * 6 == 0, which is divisible by 2.
+- nums[2] == nums[3], and 2 * 3 == 6, which is divisible by 2.
+- nums[2] == nums[4], and 2 * 4 == 8, which is divisible by 2.
+- nums[3] == nums[4], and 3 * 4 == 12, which is divisible by 2.
+
Example 2:
Input: nums = [1,2,3,4], k = 1
+Output: 0
+Explanation: Since no value in nums is repeated, there are no pairs (i,j) that meet all the requirements.
+
Constraints:
1 <= nums.length <= 100
1 <= nums[i], k <= 100
Click to open Hints
For every possible pair of indices (i, j) where i < j, check if it satisfies the given conditions.
implSolution{
+pubfncount_pairs(nums:Vec<i32>, k:i32)->i32{
+letmut ans =0;
+
+for i in0..nums.len(){
+for j in i +1..nums.len(){
+if nums[i]== nums[j]&&(i * j)% k asusize==0{
+ ans +=1;
+}
+}
+}
+
+ ans
+}
+}
+
+
You are given an array time where time[i] denotes the time taken by the ith bus to complete one trip.
Each bus can make multiple trips successively; that is, the next trip can start immediately after completing the current trip. Also, each bus operates independently; that is, the trips of one bus do not influence the trips of any other bus.
You are also given an integer totalTrips, which denotes the number of trips all buses should make in total. Return the minimum time required for all buses to complete at leasttotalTrips trips.
Example 1:
Input: time = [1,2,3], totalTrips = 5
+Output: 3
+Explanation:
+- At time t = 1, the number of trips completed by each bus are [1,0,0].
+ The total number of trips completed is 1 + 0 + 0 = 1.
+- At time t = 2, the number of trips completed by each bus are [2,1,0].
+ The total number of trips completed is 2 + 1 + 0 = 3.
+- At time t = 3, the number of trips completed by each bus are [3,1,1].
+ The total number of trips completed is 3 + 1 + 1 = 5.
+So the minimum time needed for all buses to complete at least 5 trips is 3.
+
Example 2:
Input: time = [2], totalTrips = 1
+Output: 2
+Explanation:
+There is only one bus, and it will complete its first trip at t = 2.
+So the minimum time needed to complete 1 trip is 2.
+
Constraints:
1 <= time.length <= 105
1 <= time[i], totalTrips <= 107
Click to open Hints
For a given amount of time, how can we count the total number of trips completed by all buses within that time?
Given an integer array nums, return the number of subarrays filled with 0.
A subarray is a contiguous non-empty sequence of elements within an array.
Example 1:
Input: nums = [1,3,0,0,2,0,0,4]
+Output: 6
+Explanation:
+There are 4 occurrences of [0] as a subarray.
+There are 2 occurrences of [0,0] as a subarray.
+There is no occurrence of a subarray with a size more than 2 filled with 0. Therefore, we return 6.```
+
+<p><strong class="example">Example 2:</strong></p>
+
+
Input: nums = [0,0,0,2,0,0] Output: 9 Explanation: There are 5 occurrences of [0] as a subarray. There are 3 occurrences of [0,0] as a subarray. There is 1 occurrence of [0,0,0] as a subarray. There is no occurrence of a subarray with a size more than 3 filled with 0. Therefore, we return 9.
Input: nums = [2,10,2019] Output: 0 Explanation: There is no subarray filled with 0. Therefore, we return 0.
+<p> </p>
+<p><strong>Constraints:</strong></p>
+<ul>
+<li><code>1 <= nums.length <= 10<sup>5</sup></code></li>
+<li><code>-10<sup>9</sup> <= nums[i] <= 10<sup>9</sup></code></li>
+</ul>
+
+
+::: details _Click to open Hints_
+
+- For each zero, you can calculate the number of zero-filled subarrays that end on that index, which is the number of consecutive zeros behind the current element + 1.
+- Maintain the number of consecutive zeros behind the current element, count the number of zero-filled subarrays that end on each index, sum it up to get the answer.
+
+:::
+
+## Solution:
+
+::: code-group
+
+```rs [Rust]
+impl Solution {
+ pub fn zero_filled_subarray(nums: Vec<i32>) -> i64 {
+ let mut nums = nums;
+ nums.push(1);
+
+ let (mut res, mut count) = (0, 0);
+ for num in nums {
+ if num == 0 {
+ count += 1;
+ } else {
+ res += count * (count + 1) / 2;
+ count = 0;
+ }
+ }
+
+ res
+ }
+}
+
+
An integer n is strictly palindromic if, for every base b between 2 and n - 2 (inclusive), the string representation of the integer n in base b is palindromic.
Given an integer n, return trueif n is strictly palindromic and false otherwise.
A string is palindromic if it reads the same forward and backward.
Example 1:
Input: n = 9
+Output: false
+Explanation: In base 2: 9 = 1001 (base 2), which is palindromic.
+In base 3: 9 = 100 (base 3), which is not palindromic.
+Therefore, 9 is not strictly palindromic so we return false.
+Note that in bases 4, 5, 6, and 7, n = 9 is also not palindromic.
+
Example 2:
Input: n = 4
+Output: false
+Explanation: We only consider base 2: 4 = 100 (base 2), which is not palindromic.
+Therefore, we return false.
+
+
Constraints:
4 <= n <= 105
Click to open Hints
Consider the representation of the given number in the base n - 2.
The number n in base (n - 2) is always 12, which is not palindromic.
+
+
+
+
+
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/solution/2401-2500/2427 - Number of Common Factors.html b/solution/2401-2500/2427 - Number of Common Factors.html
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..1bf49302
--- /dev/null
+++ b/solution/2401-2500/2427 - Number of Common Factors.html
@@ -0,0 +1,48 @@
+
+
+
+
+
+ 2427. Number of Common Factors | 🏆 Leetcode
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
You are given an integer array nums and two integers minK and maxK.
A fixed-bound subarray of nums is a subarray that satisfies the following conditions:
The minimum value in the subarray is equal to minK.
The maximum value in the subarray is equal to maxK.
Return the number of fixed-bound subarrays.
A subarray is a contiguous part of an array.
Example 1:
Input: nums = [1,3,5,2,7,5], minK = 1, maxK = 5
+Output: 2
+Explanation: The fixed-bound subarrays are [1,3,5] and [1,3,5,2].
+
Example 2:
Input: nums = [1,1,1,1], minK = 1, maxK = 1
+Output: 10
+Explanation: Every subarray of nums is a fixed-bound subarray. There are 10 possible subarrays.
+
Constraints:
2 <= nums.length <= 105
1 <= nums[i], minK, maxK <= 106
Click to open Hints
Can you solve the problem if all the numbers in the array were between minK and maxK inclusive?
Think of the inclusion-exclusion principle.
Divide the array into multiple subarrays such that each number in each subarray is between minK and maxK inclusive, solve the previous problem for each subarray, and sum all the answers.
implSolution{
+pubfncount_subarrays(nums:Vec<i32>, min_k:i32, max_k:i32)->i64{
+let(mut bad,mut min,mut max)=(-1,-1,-1);
+ // bad is the index of the first number that is not in the range [min_k, max_k]
+letmut res =0;
+
+for(i,&num)in nums.iter().enumerate(){
+let i = i asi64;
+
+ // set i to bad index if it is not in the range [min_k, max_k]
+if!(min_k <= num && num <= max_k){
+ bad = i;
+}
+
+ // set i to min index if num is equal to min_k
+if min_k == num {
+ min = i;
+}
+ // set i to max index if num is equal to max_k
+if max_k == num {
+ max = i;
+}
+
+ // it is the last starting point for the subarray
+let start = min.min(max);
+if start > bad {
+ res += start - bad; // add the number of subarrays b/w [bad + 1, start]
+}
+}
+
+ res
+}
+}
+
+
You are given a non-negative floating point number rounded to two decimal places celsius, that denotes the temperature in Celsius.
You should convert Celsius into Kelvin and Fahrenheit and return it as an array ans = [kelvin, fahrenheit].
Return the array ans. Answers within 10-5 of the actual answer will be accepted.
Note that:
Kelvin = Celsius + 273.15
Fahrenheit = Celsius * 1.80 + 32.00
Example 1:
Input: celsius = 36.50
+Output: [309.65000,97.70000]
+Explanation: Temperature at 36.50 Celsius converted in Kelvin is 309.65 and converted in Fahrenheit is 97.70.
+
Example 2:
Input: celsius = 122.11
+Output: [395.26000,251.79800]
+Explanation: Temperature at 122.11 Celsius converted in Kelvin is 395.26 and converted in Fahrenheit is 251.798.
+
Constraints:
0 <= celsius <= 1000
Click to open Hints
Implement formulas that are given in the statement.
+
+
+
+
+
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/solution/2401-2500/2574 - Left and Right Sum Differences.html b/solution/2401-2500/2574 - Left and Right Sum Differences.html
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..a274a1a7
--- /dev/null
+++ b/solution/2401-2500/2574 - Left and Right Sum Differences.html
@@ -0,0 +1,52 @@
+
+
+
+
+
+ 2574. Left and Right Sum Differences | 🏆 Leetcode
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
Given a 0-indexed integer array nums, find a 0-indexed integer array answer where:
answer.length == nums.length.
answer[i] = |leftSum[i] - rightSum[i]|.
Where:
leftSum[i] is the sum of elements to the left of the index i in the array nums. If there is no such element, leftSum[i] = 0.
rightSum[i] is the sum of elements to the right of the index i in the array nums. If there is no such element, rightSum[i] = 0.
Return the arrayanswer.
Example 1:
Input: nums = [10,4,8,3]
+Output: [15,1,11,22]
+Explanation: The array leftSum is [0,10,14,22] and the array rightSum is [15,11,3,0].
+The array answer is [|0 - 15|,|10 - 11|,|14 - 3|,|22 - 0|] = [15,1,11,22].
+
Example 2:
Input: nums = [1]
+Output: [0]
+Explanation: The array leftSum is [0] and the array rightSum is [0].
+The array answer is [|0 - 0|] = [0].
+
Constraints:
1 <= nums.length <= 1000
1 <= nums[i] <= 105
Click to open Hints
For each index i, maintain two variables leftSum and rightSum.
Iterate on the range j: [0 … i - 1] and add nums[j] to the leftSum and similarly iterate on the range j: [i + 1 … nums.length - 1] and add nums[j] to the rightSum.
You have k bags. You are given a 0-indexed integer array weights where weights[i] is the weight of the ith marble. You are also given the integer k.
Divide the marbles into the k bags according to the following rules:
No bag is empty.
If the ith marble and jth marble are in a bag, then all marbles with an index between the ith and jth indices should also be in that same bag.
If a bag consists of all the marbles with an index from i to j inclusively, then the cost of the bag is weights[i] + weights[j].
The score after distributing the marbles is the sum of the costs of all the k bags.
Return the difference between the maximum and minimum scores among marble distributions.
Example 1:
Input: weights = [1,3,5,1], k = 2
+Output: 4
+Explanation:
+The distribution [1],[3,5,1] results in the minimal score of (1+1) + (3+1) = 6.
+The distribution [1,3],[5,1], results in the maximal score of (1+3) + (5+1) = 10.
+Thus, we return their difference 10 - 6 = 4.
+
Example 2:
Input: weights = [1, 3], k = 2
+Output: 0
+Explanation: The only distribution possible is [1],[3].
+Since both the maximal and minimal score are the same, we return 0.
+
+
+
+
+
+
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/0001-0100/001 - Two Sum/README.md b/src/0001-0100/001 - Two Sum/README.md
deleted file mode 100644
index f8b51fdf..00000000
--- a/src/0001-0100/001 - Two Sum/README.md
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,88 +0,0 @@
-# 1. Two Sum [![][share]](https://leetcode.com/problems/two-sum)
-
-![][easy]
-
-## Problem Statement:
-
-Given an array of integers nums and an integer `target`, return indices of the two numbers such that they add up to `target`.
-
-You may assume that each input would have **exactly one solution**, and you may not use the same element twice.
-
-You can return the answer in any order.
-
-### Example 1:
-
-```
-Input: nums = [2,7,11,15], target = 9
-Output: [0,1]
-Explanation: Because nums[0] + nums[1] == 9, we return [0, 1].
-```
-
-### Example 2:
-
-```
-Input: nums = [3,2,4], target = 6
-Output: [1,2]
-```
-
-### Example 3:
-
-```
-Input: nums = [3,3], target = 6
-Output: [0,1]
-```
-
-### Constraints:
-
-- 2 <= nums.length <= 104
-- -109 <= nums[i] <= 109
-- -109 <= target <= 109
-- **Only one valid answer exists.**
-
-**Follow-up:** Can you come up with an algorithm that is less than O(n2) time complexity?
-
-## Solution:
-
-### [_Java_](./TwoSum.java)
-
-```java
-public static int[] twoSum(int nums[], int target) {
- int[] sum = new int[2];
- for (int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++)
- for (int j = i + 1; j < nums.length; j++) {
- if (i == j)
- continue;
- if (nums[i] + nums[j] == target) {
- sum[0] = i;
- sum[1] = j;
- }
- }
- return sum;
-}
-
-public static int[] twoSum2(int nums[], int target) {
- Map map = new HashMap<>();
- for (int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) {
- int complement = target - nums[i];
- if (map.containsKey(complement))
- return new int[] { map.get(complement), i };
- else {
- map.put(nums[i], i);
- }
- }
- throw new IllegalArgumentException();
-}
-```
-
-### [_..._]()
-
-```
-
-```
-
-
-
-[share]: https://img.icons8.com/external-anggara-blue-anggara-putra/20/000000/external-share-user-interface-basic-anggara-blue-anggara-putra-2.png
-[easy]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Easy-bright.svg
-[medium]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Medium-yellow.svg
-[hard]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Hard-red.svg
diff --git a/src/0001-0100/001 - Two Sum/TwoSum.java b/src/0001-0100/001 - Two Sum/TwoSum.java
deleted file mode 100644
index 09c34893..00000000
--- a/src/0001-0100/001 - Two Sum/TwoSum.java
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,31 +0,0 @@
-import java.util.HashMap;
-import java.util.Map;
-
-public class TwoSum {
- public static int[] twoSum(int nums[], int target) {
- int[] sum = new int[2];
- for (int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++)
- for (int j = i + 1; j < nums.length; j++) {
- if (i == j)
- continue;
- if (nums[i] + nums[j] == target) {
- sum[0] = i;
- sum[1] = j;
- }
- }
- return sum;
- }
-
- public static int[] twoSum2(int nums[], int target) {
- Map map = new HashMap<>();
- for (int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) {
- int complement = target - nums[i];
- if (map.containsKey(complement))
- return new int[] { map.get(complement), i };
- else {
- map.put(nums[i], i);
- }
- }
- throw new IllegalArgumentException();
- }
-}
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/0001-0100/002 - Add Two Numbers/AddTwoNumbers.java b/src/0001-0100/002 - Add Two Numbers/AddTwoNumbers.java
deleted file mode 100644
index 2aa14dd2..00000000
--- a/src/0001-0100/002 - Add Two Numbers/AddTwoNumbers.java
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,24 +0,0 @@
-import definitions.ListNode;
-
-public class AddTwoNumbers {
- public ListNode addTwoNumbers(ListNode a, ListNode b) {
- ListNode dummy = new ListNode(0),
- tail = dummy;
- int carry = 0;
- while (a != null || b != null) {
- int x = (a != null) ? a.val : 0,
- y = (b != null) ? b.val : 0,
- sum = carry + x + y;
- carry = sum / 10;
- tail.next = new ListNode(sum % 10);
- tail = tail.next;
- if (a != null)
- a = a.next;
- if (b != null)
- b = b.next;
- }
- if (carry > 0)
- tail.next = new ListNode(carry);
- return dummy.next;
- }
-}
diff --git a/src/0001-0100/002 - Add Two Numbers/README.md b/src/0001-0100/002 - Add Two Numbers/README.md
deleted file mode 100644
index abae7027..00000000
--- a/src/0001-0100/002 - Add Two Numbers/README.md
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,79 +0,0 @@
-# 2. Add Two Numbers [![][share]](https://leetcode.com/problems/add-two-numbers)
-
-![][medium]
-
-## Problem Statement:
-
-You are given two **non-empty** linked lists representing two non-negative integers. The digits are stored in **reverse order**, and each of their nodes contains a single digit. Add the two numbers and return the sum as a linked list.
-
-You may assume the two numbers do not contain any leading zero, except the number 0 itself.
-
-### Example 1:
-
-
-
-```
-Input: l1 = [2,4,3], l2 = [5,6,4]
-Output: [7,0,8]
-Explanation: 342 + 465 = 807.
-```
-
-### Example 2:
-
-```
-Input: l1 = [0], l2 = [0]
-Output: [0]
-```
-
-### Example 3:
-
-```
-Input: l1 = [9,9,9,9,9,9,9], l2 = [9,9,9,9]
-Output: [8,9,9,9,0,0,0,1]
-```
-
-### Constraints:
-
-- The number of nodes in each linked list is in the range `[1, 100]`.
-- `0 <= Node.val <= 9`
-- It is guaranteed that the list represents a number that does not have leading zeros.
-
-## Solution:
-
-### [_Java_](./AddTwoNumbers.java)
-
-```java
-public ListNode addTwoNumbers(ListNode a, ListNode b) {
- ListNode dummy = new ListNode(0),
- tail = dummy;
- int carry = 0;
- while (a != null || b != null) {
- int x = (a != null) ? a.val : 0,
- y = (b != null) ? b.val : 0,
- sum = carry + x + y;
- carry = sum / 10;
- tail.next = new ListNode(sum % 10);
- tail = tail.next;
- if (a != null)
- a = a.next;
- if (b != null)
- b = b.next;
- }
- if (carry > 0)
- tail.next = new ListNode(carry);
- return dummy.next;
-}
-```
-
-### [_..._]()
-
-```
-
-```
-
-
-
-[share]: https://img.icons8.com/external-anggara-blue-anggara-putra/20/000000/external-share-user-interface-basic-anggara-blue-anggara-putra-2.png
-[easy]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Easy-bright.svg
-[medium]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Medium-yellow.svg
-[hard]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Hard-red.svg
diff --git a/src/0001-0100/004 - Median of Two Sorted Arrays/MedianOfTwoSortedArrays.java b/src/0001-0100/004 - Median of Two Sorted Arrays/MedianOfTwoSortedArrays.java
deleted file mode 100644
index 869e713b..00000000
--- a/src/0001-0100/004 - Median of Two Sorted Arrays/MedianOfTwoSortedArrays.java
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,23 +0,0 @@
-public class MedianOfTwoSortedArrays {
- public static double findMedianSortedArrays(int[] nums1, int[] nums2) {
- int[] merged = new int[nums1.length + nums2.length];
- int startnums1 = 0, startnums2 = 0, i = 0;
- while (startnums1 < nums1.length && startnums2 < nums2.length) {
- if (nums1[startnums1] < nums2[startnums2])
- merged[i++] = nums1[startnums1++];
- else
- merged[i++] = nums2[startnums2++];
- }
- while (startnums1 < nums1.length)
- merged[i++] = nums1[startnums1++];
- while (startnums2 < nums2.length)
- merged[i++] = nums2[startnums2++];
- double median = 0;
- int mid = merged.length / 2;
- if (merged.length % 2 == 0)
- median = (double) (merged[mid] + merged[mid - 1]) / 2;
- else
- median = (double) merged[mid];
- return median;
- }
-}
diff --git a/src/0001-0100/004 - Median of Two Sorted Arrays/README.md b/src/0001-0100/004 - Median of Two Sorted Arrays/README.md
deleted file mode 100644
index fe35a13e..00000000
--- a/src/0001-0100/004 - Median of Two Sorted Arrays/README.md
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,75 +0,0 @@
-# 4. Median of Two Sorted Arrays [![share]](https://leetcode.com/problems/median-of-two-sorted-arrays)
-
-![][hard]
-
-## Problem Statement:
-
-Given two sorted arrays `nums1` and `nums2` of size `m` and `n` respectively, return **the median** of the two sorted arrays.
-
-The overall run time complexity should be `O(log (m+n))`.
-
-### Example 1:
-
-```
-Input: nums1 = [1,3], nums2 = [2]
-Output: 2.00000
-Explanation: merged array = [1,2,3] and median is 2.
-```
-
-### Example 2:
-
-```
-Input: nums1 = [1,2], nums2 = [3,4]
-Output: 2.50000
-Explanation: merged array = [1,2,3,4] and median is (2 + 3) / 2 = 2.5.
-```
-
-### Constraints:
-
-- nums1.length == m
-- nums2.length == n
-- 0 <= m <= 1000
-- 0 <= n <= 1000
-- 1 <= m + n <= 2000
-- -106 <= nums1[i], nums2[i] <= 106
-
-## Solutions
-
-### [_Java_](./MedianOfTwoSortedArrays.java)
-
-```java
-public class MedianOfTwoSortedArrays {
- public static double findMedianSortedArrays(int[] nums1, int[] nums2) {
- int[] merged = new int[nums1.length + nums2.length];
- int startnums1 = 0, startnums2 = 0, i = 0;
- while (startnums1 < nums1.length && startnums2 < nums2.length) {
- if (nums1[startnums1] < nums2[startnums2])
- merged[i++] = nums1[startnums1++];
- else
- merged[i++] = nums2[startnums2++];
- }
- while (startnums1 < nums1.length)
- merged[i++] = nums1[startnums1++];
- while (startnums2 < nums2.length)
- merged[i++] = nums2[startnums2++];
- double median = 0;
- int mid = merged.length / 2;
- if (merged.length % 2 == 0)
- median = (double) (merged[mid] + merged[mid - 1]) / 2;
- else
- median = (double) merged[mid];
- return median;
- }
-}
-```
-
-### [_..._]()
-
-```
-
-```
-
-
-
-[share]: https://img.icons8.com/external-anggara-blue-anggara-putra/20/000000/external-share-user-interface-basic-anggara-blue-anggara-putra-2.png
-[hard]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Hard-red.svg
diff --git a/src/0001-0100/007 - Reverse Integer/README.md b/src/0001-0100/007 - Reverse Integer/README.md
deleted file mode 100644
index db2b497d..00000000
--- a/src/0001-0100/007 - Reverse Integer/README.md
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,62 +0,0 @@
-# 7. Reverse Integer [![share]](https://leetcode.com/problems/reverse-integer)
-
-![][medium]
-
-## Problem Statement:
-
-Given a signed 32-bit integer `x`, return x with its digits reversed. If reversing `x` causes the value to go outside the signed 32-bit integer range [-231, 231 - 1], then return `0`.
-
-Assume the environment does not allow you to store 64-bit integers (signed or unsigned).
-
-### Example 1:
-
-```
-Input: x = 123
-Output: 321
-```
-
-### Example 2:
-
-```
-Input: x = -123
-Output: -321
-```
-
-### Example 3:
-
-```
-Input: x = 120
-Output: 21
-```
-
-### Constraints:
-
-- -231 <= x <= 231 -
-
-## Solution:
-
-### [_Java_](./ReverseInteger.java)
-
-```java
-public static int reverse(int x) {
- String reversed = new StringBuilder().append(Math.abs(x)).reverse().toString();
- try {
- return x < 0 ? Integer.parseInt(reversed) * -1 : Integer.parseInt(reversed);
- } catch (Exception e) {
- return 0;
- }
-}
-```
-
-### [_..._]()
-
-```
-
-```
-
-
-
-[share]: https://img.icons8.com/external-anggara-blue-anggara-putra/20/000000/external-share-user-interface-basic-anggara-blue-anggara-putra-2.png
-[easy]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Easy-bright.svg
-[medium]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Medium-yellow.svg
-[hard]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Hard-red.svg
diff --git a/src/0001-0100/007 - Reverse Integer/ReverseInteger.java b/src/0001-0100/007 - Reverse Integer/ReverseInteger.java
deleted file mode 100644
index fa96f3ad..00000000
--- a/src/0001-0100/007 - Reverse Integer/ReverseInteger.java
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,10 +0,0 @@
-public class ReverseInteger {
- public static int reverse(int x) {
- String reversed = new StringBuilder().append(Math.abs(x)).reverse().toString();
- try {
- return x < 0 ? Integer.parseInt(reversed) * -1 : Integer.parseInt(reversed);
- } catch (Exception e) {
- return 0;
- }
- }
-}
diff --git a/src/0001-0100/009 - Palindrome Number/PalindromeNumber.java b/src/0001-0100/009 - Palindrome Number/PalindromeNumber.java
deleted file mode 100644
index 8beb2983..00000000
--- a/src/0001-0100/009 - Palindrome Number/PalindromeNumber.java
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,12 +0,0 @@
-public class PalindromeNumber {
- public boolean isPalindrome(int x) {
- if (x < 0 || x % 10 == 0 && x != 0)
- return false;
- int reverseNum = 0;
- while (x > reverseNum) {
- reverseNum = reverseNum * 10 + x % 10;
- x /= 10;
- }
- return x == reverseNum || x == reverseNum / 10;
- }
-}
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/0001-0100/009 - Palindrome Number/README.md b/src/0001-0100/009 - Palindrome Number/README.md
deleted file mode 100644
index d5dafa80..00000000
--- a/src/0001-0100/009 - Palindrome Number/README.md
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,71 +0,0 @@
-# 9. Palindrome Number [![share]](https://leetcode.com/problems/palindrome-number)
-
-![][easy]
-
-## Problem Statement:
-
-Given an integer `x`, return `true` if `x` is palindrome integer.
-
-An integer is a **palindrome** when it reads the same backward as forward.
-
-- For example, `121` is a palindrome while `123` is not.
-
-### Example 1:
-
-```
-Input: x = 121
-Output: true
-Explanation: 121 reads as 121 from left to right and from right to left.
-```
-
-### Example 2:
-
-```
-Input: x = -121
-Output: false
-Explanation: From left to right, it reads -121. From right to left, it becomes 121-. Therefore it is not a palindrome.
-```
-
-### Example 3:
-
-```
-Input: x = 10
-Output: false
-Explanation: Reads 01 from right to left. Therefore it is not a palindrome.
-```
-
-### Constraints:
-
-- -231 <= x <= 231 - 1
-
-**Follow up**: Could you solve it without converting the integer to a string?
-
-## Solutions
-
-### [_Java_](./PalindromeNumber.java)
-
-```java
-public static boolean isPalindrome(int x) {
- if (x < 0 || x % 10 == 0 && x != 0)
- return false;
- int reverseNum = 0;
- while (x > reverseNum) {
- reverseNum = reverseNum * 10 + x % 10;
- x /= 10;
- }
- return x == reverseNum || x == reverseNum / 10;
-}
-```
-
-### [_..._]()
-
-```
-
-```
-
-
-
-[share]: https://img.icons8.com/external-anggara-blue-anggara-putra/20/000000/external-share-user-interface-basic-anggara-blue-anggara-putra-2.png
-[easy]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Easy-bright.svg
-[medium]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Medium-yellow.svg
-[hard]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Hard-red.svg
diff --git a/src/0001-0100/012 - Integer to Roman/integer_to_roman.go b/src/0001-0100/012 - Integer to Roman/integer_to_roman.go
deleted file mode 100644
index fefa94bc..00000000
--- a/src/0001-0100/012 - Integer to Roman/integer_to_roman.go
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,15 +0,0 @@
-package main
-
-func intToRoman(num int) string {
- ones := []string{"", "I", "II", "III", "IV", "V", "VI", "VII", "VIII", "IX"}
- tens := []string{"", "X", "XX", "XXX", "XL", "L", "LX", "LXX", "LXXX", "XC"}
- hundreds := []string{"", "C", "CC", "CCC", "CD", "D", "DC", "DCC", "DCCC", "CM"}
- thousands := []string{"", "M", "MM", "MMM"}
-
- thousand := num / 1000
- hundred := (num / 100) % 10
- ten := (num / 10) % 10
- one := num % 10
-
- return thousands[thousand] + hundreds[hundred] + tens[ten] + ones[one]
-}
diff --git a/src/0001-0100/012 - Integer to Roman/integer_to_roman.rs b/src/0001-0100/012 - Integer to Roman/integer_to_roman.rs
deleted file mode 100644
index 0ac099a0..00000000
--- a/src/0001-0100/012 - Integer to Roman/integer_to_roman.rs
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,18 +0,0 @@
-const ONES: [&str; 10] = ["", "I", "II", "III", "IV", "V", "VI", "VII", "VIII", "IX"];
-const TENS: [&str; 10] = ["", "X", "XX", "XXX", "XL", "L", "LX", "LXX", "LXXX", "XC"];
-const HUNDS: [&str; 10] = ["", "C", "CC", "CCC", "CD", "D", "DC", "DCC", "DCCC", "CM"];
-const THOUSANDS: [&str; 4] = ["", "M", "MM", "MMM"];
-
-impl Solution {
- pub fn int_to_roman(num: i32) -> String {
- let num = num as usize;
-
- format!(
- "{}{}{}{}",
- THOUSANDS[(num / 1000)],
- HUNDS[(num / 100 % 10)],
- TENS[(num / 10 % 10)],
- ONES[(num % 10)]
- )
- }
-}
diff --git a/src/0001-0100/013 - Roman to Integer/README.md b/src/0001-0100/013 - Roman to Integer/README.md
deleted file mode 100644
index 7e323959..00000000
--- a/src/0001-0100/013 - Roman to Integer/README.md
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,97 +0,0 @@
-# 13. Roman to Integer [![share]](https://leetcode.com/problems/roman-to-integer/)
-
-![][easy]
-
-## Problem Statement:
-
-Roman numerals are represented by seven different symbols: `I`, `V`, `X`, `L`, `C`, `D` and `M`.
-
-```
-Symbol Value
-I 1
-V 5
-X 10
-L 50
-C 100
-D 500
-M 1000
-```
-
-For example, `2` is written as `II` in Roman numeral, just two ones added together. `12` is written as `XII`, which is simply `X + II`. The number `27` is written as `XXVII`, which is `XX + V + II`.
-
-Roman numerals are usually written largest to smallest from left to right. However, the numeral for four is not `IIII`. Instead, the number four is written as `IV`. Because the one is before the five we subtract it making four. The same principle applies to the number nine, which is written as `IX`. There are six instances where subtraction is used:
-
-- I can be placed before `V` (5) and `X` (10) to make 4 and 9.
-- X can be placed before `L` (50) and `C` (100) to make 40 and 90.
-- C can be placed before `D` (500) and `M` (1000) to make 400 and 900.
- Given a roman numeral, convert it to an integer.
-
-### Example 1:
-
-```
-Input: s = "III"
-Output: 3
-Explanation: III = 3.
-```
-
-### Example 2:
-
-```
-Input: s = "LVIII"
-Output: 58
-Explanation: L = 50, V= 5, III = 3.
-```
-
-### Example 3:
-
-```
-Input: s = "MCMXCIV"
-Output: 1994
-Explanation: M = 1000, CM = 900, XC = 90 and IV = 4.
-```
-
-### Constraints:
-
-```
-- 1 <= s.length <= 15
-- s contains only the characters `('I', 'V', 'X', 'L', 'C', 'D', 'M')`.
-- It is guaranteed that s is a valid roman numeral in the range [`1, 3999]`.
-```
-
-## Solutions:
-
-### [_Java_](./RomanToInteger.java)
-
-```java
-public int romanToInt(String s) {
- Map map = Map.of(
- 'I', 1,
- 'V', 5,
- 'X', 10,
- 'L', 50,
- 'C', 100,
- 'D', 500,
- 'M', 1000);
- int res = map.get(s.charAt(s.length() - 1));
- for (int i = s.length() - 2; i >= 0; i--) {
- if (map.get(s.charAt(i)) < map.get(s.charAt(i + 1)))
- res -= map.get(s.charAt(i));
- else
- res += map.get(s.charAt(i));
- }
- return res;
-}
-```
-
-### [_..._]()
-
-```
-
-```
-
-
-
-[share]: https://img.icons8.com/external-anggara-blue-anggara-putra/20/000000/external-share-user-interface-basic-anggara-blue-anggara-putra-2.png
-[easy]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Easy-bright.svg
-[medium]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Medium-yellow.svg
-[hard]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Hard-red.svg
diff --git a/src/0001-0100/013 - Roman to Integer/RomanToInteger.java b/src/0001-0100/013 - Roman to Integer/RomanToInteger.java
deleted file mode 100644
index b21bdb14..00000000
--- a/src/0001-0100/013 - Roman to Integer/RomanToInteger.java
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,22 +0,0 @@
-import java.util.Map;
-
-public class RomanToInteger {
- public int romanToInt(String s) {
- Map map = Map.of(
- 'I', 1,
- 'V', 5,
- 'X', 10,
- 'L', 50,
- 'C', 100,
- 'D', 500,
- 'M', 1000);
- int res = map.get(s.charAt(s.length() - 1));
- for (int i = s.length() - 2; i >= 0; i--) {
- if (map.get(s.charAt(i)) < map.get(s.charAt(i + 1)))
- res -= map.get(s.charAt(i));
- else
- res += map.get(s.charAt(i));
- }
- return res;
- }
-}
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/0001-0100/014 - Longest Common Prefix/LongestCommonPrefix.java b/src/0001-0100/014 - Longest Common Prefix/LongestCommonPrefix.java
deleted file mode 100644
index c847a8d4..00000000
--- a/src/0001-0100/014 - Longest Common Prefix/LongestCommonPrefix.java
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,12 +0,0 @@
-class Solution {
-
- public String longestCommonPrefix(String[] strs) {
- String res = strs[0];
-
- for (int i = 1; i < strs.length; i++)
- while (!strs[i].startsWith(res))
- res = res.substring(0, res.length() - 1);
-
- return res;
- }
-}
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/0001-0100/014 - Longest Common Prefix/README.md b/src/0001-0100/014 - Longest Common Prefix/README.md
deleted file mode 100644
index aafc20af..00000000
--- a/src/0001-0100/014 - Longest Common Prefix/README.md
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,66 +0,0 @@
-# 14. Longest Common Prefix [![share]](https://leetcode.com/problems/longest-common-prefix/)
-
-![][easy]
-
-## Problem Statement
-
-
Write a function to find the longest common prefix string amongst an array of strings.
-
-
If there is no common prefix, return an empty string "".
Given n pairs of parentheses, write a function to generate all combinations of well-formed parentheses.
-
-
-
Example 1:
-
Input: n = 3
-Output: ["((()))","(()())","(())()","()(())","()()()"]
-
Example 2:
-
Input: n = 1
-Output: ["()"]
-
-
-
Constraints:
-
-
-
1 <= n <= 8
-
-
-## Solutions
-
-### [_Java_](GenerateParentheses.java)
-
-```java
-import java.util.ArrayList;
-import java.util.List;
-
-class Solution {
- public List generateParenthesis(int n) {
- List ans = new ArrayList<>();
- backtrack(ans, "", 0, 0, n);
- return ans;
- }
-
- private void backtrack(List ans, String str, int open, int close, int n) {
- if (str.length() == n * 2) {
- ans.add(str);
- return;
- }
-
- if (open < n)
- backtrack(ans, str + "(", open + 1, close, n);
-
- if (close < open)
- backtrack(ans, str + ")", open, close + 1, n);
- }
-}
-```
-
-### [_..._]()
-
-```
-
-```
-
-
-
-[share]: https://graph.org/file/3ea5234dda646b71c574a.png
-[easy]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Easy-bright.svg
-[medium]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Medium-yellow.svg
-[hard]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Hard-red.svg
diff --git a/src/0001-0100/024 - Swap Nodes in Pairs/README.md b/src/0001-0100/024 - Swap Nodes in Pairs/README.md
deleted file mode 100644
index 69708b69..00000000
--- a/src/0001-0100/024 - Swap Nodes in Pairs/README.md
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,79 +0,0 @@
-# 24. Swap Nodes in Pairs [![share]](https://leetcode.com/problems/swap-nodes-in-pairs)
-
-![][medium]
-
-## Problem Statement:
-
-Given a linked list, swap every two adjacent nodes and return its head. You must solve the problem without modifying the values in the list's nodes (i.e., only nodes themselves may be changed.)
-
-
-
-### Example 1:
-
-```
-Input: head = [1,2,3,4]
-Output: [2,1,4,3]
-```
-
-### Example 2:
-
-```
-Input: head = []
-Output: []
-```
-
-### Example 3:
-
-```
-Input: head = [1]
-Output: [1]
-```
-
-### Constraints:
-
-- The number of nodes in the list is in the range `[0, 100]`.
-- 0 <= Node.val <= 100
-
-## Solutions:
-
-### [_Java_](./SwapNodesInPairs.java)
-
-```java
-public ListNode swapPairs(ListNode head) {
- ListNode p1 = null,
- p2 = null,
- p3 = null;
- if (head == null || head.next == null)
- return head;
- p1 = head;
- p2 = head.next;
- p3 = p2.next;
- p1.next = p3;
- p2.next = p1;
- if (p3 != null)
- p1.next = swapPairs(p3);
- return p2;
-}
-
-public ListNode swapPairs1(ListNode head) {
- ListNode newNode = head;
- while (newNode != null && newNode.next != null) {
- int temp = newNode.val;
- newNode.val = newNode.next.val;
- newNode.next.val = temp;
- newNode = newNode.next.next;
- }
- return head;
-}
-```
-
-### [_..._]()
-
-```
-
-```
-
-
-
-[share]: https://img.icons8.com/external-anggara-blue-anggara-putra/20/000000/external-share-user-interface-basic-anggara-blue-anggara-putra-2.png
-[medium]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Medium-yellow.svg
diff --git a/src/0001-0100/024 - Swap Nodes in Pairs/SwapNodesInPairs.java b/src/0001-0100/024 - Swap Nodes in Pairs/SwapNodesInPairs.java
deleted file mode 100644
index 06290205..00000000
--- a/src/0001-0100/024 - Swap Nodes in Pairs/SwapNodesInPairs.java
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,30 +0,0 @@
-import definitions.ListNode;
-
-public class SwapNodesInPairs {
- public ListNode swapPairs(ListNode head) {
- ListNode p1 = null,
- p2 = null,
- p3 = null;
- if (head == null || head.next == null)
- return head;
- p1 = head;
- p2 = head.next;
- p3 = p2.next;
- p1.next = p3;
- p2.next = p1;
- if (p3 != null)
- p1.next = swapPairs(p3);
- return p2;
- }
-
- public ListNode swapPairs1(ListNode head) {
- ListNode newNode = head;
- while (newNode != null && newNode.next != null) {
- int temp = newNode.val;
- newNode.val = newNode.next.val;
- newNode.next.val = temp;
- newNode = newNode.next.next;
- }
- return head;
- }
-}
diff --git a/src/0001-0100/026 - Remove Duplicates from Sorted Array/README.md b/src/0001-0100/026 - Remove Duplicates from Sorted Array/README.md
deleted file mode 100644
index ed592685..00000000
--- a/src/0001-0100/026 - Remove Duplicates from Sorted Array/README.md
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,101 +0,0 @@
-# 26. Remove Duplicates from Sorted Array [![share]](https://leetcode.com/problems/remove-duplicates-from-sorted-array/)
-
-![][easy]
-
-## Problem Statement:
-
-Given an integer array `nums` sorted in **non-decreasing order**, remove the duplicates in-place such that each unique element appears only once. The **relative order** of the elements should be kept the **same**.
-
-Since it is impossible to change the length of the array in some languages, you must instead have the result be placed in the **first part** of the array `nums`. More formally, if there are `k` elements after removing the duplicates, then the first `k` elements of `nums` should hold the final result. It does not matter what you leave beyond the first `k` elements.
-
-Return `k` after placing the final result in the first `k` slots of `nums`.
-
-Do **not** allocate extra space for another array. You must do this by **modifying the input array** in-place with O(1) extra memory.
-
-### Custom Judge:
-
-```
-The judge will test your solution with the following code:
-
-int[] nums = [...]; // Input array
-int[] expectedNums = [...]; // The expected answer with correct length
-
-int k = removeDuplicates(nums); // Calls your implementation
-
-assert k == expectedNums.length;
-for (int i = 0; i < k; i++) {
- assert nums[i] == expectedNums[i];
-}
-```
-
-If all assertions pass, then your solution will be **accepted**.
-
-### Example 1:
-
-```
-Input: nums = [1,1,2]
-Output: 2, nums = [1,2,_]
-Explanation: Your function should return k = 2, with the first two elements of nums being 1 and 2 respectively.
-It does not matter what you leave beyond the returned k (hence they are underscores).
-```
-
-### Example 2:
-
-```
-Input: nums = [0,0,1,1,1,2,2,3,3,4]
-Output: 5, nums = [0,1,2,3,4,_,_,_,_,_]
-Explanation: Your function should return k = 5, with the first five elements of nums being 0, 1, 2, 3, and 4 respectively.
-It does not matter what you leave beyond the returned k (hence they are underscores).
-```
-
-### Constraints:
-
-- 1 <= nums.length <= 3 \* 104
-- -100 <= nums[i] <= 100
-- nums is sorted in non-decreasing order.
-
-## Solutions:
-
-### [_Python_](RemoveDuplicatesFromSortedArray.py)
-
-```py [Python]
-def removeDuplicates(nums: list[int]) -> int:
- k = 0
- for i, item in enumerate(nums):
- if i < len(nums) - 1 and item == nums[i + 1]:
- continue
- nums[k] = item
- k += 1
- return k
-
-```
-
-### [_Go_](remove_duplicates_from_sorted_array.go)
-
-```go [Go]
-package main
-
-func removeDuplicates(nums []int) int {
- k := 0
- for i := 1; i < len(nums); i++ {
- if nums[i] != nums[k] {
- k++
- nums[k] = nums[i]
- }
- }
-
- return k + 1
-}
-
-```
-
-### [_..._]()
-
-```
-
-```
-
-
-
-[share]: https://img.icons8.com/external-anggara-blue-anggara-putra/20/000000/external-share-user-interface-basic-anggara-blue-anggara-putra-2.png
-[easy]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Easy-green.svg
diff --git a/src/0001-0100/026 - Remove Duplicates from Sorted Array/RemoveDuplicatesFromSortedArray.py b/src/0001-0100/026 - Remove Duplicates from Sorted Array/RemoveDuplicatesFromSortedArray.py
deleted file mode 100644
index d1987bef..00000000
--- a/src/0001-0100/026 - Remove Duplicates from Sorted Array/RemoveDuplicatesFromSortedArray.py
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,8 +0,0 @@
-def removeDuplicates(nums: list[int]) -> int:
- k = 0
- for i, item in enumerate(nums):
- if i < len(nums) - 1 and item == nums[i + 1]:
- continue
- nums[k] = item
- k += 1
- return k
diff --git a/src/0001-0100/026 - Remove Duplicates from Sorted Array/remove_duplicates_from_sorted_array.go b/src/0001-0100/026 - Remove Duplicates from Sorted Array/remove_duplicates_from_sorted_array.go
deleted file mode 100644
index 0851ae64..00000000
--- a/src/0001-0100/026 - Remove Duplicates from Sorted Array/remove_duplicates_from_sorted_array.go
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,13 +0,0 @@
-package main
-
-func removeDuplicates(nums []int) int {
- k := 0
- for i := 1; i < len(nums); i++ {
- if nums[i] != nums[k] {
- k++
- nums[k] = nums[i]
- }
- }
-
- return k + 1
-}
diff --git a/src/0001-0100/027 - Remove Element/README.md b/src/0001-0100/027 - Remove Element/README.md
deleted file mode 100644
index 8ae3fb7c..00000000
--- a/src/0001-0100/027 - Remove Element/README.md
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,87 +0,0 @@
-# 27. Remove Element [![share]](https://leetcode.com/problems/remove-element)
-
-![][easy]
-
-## Problem Statement:
-
-Given an integer array `nums` and an integer `val`, remove all occurrences of `val` in `nums` in-place. The relative order of the elements may be changed.
-
-Since it is impossible to change the length of the array in some languages, you must instead have the result be placed in the **first part** of the array `nums`. More formally, if there are k elements after removing the duplicates, then the first `k` elements of `nums` should hold the final result. It does not matter what you leave beyond the first `k` elements.
-
-Return `k` after placing the final result in the first `k` slots of `nums`.
-
-Do **not** allocate extra space for another array. You must do this by **modifying the input arra**y in-place with O(1) extra memory.
-
-### Custom Judge:
-
-```
-The judge will test your solution with the following code:
-
-int[] nums = [...]; // Input array
-int val = ...; // Value to remove
-int[] expectedNums = [...]; // The expected answer with correct length.
-// It is sorted with no values equaling val.
-
-int k = removeElement(nums, val); // Calls your implementation
-
-assert k == expectedNums.length;
-sort(nums, 0, k); // Sort the first k elements of nums
-for (int i = 0; i < actualLength; i++) {
-assert nums[i] == expectedNums[i];
-}
-```
-
-If all assertions pass, then your solution will be **accepted**.
-
-### Example 1:
-
-```
-Input: nums = [3,2,2,3], val = 3
-Output: 2, nums = [2,2,_,_]
-Explanation: Your function should return k = 2, with the first two elements of nums being 2.
-It does not matter what you leave beyond the returned k (hence they are underscores).
-```
-
-### Example 2:
-
-```
-Input: nums = [0,1,2,2,3,0,4,2], val = 2
-Output: 5, nums = [0,1,4,0,3,_,_,_]
-Explanation: Your function should return k = 5, with the first five elements of nums containing 0, 0, 1, 3, and 4.
-Note that the five elements can be returned in any order.
-It does not matter what you leave beyond the returned k (hence they are underscores).
-```
-
-### Constraints:
-
-- 0 <= nums.length <= 100
-- 0 <= nums[i] <= 50
-- 0 <= val <= 100
-
-## Solutions:
-
-### [_Java_](./RemoveElement.java)
-
-```java
-public int removeElement(int[] nums, int val) {
- int count = 0;
- for (int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++)
- if (nums[i] != val) {
- nums[count] = nums[i];
- }
- return count;
-}
-```
-
-### [_..._]()
-
-```
-
-```
-
-
-
-[share]: https://img.icons8.com/external-anggara-blue-anggara-putra/20/000000/external-share-user-interface-basic-anggara-blue-anggara-putra-2.png
-[easy]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Easy-bright.svg
-[medium]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Medium-yellow.svg
-[hard]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Hard-red.svg
diff --git a/src/0001-0100/027 - Remove Element/RemoveElement.java b/src/0001-0100/027 - Remove Element/RemoveElement.java
deleted file mode 100644
index 5b519caf..00000000
--- a/src/0001-0100/027 - Remove Element/RemoveElement.java
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,10 +0,0 @@
-public class RemoveElement {
- public int removeElement(int[] nums, int val) {
- int count = 0;
- for (int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++)
- if (nums[i] != val) {
- nums[count] = nums[i];
- }
- return count;
- }
-}
diff --git a/src/0001-0100/028 - Find the Index of the First Occurrence in a String/README.md b/src/0001-0100/028 - Find the Index of the First Occurrence in a String/README.md
deleted file mode 100644
index eb677f61..00000000
--- a/src/0001-0100/028 - Find the Index of the First Occurrence in a String/README.md
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,71 +0,0 @@
-# 28. Find the Index of the First Occurrence in a String [![share]](https://leetcode.com/problems/find-the-index-of-the-first-occurrence-in-a-string/)
-
-![][medium]
-
-## Problem Statement
-
-
Given two strings needle and haystack, return the index of the first occurrence of needle in haystack, or -1 if needle is not part of haystack.
-
-
Example 1:
-
-```
-Input: haystack = "sadbutsad", needle = "sad"
-Output: 0
-Explanation: "sad" occurs at index 0 and 6.
-The first occurrence is at index 0, so we return 0.
-```
-
-
Example 2:
-
-```
-Input: haystack = "leetcode", needle = "leeto"
-Output: -1
-Explanation: "leeto" did not occur in "leetcode", so we return -1.
-```
-
-
-
Constraints:
-
-
1 <= haystack.length, needle.length <= 104
-
haystack and needle consist of only lowercase English characters.
-
-
-## Solutions
-
-### [_Rust_](find_the_index_of_the_first_ccurrence_in_a_string.rs)
-
-```rs [Rust]
-impl Solution {
- pub fn str_str(haystack: String, needle: String) -> i32 {
- let (m, n) = (haystack.len(), needle.len());
-
- if m < n {
- return -1;
- }
-
- // iterate over the haystack from 0 to m - n
- // because the needle can't be longer than the haystack
- for i in 0..=m - n {
- if haystack[i..i + n] == needle {
- return i as i32;
- }
- }
-
- -1
- }
-}
-
-```
-
-### [_..._]()
-
-```
-
-```
-
-
-
-[share]: https://graph.org/file/3ea5234dda646b71c574a.png
-[easy]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Easy-bright.svg
-[medium]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Medium-yellow.svg
-[hard]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Hard-red.svg
diff --git a/src/0001-0100/028 - Find the Index of the First Occurrence in a String/find_the_index_of_the_first_ccurrence_in_a_string.rs b/src/0001-0100/028 - Find the Index of the First Occurrence in a String/find_the_index_of_the_first_ccurrence_in_a_string.rs
deleted file mode 100644
index 084f60ba..00000000
--- a/src/0001-0100/028 - Find the Index of the First Occurrence in a String/find_the_index_of_the_first_ccurrence_in_a_string.rs
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,19 +0,0 @@
-impl Solution {
- pub fn str_str(haystack: String, needle: String) -> i32 {
- let (m, n) = (haystack.len(), needle.len());
-
- if m < n {
- return -1;
- }
-
- // iterate over the haystack from 0 to m - n
- // because the needle can't be longer than the haystack
- for i in 0..=m - n {
- if haystack[i..i + n] == needle {
- return i as i32;
- }
- }
-
- -1
- }
-}
diff --git a/src/0001-0100/035 - Search Insert Position/README.md b/src/0001-0100/035 - Search Insert Position/README.md
deleted file mode 100644
index 15ab61da..00000000
--- a/src/0001-0100/035 - Search Insert Position/README.md
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,97 +0,0 @@
-# 35. Search Insert Position [![share]](https://leetcode.com/problems/search-insert-position/)
-
-![][easy]
-
-## Problem Statement
-
-
Given a sorted array of distinct integers and a target value, return the index if the target is found. If not, return the index where it would be if it were inserted in order.
-
You must write an algorithm with O(log n) runtime complexity.
nums contains distinct values sorted in ascending order.
-
-104 <= target <= 104
-
-
-## Solutions
-
-### [_Python_](solution.py)
-
-```py [Python]
-class Solution:
- def searchInsert(self, nums: list[int], target: int) -> int:
- if target in nums:
- return nums.index(target)
- else:
- nums.append(target)
- nums.sort()
- return nums.index(target)
-
- # Using binary search
- # start = 0
- # end = len(nums) - 1
- # while start <= end:
- # mid = (start + end) // 2
- # if nums[mid] == target:
- # return mid
- # elif nums[mid] < target:
- # start = mid + 1
- # else:
- # end = mid - 1
- # return start
-
-```
-
-### [_Rust_](search_insert_position.rs)
-
-```rs [Rust]
-impl Solution {
- pub fn search_insert(nums: Vec, target: i32) -> i32 {
- for (idx, val) in nums.iter().enumerate() {
- if target <= *val {
- return idx as i32;
- }
- }
-
- nums.len() as i32
- }
-}
-
-```
-
-### [_..._]()
-
-```
-
-```
-
-
-
-[share]: https://graph.org/file/3ea5234dda646b71c574a.png
-[easy]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Easy-bright.svg
-[medium]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Medium-yellow.svg
-[hard]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Hard-red.svg
diff --git a/src/0001-0100/035 - Search Insert Position/search_insert_position.rs b/src/0001-0100/035 - Search Insert Position/search_insert_position.rs
deleted file mode 100644
index 0ae317bd..00000000
--- a/src/0001-0100/035 - Search Insert Position/search_insert_position.rs
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,11 +0,0 @@
-impl Solution {
- pub fn search_insert(nums: Vec, target: i32) -> i32 {
- for (idx, val) in nums.iter().enumerate() {
- if target <= *val {
- return idx as i32;
- }
- }
-
- nums.len() as i32
- }
-}
diff --git a/src/0001-0100/035 - Search Insert Position/solution.py b/src/0001-0100/035 - Search Insert Position/solution.py
deleted file mode 100644
index 71083d8f..00000000
--- a/src/0001-0100/035 - Search Insert Position/solution.py
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,21 +0,0 @@
-class Solution:
- def searchInsert(self, nums: list[int], target: int) -> int:
- if target in nums:
- return nums.index(target)
- else:
- nums.append(target)
- nums.sort()
- return nums.index(target)
-
- # Using binary search
- # start = 0
- # end = len(nums) - 1
- # while start <= end:
- # mid = (start + end) // 2
- # if nums[mid] == target:
- # return mid
- # elif nums[mid] < target:
- # start = mid + 1
- # else:
- # end = mid - 1
- # return start
diff --git a/src/0001-0100/037 - Sudoku Solver/README.md b/src/0001-0100/037 - Sudoku Solver/README.md
deleted file mode 100644
index 49ad5106..00000000
--- a/src/0001-0100/037 - Sudoku Solver/README.md
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,156 +0,0 @@
-# 37. Sudoku Solver [![share]](https://leetcode.com/problems/sudoku-solver/)
-
-![][hard]
-
-## Problem Statement:
-
-Write a program to solve a Sudoku puzzle by filling the empty cells.
-
-A sudoku solution must satisfy **all of the following rules:**
-
-- Each of the digits `1-9` must occur exactly once in each row.
-- Each of the digits `1-9` must occur exactly once in each column.
-- Each of the digits `1-9` must occur exactly once in each of the 9 `3x3` sub-boxes of the grid.
-- The '.' character indicates empty cells.
-
-### Example 1:
-
-
-
-```
-Input: board =
-[["5","3",".",".","7",".",".",".","."],
-["6",".",".","1","9","5",".",".","."],
-[".","9","8",".",".",".",".","6","."],
-["8",".",".",".","6",".",".",".","3"],
-["4",".",".","8",".","3",".",".","1"],
-["7",".",".",".","2",".",".",".","6"],
-[".","6",".",".",".",".","2","8","."],
-[".",".",".","4","1","9",".",".","5"],
-[".",".",".",".","8",".",".","7","9"]]
-
-Output:
-[["5","3","4","6","7","8","9","1","2"],
-["6","7","2","1","9","5","3","4","8"],
-["1","9","8","3","4","2","5","6","7"],
-["8","5","9","7","6","1","4","2","3"],
-["4","2","6","8","5","3","7","9","1"],
-["7","1","3","9","2","4","8","5","6"],
-["9","6","1","5","3","7","2","8","4"],
-["2","8","7","4","1","9","6","3","5"],
-["3","4","5","2","8","6","1","7","9"]]
-```
-
-**Explanation**: The input board is shown above and the only valid solution is shown below:
-
-
-
-### Constraints:
-
-- board.length == 9
-- board[i].length == 9
-- board[i][j] is a digit or '.'.
-- It is **guaranteed** that the input board has only one solution.
-
-## Solutions:
-
-### [_Java_](./SudokuSolver2.java)
-
-```java
-/*
-A sudoku solution must satisfy all of the following rules:
--> Each of the digits 1-9 must occur exactly once in each row.
--> Each of the digits 1-9 must occur exactly once in each column.
--> Each of the digits 1-9 must occur exactly once in each of the 9 3x3 sub-boxes of the grid.
-The "." character indicates empty cells.
-*/
-
-public class SudokuSolver2 {
- public void solveSudoku(char[][] board) {
- helper(board, 0, 0);
- }
-
- // a utility function to solve the board
- boolean helper(char[][] board, int row, int col) {
- // base case -> recursion stops at the 10th row
- if (row == board.length)
- return true;
- int newRow = 0, newCol = 0;
- // when its the last col of the board, goto next row & first col
- if (col == board.length - 1) {
- newRow = row + 1;
- newCol = 0;
- }
- // else, keep increasing the col by one & the row remains the same
- else {
- newRow = row;
- newCol = col + 1;
- }
- // if the cell isn't empty, i.e. there is a number present in that cell
- if (board[row][col] != '.') {
- // do a recursive call, if the fn returns true, i.e. the board is solved,
- // we'll also return true
- if (helper(board, newRow, newCol))
- return true;
- }
- // if cell is empty
- else {
- for (int i = 1; i <= 9; i++) {
- // if it's safe to place 'i' at that cell
- if (isValidPlacement(board, row, col, i)) {
- board[row][col] = (char) (i + '0');
- // after placing the number, do a recursive call,
- // if the fn returns true, we'll also return true
- if (helper(board, newRow, newCol))
- return true;
- // if the recursive call returns false, i.e. it wasn't safe to place 'i',
- // we'll empty the cell & and will try for the next value of 'i' (backtracking)
- else
- board[row][col] = '.';
- }
- }
- }
- // return false if it isn't posssible to place a number in the cell
- return false;
- }
-
- // a utility fn to check for valid placement of a number in cell of Sudoku Board
- boolean isValidPlacement(char[][] board, int row, int col, int number) {
- // to check if 'number' is present in the row or the col
- for (int i = 0; i < board.length; i++) {
- // return false if 'number' is present in the col
- if (board[i][col] == (char) (number + '0'))
- return false;
- // return false if 'number' is present in the row
- if (board[row][i] == (char) (number + '0'))
- return false;
- }
- // to check if the 'number' is present in the 3X3 grid
- // There are two ways to get the initial row and column of 3X3 grid
- // 1
- int startingRow = (row / 3) * 3;
- int startingCol = (col / 3) * 3;
- // 2
- // int startingRow = (row % 3) - row;
- // int startingCol = (col % 3) - col;
- for (int i = startingRow; i < startingRow + 3; i++)
- for (int j = startingCol; j < startingCol + 3; j++)
- // return false if 'number' is present in the 3X3 grid or matrix
- if (board[i][j] == (char) (number + '0'))
- return false;
- // return true if 'number' isn't present in row, col & grid
- return true;
- }
-}
-```
-
-### [_..._]()
-
-```
-
-```
-
-
-
-[share]: https://img.icons8.com/external-anggara-blue-anggara-putra/20/000000/external-share-user-interface-basic-anggara-blue-anggara-putra-2.png
-[hard]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Hard-red.svg
diff --git a/src/0001-0100/037 - Sudoku Solver/SudokuSolver2.java b/src/0001-0100/037 - Sudoku Solver/SudokuSolver2.java
deleted file mode 100644
index 7e3a1a7d..00000000
--- a/src/0001-0100/037 - Sudoku Solver/SudokuSolver2.java
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,85 +0,0 @@
-/*
-A sudoku solution must satisfy all of the following rules:
--> Each of the digits 1-9 must occur exactly once in each row.
--> Each of the digits 1-9 must occur exactly once in each column.
--> Each of the digits 1-9 must occur exactly once in each of the 9 3x3 sub-boxes of the grid.
-The "." character indicates empty cells.
-*/
-
-public class SudokuSolver2 {
- public void solveSudoku(char[][] board) {
- helper(board, 0, 0);
- }
-
- // a utility function to solve the board
- boolean helper(char[][] board, int row, int col) {
- // base case -> recursion stops at the 10th row
- if (row == board.length)
- return true;
- int newRow = 0, newCol = 0;
- // when its the last col of the board, goto next row & first col
- if (col == board.length - 1) {
- newRow = row + 1;
- newCol = 0;
- }
- // else, keep increasing the col by one & the row remains the same
- else {
- newRow = row;
- newCol = col + 1;
- }
- // if the cell isn't empty, i.e. there is a number present in that cell
- if (board[row][col] != '.') {
- // do a recursive call, if the fn returns true, i.e. the board is solved,
- // we'll also return true
- if (helper(board, newRow, newCol))
- return true;
- }
- // if cell is empty
- else {
- for (int i = 1; i <= 9; i++) {
- // if it's safe to place 'i' at that cell
- if (isValidPlacement(board, row, col, i)) {
- board[row][col] = (char) (i + '0');
- // after placing the number, do a recursive call,
- // if the fn returns true, we'll also return true
- if (helper(board, newRow, newCol))
- return true;
- // if the recursive call returns false, i.e. it wasn't safe to place 'i',
- // we'll empty the cell & and will try for the next value of 'i' (backtracking)
- else
- board[row][col] = '.';
- }
- }
- }
- // return false if it isn't posssible to place a number in the cell
- return false;
- }
-
- // a utility fn to check for valid placement of a number in cell of Sudoku Board
- boolean isValidPlacement(char[][] board, int row, int col, int number) {
- // to check if 'number' is present in the row or the col
- for (int i = 0; i < board.length; i++) {
- // return false if 'number' is present in the col
- if (board[i][col] == (char) (number + '0'))
- return false;
- // return false if 'number' is present in the row
- if (board[row][i] == (char) (number + '0'))
- return false;
- }
- // to check if the 'number' is present in the 3X3 grid
- // There are two ways to get the initial row and column of 3X3 grid
- // 1
- int startingRow = (row / 3) * 3;
- int startingCol = (col / 3) * 3;
- // 2
- // int startingRow = (row % 3) - row;
- // int startingCol = (col % 3) - col;
- for (int i = startingRow; i < startingRow + 3; i++)
- for (int j = startingCol; j < startingCol + 3; j++)
- // return false if 'number' is present in the 3X3 grid or matrix
- if (board[i][j] == (char) (number + '0'))
- return false;
- // return true if 'number' isn't present in row, col & grid
- return true;
- }
-}
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/0001-0100/041 - First Missing Positive/README.md b/src/0001-0100/041 - First Missing Positive/README.md
deleted file mode 100644
index 4817058e..00000000
--- a/src/0001-0100/041 - First Missing Positive/README.md
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,126 +0,0 @@
-# 41. First Missing Positive [![share]](https://leetcode.com/problems/first-missing-positive/)
-
-![][hard]
-
-## Problem Statement
-
-
Given an unsorted integer array nums, return the smallest missing positive integer.
-
You must implement an algorithm that runs in O(n) time and uses O(1) auxiliary space.
-
-
Example 1:
-
-```
-Input: nums = [1,2,0]
-Output: 3
-Explanation: The numbers in the range [1,2] are all in the array.
-```
-
-
Example 2:
-
-```
-Input: nums = [3,4,-1,1]
-Output: 2
-Explanation: 1 is in the array but 2 is missing.
-```
-
-
Example 3:
-
-```
-Input: nums = [7,8,9,11,12]
-Output: 1
-Explanation: The smallest positive integer 1 is missing.
-```
-
-
-
Constraints:
-
-
1 <= nums.length <= 105
-
-231 <= nums[i] <= 231 - 1
-
-
-
-
-
-#### _Click to open Hints_
-
-
-
-- Think about how you would solve the problem in non-constant space. Can you apply that logic to the existing space?
-- We don't care about duplicates or non-positive integers
-- Remember that O(2n) = O(n)
-
-
-
-## Solutions
-
-### [_Go_](first_missing_positive.go)
-
-```go [Go]
-package main
-
-func firstMissingPositive(nums []int) int {
- i := 0
-
- for i < len(nums) {
- if nums[i] > 0 && nums[i] <= len(nums) && nums[nums[i]-1] != nums[i] {
- nums[nums[i]-1], nums[i] = nums[i], nums[nums[i]-1]
- } else {
- i++
- }
- }
-
- for i, num := range nums {
- if num != i+1 {
- return i + 1
- }
- }
-
- return len(nums) + 1
-}
-
-```
-
-### [_Rust_](first_missing_positive.rs)
-
-```rs [Rust]
-impl Solution {
- pub fn first_missing_positive(nums: Vec) -> i32 {
- let (mut nums, mut i) = (nums, 0);
-
- while i < nums.len() {
- let num = nums[i];
-
- // if the number is in the range [1, nums.len()] and not in the right position
- // swap it with the number at the right position
- if num > 0 && num <= nums.len() as i32 && num != nums[num as usize - 1] {
- nums.swap(i, num as usize - 1);
- } else {
- i += 1;
- }
- }
-
- // find the first missing positive number
- for (i, num) in nums.iter().enumerate() {
- if num != &(i as i32 + 1) {
- return i as i32 + 1;
- }
- }
-
- nums.len() as i32 + 1
- }
-}
-
-```
-
-### [_..._]()
-
-```
-
-```
-
-
-
-[share]: https://graph.org/file/3ea5234dda646b71c574a.png
-[easy]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Easy-bright.svg
-[medium]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Medium-yellow.svg
-[hard]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Hard-red.svg
diff --git a/src/0001-0100/041 - First Missing Positive/first_missing_positive.go b/src/0001-0100/041 - First Missing Positive/first_missing_positive.go
deleted file mode 100644
index 9ea971e4..00000000
--- a/src/0001-0100/041 - First Missing Positive/first_missing_positive.go
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,21 +0,0 @@
-package main
-
-func firstMissingPositive(nums []int) int {
- i := 0
-
- for i < len(nums) {
- if nums[i] > 0 && nums[i] <= len(nums) && nums[nums[i]-1] != nums[i] {
- nums[nums[i]-1], nums[i] = nums[i], nums[nums[i]-1]
- } else {
- i++
- }
- }
-
- for i, num := range nums {
- if num != i+1 {
- return i + 1
- }
- }
-
- return len(nums) + 1
-}
diff --git a/src/0001-0100/041 - First Missing Positive/first_missing_positive.rs b/src/0001-0100/041 - First Missing Positive/first_missing_positive.rs
deleted file mode 100644
index e50f87f1..00000000
--- a/src/0001-0100/041 - First Missing Positive/first_missing_positive.rs
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,26 +0,0 @@
-impl Solution {
- pub fn first_missing_positive(nums: Vec) -> i32 {
- let (mut nums, mut i) = (nums, 0);
-
- while i < nums.len() {
- let num = nums[i];
-
- // if the number is in the range [1, nums.len()] and not in the right position
- // swap it with the number at the right position
- if num > 0 && num <= nums.len() as i32 && num != nums[num as usize - 1] {
- nums.swap(i, num as usize - 1);
- } else {
- i += 1;
- }
- }
-
- // find the first missing positive number
- for (i, num) in nums.iter().enumerate() {
- if num != &(i as i32 + 1) {
- return i as i32 + 1;
- }
- }
-
- nums.len() as i32 + 1
- }
-}
diff --git a/src/0001-0100/042 - Trapping Rain Water/README.md b/src/0001-0100/042 - Trapping Rain Water/README.md
deleted file mode 100644
index 69cf4266..00000000
--- a/src/0001-0100/042 - Trapping Rain Water/README.md
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,86 +0,0 @@
-# 42. Trapping Rain Water [![share]](https://leetcode.com/problems/trapping-rain-water/)
-
-![][hard]
-
-## Problem Statement
-
-
Given n non-negative integers representing an elevation map where the width of each bar is 1, compute how much water it can trap after raining.
-
-
Example 1:
-
-
-```
-Input: height = [0,1,0,2,1,0,1,3,2,1,2,1]
-Output: 6
-Explanation: The above elevation map (black section) is represented by array [0,1,0,2,1,0,1,3,2,1,2,1]. In this case, 6 units of rain water (blue section) are being trapped.
-```
-
-
-
-## Solutions
-
-### [_Rust_](trapping_rain_water.rs)
-
-```rs [Rust]
-impl Solution {
- pub fn trap(height: Vec) -> i32 {
- let (mut left, mut right) = (0, height.len() - 1);
- let (mut left_max, mut right_max) = (0, 0);
- let mut ans = 0;
-
- // iterate from both sides to the middle
- while left < right {
- // if left is lower than right, then the water level depends on left
- // else the water level depends on right
- if height[left] < height[right] {
- // if left height is higher than left_max, then update left_max
- // else add the difference between left_max and left height to ans
- if height[left] >= left_max {
- left_max = height[left];
- } else {
- ans += left_max - height[left];
- }
- left += 1;
- } else {
- // if right height is higher than right_max, then update right_max
- // else add the difference between right_max and right height to ans
- if height[right] >= right_max {
- right_max = height[right];
- } else {
- ans += right_max - height[right];
- }
- right -= 1;
- }
- }
-
- ans
- }
-}
-
-```
-
-### [_..._]()
-
-```
-
-```
-
-
-
-[share]: https://graph.org/file/3ea5234dda646b71c574a.png
-[easy]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Easy-bright.svg
-[medium]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Medium-yellow.svg
-[hard]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Hard-red.svg
diff --git a/src/0001-0100/042 - Trapping Rain Water/trapping_rain_water.rs b/src/0001-0100/042 - Trapping Rain Water/trapping_rain_water.rs
deleted file mode 100644
index 3f1b3924..00000000
--- a/src/0001-0100/042 - Trapping Rain Water/trapping_rain_water.rs
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,34 +0,0 @@
-impl Solution {
- pub fn trap(height: Vec) -> i32 {
- let (mut left, mut right) = (0, height.len() - 1);
- let (mut left_max, mut right_max) = (0, 0);
- let mut ans = 0;
-
- // iterate from both sides to the middle
- while left < right {
- // if left is lower than right, then the water level depends on left
- // else the water level depends on right
- if height[left] < height[right] {
- // if left height is higher than left_max, then update left_max
- // else add the difference between left_max and left height to ans
- if height[left] >= left_max {
- left_max = height[left];
- } else {
- ans += left_max - height[left];
- }
- left += 1;
- } else {
- // if right height is higher than right_max, then update right_max
- // else add the difference between right_max and right height to ans
- if height[right] >= right_max {
- right_max = height[right];
- } else {
- ans += right_max - height[right];
- }
- right -= 1;
- }
- }
-
- ans
- }
-}
diff --git a/src/0001-0100/048 - Rotate Image/README.md b/src/0001-0100/048 - Rotate Image/README.md
deleted file mode 100644
index 6c463fc6..00000000
--- a/src/0001-0100/048 - Rotate Image/README.md
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,68 +0,0 @@
-# 48. Rotate Image [![share]](https://leetcode.com/problems/rotate-image/)
-
-![][medium]
-
-## Problem Statement
-
-
You are given an n x n 2D matrix representing an image, rotate the image by 90 degrees (clockwise).
-
You have to rotate the image in-place, which means you have to modify the input 2D matrix directly. DO NOT allocate another 2D matrix and do the rotation.
-
-## Solutions
-
-### [_Rust_](rotate_image.rs)
-
-```rs [Rust]
-impl Solution {
- pub fn rotate(matrix: &mut Vec>) {
- let n = matrix.len();
-
- for i in 0..n {
- for j in i..n {
- let temp = matrix[i][j];
- matrix[i][j] = matrix[j][i];
- matrix[j][i] = temp;
- }
-
- matrix[i].reverse();
- }
- }
-}
-
-```
-
-### [_..._]()
-
-```
-
-```
-
-
-
-[share]: https://graph.org/file/3ea5234dda646b71c574a.png
-[easy]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Easy-bright.svg
-[medium]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Medium-yellow.svg
-[hard]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Hard-red.svg
diff --git a/src/0001-0100/048 - Rotate Image/rotate_image.rs b/src/0001-0100/048 - Rotate Image/rotate_image.rs
deleted file mode 100644
index 8b00aaa5..00000000
--- a/src/0001-0100/048 - Rotate Image/rotate_image.rs
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,15 +0,0 @@
-impl Solution {
- pub fn rotate(matrix: &mut Vec>) {
- let n = matrix.len();
-
- for i in 0..n {
- for j in i..n {
- let temp = matrix[i][j];
- matrix[i][j] = matrix[j][i];
- matrix[j][i] = temp;
- }
-
- matrix[i].reverse();
- }
- }
-}
diff --git a/src/0001-0100/051 - N-Queens/NQueens2.java b/src/0001-0100/051 - N-Queens/NQueens2.java
deleted file mode 100644
index f086c941..00000000
--- a/src/0001-0100/051 - N-Queens/NQueens2.java
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,89 +0,0 @@
-import java.util.*;
-
-public class NQueens2 {
-
- public static List> nQueens(int n) {
- // List of Lists of boards
- List> allBoards = new ArrayList<>();
- char[][] board = new char[n][n];
- helper(board, allBoards, 0);
- return allBoards;
- }
-
- static void helper(char[][] board, List> allBoards, int col) {
- // save board to allBoards after placing Queens on all possible cols
- if (col == board.length) {
- saveBoard(board, allBoards);
- return;
- }
- for (int row = 0; row < board.length; row++) {
- // if it's safe, place queen at row
- if (isSafe(row, col, board)) {
- board[row][col] = 'Q';
- helper(board, allBoards, col + 1);
- // backtracking
- board[row][col] = '.';
- }
- }
- }
-
- // Fn to check if it's safe to place Queen
- static boolean isSafe(int row, int col, char[][] board) {
- int len = board.length;
- // traverse in all cols to check if a queen is already present or not
- for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) {
- if (board[row][i] == 'Q')
- return false;
- }
- // traverse in all rows to check if a queen is already present or not
- for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) {
- if (board[i][col] == 'Q')
- return false;
- }
- // traverse through upper left diagonal to check if queen is present
- int r = row;
- for (int c = col; c >= 0 && r >= 0; r--, c--) {
- if (board[r][c] == 'Q')
- return false;
- }
- // traverse through upper right diagonal to check if queen is present
- r = row;
- for (int c = col; c < len && r >= 0; r--, c++) {
- if (board[r][c] == 'Q')
- return false;
- }
- // traverse through lower left diagonal to check if queen is present
- r = row;
- for (int c = col; c >= 0 && r < len; r++, c--) {
- if (board[r][c] == 'Q')
- return false;
- }
- // traverse through lower right diagonal to check if queen is present
- r = row;
- for (int c = col; c < len && r < len; r++, c++) {
- if (board[r][c] == 'Q')
- return false;
- }
- return true;
- }
-
- // Fn to save a board to List of Boards
- static void saveBoard(char[][] board, List> allBoards) {
- int len = board.length;
- String row = "";
- List newBoard = new ArrayList<>();
- for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) {
- row = "";
- for (int j = 0; j < len; j++) {
- if (board[i][j] == 'Q')
- row += 'Q';
- else
- row += '.';
- }
- // this adds the row to the newBoards -> "Q..." or "..Q."
- newBoard.add(row);
- }
- // this add the board to the list of boards -> [[..Q., Q..., ...Q, .Q..],...]
- allBoards.add(newBoard);
- }
-}
diff --git a/src/0001-0100/051 - N-Queens/README.md b/src/0001-0100/051 - N-Queens/README.md
deleted file mode 100644
index dd11fdbb..00000000
--- a/src/0001-0100/051 - N-Queens/README.md
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,138 +0,0 @@
-# 51. N-Queens [![share]](https://leetcode.com/problems/n-queens/)
-
-![][hard]
-
-## Problem Statement:
-
-The **n-queens** puzzle is the problem of placing `n` queens on an `n x n` chessboard such that no two queens attack each other.
-
-Given an integer `n`, return all distinct solutions to the `n-queens puzzle`. You may return the answer in `any order`.
-
-Each solution contains a distinct board configuration of the n-queens' placement, where `'Q'` and `'.'` both indicate a queen and an empty space, respectively.
-
-### Example 1:
-
-
-
-```
-Input: n = 4
-Output: [[".Q..","...Q","Q...","..Q."],["..Q.","Q...","...Q",".Q.."]]
-```
-
-**Explanation**: There exist two distinct solutions to the 4-queens puzzle as shown above
-
-### Example 2:
-
-```
-Input: n = 1
-Output: [["Q"]]
-```
-
-### Constraints:
-
-- 1 <= n <= 9
-
-## Solution:
-
-### [_Java_](./NQueens2.java)
-
-```java
-public class NQueens2 {
-
- public static List> nQueens(int n) {
- // List of Lists of boards
- List> allBoards = new ArrayList<>();
- char[][] board = new char[n][n];
- helper(board, allBoards, 0);
- return allBoards;
- }
-
- static void helper(char[][] board, List> allBoards, int col) {
- // save board to allBoards after placing Queens on all possible cols
- if (col == board.length) {
- saveBoard(board, allBoards);
- return;
- }
- for (int row = 0; row < board.length; row++) {
- // if it's safe, place queen at row
- if (isSafe(row, col, board)) {
- board[row][col] = 'Q';
- helper(board, allBoards, col + 1);
- // backtracking
- board[row][col] = '.';
- }
- }
- }
-
- // Fn to check if it's safe to place Queen
- static boolean isSafe(int row, int col, char[][] board) {
- int len = board.length;
- // traverse in all cols to check if a queen is already present or not
- for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) {
- if (board[row][i] == 'Q')
- return false;
- }
- // traverse in all rows to check if a queen is already present or not
- for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) {
- if (board[i][col] == 'Q')
- return false;
- }
- // traverse through upper left diagonal to check if queen is present
- int r = row;
- for (int c = col; c >= 0 && r >= 0; r--, c--) {
- if (board[r][c] == 'Q')
- return false;
- }
- // traverse through upper right diagonal to check if queen is present
- r = row;
- for (int c = col; c < len && r >= 0; r--, c++) {
- if (board[r][c] == 'Q')
- return false;
- }
- // traverse through lower left diagonal to check if queen is present
- r = row;
- for (int c = col; c >= 0 && r < len; r++, c--) {
- if (board[r][c] == 'Q')
- return false;
- }
- // traverse through lower right diagonal to check if queen is present
- r = row;
- for (int c = col; c < len && r < len; r++, c++) {
- if (board[r][c] == 'Q')
- return false;
- }
- return true;
- }
-
- // Fn to save a board to List of Boards
- static void saveBoard(char[][] board, List> allBoards) {
- int len = board.length;
- String row = "";
- List newBoard = new ArrayList<>();
- for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) {
- row = "";
- for (int j = 0; j < len; j++) {
- if (board[i][j] == 'Q')
- row += 'Q';
- else
- row += '.';
- }
- // this adds the row to the newBoards -> "Q..." or "..Q."
- newBoard.add(row);
- }
- // this add the board to the list of boards -> [[..Q., Q..., ...Q, .Q..],...]
- allBoards.add(newBoard);
- }
-}
-```
-
-### [_..._]()
-
-```
-
-```
-
-
-
-[share]: https://img.icons8.com/external-anggara-blue-anggara-putra/20/000000/external-share-user-interface-basic-anggara-blue-anggara-putra-2.png
-[hard]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Hard-red.svg
diff --git a/src/0001-0100/053 - Maximum Subarray/README.md b/src/0001-0100/053 - Maximum Subarray/README.md
deleted file mode 100644
index 7f269c03..00000000
--- a/src/0001-0100/053 - Maximum Subarray/README.md
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,78 +0,0 @@
-# 53. Maximum Subarray [![share]](https://leetcode.com/problems/maximum-subarray/)
-
-![][medium]
-
-## Problem Statement
-
-
Given an integer array nums, find the subarray with the largest sum, and return its sum.
-
-
Example 1:
-
-```
-Input: nums = [-2,1,-3,4,-1,2,1,-5,4]
-Output: 6
-Explanation: The subarray [4,-1,2,1] has the largest sum 6.
-```
-
-
Example 2:
-
-```
-Input: nums = [1]
-Output: 1
-Explanation: The subarray [1] has the largest sum 1.
-```
-
-
Example 3:
-
-```
-Input: nums = [5,4,-1,7,8]
-Output: 23
-Explanation: The subarray [5,4,-1,7,8] has the largest sum 23.
-```
-
-
-
Constraints:
-
-
1 <= nums.length <= 105
-
-104 <= nums[i] <= 104
-
-
-
Follow up: If you have figured out the O(n) solution, try coding another solution using the divide and conquer approach, which is more subtle.
-
-## Solutions
-
-### [_Go_](maximum_subarray.go)
-
-```go [Go]
-package main
-
-import "math"
-
-func maxSubArray(nums []int) int {
- currSum, maxSum := 0, math.MinInt
-
- for _, num := range nums {
- currSum += num
- maxSum = int(math.Max(float64(maxSum), float64(currSum)))
- if currSum < 0 {
- currSum = 0
- }
- }
-
- return maxSum
-}
-
-```
-
-### [_..._]()
-
-```
-
-```
-
-
-
-[share]: https://graph.org/file/3ea5234dda646b71c574a.png
-[easy]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Easy-bright.svg
-[medium]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Medium-yellow.svg
-[hard]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Hard-red.svg
diff --git a/src/0001-0100/053 - Maximum Subarray/maximum_subarray.go b/src/0001-0100/053 - Maximum Subarray/maximum_subarray.go
deleted file mode 100644
index 4fcbf704..00000000
--- a/src/0001-0100/053 - Maximum Subarray/maximum_subarray.go
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,17 +0,0 @@
-package main
-
-import "math"
-
-func maxSubArray(nums []int) int {
- currSum, maxSum := 0, math.MinInt
-
- for _, num := range nums {
- currSum += num
- maxSum = int(math.Max(float64(maxSum), float64(currSum)))
- if currSum < 0 {
- currSum = 0
- }
- }
-
- return maxSum
-}
diff --git a/src/0001-0100/055 - Jump Game/JumpGame.java b/src/0001-0100/055 - Jump Game/JumpGame.java
deleted file mode 100644
index a0070e37..00000000
--- a/src/0001-0100/055 - Jump Game/JumpGame.java
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,15 +0,0 @@
-public class JumpGame {
- public boolean canJump(int[] nums) {
- int n = nums.length,
- max = 0;
- if (n == 1)
- return true;
- for (int i = 0; i < n - 1 && max >= i; i++) {
- if (max < i + nums[i])
- max = i + nums[i];
- if (max >= n - 1)
- return true;
- }
- return false;
- }
-}
diff --git a/src/0001-0100/055 - Jump Game/README.md b/src/0001-0100/055 - Jump Game/README.md
deleted file mode 100644
index a80ee19a..00000000
--- a/src/0001-0100/055 - Jump Game/README.md
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,63 +0,0 @@
-# 55. Jump Game [![share]](https://leetcode.com/problems/jump-game)
-
-![][medium]
-
-## Problem Statement:
-
-You are given an integer array `nums`. You are initially positioned at the array's **first index**, and each element in the array represents your maximum jump length at that position.
-
-Return `true` if you can reach the last index, or `false` otherwise.
-
-### Example 1:
-
-```
-Input: nums = [2,3,1,1,4]
-Output: true
-Explanation: Jump 1 step from index 0 to 1, then 3 steps to the last index.
-```
-
-### Example 2:
-
-```
-Input: nums = [3,2,1,0,4]
-Output: false
-Explanation: You will always arrive at index 3 no matter what. Its maximum jump length is 0, which makes it impossible to reach the last index.
-```
-
-### Constraints:
-
-- 1 <= nums.length <= 104
-- 0 <= nums[i] <= 105
-
-## Solution:
-
-### [_Java_](./JumpGame.java)
-
-```java
-public boolean canJump(int[] nums) {
- int n = nums.length,
- max = 0;
- if (n == 1)
- return true;
- for (int i = 0; i < n - 1 && max >= i; i++) {
- if (max < i + nums[i])
- max = i + nums[i];
- if (max >= n - 1)
- return true;
- }
- return false;
-}
-```
-
-### [_..._]()
-
-```
-
-```
-
-
-
-[share]: https://img.icons8.com/external-anggara-blue-anggara-putra/20/000000/external-share-user-interface-basic-anggara-blue-anggara-putra-2.png
-[easy]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Easy-bright.svg
-[medium]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Medium-yellow.svg
-[hard]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Hard-red.svg
diff --git a/src/0001-0100/058 - Length of Last Word/LengthOfLastWord.java b/src/0001-0100/058 - Length of Last Word/LengthOfLastWord.java
deleted file mode 100644
index 11d7cec1..00000000
--- a/src/0001-0100/058 - Length of Last Word/LengthOfLastWord.java
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,12 +0,0 @@
-public class LengthOfLastWord {
- public int lengthOfLastWord(String s) {
- int count = 0;
- for (int i = s.length() - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
- if (s.charAt(i) != ' ')
- count++;
- else if (count > 0)
- return count;
- }
- return count;
- }
-}
diff --git a/src/0001-0100/058 - Length of Last Word/README.md b/src/0001-0100/058 - Length of Last Word/README.md
deleted file mode 100644
index 7404e745..00000000
--- a/src/0001-0100/058 - Length of Last Word/README.md
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,67 +0,0 @@
-# 58. Length of Last Word [![share]](https://leetcode.com/problems/length-of-last-word)
-
-![][easy]
-
-## Problem Statement:
-
-Given a string `s` consisting of words and spaces, return the length of the **last** word in the string.
-
-- A **word** is a maximal substring consisting of non-space characters only.
-
-### Example 1:
-
-```
-Input: s = "Hello World"
-Output: 5
-Explanation: The last word is "World" with length 5.
-```
-
-### Example 2:
-
-```
-Input: s = " fly me to the moon "
-Output: 4
-Explanation: The last word is "moon" with length 4.
-```
-
-### Example 3:
-
-```
-Input: s = "luffy is still joyboy"
-Output: 6
-Explanation: The last word is "joyboy" with length 6.
-```
-
-### Constraints:
-
-- 1 <= s.length <= 105
-- s consists of only English letters and spaces ' '.
-- There will be at least one word in s.
-
-## Solution:
-
-### [_Java_](./LengthOfLastWord.java)
-
-```java
-public int lengthOfLastWord(String s) {
- int count = 0;
- for (int i = s.length() - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
- if (s.charAt(i) != ' ')
- count++;
- else if (count > 0)
- return count;
- }
- return count;
-}
-```
-
-### [_..._]()
-
-```
-
-```
-
-
-
-[share]: https://img.icons8.com/external-anggara-blue-anggara-putra/20/000000/external-share-user-interface-basic-anggara-blue-anggara-putra-2.png
-[easy]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Easy-green.svg
diff --git a/src/0001-0100/061 - Rotate List /README.md b/src/0001-0100/061 - Rotate List /README.md
deleted file mode 100644
index 1705e1de..00000000
--- a/src/0001-0100/061 - Rotate List /README.md
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,75 +0,0 @@
-# 61. Rotate List [![][share]](https://leetcode.com/problems/rotate-list/)
-
-![][medium]
-
-## Problem Statement:
-
-Given the `head` of a linked list, rotate the list to the right by `k` places.
-
-### Example 1:
-
-
-
-```
-Input: head = [1,2,3,4,5], k = 2
-Output: [4,5,1,2,3]
-```
-
-### Example 2:
-
-
-
-```
-Input: head = [0,1,2], k = 4
-Output: [2,0,1]
-```
-
-### Constraints:
-
-- The number of nodes in the list is in the range `[0, 500]`.
-- -100 <= Node.val <= 100
-- 0 <= k <= 2 \* 109
-
-## Solution:
-
-### [_Java_](./RotateList.java)
-
-```java
-public ListNode rotateRight(ListNode head, int k) {
- if (head == null)
- return null;
- int size = 0;
- ListNode temp = head,
- newHead = null,
- p1 = head,
- p2 = head;
- while (temp != null) {
- size++;
- temp = temp.next;
- }
- k %= size;
- for (int i = 0; i < k; i++)
- p2 = p2.next;
- while (p2.next != null) {
- p1 = p1.next;
- p2 = p2.next;
- }
- p2.next = head;
- newHead = p1.next;
- p1.next = null;
- return newHead;
-}
-```
-
-### [_..._]()
-
-```
-
-```
-
-
-
-[share]: https://img.icons8.com/external-anggara-blue-anggara-putra/20/000000/external-share-user-interface-basic-anggara-blue-anggara-putra-2.png
-[easy]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Easy-bright.svg
-[medium]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Medium-yellow.svg
-[hard]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Hard-red.svg
diff --git a/src/0001-0100/061 - Rotate List /RotateList.java b/src/0001-0100/061 - Rotate List /RotateList.java
deleted file mode 100644
index 7c853461..00000000
--- a/src/0001-0100/061 - Rotate List /RotateList.java
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,28 +0,0 @@
-import definitions.ListNode;
-
-public class RotateList {
- public ListNode rotateRight(ListNode head, int k) {
- if (head == null)
- return null;
- int size = 0;
- ListNode temp = head,
- newHead = null,
- p1 = head,
- p2 = head;
- while (temp != null) {
- size++;
- temp = temp.next;
- }
- k %= size;
- for (int i = 0; i < k; i++)
- p2 = p2.next;
- while (p2.next != null) {
- p1 = p1.next;
- p2 = p2.next;
- }
- p2.next = head;
- newHead = p1.next;
- p1.next = null;
- return newHead;
- }
-}
diff --git a/src/0001-0100/066 - Plus One/README.md b/src/0001-0100/066 - Plus One/README.md
deleted file mode 100644
index f0ad94cc..00000000
--- a/src/0001-0100/066 - Plus One/README.md
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,81 +0,0 @@
-# 66. Plus One [![share]](https://leetcode.com/problems/plus-one/)
-
-![][easy]
-
-## Problem Statement
-
-
You are given a large integer represented as an integer array digits, where each digits[i] is the ith digit of the integer. The digits are ordered from most significant to least significant in left-to-right order. The large integer does not contain any leading 0's.
-
Increment the large integer by one and return the resulting array of digits.
-
-
Example 1:
-
-```
-Input: digits = [1,2,3]
-Output: [1,2,4]
-Explanation: The array represents the integer 123.
-Incrementing by one gives 123 + 1 = 124.
-Thus, the result should be [1,2,4].
-```
-
-
Example 2:
-
-```
-Input: digits = [4,3,2,1]
-Output: [4,3,2,2]
-Explanation: The array represents the integer 4321.
-Incrementing by one gives 4321 + 1 = 4322.
-Thus, the result should be [4,3,2,2].
-```
-
-
Example 3:
-
-```
-Input: digits = [9]
-Output: [1,0]
-Explanation: The array represents the integer 9.
-Incrementing by one gives 9 + 1 = 10.
-Thus, the result should be [1,0].
-```
-
-
Given a non-negative integer x, return the square root of x rounded down to the nearest integer. The returned integer should be non-negative as well.
-
You must not use any built-in exponent function or operator.
-
-
For example, do not use pow(x, 0.5) in c++ or x ** 0.5 in python.
-
-
-
Example 1:
-
-```
-Input: x = 4
-Output: 2
-Explanation: The square root of 4 is 2, so we return 2.
-```
-
-
Example 2:
-
-```
-Input: x = 8
-Output: 2
-Explanation: The square root of 8 is 2.82842..., and since we round it down to the nearest integer, 2 is returned.
-```
-
-
-
Constraints:
-
-
0 <= x <= 231 - 1
-
-
-
-
-
-#### _Click to open Hints_
-
-
-
-- Try exploring all integers. (Credits: @annujoshi)
-- Use the sorted property of integers to reduced the search space. (Credits: @annujoshi)
-
-
-
-## Solutions
-
-### [_Go_](sqrt_x.go)
-
-```go [Go]
-package main
-
-func mySqrt(x int) int {
- start := 0
- end := x
-
- for start < end {
- // this is to floor the mid value
- // mid of 8 will be 4 , (8+1)/2 = 4.5
- // mid of 9 will be 5 , (9+1)/2 = 5
- mid := start + (end-start+1)/2
- if mid*mid > x {
- end = mid - 1
- } else {
- start = mid
- }
- }
-
- return end
-}
-
-```
-
-### [_..._]()
-
-```
-
-```
-
-
-
-[share]: https://graph.org/file/3ea5234dda646b71c574a.png
-[easy]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Easy-bright.svg
-[medium]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Medium-yellow.svg
-[hard]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Hard-red.svg
diff --git a/src/0001-0100/069 - Sqrt(x)/sqrt_x.go b/src/0001-0100/069 - Sqrt(x)/sqrt_x.go
deleted file mode 100644
index 4a0a9608..00000000
--- a/src/0001-0100/069 - Sqrt(x)/sqrt_x.go
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,20 +0,0 @@
-package main
-
-func mySqrt(x int) int {
- start := 0
- end := x
-
- for start < end {
- // this is to floor the mid value
- // mid of 8 will be 4 , (8+1)/2 = 4.5
- // mid of 9 will be 5 , (9+1)/2 = 5
- mid := start + (end-start+1)/2
- if mid*mid > x {
- end = mid - 1
- } else {
- start = mid
- }
- }
-
- return end
-}
diff --git a/src/0001-0100/070 - Climbing Stairs/ClimbingStairs.java b/src/0001-0100/070 - Climbing Stairs/ClimbingStairs.java
deleted file mode 100644
index 307b1c94..00000000
--- a/src/0001-0100/070 - Climbing Stairs/ClimbingStairs.java
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,10 +0,0 @@
-public class ClimbingStairs {
- public int climbStairs(int n) {
- int[] dp = new int[n + 1];
- dp[0] = 1;
- dp[1] = 1;
- for (int i = 2; i <= n; i++)
- dp[i] = dp[i - 1] + dp[i - 2];
- return dp[n];
- }
-}
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/0001-0100/070 - Climbing Stairs/README.md b/src/0001-0100/070 - Climbing Stairs/README.md
deleted file mode 100644
index f9701e4d..00000000
--- a/src/0001-0100/070 - Climbing Stairs/README.md
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,60 +0,0 @@
-# 70. Climbing Stairs [![share]](https://leetcode.com/problems/climbing-stairs)
-
-![][easy]
-
-## Problem Statement:
-
-You are climbing a staircase. It takes `n` steps to reach the top.
-
-Each time you can either climb `1` or `2` steps. In how many distinct ways can you climb to the top?
-
-### Example 1:
-
-```
-Input: n = 2
-Output: 2
-Explanation: There are two ways to climb to the top.
-1. 1 step + 1 step
-2. 2 steps
-```
-
-### Example 2:
-
-```
-Input: n = 3
-Output: 3
-Explanation: There are three ways to climb to the top.
-1. 1 step + 1 step + 1 step
-2. 1 step + 2 steps
-3. 2 steps + 1 step
-```
-
-### Constraints:
-
-- 1 <= n <= 45
-
-## Solution:
-
-### [_Java_](./ClimbingStairs.java)
-
-```java
-public int climbStairs(int n) {
- int[] dp = new int[n + 1];
- dp[0] = 1;
- dp[1] = 1;
- for (int i = 2; i <= n; i++)
- dp[i] = dp[i - 1] + dp[i - 2];
- return dp[n];
-}
-```
-
-### [_..._]()
-
-```
-
-```
-
-
-
-[share]: https://img.icons8.com/external-anggara-blue-anggara-putra/20/000000/external-share-user-interface-basic-anggara-blue-anggara-putra-2.png
-[easy]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Easy-green.svg
diff --git a/src/0001-0100/072 - Edit Distance/EditDistance.cpp b/src/0001-0100/072 - Edit Distance/EditDistance.cpp
deleted file mode 100644
index e73d7466..00000000
--- a/src/0001-0100/072 - Edit Distance/EditDistance.cpp
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,27 +0,0 @@
-#include
-using namespace std;
-
-int minDistance(string word1, string word2)
-{
- int m = word1.length(),
- n = word2.length();
- vector> dp(m + 1, vector(n + 1));
- for (int i = 0; i < m + 1; i++)
- for (int j = 0; j < n + 1; j++)
- {
- if (i == 0)
- dp[i][j] = j;
- else if (j == 0)
- dp[i][j] = i;
- else if (word1[i - 1] == word2[j - 1])
- dp[i][j] = dp[i - 1][j - 1];
- else
- dp[i][j] = 1 + min(dp[i - 1][j - 1], min(dp[i - 1][j], dp[i][j - 1]));
- }
- return dp[m][n];
-}
-
-// int main()
-// {
-// cout << getMinConversions("intention", "execution") << endl;
-// }
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/0001-0100/072 - Edit Distance/EditDistance.java b/src/0001-0100/072 - Edit Distance/EditDistance.java
deleted file mode 100644
index c0a89e33..00000000
--- a/src/0001-0100/072 - Edit Distance/EditDistance.java
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,33 +0,0 @@
-public class EditDistance {
-
- /**
- * Time Complexity => O(n^2)
- *
- * @param str1 String
- * @param str2 String
- * @return the minimum number of operations required to convert {@code str1} to
- * {@code str2}
- */
- public int minDistance(String word1, String word2) {
- int m = word1.length(),
- n = word2.length();
- int[][] dp = new int[m + 1][n + 1];
- for (int i = 0; i < m + 1; i++)
- for (int j = 0; j < n + 1; j++) {
- if (i == 0)
- dp[i][j] = j;
- else if (j == 0)
- dp[i][j] = i;
- else if (word1.charAt(i - 1) == word2.charAt(j - 1))
- dp[i][j] = dp[i - 1][j - 1];
- else
- dp[i][j] = 1 + Math.min(dp[i - 1][j - 1], Math.min(dp[i - 1][j], dp[i][j - 1]));
- }
- return dp[m][n];
- }
-
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- EditDistance ob = new EditDistance();
- System.out.println(ob.minDistance("intention", "execution"));
- }
-}
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/0001-0100/072 - Edit Distance/README.md b/src/0001-0100/072 - Edit Distance/README.md
deleted file mode 100644
index 61fdadc9..00000000
--- a/src/0001-0100/072 - Edit Distance/README.md
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,220 +0,0 @@
-# 72. Edit Distance [![share]](https://leetcode.com/problems/edit-distance/)
-
-![][hard]
-
-## Problem Statement:
-
-Given two strings `word1` and `word2`, return the minimum number of operations required to convert `word1` to `word2`.
-
-You have the following three operations permitted on a word:
-
-- Insert a character
-- Delete a character
-- Replace a character
-
-### Example 1:
-
-```
-Input: word1 = "horse", word2 = "ros"
-Output: 3
-Explanation:
-horse -> rorse (replace 'h' with 'r')
-rorse -> rose (remove 'r')
-rose -> ros (remove 'e')
-```
-
-### Example 2:
-
-```
-Input: word1 = "intention", word2 = "execution"
-Output: 5
-Explanation:
-intention -> inention (remove 't')
-inention -> enention (replace 'i' with 'e')
-enention -> exention (replace 'n' with 'x')
-exention -> exection (replace 'n' with 'c')
-exection -> execution (insert 'u')
-```
-
-### Constraints:
-
-- 0 <= word1.length, word2.length <= 500
-- word1 and word2 consist of lowercase English letters.
-
-## Solution:
-
-### [_Rust_](edit_distance.rs)
-
-```rs [Rust]
-impl Solution {
- fn min_distance(word1: String, word2: String) -> i32 {
- let (m, n) = (word1.len(), word2.len());
- let (word1, word2) = (word1.as_bytes(), word2.as_bytes());
- let mut dp = vec![vec![0; n + 1]; m + 1];
-
- for i in 0..=m {
- for j in 0..=n {
- if i == 0 {
- dp[i][j] = j as i32;
- } else if j == 0 {
- dp[i][j] = i as i32;
- } else if word1[i - 1] == word2[j - 1] {
- dp[i][j] = dp[i - 1][j - 1];
- } else {
- dp[i][j] = 1 + dp[i - 1][j - 1].min(dp[i - 1][j].min(dp[i][j - 1]));
- }
- }
- }
-
- dp[m][n]
- }
-}
-
-```
-
-### [_C++_](EditDistance.cpp)
-
-```cpp [C++]
-#include
-using namespace std;
-
-int minDistance(string word1, string word2)
-{
- int m = word1.length(),
- n = word2.length();
- vector> dp(m + 1, vector(n + 1));
- for (int i = 0; i < m + 1; i++)
- for (int j = 0; j < n + 1; j++)
- {
- if (i == 0)
- dp[i][j] = j;
- else if (j == 0)
- dp[i][j] = i;
- else if (word1[i - 1] == word2[j - 1])
- dp[i][j] = dp[i - 1][j - 1];
- else
- dp[i][j] = 1 + min(dp[i - 1][j - 1], min(dp[i - 1][j], dp[i][j - 1]));
- }
- return dp[m][n];
-}
-
-// int main()
-// {
-// cout << getMinConversions("intention", "execution") << endl;
-// }
-```
-
-### [_Python_](edit_distance.py)
-
-```py [Python]
-def minDistance(word1: str, word2: str) -> int:
- m, n = len(word1), len(word2)
- dp = [[None] * (n + 1) for _ in range(m + 1)]
- for i in range(m + 1):
- for j in range(n + 1):
- if i == 0:
- dp[i][j] = j
- elif j == 0:
- dp[i][j] = i
- elif word1[i - 1] == word2[j - 1]:
- dp[i][j] = dp[i - 1][j - 1]
- else:
- dp[i][j] = 1 + min(dp[i - 1][j - 1], min(dp[i - 1][j], dp[i][j - 1]))
- return dp[m][n]
-
-
-if __name__ == "__main__":
- print(minDistance("intention", "execution"))
-
-```
-
-### [_Go_](edit_distance.go)
-
-```go [Go]
-package main
-
-func minDistance(word1 string, word2 string) int {
- m, n := len(word1), len(word2)
-
- dp := make([][]int, m+1)
-
- for i := 0; i <= m; i++ {
- dp[i] = make([]int, n+1)
- }
-
- for i := 0; i <= m; i++ {
- for j := 0; j <= n; j++ {
- if i == 0 {
- dp[i][j] = j
- } else if j == 0 {
- dp[i][j] = i
- } else if word1[i-1] == word2[j-1] {
- dp[i][j] = dp[i-1][j-1]
- } else {
- dp[i][j] = 1 + min(dp[i-1][j-1], min(dp[i-1][j], dp[i][j-1]))
- }
- }
- }
-
- return dp[m][n]
-}
-
-func min(a, b int) int {
- if a < b {
- return a
- }
- return b
-}
-
-```
-
-### [_Java_](EditDistance.java)
-
-```java [Java]
-public class EditDistance {
-
- /**
- * Time Complexity => O(n^2)
- *
- * @param str1 String
- * @param str2 String
- * @return the minimum number of operations required to convert {@code str1} to
- * {@code str2}
- */
- public int minDistance(String word1, String word2) {
- int m = word1.length(),
- n = word2.length();
- int[][] dp = new int[m + 1][n + 1];
- for (int i = 0; i < m + 1; i++)
- for (int j = 0; j < n + 1; j++) {
- if (i == 0)
- dp[i][j] = j;
- else if (j == 0)
- dp[i][j] = i;
- else if (word1.charAt(i - 1) == word2.charAt(j - 1))
- dp[i][j] = dp[i - 1][j - 1];
- else
- dp[i][j] = 1 + Math.min(dp[i - 1][j - 1], Math.min(dp[i - 1][j], dp[i][j - 1]));
- }
- return dp[m][n];
- }
-
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- EditDistance ob = new EditDistance();
- System.out.println(ob.minDistance("intention", "execution"));
- }
-}
-```
-
-### [_..._]()
-
-```
-
-```
-
-
-
-[share]: https://img.icons8.com/external-anggara-blue-anggara-putra/20/000000/external-share-user-interface-basic-anggara-blue-anggara-putra-2.png
-[easy]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Easy-bright.svg
-[medium]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Medium-yellow.svg
-[hard]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Hard-red.svg
diff --git a/src/0001-0100/072 - Edit Distance/edit_distance.go b/src/0001-0100/072 - Edit Distance/edit_distance.go
deleted file mode 100644
index 13de92ad..00000000
--- a/src/0001-0100/072 - Edit Distance/edit_distance.go
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,34 +0,0 @@
-package main
-
-func minDistance(word1 string, word2 string) int {
- m, n := len(word1), len(word2)
-
- dp := make([][]int, m+1)
-
- for i := 0; i <= m; i++ {
- dp[i] = make([]int, n+1)
- }
-
- for i := 0; i <= m; i++ {
- for j := 0; j <= n; j++ {
- if i == 0 {
- dp[i][j] = j
- } else if j == 0 {
- dp[i][j] = i
- } else if word1[i-1] == word2[j-1] {
- dp[i][j] = dp[i-1][j-1]
- } else {
- dp[i][j] = 1 + min(dp[i-1][j-1], min(dp[i-1][j], dp[i][j-1]))
- }
- }
- }
-
- return dp[m][n]
-}
-
-func min(a, b int) int {
- if a < b {
- return a
- }
- return b
-}
diff --git a/src/0001-0100/072 - Edit Distance/edit_distance.py b/src/0001-0100/072 - Edit Distance/edit_distance.py
deleted file mode 100644
index 4b0e0f48..00000000
--- a/src/0001-0100/072 - Edit Distance/edit_distance.py
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,18 +0,0 @@
-def minDistance(word1: str, word2: str) -> int:
- m, n = len(word1), len(word2)
- dp = [[None] * (n + 1) for _ in range(m + 1)]
- for i in range(m + 1):
- for j in range(n + 1):
- if i == 0:
- dp[i][j] = j
- elif j == 0:
- dp[i][j] = i
- elif word1[i - 1] == word2[j - 1]:
- dp[i][j] = dp[i - 1][j - 1]
- else:
- dp[i][j] = 1 + min(dp[i - 1][j - 1], min(dp[i - 1][j], dp[i][j - 1]))
- return dp[m][n]
-
-
-if __name__ == "__main__":
- print(minDistance("intention", "execution"))
diff --git a/src/0001-0100/072 - Edit Distance/edit_distance.rs b/src/0001-0100/072 - Edit Distance/edit_distance.rs
deleted file mode 100644
index 6a17fbbc..00000000
--- a/src/0001-0100/072 - Edit Distance/edit_distance.rs
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,23 +0,0 @@
-impl Solution {
- fn min_distance(word1: String, word2: String) -> i32 {
- let (m, n) = (word1.len(), word2.len());
- let (word1, word2) = (word1.as_bytes(), word2.as_bytes());
- let mut dp = vec![vec![0; n + 1]; m + 1];
-
- for i in 0..=m {
- for j in 0..=n {
- if i == 0 {
- dp[i][j] = j as i32;
- } else if j == 0 {
- dp[i][j] = i as i32;
- } else if word1[i - 1] == word2[j - 1] {
- dp[i][j] = dp[i - 1][j - 1];
- } else {
- dp[i][j] = 1 + dp[i - 1][j - 1].min(dp[i - 1][j].min(dp[i][j - 1]));
- }
- }
- }
-
- dp[m][n]
- }
-}
diff --git a/src/0001-0100/074 - Search a 2D Matrix/README.md b/src/0001-0100/074 - Search a 2D Matrix/README.md
deleted file mode 100644
index 91c89102..00000000
--- a/src/0001-0100/074 - Search a 2D Matrix/README.md
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,76 +0,0 @@
-# 74. Search a 2D Matrix [![share]](https://leetcode.com/problems/search-a-2d-matrix/)
-
-![][medium]
-
-## Problem Statement
-
-
You are given an m x n integer matrix matrix with the following two properties:
-
-
Each row is sorted in non-decreasing order.
-
The first integer of each row is greater than the last integer of the previous row.
-
-
Given an integer target, return trueiftargetis inmatrixorfalseotherwise.
-
You must write a solution in O(log(m * n)) time complexity.
The number of nodes in the list is in the range [0, 300].
-
-100 <= Node.val <= 100
-
The list is guaranteed to be sorted in ascending order.
-
-
-## Solutions
-
-### [_Go_](remove_duplicates_from_sorted_list.go)
-
-```go [Go]
-package main
-
-// Definition for singly-linked list.
-type ListNode struct {
- Val int
- Next *ListNode
-}
-
-func deleteDuplicates(head *ListNode) *ListNode {
- if head == nil {
- return head
- }
- current := head
- for current != nil && current.Next != nil {
- if current.Val == current.Next.Val {
- current.Next = current.Next.Next
- } else {
- current = current.Next
- }
- }
-
- return head
-}
-
-```
-
-### [_..._]()
-
-```
-
-```
-
-
-
-[share]: https://graph.org/file/3ea5234dda646b71c574a.png
-[easy]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Easy-bright.svg
-[medium]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Medium-yellow.svg
-[hard]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Hard-red.svg
diff --git a/src/0001-0100/083 - Remove Duplicates from Sorted List/remove_duplicates_from_sorted_list.go b/src/0001-0100/083 - Remove Duplicates from Sorted List/remove_duplicates_from_sorted_list.go
deleted file mode 100644
index 8d071378..00000000
--- a/src/0001-0100/083 - Remove Duplicates from Sorted List/remove_duplicates_from_sorted_list.go
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,23 +0,0 @@
-package main
-
-// Definition for singly-linked list.
-type ListNode struct {
- Val int
- Next *ListNode
-}
-
-func deleteDuplicates(head *ListNode) *ListNode {
- if head == nil {
- return head
- }
- current := head
- for current != nil && current.Next != nil {
- if current.Val == current.Next.Val {
- current.Next = current.Next.Next
- } else {
- current = current.Next
- }
- }
-
- return head
-}
diff --git a/src/0001-0100/088 - Merge Sorted Array/README.md b/src/0001-0100/088 - Merge Sorted Array/README.md
deleted file mode 100644
index c3acaa7d..00000000
--- a/src/0001-0100/088 - Merge Sorted Array/README.md
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,98 +0,0 @@
-# 88. Merge Sorted Array [![share]](https://leetcode.com/problems/merge-sorted-array/)
-
-![][easy]
-
-## Problem Statement
-
-
You are given two integer arrays nums1 and nums2, sorted in non-decreasing order, and two integers m and n, representing the number of elements in nums1 and nums2 respectively.
-
Mergenums1 and nums2 into a single array sorted in non-decreasing order.
-
The final sorted array should not be returned by the function, but instead be stored inside the array nums1. To accommodate this, nums1 has a length of m + n, where the first m elements denote the elements that should be merged, and the last n elements are set to 0 and should be ignored. nums2 has a length of n.
-
-
Example 1:
-
-```
-Input: nums1 = [1,2,3,0,0,0], m = 3, nums2 = [2,5,6], n = 3
-Output: [1,2,2,3,5,6]
-Explanation: The arrays we are merging are [1,2,3] and [2,5,6].
-The result of the merge is [1,2,2,3,5,6] with the underlined elements coming from nums1.
-```
-
-
Example 2:
-
-```
-Input: nums1 = [1], m = 1, nums2 = [], n = 0
-Output: [1]
-Explanation: The arrays we are merging are [1] and [].
-The result of the merge is [1].
-```
-
-
Example 3:
-
-```
-Input: nums1 = [0], m = 0, nums2 = [1], n = 1
-Output: [1]
-Explanation: The arrays we are merging are [] and [1].
-The result of the merge is [1].
-Note that because m = 0, there are no elements in nums1. The 0 is only there to ensure the merge result can fit in nums1.
-```
-
-
-
Constraints:
-
-
nums1.length == m + n
-
nums2.length == n
-
0 <= m, n <= 200
-
1 <= m + n <= 200
-
-109 <= nums1[i], nums2[j] <= 109
-
-
-
Follow up: Can you come up with an algorithm that runs in O(m + n) time?
-
-
-
-
-#### _Click to open Hints_
-
-
-
-- You can easily solve this problem if you simply think about two elements at a time rather than two arrays. We know that each of the individual arrays is sorted. What we don't know is how they will intertwine. Can we take a local decision and arrive at an optimal solution?
-- If you simply consider one element each at a time from the two arrays and make a decision and proceed accordingly, you will arrive at the optimal solution.
-
-
-
-## Solutions
-
-### [_Go_](merge_sorted_array.go)
-
-```go [Go]
-package main
-
-func merge(nums1 []int, m int, nums2 []int, n int) {
- i, j, k := m-1, n-1, m+n-1
-
- for j >= 0 {
- if i >= 0 && nums1[i] > nums2[j] {
- nums1[k] = nums1[i]
- i--
- } else {
- nums1[k] = nums2[j]
- j--
- }
- k--
- }
-}
-
-```
-
-### [_..._]()
-
-```
-
-```
-
-
-
-[share]: https://graph.org/file/3ea5234dda646b71c574a.png
-[easy]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Easy-bright.svg
-[medium]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Medium-yellow.svg
-[hard]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Hard-red.svg
diff --git a/src/0001-0100/088 - Merge Sorted Array/merge_sorted_array.go b/src/0001-0100/088 - Merge Sorted Array/merge_sorted_array.go
deleted file mode 100644
index f65cc3ff..00000000
--- a/src/0001-0100/088 - Merge Sorted Array/merge_sorted_array.go
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,16 +0,0 @@
-package main
-
-func merge(nums1 []int, m int, nums2 []int, n int) {
- i, j, k := m-1, n-1, m+n-1
-
- for j >= 0 {
- if i >= 0 && nums1[i] > nums2[j] {
- nums1[k] = nums1[i]
- i--
- } else {
- nums1[k] = nums2[j]
- j--
- }
- k--
- }
-}
diff --git a/src/0001-0100/094 - Binary Tree Inorder Traversal/BinaryTreeInorderTraversal.java b/src/0001-0100/094 - Binary Tree Inorder Traversal/BinaryTreeInorderTraversal.java
deleted file mode 100644
index 1657fd0b..00000000
--- a/src/0001-0100/094 - Binary Tree Inorder Traversal/BinaryTreeInorderTraversal.java
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,38 +0,0 @@
-import java.util.ArrayList;
-import java.util.List;
-import java.util.Stack;
-
-import definitions.TreeNode;
-
-public class BinaryTreeInorderTraversal {
- private List list = new ArrayList<>();
-
- // Iterative Approach
- public List inorderTraversal(TreeNode root) {
- if (root == null)
- return list;
- Stack stack = new Stack<>();
- TreeNode current = root;
- while (!stack.isEmpty() || current != null) {
- if (current != null) {
- stack.push(current);
- current = current.left;
- } else {
- current = stack.pop();
- list.add(current.val);
- current = current.right;
- }
- }
- return list;
- }
-
- // Recursive Approach
- public List inorderTraversalRecursive(TreeNode root) {
- if (root == null)
- return list;
- inorderTraversalRecursive(root.left);
- list.add(root.val);
- inorderTraversalRecursive(root.right);
- return list;
- }
-}
diff --git a/src/0001-0100/094 - Binary Tree Inorder Traversal/README.md b/src/0001-0100/094 - Binary Tree Inorder Traversal/README.md
deleted file mode 100644
index 9bf14be9..00000000
--- a/src/0001-0100/094 - Binary Tree Inorder Traversal/README.md
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,67 +0,0 @@
-# 94. Binary Tree Inorder Traversal [![share]](https://leetcode.com/problems/binary-tree-inorder-traversal/)
-
-![][easy]
-
-## Problem Statement:
-
-Given the root of a binary tree, return the inorder traversal of its nodes' values.
-
-### Example 1:
-
-
-
-```
-Input: root = [1,null,2,3]
-Output: [1,3,2]
-```
-
-### Example 2:
-
-```
-Input: root = []
-Output: []
-```
-
-### Example 3:
-
-```
-Input: root = [1]
-Output: [1]
-```
-
-### Constraints:
-
-- The number of nodes in the tree is in the range [0, 100].
-- -100 <= Node.val <= 100
-
-**Follow up:** Recursive solution is trivial, could you do it iteratively?
-
-## Solution:
-
-### [_Java_](./BinaryTreeInorderTraversal.java)
-
-```java
-public class BinaryTreeInorderTraversal {
- List list = new ArrayList<>();
-
- public List inorderTraversal(TreeNode root) {
- if (root == null)
- return list;
- inorderTraversal(root.left);
- list.add(root.val);
- inorderTraversal(root.right);
- return list;
- }
-}
-```
-
-### [_..._]()
-
-```
-
-```
-
-
-
-[share]: https://img.icons8.com/external-anggara-blue-anggara-putra/20/000000/external-share-user-interface-basic-anggara-blue-anggara-putra-2.png
-[easy]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Easy-green.svg
diff --git a/src/0001-0100/098 - Validate Binary Search Tree/README.md b/src/0001-0100/098 - Validate Binary Search Tree/README.md
deleted file mode 100644
index 7df3117c..00000000
--- a/src/0001-0100/098 - Validate Binary Search Tree/README.md
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,70 +0,0 @@
-# 98. Validate Binary Search Tree [![share]](https://leetcode.com/problems/validate-binary-search-tree/)
-
-![][medium]
-
-## Problem Statement:
-
-Given the `root` of a binary tree, determine if it is a valid binary search tree (BST).
-
-A **valid BST** is defined as follows:
-
-- The left subtree of a node contains only nodes with keys **less than** the node's key.
-- The right subtree of a node contains only nodes with keys **greater than** the node's key.
-- Both the left and right subtrees must also be binary search trees.
-
-### Example 1:
-
-
-
-```
-Input: root = [2,1,3]
-Output: true
-```
-
-### Example 2:
-
-
-
-```
-Input: root = [5,1,4,null,null,3,6]
-Output: false
-```
-
-**Explanation**: The root node's value is 5 but its right child's value is 4.
-
-### Constraints:
-
-- The number of nodes in the tree is in the range [1, 104].
-- -231 <= Node.val <= 231 - 1
-
-## Solution:
-
-### [_Java_](./ValidateBinarySearchTree.java)
-
-```java
-public class ValidateBinarySearchTree {
- public boolean isValidBST(TreeNode root) {
- return isValidBST(root, Long.MIN_VALUE, Long.MAX_VALUE);
- }
-
- private boolean isValidBST(TreeNode root, long min, long max) {
- if (root == null)
- return true;
- return (root.val > min &&
- root.val < max &&
- isValidBST(root.left, min, root.val) &&
- isValidBST(root.right, root.val, max));
- }
-}
-```
-
-### [_..._]()
-
-```
-
-```
-
-
-
-[share]: https://img.icons8.com/external-anggara-blue-anggara-putra/20/000000/external-share-user-interface-basic-anggara-blue-anggara-putra-2.png
-[medium]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Medium-yellow.svg
diff --git a/src/0001-0100/098 - Validate Binary Search Tree/ValidateBinarySearchTree.java b/src/0001-0100/098 - Validate Binary Search Tree/ValidateBinarySearchTree.java
deleted file mode 100644
index e144879d..00000000
--- a/src/0001-0100/098 - Validate Binary Search Tree/ValidateBinarySearchTree.java
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,16 +0,0 @@
-import definitions.TreeNode;
-
-public class ValidateBinarySearchTree {
- public boolean isValidBST(TreeNode root) {
- return isValidBST(root, Long.MIN_VALUE, Long.MAX_VALUE);
- }
-
- private boolean isValidBST(TreeNode root, long min, long max) {
- if (root == null)
- return true;
- return (root.val > min &&
- root.val < max &&
- isValidBST(root.left, min, root.val) &&
- isValidBST(root.right, root.val, max));
- }
-}
diff --git a/src/0001-0100/100 - Same Tree/README.md b/src/0001-0100/100 - Same Tree/README.md
deleted file mode 100644
index 349b6ede..00000000
--- a/src/0001-0100/100 - Same Tree/README.md
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,72 +0,0 @@
-# 100. Same Tree [![][share]](https://leetcode.com/problems/same-tree/)
-
-![][easy]
-
-## Problem Statement:
-
-Given the roots of two binary trees `p` and `q`, write a function to check if they are the same or not.
-
-Two binary trees are considered the same if they are structurally identical, and the nodes have the same value.
-
-### Example 1:
-
-
-
-```
-Input: p = [1,2,3], q = [1,2,3]
-Output: true
-```
-
-### Example 2:
-
-
-
-```
-Input: p = [1,2], q = [1,null,2]
-Output: false
-```
-
-### Example 3:
-
-
-
-```
-Input: p = [1,2,1], q = [1,1,2]
-Output: false
-```
-
-### Constraints:
-
-- The number of nodes in both trees is in the range `[0, 100]`.
-- -104 <= Node.val <= 104
-
-## Solution:
-
-### [_Java_](./SameTree.java)
-
-```java
-public boolean isSameTree(TreeNode p, TreeNode q) {
- if (p == null && q == null)
- return true;
- if (q == null || p == null)
- return false;
- if (p.val != q.val)
- return false;
- boolean left = isSameTree(p.left, q.left);
- boolean right = isSameTree(p.right, q.right);
- return left && right;
-}
-```
-
-### [_..._]()
-
-```
-
-```
-
-
-
-[share]: https://img.icons8.com/external-anggara-blue-anggara-putra/20/000000/external-share-user-interface-basic-anggara-blue-anggara-putra-2.png
-[easy]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Easy-bright.svg
-[medium]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Medium-yellow.svg
-[hard]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Difficulty-Hard-red.svg
diff --git a/src/0001-0100/100 - Same Tree/SameTree.java b/src/0001-0100/100 - Same Tree/SameTree.java
deleted file mode 100644
index 88c87edc..00000000
--- a/src/0001-0100/100 - Same Tree/SameTree.java
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,15 +0,0 @@
-import definitions.TreeNode;
-
-public class SameTree {
- public boolean isSameTree(TreeNode p, TreeNode q) {
- if (p == null && q == null)
- return true;
- if (q == null || p == null)
- return false;
- if (p.val != q.val)
- return false;
- boolean left = isSameTree(p.left, q.left);
- boolean right = isSameTree(p.right, q.right);
- return left && right;
- }
-}
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/0101-0200/101 - Symmetric Tree/README.md b/src/0101-0200/101 - Symmetric Tree/README.md
deleted file mode 100644
index 0249502e..00000000
--- a/src/0101-0200/101 - Symmetric Tree/README.md
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,100 +0,0 @@
-# 101. Symmetric Tree [![share]](https://leetcode.com/problems/symmetric-tree/)
-
-![][easy]
-
-## Problem Statement
-
-
Given the root of a binary tree, check whether it is a mirror of itself (i.e., symmetric around its center).